YOLOv8优化:注意力系列篇 | 全局多头自注意力MHSA,效果秒杀CBAM、SE
本文改进:MHSA注意力,引入到YOLOv8,多种实现方式
MHSA在不同检测领域中应用广泛
YOLOv8改进专栏:http://t.csdnimg.cn/hGhVK
学姐带你学习YOLOv8,从入门到创新,轻轻松松搞定科研;
![]()
1. BoTNet
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11605
本文介绍了BoTNet,这是一个概念简单但功能强大的主干架构,它将自注意力整合到多个计算机视觉任务中,包括图像分类、对象检测和实例分割。通过在ResNet的最后三个瓶颈块中用全局自注意力替换空间卷积,而不做其他更改,本方法在实例分割和对象检测方面显著改进了基线,同时也减少了参数,延迟开销最小。作者还指出了如何将自注意力的ResNet瓶颈块视为转换器块。在没有任何提示的情况下,最后,作者还提出了一种简单的BoTNet网络图像分类设计。
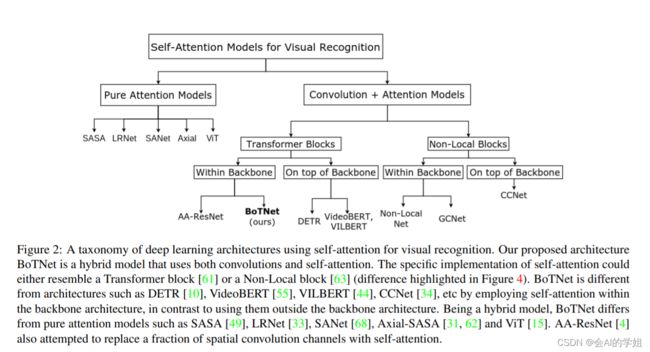
下图给出了利用自注意力实现的深度学习体系结构的分类。在本节中,将重点介绍:(1)Transformer vs BoTNet;(2) DETR vs BoTNet;(3)Non-Local vs BoTNet。
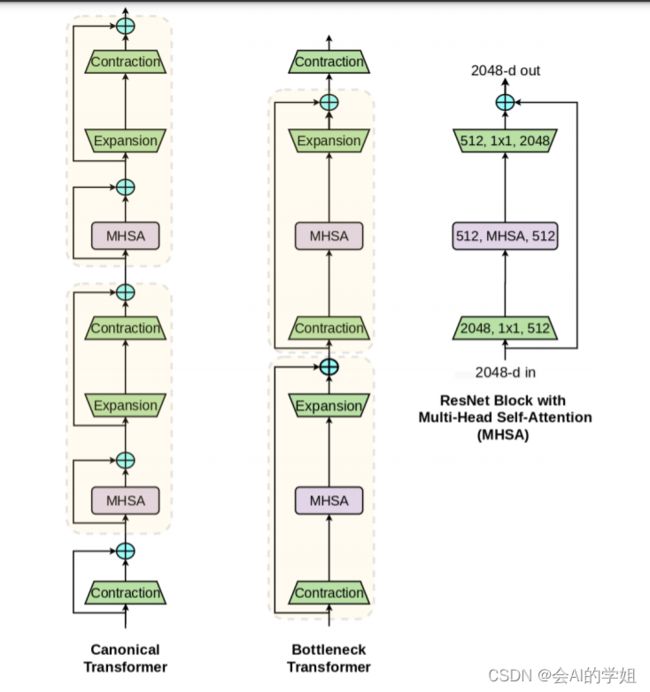
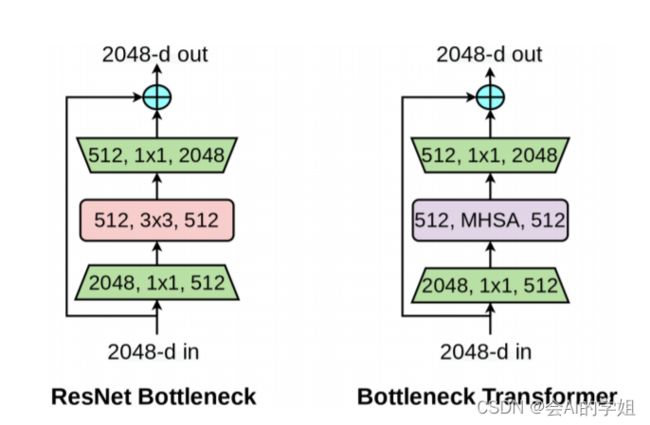
本文的一个关键信息是,具有多头自注意力(MHSA)层的ResNet瓶颈块可以被视为具有瓶颈结构的Transformer。下图直观地解释了这一点,作者将此块命名为瓶颈转换器(BoT)。除了图中已经可见的差异(残差连接和块连接)之外,还有一些差异:(1)Normalization:Transformer使用LN,而BoT 使用BN,这在ResNet瓶颈块中是典型的;(2) 非线性:Transformer在FFN块中使用一个非线性函数,而ResNet结构允许BoT块使用三个非线性函数;(3) 输出投影:Transformer中的MHSA块包含输出投影,而BoT块(图1)中的MHSA层(图4)不包含输出投影;(4) 使用SGD和动量优化器(通常用于计算机视觉),而Transformer通常使用Adam优化器]进行训练。
BoTNet(Bottleneck Transformer Network):一种基于Transformer的新骨干架构。BoTNet同时使用卷积和自注意力机制,即在ResNet的最后3个bottleneck blocks中使用全局多头自注意力(Multi-Head Self-Attention, MHSA)替换3 × 3空间卷积。
2.BoTNet、MHSA加入YOLOv8
2.1加入ultralytics/nn/attention/attention.py
###################### MHSA#### start ###############################
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MHSA(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_dims, width=14, height=14, heads=4, pos_emb=False):
super(MHSA, self).__init__()
self.heads = heads
self.query = nn.Conv2d(n_dims, n_dims, kernel_size=1)
self.key = nn.Conv2d(n_dims, n_dims, kernel_size=1)
self.value = nn.Conv2d(n_dims, n_dims, kernel_size=1)
self.pos = pos_emb
if self.pos:
self.rel_h_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([1, heads, (n_dims) // heads, 1, int(height)]),
requires_grad=True)
self.rel_w_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn([1, heads, (n_dims) // heads, int(width), 1]),
requires_grad=True)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
def forward(self, x):
n_batch, C, width, height = x.size()
q = self.query(x).view(n_batch, self.heads, C // self.heads, -1)
k = self.key(x).view(n_batch, self.heads, C // self.heads, -1)
v = self.value(x).view(n_batch, self.heads, C // self.heads, -1)
# print('q shape:{},k shape:{},v shape:{}'.format(q.shape,k.shape,v.shape)) #1,4,64,256
content_content = torch.matmul(q.permute(0, 1, 3, 2), k) # 1,C,h*w,h*w
# print("qkT=",content_content.shape)
c1, c2, c3, c4 = content_content.size()
if self.pos:
# print("old content_content shape",content_content.shape) #1,4,256,256
content_position = (self.rel_h_weight + self.rel_w_weight).view(1, self.heads, C // self.heads, -1).permute(
0, 1, 3, 2) # 1,4,1024,64
content_position = torch.matmul(content_position, q) # ([1, 4, 1024, 256])
content_position = content_position if (
content_content.shape == content_position.shape) else content_position[:, :, :c3, ]
assert (content_content.shape == content_position.shape)
# print('new pos222-> shape:',content_position.shape)
# print('new content222-> shape:',content_content.shape)
energy = content_content + content_position
else:
energy = content_content
attention = self.softmax(energy)
out = torch.matmul(v, attention.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)) # 1,4,256,64
out = out.view(n_batch, C, width, height)
return out
class BottleneckTransformer(nn.Module):
# Transformer bottleneck
# expansion = 1
def __init__(self, c1, c2, stride=1, heads=4, mhsa=True, resolution=None, expansion=1):
super(BottleneckTransformer, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * expansion)
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
# self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
if not mhsa:
self.cv2 = Conv(c_, c2, 3, 1)
else:
self.cv2 = nn.ModuleList()
self.cv2.append(MHSA(c2, width=int(resolution[0]), height=int(resolution[1]), heads=heads))
if stride == 2:
self.cv2.append(nn.AvgPool2d(2, 2))
self.cv2 = nn.Sequential(*self.cv2)
self.shortcut = c1 == c2
if stride != 1 or c1 != expansion * c2:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c1, expansion * c2, kernel_size=1, stride=stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(expansion * c2)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(c2, c2)
def forward(self, x):
out = x + self.cv2(self.cv1(x)) if self.shortcut else self.cv2(self.cv1(x))
return out
class BoT3(nn.Module):
# CSP Bottleneck with 3 convolutions
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, e=0.5, e2=1, w=20, h=20): # ch_in, ch_out, number, , expansion,w,h
super(BoT3, self).__init__()
c_ = int(c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1) # act=FReLU(c2)
self.m = nn.Sequential(
*[BottleneckTransformer(c_, c_, stride=1, heads=4, mhsa=True, resolution=(w, h), expansion=e2) for _ in
range(n)])
# self.m = nn.Sequential(*[CrossConv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g, 1.0, shortcut) for _ in range(n)])
def forward(self, x):
return self.cv3(torch.cat((self.m(self.cv1(x)), self.cv2(x)), dim=1))
###################### MHSA#### end ###############################2.2 修改tasks.py
首先BoTNet、MHSA进行注册
from ultralytics.nn.attention.attention import *函数def parse_model(d, ch, verbose=True): # model_dict, input_channels(3)进行修改
BoT定义
if m in (Classify, Conv, ConvTranspose, GhostConv, Bottleneck, GhostBottleneck, SPP, SPPF, DWConv, Focus,
BottleneckCSP, C1, C2, C2f, C3, C3TR, C3Ghost, nn.ConvTranspose2d, DWConvTranspose2d, C3x, RepC3
,BoT3):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc: # if c2 not equal to number of classes (i.e. for Classify() output)
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)MHSA定义
elif m in (MHSA,ECAAttention,TripletAttention,BAM,CoTAttention,PolarizedSelfAttention):
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != nc:
c2 = make_divisible(min(c2, max_channels) * width, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]2.3 yaml实现
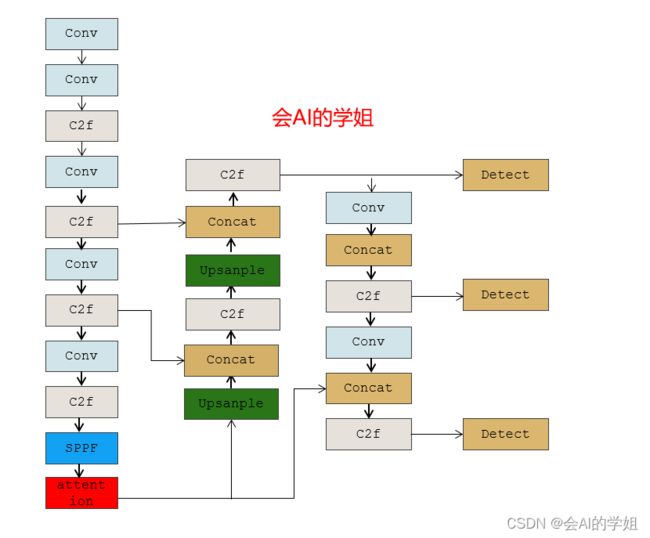
2.3.1 yolov8_MHSA.yaml
加入backbone SPPF后
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 1, MHSA, [1024]] # 10
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
2.3.2 yolov8_BoT3.yaml
# Ultralytics YOLO , AGPL-3.0 license
# YOLOv8 object detection model with P3-P5 outputs. For Usage examples see https://docs.ultralytics.com/tasks/detect
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
scales: # model compound scaling constants, i.e. 'model=yolov8n.yaml' will call yolov8.yaml with scale 'n'
# [depth, width, max_channels]
n: [0.33, 0.25, 1024] # YOLOv8n summary: 225 layers, 3157200 parameters, 3157184 gradients, 8.9 GFLOPs
s: [0.33, 0.50, 1024] # YOLOv8s summary: 225 layers, 11166560 parameters, 11166544 gradients, 28.8 GFLOPs
m: [0.67, 0.75, 768] # YOLOv8m summary: 295 layers, 25902640 parameters, 25902624 gradients, 79.3 GFLOPs
l: [1.00, 1.00, 512] # YOLOv8l summary: 365 layers, 43691520 parameters, 43691504 gradients, 165.7 GFLOPs
x: [1.00, 1.25, 512] # YOLOv8x summary: 365 layers, 68229648 parameters, 68229632 gradients, 258.5 GFLOPs
# YOLOv8.0n backbone
backbone:
# [from, repeats, module, args]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [64, 3, 2]] # 0-P1/2
- [-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]] # 1-P2/4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [128, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]] # 3-P3/8
- [-1, 6, C2f, [256, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]] # 5-P4/16
- [-1, 6, C2f, [512, True]]
- [-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]] # 7-P5/32
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024, True]]
- [-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]] # 9
- [-1, 1, BoT3, [1024]] # 10
# YOLOv8.0n head
head:
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 13
- [-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']]
- [[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat backbone P3
- [-1, 3, C2f, [256]] # 16 (P3/8-small)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 13], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P4
- [-1, 3, C2f, [512]] # 19 (P4/16-medium)
- [-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]]
- [[-1, 10], 1, Concat, [1]] # cat head P5
- [-1, 3, C2f, [1024]] # 22 (P5/32-large)
- [[16, 19, 22], 1, Detect, [nc]] # Detect(P3, P4, P5)