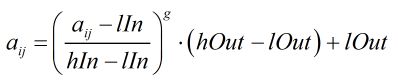imadjust函数分析一
声明:本文涉及到的行数皆指本文提供的附件imadjust.m的代码中行数
本文只讨论imadjust函数是一种用法,即
J = IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT],GAMMA)
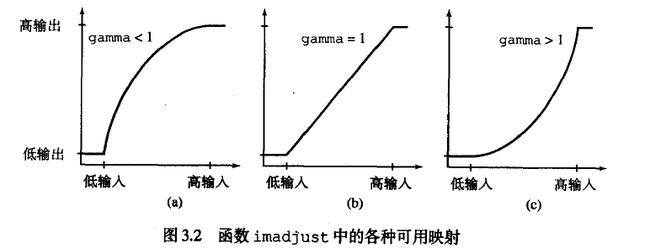
处理效果如下图
图像矩阵I要求数据类型uint8、uint16、double、single和int16,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]和[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT] 要求范围都要在[0 1]区间中,不然会出问题。
1.函数首先获得输入参数(行97)
[img,imageType,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma] = ...
parseInputs(varargin{:});
根据用法
J = IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT],GAMMA)
其中I赋值给img,imgeType后续有说明,LOW_IN赋值给lowIn,HIGH_IN赋值给highIn,LOW_OUT赋值给lowOUt,HIGH_OUT赋值给highOut,GAMMA赋值给gamma。
进入子函数paraseInputs(行196)
函数会判断输出参数个数多少,本文主要讨论参数个数>1,从行231看起
if nargin == 1 %如果输入参数个数为1 % IMADJUST(I) if ndims(img) ~= 2 % 图像矩阵维数不为2 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:oneArgOnlyGrayscale',mfilename); error(eid, ... 'IMADJUST(I) is only supported for 2-D grayscale images.'); end % 检验图像矩阵数据类型是否double、uint8、uint16、int16和single iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... {'2d'}, mfilename, 'I', 1); % If a user passes in a m-by-3 double array, assume it is an intensity % image (there is really no way to tell). imageType = 'intensity'; % Turn off warning 'Images:imhistc:inputHasNans' before calling STRETCHLIM and % restore afterwards. STRETCHLIM calls IMHIST/IMHISTC and the warning confuses % a user who calls IMADJUST with NaNs. s = warning('off','Images:imhistc:inputHasNaNs'); lowhigh_in = stretchlim(img); warning(s) else % 如果输入参数个数不为1 if nargin == 2 %如果输入参数个数为2 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) if ~isempty(varargin{2}) %如果输入参数2的数组不为空 lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; end elseif nargin == 3 %如果输入参数个数为3 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) if ~isempty(varargin{2}) lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; end if ~isempty(varargin{3}) lowhigh_out = varargin{3}; end else %如果输入参数个数为4 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) if ~isempty(varargin{2}) lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; end if ~isempty(varargin{3}) lowhigh_out = varargin{3}; end if ~isempty(varargin{4}) gamma = varargin{4}; end end imageType = findImageType(img, lowhigh_in, lowhigh_out); checkRange(lowhigh_in, imageType, 2,'[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN]'); checkRange(lowhigh_out, imageType, 3,'[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT]'); end
这个if-else语句代码很明显看到函数输入参数[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]赋值给了lowhigh_in,参数[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]赋值给了lowhigh_out,而参数GAMMA赋值给了gamma,然后执行参数有效性判断。(行265)
imageType = findImageType(img, lowhigh_in, lowhigh_out); checkRange(lowhigh_in, imageType, 2,'[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN]'); checkRange(lowhigh_out, imageType, 3,'[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT]');
第一个语句主要用于根据输入图像矩阵判断图像类型,第二个和第三个主要是判断[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]和[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]的正确性。
(1)findImageType函数如下(行274)
function imageType = findImageType(img, lowhigh_in, lowhigh_out) if (ndims(img)==3 && size(img,3)==3) % RGB image % RGB图像 第三维的维数为3 iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... {}, mfilename, 'RGB1', 1); imageType = 'truecolor'; elseif (numel(lowhigh_in) == 2 && numel(lowhigh_out) == 2) || ... size(img,2) ~= 3 % Assuming that a user passed in an intensity image if lowhigh_in and % lowhigh_out are 2-element vectors, e.g., imadjust(3 column image, % [1;2], [2;3]). % 输入图像矩阵维数中列数不为3 iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... {'2d'}, mfilename, 'I', 1); imageType = 'intensity'; else %Colormap iptcheckmap(img,mfilename,'MAP',1); imageType = 'indexed'; end
图像类型分为三种,第一种是'truecolor'图像,第二种是'intensity',第三种为'indexed'。本文讨论的为第二种(一般情况使用的就是第二种,其他的目前没遇到,后续文章更新),即'intensity',判定第二种条件为[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]和[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]的元素个数为2并且输入图像矩阵列数不为3。
(2)chackRange函数如下(行300)
function checkRange(range, imageType, argumentPosition, variableName) if strcmp(imageType, 'intensity') if numel(range) ~= 2 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:InputMustBe2ElVec',mfilename); error(eid, ... 'Function %s expected its %s input argument, %s\n%s', ... mfilename, iptnum2ordinal(argumentPosition), variableName, ... 'to be a two-element vector.'); end else if ~(numel(range) == 2 || isequal(size(range), [2 3])) eid = sprintf('Images:%s:InputMustBe2ElVecOr2by3Matrix',mfilename); error(eid, ... 'Function %s expected its %s input argument, %s\n%s', ... mfilename, iptnum2ordinal(argumentPosition), variableName, ... 'to be a two-element vector or a 2-by-3 matrix.'); end end
前面判定图像为'intensity',这里主要判断[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]和[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]元素个数必须为2,不然报错,这里就是第一个检查,后面还有检查。
最后
[low_in high_in] = splitRange(lowhigh_in, imageType);
[low_out high_out] = splitRange(lowhigh_out, imageType);
获取参数[low_in high_in] 和 [low_out high_out] ,然后函数返回。
2.参数检查
前面通过函数paraseInputs获取了用户输入的参数,接下来进行参数有效性检验
validateLowHigh(lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut);
gamma = validateGamma(gamma,imageType);
(1)函数validateLowHigh(行340)
function validateLowHigh(lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut) if any(lowIn >= highIn) eid = sprintf('Images:%s:lowMustBeSmallerThanHigh',mfilename); error(eid, '%s: LOW_IN must be less than HIGH_IN.',... upper(mfilename)); end if isInvalidRange(lowIn) || isInvalidRange(highIn) ... || isInvalidRange(lowOut) || isInvalidRange(highOut) eid = sprintf('Images:%s:parametersAreOutOfRange',mfilename); error(eid, '%s: LOW_IN, HIGH_IN, LOW_OUT and HIGH_OUT %s',... upper(mfilename), 'must be in the range [0.0, 1.0].'); end
该函数首先检查了lowIn要小于highIn,但是没要求lowOut要小于highOut,因为这个函数有个运用,在于可以反转图像,即[0 1]变换到[1 0]。
然后使用函数isInvalidRange限制了输入lowIn、highIn、lowOut和highOut范围为[0 1],这就是开头所说[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]和[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT] 要求范围都要在[0 1]区间中的出处。
(2)函数validateGamma(行362)
function gamma = validateGamma(gamma,image_type) if strcmp(image_type,'intensity') iptcheckinput(gamma,{'double'},{'scalar', 'nonnegative'}, ... mfilename, 'GAMMA', 4) else iptcheckinput(gamma,{'double'},{'nonnegative','2d'},... mfilename, 'GAMMA', 4) if numel(gamma) == 1, gamma = gamma*ones(1,3); end end
前面判定图像类型为'intensity',这里判定gamma参数必须为正数。
3.执行变换(行104)
if ~isfloat(img) && numel(img) > 65536 % integer data type image with more than 65536 elements out = adjustWithLUT(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); else classin = class(img); classChanged = false; if ~isa(img,'double') %如果图像矩阵数据类型不为double, 图像矩阵数据范围转为[0,1] classChanged = true; img = im2double(img); end if strcmp(imageType, 'intensity') out = adjustGrayscaleImage(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); elseif strcmp(imageType, 'indexed') out = adjustColormap(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); else out = adjustTruecolorImage(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); end if classChanged out = changeclass(classin,out); end end
首先判断如果图像矩阵数据不为浮点数(double和single)并且矩阵元素个数>65536,则执行函数adjustWithLUT函数。
(1)adjustWithLUT函数如下
function out = adjustWithLUT(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma) imgClass = class(img); out = zeros(size(img),imgClass); %initialize for lut switch imgClass case 'uint8' lutLength = 256; conversionFcn = @im2uint8; case 'uint16' lutLength = 65536; conversionFcn = @im2uint16; case 'int16' lutLength = 65536; conversionFcn = @im2int16; otherwise eid = sprintf('Images:%s:internalError',mfilename); msg = 'Internal error: invalid class type.'; error(eid,'%s',msg); end
关键部分
for p = 1:size(img,3) lut = linspace(0,1,lutLength); scalingFactor = 1; lut = adjustArray(lut,lowIn(p),highIn(p),lowOut(p),highOut(p), ... gamma(p),scalingFactor); lut = conversionFcn(lut); out(:,:,p) = intlut(img(:,:,p),lut); end
首先创建一个数组作为筛选数组,不需要对图像矩阵进行变换,直接根据筛选数组的筛选图像矩阵。以下语句为灰度值归一化,将灰度归一化到[0 1]范围,这是为了后面变换方便。
lut = linspace(0,1,lutLength);
lutLength的大小为图像矩阵数据类型对应该类型的最大值,例如图像矩阵数据类型为uint8,则lutLength=256。该语句作用在于创建一个数组lut,数组储存归一化后的灰度值,每个元素分别对于相应的灰度等级。
lut = adjustArray(lut,lowIn(p),highIn(p),lowOut(p),highOut(p), ...
gamma(p),scalingFactor);
对lut进行变换,变换结果如开头的图
lowIn=低输入 highIn=高输入 lowOut=低输出 highOut=高输出
由于数组lut元素范围[0 1],这是归一化数据,因此要还原对应的值
lut = conversionFcn(lut);
剩下就是筛选了
out(:,:,p) = intlut(img(:,:,p),lut);
(2)adjustArray函数(行187)
function out = adjustArray(img,lIn,hIn,lOut,hOut,g,d) %make sure img is in the range [lIn;hIn] img(:) = max(lIn(d,:), min(hIn(d,:),img)); out = ( (img - lIn(d,:)) ./ (hIn(d,:) - lIn(d,:)) ) .^ (g(d,:)); out(:) = out .* (hOut(d,:) - lOut(d,:)) + lOut(d,:);
首先筛选掉矩阵img中小于lIn的数的数值变为lIn,大于hIn的数的数值变为hIn,筛选语句如下
img(:) = max(lIn(d,:), min(hIn(d,:),img));
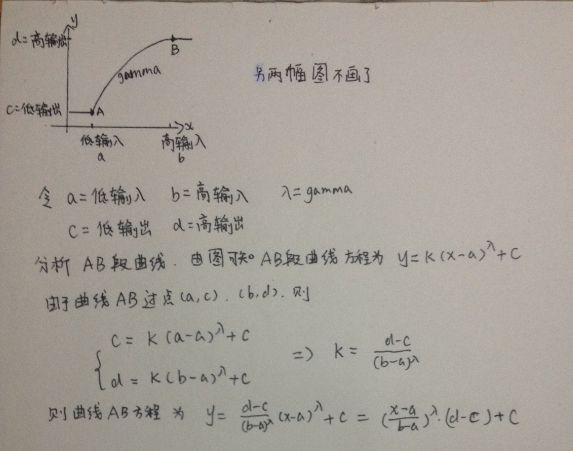
接着进行变换,令![]() 并且d=1,则该函数处理的效果等价于:
并且d=1,则该函数处理的效果等价于:
至于为什么这样,我手写推导过程如下
表达式就是曲线AB的方程
附件:imadjust.m代码
1 function out = imadjust(varargin) 2 %IMADJUST Adjust image intensity values or colormap. 3 % J = IMADJUST(I) maps the values in intensity image I to new values in J 4 % such that 1% of data is saturated at low and high intensities of I. 5 % This increases the contrast of the output image J. 6 % 7 % J = IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT]) maps the values 8 % in intensity image I to new values in J such that values between LOW_IN 9 % and HIGH_IN map to values between LOW_OUT and HIGH_OUT. Values below 10 % LOW_IN and above HIGH_IN are clipped; that is, values below LOW_IN map 11 % to LOW_OUT, and those above HIGH_IN map to HIGH_OUT. You can use an 12 % empty matrix ([]) for [LOW_IN; HIGH_IN] or for [LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT] to 13 % specify the default of [0 1]. If you omit the argument, [LOW_OUT; 14 % HIGH_OUT] defaults to [0 1]. 15 % 16 % J = IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) maps the 17 % values of I to new values in J as described in the previous syntax. 18 % GAMMA specifies the shape of the curve describing the relationship 19 % between the values in I and J. If GAMMA is less than 1, the mapping is 20 % weighted toward higher (brighter) output values. If GAMMA is greater 21 % than 1, the mapping is weighted toward lower (darker) output values. If 22 % you omit the argument, GAMMA defaults to 1 (linear mapping). 23 % 24 % NEWMAP = IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) 25 % transforms the colormap associated with an indexed image. If LOW_IN, 26 % HIGH_IN, LOW_OUT, HIGH_OUT, and GAMMA are scalars, then the same 27 % mapping applies to red, green and blue components. Unique mappings for 28 % each color component are possible when: LOW_IN and HIGH_IN are both 29 % 1-by-3 vectors, LOW_OUT and HIGH_OUT are both 1-by-3 vectors, OR GAMMA 30 % is a 1-by-3 vector. The rescaled colormap, NEWMAP, is the same size as 31 % MAP. 32 % 33 % RGB2 = IMADJUST(RGB1,...) performs the adjustment on each image plane 34 % (red, green, and blue) of the RGB image RGB1. As with the colormap 35 % adjustment, you can apply unique mappings to each plane. 36 % 37 % Note that IMADJUST(I) is equivalent to IMADJUST(I,STRETCHLIM(I)). 38 % 39 % Note that if HIGH_OUT < LOW_OUT, the output image is reversed, as in a 40 % photographic negative. 41 % 42 % Class Support 43 % ------------- 44 % For syntaxes that include an input image (rather than a colormap), the 45 % input image can be uint8, uint16, int16, double, or single. The output 46 % image has the same class as the input image. For syntaxes that include 47 % a colormap, the input and output colormaps are double. 48 % 49 % Examples 50 % -------- 51 % I = imread('pout.tif'); 52 % J = imadjust(I); 53 % figure, imshow(I), figure, imshow(J) 54 % 55 % K = imadjust(I,[0.3 0.7],[]); 56 % figure, imshow(K) 57 % 58 % RGB1 = imread('football.jpg'); 59 % RGB2 = imadjust(RGB1,[.2 .3 0; .6 .7 1],[]); 60 % figure, imshow(RGB1), figure, imshow(RGB2) 61 % 62 % See also BRIGHTEN, DECORRSTRETCH, HISTEQ, IMCONTRAST, STRETCHLIM. 63 64 % Copyright 1992-2007 The MathWorks, Inc. 65 % $Revision: 5.26.4.9 $ $Date: 2007/12/10 21:37:18 $ 66 67 % Input-output specs 68 % ------------------ 69 % I,J real, full matrix, 2-D 70 % uint8, uint16, double, single, int16 71 % 72 % RGB1,RGB2 real, full matrix 73 % M-by-N-by-3 74 % uint8, uint16, double, single, int16 75 % 76 % MAP,NEWMAP real, full matrix 77 % M-by-3 78 % double with values in the range [0,1]. 79 % 80 % [LOW_IN; HIGH_IN] double, real, full matrix 81 % For I, size can only be 2 elements. 82 % For RGB or MAP, size can be 2 elements OR 83 % 2-by-3 matrix. 84 % LOW_IN < HIGH_IN 85 % 86 % [LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT] Same size restrictions as [LOW_IN; HIGH_IN] 87 % LOW_OUT can be less than HIGH_OUT 88 % 89 % LOW_IN, HIGH_IN, LOW_OUT, HIGH_OUT all must be in the range [0,1]; 90 % 91 % GAMMA real, double, nonnegative 92 % scalar for I 93 % scalar or 1-by-3 vector for RGB and MAP 94 95 96 97 %Parse inputs and initialize variables 98 [img,imageType,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma] = ... 99 parseInputs(varargin{:}); 100 101 validateLowHigh(lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut); 102 gamma = validateGamma(gamma,imageType); 103 104 if ~isfloat(img) && numel(img) > 65536 105 % integer data type image with more than 65536 elements 106 out = adjustWithLUT(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); 107 108 else 109 classin = class(img); 110 classChanged = false; 111 if ~isa(img,'double') %如果图像矩阵数据类型不为double, 图像矩阵数据范围转为[0,1] 112 classChanged = true; 113 img = im2double(img); 114 end 115 116 if strcmp(imageType, 'intensity') 117 out = adjustGrayscaleImage(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); 118 elseif strcmp(imageType, 'indexed') 119 out = adjustColormap(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); 120 else 121 out = adjustTruecolorImage(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma); 122 end 123 124 if classChanged 125 out = changeclass(classin,out); 126 end 127 128 end 129 130 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 131 function out = adjustWithLUT(img,lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut,gamma) 132 133 imgClass = class(img); 134 out = zeros(size(img),imgClass); 135 136 %initialize for lut 137 138 switch imgClass 139 case 'uint8' 140 lutLength = 256; 141 conversionFcn = @im2uint8; 142 case 'uint16' 143 lutLength = 65536; 144 conversionFcn = @im2uint16; 145 case 'int16' 146 lutLength = 65536; 147 conversionFcn = @im2int16; 148 otherwise 149 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:internalError',mfilename); 150 msg = 'Internal error: invalid class type.'; 151 error(eid,'%s',msg); 152 end 153 154 for p = 1:size(img,3) 155 lut = linspace(0,1,lutLength); 156 scalingFactor = 1; 157 lut = adjustArray(lut,lowIn(p),highIn(p),lowOut(p),highOut(p), ... 158 gamma(p),scalingFactor); 159 lut = conversionFcn(lut); 160 out(:,:,p) = intlut(img(:,:,p),lut); 161 end 162 163 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 164 function out = adjustColormap(cmap,lIn,hIn,lOut,hOut,g) 165 166 % expansion factor that can expand a 1-by-3 range to the size of cmap. 167 expansionFactor = ones(size(cmap,1), 1); 168 out = adjustArray(cmap, lIn, hIn, lOut, hOut, g, expansionFactor); 169 170 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 171 function out = adjustGrayscaleImage(img,lIn,hIn,lOut,hOut,g) 172 173 expansionFactor = 1; 174 out = adjustArray(img, lIn, hIn, lOut, hOut, g, expansionFactor); 175 176 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 177 function out = adjustTruecolorImage(rgb,lIn,hIn,lOut,hOut,g) 178 179 out = zeros(size(rgb), class(rgb)); 180 expansionFactor = 1; 181 for p = 1 : 3 182 out(:,:,p) = adjustArray(rgb(:,:,p), lIn(p),hIn(p), lOut(p), ... 183 hOut(p), g(p), expansionFactor); 184 end 185 186 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 187 function out = adjustArray(img,lIn,hIn,lOut,hOut,g,d) 188 189 %make sure img is in the range [lIn;hIn] 190 img(:) = max(lIn(d,:), min(hIn(d,:),img)); 191 192 out = ( (img - lIn(d,:)) ./ (hIn(d,:) - lIn(d,:)) ) .^ (g(d,:)); 193 out(:) = out .* (hOut(d,:) - lOut(d,:)) + lOut(d,:); 194 195 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 196 % 参数获取 197 function [img,imageType,low_in,high_in,low_out,high_out,gamma] = ... 198 parseInputs(varargin) 199 200 iptchecknargin(1,4,nargin,mfilename); % 输入参数个数在1-4个 201 img = varargin{1}; % img保存图像矩阵 202 203 204 % Default values (默认值) 205 lowhigh_in = [0; 1]; 206 lowhigh_out = [0; 1]; 207 gamma = 1; 208 209 if nargin == 1 %如果输入参数个数为1 210 % IMADJUST(I) 211 if ndims(img) ~= 2 % 图像矩阵维数不为2 212 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:oneArgOnlyGrayscale',mfilename); 213 error(eid, ... 214 'IMADJUST(I) is only supported for 2-D grayscale images.'); 215 end 216 % 检验图像矩阵数据类型是否double、uint8、uint16、int16和single 217 iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... 218 {'2d'}, mfilename, 'I', 1); 219 220 % If a user passes in a m-by-3 double array, assume it is an intensity 221 % image (there is really no way to tell). 222 imageType = 'intensity'; 223 224 % Turn off warning 'Images:imhistc:inputHasNans' before calling STRETCHLIM and 225 % restore afterwards. STRETCHLIM calls IMHIST/IMHISTC and the warning confuses 226 % a user who calls IMADJUST with NaNs. 227 s = warning('off','Images:imhistc:inputHasNaNs'); 228 lowhigh_in = stretchlim(img); 229 warning(s) 230 231 else % 如果输入参数个数不为1 232 if nargin == 2 %如果输入参数个数为2 233 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) 234 % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) 235 % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN]) 236 if ~isempty(varargin{2}) %如果输入参数2的数组不为空 237 lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; 238 end 239 240 elseif nargin == 3 %如果输入参数个数为3 241 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) 242 % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) 243 % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT]) 244 245 if ~isempty(varargin{2}) 246 lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; 247 end 248 if ~isempty(varargin{3}) 249 lowhigh_out = varargin{3}; 250 end 251 else %如果输入参数个数为4 252 % IMADJUST(I,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) 253 % IMADJUST(MAP,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) 254 % IMADJUST(RGB,[LOW_IN HIGH_IN],[LOW_OUT HIGH_OUT],GAMMA) 255 if ~isempty(varargin{2}) 256 lowhigh_in = varargin{2}; 257 end 258 if ~isempty(varargin{3}) 259 lowhigh_out = varargin{3}; 260 end 261 if ~isempty(varargin{4}) 262 gamma = varargin{4}; 263 end 264 end 265 imageType = findImageType(img, lowhigh_in, lowhigh_out); 266 checkRange(lowhigh_in, imageType, 2,'[LOW_IN; HIGH_IN]'); 267 checkRange(lowhigh_out, imageType, 3,'[LOW_OUT; HIGH_OUT]'); 268 end 269 270 [low_in high_in] = splitRange(lowhigh_in, imageType); 271 [low_out high_out] = splitRange(lowhigh_out, imageType); 272 273 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 274 function imageType = findImageType(img, lowhigh_in, lowhigh_out) 275 276 if (ndims(img)==3 && size(img,3)==3) 277 % RGB image 278 % RGB图像 第三维的维数为3 279 iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... 280 {}, mfilename, 'RGB1', 1); 281 imageType = 'truecolor'; 282 283 elseif (numel(lowhigh_in) == 2 && numel(lowhigh_out) == 2) || ... 284 size(img,2) ~= 3 285 % Assuming that a user passed in an intensity image if lowhigh_in and 286 % lowhigh_out are 2-element vectors, e.g., imadjust(3 column image, 287 % [1;2], [2;3]). 288 % 输入图像矩阵维数中列数不为3 289 iptcheckinput(img, {'double' 'uint8' 'uint16' 'int16' 'single'}, ... 290 {'2d'}, mfilename, 'I', 1); 291 imageType = 'intensity'; 292 293 else 294 %Colormap 295 iptcheckmap(img,mfilename,'MAP',1); 296 imageType = 'indexed'; 297 end 298 299 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 300 function checkRange(range, imageType, argumentPosition, variableName) 301 302 if strcmp(imageType, 'intensity') 303 if numel(range) ~= 2 304 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:InputMustBe2ElVec',mfilename); 305 error(eid, ... 306 'Function %s expected its %s input argument, %s\n%s', ... 307 mfilename, iptnum2ordinal(argumentPosition), variableName, ... 308 'to be a two-element vector.'); 309 end 310 else 311 if ~(numel(range) == 2 || isequal(size(range), [2 3])) 312 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:InputMustBe2ElVecOr2by3Matrix',mfilename); 313 error(eid, ... 314 'Function %s expected its %s input argument, %s\n%s', ... 315 mfilename, iptnum2ordinal(argumentPosition), variableName, ... 316 'to be a two-element vector or a 2-by-3 matrix.'); 317 end 318 end 319 320 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 321 function [rangeMin rangeMax] = splitRange(range, imageType) 322 323 if numel(range) == 2 324 if strcmp(imageType, 'intensity') 325 rangeMin = range(1); 326 rangeMax = range(2); 327 else 328 % Create triples for RGB image or Colormap 329 rangeMin = range(1) * ones(1,3); 330 rangeMax = range(2) * ones(1,3); 331 end 332 else 333 % range is a 2 by 3 array 334 rangeMin = range(1,:); 335 rangeMax = range(2,:); 336 end 337 338 339 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 340 function validateLowHigh(lowIn,highIn,lowOut,highOut) 341 342 if any(lowIn >= highIn) 343 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:lowMustBeSmallerThanHigh',mfilename); 344 error(eid, '%s: LOW_IN must be less than HIGH_IN.',... 345 upper(mfilename)); 346 end 347 348 if isInvalidRange(lowIn) || isInvalidRange(highIn) ... 349 || isInvalidRange(lowOut) || isInvalidRange(highOut) 350 eid = sprintf('Images:%s:parametersAreOutOfRange',mfilename); 351 error(eid, '%s: LOW_IN, HIGH_IN, LOW_OUT and HIGH_OUT %s',... 352 upper(mfilename), 'must be in the range [0.0, 1.0].'); 353 end 354 355 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 356 function isInvalid = isInvalidRange(range) 357 358 isInvalid = min(range) < 0 || max(range) > 1; 359 360 361 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% 362 function gamma = validateGamma(gamma,image_type) 363 364 if strcmp(image_type,'intensity') 365 iptcheckinput(gamma,{'double'},{'scalar', 'nonnegative'}, ... 366 mfilename, 'GAMMA', 4) 367 else 368 iptcheckinput(gamma,{'double'},{'nonnegative','2d'},... 369 mfilename, 'GAMMA', 4) 370 if numel(gamma) == 1, 371 gamma = gamma*ones(1,3); 372 end 373 end