虚幻引擎游戏技能系统文档
GASDocumentation
通过一个简单的多人示例项目分享我对UE4中GAS插件的理解。 由于这不是官方文档,示例项目和我都不是来自Epic Games。因此我并不能保证描述的准确性。(译注:本人才疏学浅,还请大家多多指教)
这个文档的主要目的是讲解GAS的主要概念和其中的一些类,同时分享一些我的使用经验。
当前文档和项目基于Unreal Engine 4.25。
GASShooter是此文档的姊妹篇,主要通过多人FPS/TPS项目演示GAS的一些高级应用。
当然,最好的文档是GAS源代码本身(Plugins\Runtime\GameplayAbilities)。
文章目录
- GASDocumentation
-
- 1. 初识游戏技能系统GAS
- 2. 示例项目
- 3. 启用GAS
- 4. GAS概念
-
- 4.1 技能系统组件 Ability System Component
- 4.1.1 ASC复制模式
- 4.1.2 设置和初始化
- 4.2 游戏标签 Gameplay Tags
- 4.2.1 响应Gameplay Tags的改变
- 4.3 属性 Attributes
-
- 4.3.1 Attribute 定义
- 4.3.2 BaseValue vs CurrentValue
- 4.3.3 Meta Attributes
- 4.3.4 响应Attribute的改变
- 4.3.5 推导属性(Derived Attributes)
- 4.4 属性集 Attribute Set
-
- 4.4.1 Attribute Set 定义
- 4.4.2 Attribute Set 设计
-
- 具有个别属性的子组件
- 在运行时添加和删除属性集
- 物品属性 (武器弹药)
-
- 在物品上使用`floats`
- 在物品上使用`AttributeSet`
- 在物品上使用`ASC`
- 4.4.3 定义Attributes
- 4.4.4 初始化Attributes
- 4.4.5 PreAttributeChange()
- 4.4.6 PostGameplayEffectExecute()
- 4.4.7 OnAttributeAggregatorCreated()
- 4.5 游戏效果 Gameplay Effects
-
- 4.5.1 Gameplay Effect定义
- 4.5.2 应用Gameplay Effects
- 4.5.3 删除Gameplay Effects
- 4.5.4 Gameplay Effect修改器
- 4.5.5 叠加Gameplay Effects
- 4.5.6 赋予Abilities
- 4.5.7 游戏效果标签 Gameplay Effect Tags
- 4.5.8 免疫游戏效果
- 4.5.9 游戏效果细则 Gameplay Effect Spec
-
- SetByCallers
- 4.5.10 游戏效果上下文 Gameplay Effect Context
- 4.5.11 修改器量计算 Modifier Magnitude Calculation
- 4.5.12 游戏效果执行计算 Gameplay Effect Execution Calculation
- 4.5.13 自定义应用条件 Custom Application Requirement
- 4.5.14 技能消耗 Cost Gameplay Effect
- 4.5.15 技能冷却 Cooldown Gameplay Effect
-
- 获取冷却剩余时间
- 监听冷却的开始和结束
- 冷却预测
- 4.5.16 修改活动游戏效果的持续时间
- 4.5.17 在运行时创建动态游戏效果
- 4.5.18 游戏效果容器 Gameplay Effect Containers
- 4.6 游戏技能 Gameplay Abilities
-
- 4.6.1 Gameplay Ability定义
-
- 复制策略 Replication Policy
- 服务器端远程技能取消 Server Respects Remote Ability Cancellation
- 直接输入复制 Replicate Input Directly
- 4.6.2 输入绑定
- 4.6.3 赋予技能 Granting Abilities
- 4.6.4 激活技能 Activating Abilities
-
- 被动技能 Passive Abilities
- 4.6.5 取消技能 Canceling Abilities
- 4.6.6 获取当前活动的技能 Getting Active Abilities
- 4.6.7 实例化策略 Instancing Policy
- 4.6.8 网络执行策略 Net Execution Policy
- 4.6.9 技能标签 Ability Tags
- 4.6.10 游戏技能细则 Gameplay Ability Spec
- 4.6.11 为技能传递数据 Passing Data to Abilities
- 4.6.12 技能的消耗与冷却
- 4.6.13 技能升级
- 4.6.14 技能集 Ability Sets
- 4.6.15 技能批处理 Ability Batching
- 4.6.15 网络安全策略 Net Security Policy
- 4.7 技能任务 Ability Tasks
- 4.7.1 Ability Task定义
- 4.7.2 自定义Ability Tasks
- 4.7.3 使用Ability Tasks
- 4.7.4 Root Motion Source Ability Tasks
- 4.8 游戏表现 Gameplay Cues
-
- 4.8.1 Gameplay Cue定义
- 4.8.2 触发Gameplay Cues
- 4.8.3 本地游戏表现 Local Gameplay Cues
- 4.8.4 游戏表现参数 Gameplay Cue Parameters
- 4.8.5 游戏表现管理器 Gameplay Cue Manager
- 4.8.6 阻止触发游戏表现 Prevent Gameplay Cues from Firing
- 4.8.7 游戏表现批处理
-
- 手动RPC
- 一个游戏技能上的多个游戏表现
- 4.9 技能系统全局数据
-
- 4.9.1 InitGlobalData()
- 4.10 预测 Prediction
-
- 4.10.1 预测键 Prediction Key
- 4.10.2 在技能中创建新的预测窗口
- 4.10.3 可预测的生产Actor
- 4.10.4 GAS预测机制的开发计划
- 4.10.5 网络预测插件
- 4.11 技能目标
-
- 4.11.1 目标数据
- 4.11.2 目标Actor
- 4.11.3 游戏技能的标线
- 4.11.4 游戏效果容器
- 5. 常用的技能和效果
-
- 5.1 眩晕
- 5.2 冲刺
- 5.3 瞄准
- 5.4 生命偷取
- 5.5 服务器和客户端的随机数生成
- 5.6 致命一击
- 5.7 减速效果
- 5.8 暂停游戏时生成目标数据
- 6. GAS调试
-
- 6.1 showdebug abilitysystem
- 6.2 Gameplay Debugger
- 6.3 GAS 日志
- 7. 优化
-
- 7.1 技能批处理
- 7.2 游戏表现批处理
- 7.3 AbilitySystemComponent 复制模式
- 7.4 属性代理复制
- 7.5 ASC 延迟加载
- 8. 建议
-
- 8.1 Gameplay Effect Containers
- Blueprint AsyncTasks to Bind to ASC Delegates
- 9. 疑难解答
-
- `LogAbilitySystem: Warning: Can't activate LocalOnly or LocalPredicted ability %s when not local!`
- `ScriptStructCache` errors
- 10. GAS名词缩写
- 11. 其他资源
- 12. GAS 更新日志
-
- 4.25
- 4.24
1. 初识游戏技能系统GAS
来自 官方文档:
Gameplay技能系统 是一个高度灵活的框架,可用于构建你可能会在RPG或MOBA游戏中看到的技能和属性类型。你可以构建可供游戏中的角色使用的动作或被动技能,使这些动作导致各种属性累积或损耗的状态效果,实现约束这些动作使用的“冷却”计时器或资源消耗,更改技能等级及每个技能等级的技能效果,激活粒子或音效,等等。简单来说,此系统可帮助你在任何现代RPG或MOBA游戏中设计、实现及高效关联各种游戏中的技能,既包括跳跃等简单技能,也包括你喜欢的角色的复杂技能集。
GAS是由虚幻官方(Epic Games)开发的虚幻4引擎自带的一个插件,已被应用于Paragon和Fortnite中。
GAS插件提供了对于无论是单人还是多人游戏来说拆箱即用的解决方案:
- 实现了带有消耗和冷却功能且基于等级的角色技能
- 处理数值属性
- 应用状态效果
- 应用游戏标签
- 生成特效和音效
- 上述内容的网络复制
在多人游戏中,GAS同时提供了客户端预测的支持:
- 技能激活
- 播放动画蒙太奇
- 修改属性
- 应用游戏标签
- 生成游戏表现
- 基于
CharacterMovementComponent的移动
GAS必须在C++项目中才可使用,不过GameplayAbilities和GameplayEffects能够被设计师通过蓝图创建。
GAS当前的问题和使用的一些难处:
GameplayEffect延迟和解 ( can’t predict ability cooldowns resulting in players with higher latencies having lower rate of fire for low cooldown abilities compared to players with lower latencies)。- 无法预测
GameplayEffects的删除。不过我们可以通过添加一个反效果的GameplayEffects变相的实现此需求。当然这并不总是可行,这仍然是GAS的一个问题。 - 官方缺少多人游戏的示例和相关文档。希望此文档能够有所帮助!
2. 示例项目
通过一个多人的第三人称射击游戏演示文档中的内容,读者可以没有GAS基础,但需要有虚幻引擎的使用基础。比如C++,蓝图,UMG,网络同步等。这个示例项目通过创建两种类型的角色演示了如何使用GAS创建FPS多人游戏,其一:为PlayerState添加AbilitySystemComponent(后面简称为ASC)用以实现玩家和AI控制的英雄角色,其二:直接将ASC添加给Character用以创建AI控制的小怪或杂兵。
本文档主要讲解GAS的基本概念和基础实践,并不会包括高级主题比如可预测的炮弹。
具体涉及:
ASC应该属于PlayerState还是Character- 复制
Attributes - 复制动画蒙太奇
GameplayTags- 应用和删除
GameplayEffects - 应用被护甲降低的伤害以修改角色HP
GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations- 眩晕效果
- 死亡和重生
- 在服务器端通过Ability创建Actor(炮弹)
- 在瞄准和冲刺时可预测地改变本地玩家的速度
- 在冲刺时持续消耗耐力
- 消耗法力值的技能
- 被动技能
- 可叠加的
GameplayEffects - 目标选择
- 在蓝图中创建
GameplayAbilities - 在C++中创建
GameplayAbilities - 实例化的
GameplayAbilities - 非实例化的
GameplayAbilities(Jump) - 静态
GameplayCues(FireGun projectile impact particle effect) - Actor
GameplayCues(Sprint and Stun particle effects)
英雄角色有如下技能:
| 技能 | 绑定按键 | 可预测 | C++ / Blueprint | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jump | Space Bar | Yes | C++ | 跳跃 |
| Gun | Left Mouse Button | No | C++ | 射击, 动画支持预测炮弹不支持 |
| Aim Down Sights | Right Mouse Button | Yes | Blueprint | 瞄准,角色将降低移动速度 |
| Sprint | Left Shift | Yes | Blueprint | 冲刺,冲刺过程中会持续消耗耐力值 |
| Forward Dash | Q | Yes | Blueprint | 闪冲,一次性消耗耐力值 |
| Passive Armor Stacks | Passive | No | Blueprint | 每4秒可获取一个护甲的被动技能,最多4层,每次受伤掉一层护甲 |
| Meteor | R | No | Blueprint | 流星技能,范围伤害,同时可以击晕目标。 目标选取是可预测的,砸下来的流星不是 |
C++或者蓝图创建GameplayAbilities皆可,示例中会以这两种方式为例说明各自用法。
示例中的小怪没有任何技能,木桩而已。红色的小怪有回血BUFF,蓝色的小怪初始血量高。
关于GameplayAbility的命名,带有_BP的GameplayAbility是由蓝图创建,不带的是由C++创建。
蓝图资产命名前缀
| Prefix | Asset Type |
|---|---|
| GA_ | GameplayAbility |
| GC_ | GameplayCue |
| GE_ | GameplayEffect |
3. 启用GAS
使用GAS的基本步骤:
- 在虚幻引擎编辑器中启用GameplayAbilitySystem插件
- 编辑
YourProjectName.Build.cs添加"GameplayAbilities", "GameplayTags", "GameplayTasks"到PrivateDependencyModuleNames - 刷新Visual Studio工程
- 从4.24开始,必须要调用
UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData()才能使用TargetData。示例项目在UEngineSubsystem::Initialize()中调用InitGlobalData。详见InitGlobalData()
这就是启用GAS的全部步骤。下面将为Character 或者 PlayerState添加ASC和AttributeSet并开始创建 GameplayAbilities 和GameplayEffects!
4. GAS概念
4.1 技能系统组件 Ability System Component
AbilitySystemComponent (ASC)是整个技能系统的心脏。 ASC本质上是一个UActorComponent (UAbilitySystemComponent) 用于处理技能系统中的所有交互。任何希望使用Abilities或者想要包含Attributes或者想要接收GameplayEffects的Actor 必须拥有一个ASC。 这些对象存在于、被管理于、被复制于ASC(Attributes 的复制除外,其复制由 AttributeSet完成)。开发者可以子类化ASC,但这并不是必须的。
带有ASC的Actor也被称为ASC的OwnerActor。ASC实际作用的Actor叫作AvatarActor。OwnerActor和AvatarActor可以是同一个Actor,比如MOBA游戏中的野怪。它们也可以是不同的 Actors,比如MOBA游戏中玩家和AI控制的英雄角色,OwnerActor是PlayerState、AvatarActor是HeroCharacter。大部分情况下OwnerActor和AvatarActor可以是角色Actor。不过想像一下你控制的英雄角色死亡然后重生的过程,如果此时要保留死亡前的Attributes或者GameplayEffects,那么最理想的做法是将ASC交给PlayerState。
注意: 如果你将ASC给了PlayerState,那么你需要增加PlayerState的网络更新频率NetUpdateFrequency。 由于PlayerState默认的更新频率非常低,会导致 Attributes and GameplayTags的同步延迟。确保启用 Adaptive Network Update Frequency, Fortnite用了这个。
如果OwnerActor和AvatarActor是不同的Actors,那么两者都需要实现IAbilitySystemInterface。这个接口只有一个方法需要被重载UAbilitySystemComponent* GetAbilitySystemComponent() const,此方法将返回ASC。
ASC持有当前活动的GameplayEffects,详见FActiveGameplayEffectsContainer ActiveGameplayEffects。
ASC持有赋予的Gameplay Abilities,详见 FGameplayAbilitySpecContainer ActivatableAbilities。确保迭代ActivatableAbilities.Items时一定要在迭代之前添加ABILITYLIST_SCOPE_LOCK();。在ABILITYLIST_SCOPE_LOCK();的过程中更不要删除Ability。
4.1.1 ASC复制模式
ASC提供了三种不同的复制模式,用以复制GameplayEffects、GameplayTags 和 GameplayCues,分别是Full, Mixed, 和 Minimal。Attributes是由 AttributeSet复制。
| 复制模式 | 使用场景 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
Full |
单人 | GameplayEffect会被复制到所有客户端。 |
Mixed |
多人,玩家控制的Actors |
GameplayEffects仅被复制到拥有者的客户端. 仅 GameplayTags 和 GameplayCues 会被复制到所有客户端 |
Minimal |
多人, AI控制的Actors |
GameplayEffects不会复制到任何客户端. 仅 GameplayTags 和 GameplayCues 会被复制到所有客户端 |
注意: Mixed 复制模式要求OwnerActor的 Owner必须是Controller。 PlayerState的 Owner默认是Controller,但是Character不是。如果使用Mixed复制模式的OwnerActor不是PlayerState那么你需要在OwnerActor上调用SetOwner()并传递一个有效的Controller。(不过从4.24开始, PossessedBy() 会为Pawn设置一个新的Controller。)
4.1.2 设置和初始化
ASCs通常在OwnerActor的构建方法中创建并且显示的标记复制(Replicated)。 这一步必须在C++中完成。
AGDPlayerState::AGDPlayerState()
{
// Create ability system component, and set it to be explicitly replicated
AbilitySystemComponent = CreateDefaultSubobject(TEXT("AbilitySystemComponent"));
AbilitySystemComponent->SetIsReplicated(true);
//...
}
ASC需要有OwnerActor和AvatarActor进行初始化,而且必须在服务器和客户端都要完成初始化。
对于玩家控制的角色,ASC存在于Pawn中,我通常在Pawn的 PossessedBy()方法中完成ASC在服务器端的初始化,在PlayerController的AcknowledgePawn()方法中完成ASC在客户端的初始化。
void APACharacterBase::PossessedBy(AController * NewController)
{
Super::PossessedBy(NewController);
if (AbilitySystemComponent)
{
AbilitySystemComponent->InitAbilityActorInfo(this, this);
}
// ASC MixedMode replication requires that the ASC Owner's Owner be the Controller.
SetOwner(NewController);
}
void APAPlayerControllerBase::AcknowledgePossession(APawn* P)
{
Super::AcknowledgePossession(P);
APACharacterBase* CharacterBase = Cast(P);
if (CharacterBase)
{
CharacterBase->GetAbilitySystemComponent()->InitAbilityActorInfo(CharacterBase, CharacterBase);
}
//...
}
对于玩家控制的角色,ASC存在于PlayerState中,我通常在Pawn 的PossessedBy() 方法中完成ASC在服务器端的初始化(这一点与上述相同),在 Pawn的 OnRep_PlayerState()方法中完成ASC在客户端的初始化(这将确保PlayerState在客户端已存在)。
// Server only
void AGDHeroCharacter::PossessedBy(AController * NewController)
{
Super::PossessedBy(NewController);
AGDPlayerState* PS = GetPlayerState();
if (PS)
{
// Set the ASC on the Server. Clients do this in OnRep_PlayerState()
AbilitySystemComponent = Cast(PS->GetAbilitySystemComponent());
// AI won't have PlayerControllers so we can init again here just to be sure. No harm in initing twice for heroes that have PlayerControllers.
PS->GetAbilitySystemComponent()->InitAbilityActorInfo(PS, this);
}
//...
}
// Client only
void AGDHeroCharacter::OnRep_PlayerState()
{
Super::OnRep_PlayerState();
AGDPlayerState* PS = GetPlayerState();
if (PS)
{
// Set the ASC for clients. Server does this in PossessedBy.
AbilitySystemComponent = Cast(PS->GetAbilitySystemComponent());
// Init ASC Actor Info for clients. Server will init its ASC when it possesses a new Actor.
AbilitySystemComponent->InitAbilityActorInfo(PS, this);
}
// ...
}
如果你看到如下日志LogAbilitySystem: Warning: Can't activate LocalOnly or LocalPredicted ability %s when not local!说明你没有在客户端初始化ASC。
4.2 游戏标签 Gameplay Tags
FGameplayTags是一系列层次化的名字,如Parent.Child.Grandchild...这种格式。这些名字通过GameplayTagManager进行注册。 这些标签对于描述和归类一个对象的状态非常有用。例如,如果角色处于眩晕状态,我们可以给它一个State.Debuff.Stun的 GameplayTag在整个眩晕的过程中。
你会发现自己用GameplayTags替换了以前用布尔值或枚举处理的东西,并对对象是否具有某些GameplayTags进行了布尔逻辑。
为对象赋予标签,我们通常将标签添加到对象拥有的ASC中,这样GAS就能与标签交互。UAbilitySystemComponent实现了IGameplayTagAssetInterface接口中的方法以便访问它拥有的GameplayTags。
多个GameplayTags可以被存储到FGameplayTagContainer中。强烈建议使用GameplayTagContainer而不是TArray,因为GameplayTagContainers添加了一些例其高效的魔法。 标签是标准的FNames,在FGameplayTagContainers中他们可以被高效的打包在一起以完成网络复制,当然需要先在项目设置中开启Fast Replication。Fast Replication要求服务器和客户端拥有相同的GameplayTags列表。为了遍历GameplayTagContainers也可以返回一个TArray。
GameplayTags存储在 FGameplayTagCountContainer里有一个TagMap,存储了GameplayTag实例的数量。FGameplayTagCountContainer可以有一个GameplayTag 但是TagMapCount是0。任何HasTag()或HasMatchingTag()或其他类似的方法都会检查TagMapCount,如果GameplayTag不存在或者TagMapCount等于0将返回false。
GameplayTags需要在DefaultGameplayTags.ini中提早定义。 虚幻4的编辑器在项目设置中提供了一个界面可以让开发者管理GameplayTags而不需要手动编辑DefaultGameplayTags.ini。GameplayTag编辑器可以创建、重命名、删除GameplayTags,也可以查找标签的引用。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yJOhlMIH-1591700466338)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/gameplaytageditor.png)]
查找GameplayTag的引用将打开一个类似Reference Viewer的界面,显示引用GameplayTag的全部资源(不包括C++)。
重命名GameplayTags将会创建一个重定向,相关资源仍然引用原始的GameplayTag,GameplayTag将会被定向到新的GameplayTag。我推荐创建一个新的GameplayTag, 然后手动更新所有引用到这个新GameplayTag,然后删除旧的GameplayTag,这样可以避免重定向。(译者注:前面多花精力想好结构和名字,这玩意尽可能的不要在后面改)
另外,当开启Fast Replication后,GameplayTag编辑器可配置进一步优化GameplayTags的网络复制。
由GameplayEffect添加的GameplayTags会被复制。 ASC 也可以添加不会被复制并且需要手动管理的LooseGameplayTags。示例项目使用LooseGameplayTag处理State.Dead标签,因此当HP为0的时候所属客户端可以立即响应。重生时需要手动将TagMapCount设置为0。当使用LooseGameplayTags时仅需设置TagMapCount。建议使用UAbilitySystemComponent::AddLooseGameplayTag() 和 UAbilitySystemComponent::RemoveLooseGameplayTag() 方法设置TagMapCount。
在C++中获取GameplayTag的引用:
FGameplayTag::RequestGameplayTag(FName("Your.GameplayTag.Name"))
对于获取GameplayTag的父或子标签这类处理,可以通过GameplayTagManager中的一系列方法完成。要使用 GameplayTagManager, 首先include GameplayTagManager.h然后调用 UGameplayTagManager::Get().FunctionName即可。 GameplayTagManager 实际上以关系节点的方式存储了 GameplayTags 速度上要远优于字符串的处理和比较。
GameplayTags 和GameplayTagContainers 有可选的 UPROPERTY 说明符Meta = (Categories = "GameplayCue") ,可以用来在蓝图中实现标签的过滤,仅展示出属于父标签为GameplayCue的GameplayTags 。 要实现此功能也可以通过直接使用 FGameplayCueTag 其内部封装了一个带有Meta = (Categories = "GameplayCue")的 FGameplayTag 。
当把 GameplayTag 当作方法的参数时,可以通过 UFUNCTION specifier Meta = (GameplayTagFilter = "GameplayCue")完成过滤。(译者注:GameplayTagContainer 也已经支持Filter,不再赘述)
示例项目广泛的使用了 GameplayTags。
4.2.1 响应Gameplay Tags的改变
ASC提供了 GameplayTags 添加和删除的委托。可以通过 EGameplayTagEventType 枚举指明要监听 GameplayTag的添加和删除还是任何关于GameplayTag的TagMapCount变化。
AbilitySystemComponent->RegisterGameplayTagEvent(FGameplayTag::RequestGameplayTag(FName("State.Debuff.Stun")), EGameplayTagEventType::NewOrRemoved).AddUObject(this, &AGDPlayerState::StunTagChanged);
委托的回调方法会带有相关的 GameplayTag 和新的 TagCount。
virtual void StunTagChanged(const FGameplayTag CallbackTag, int32 NewCount);
4.3 属性 Attributes
4.3.1 Attribute 定义
Attributes 是由 FGameplayAttributeData定义的浮点值。 Attributes能够表达从角色的生命值到角色等级到药瓶的价格等任何数值。 如果Actor拥有游戏性相关的数值,那么可以考虑使用Attribute。Attributes 通常只能被GameplayEffects 修改,因此ASC可以 预测 这个修改。
Attributes 被定义并且存活在AttributeSet中。 AttributeSet也会负责处理 Attributes的复制。如何定义Attributes详见 AttributeSets。
提示: 如果你不想要Attribute显示在编辑器的属性详情中,可以使用 Meta = (HideInDetailsView) 属性说明符。
4.3.2 BaseValue vs CurrentValue
一个Attribute 由两个值构成 - 一个基值 BaseValue 和一个当前值CurrentValue. 基值BaseValue是属性 Attribute的一个恒值, 而当前值 CurrentValue 是 BaseValue 加上GameplayEffects的临时修改值。 例如,你的角色有个移动速度movespeed的属性Attribute其BaseValue为600 单位/秒。由于没有任何GameplayEffects修改movespeed,所以其CurrentValue也是600单位/秒。如果角色获取了一个50单位/秒的速度加成(BUFF),BaseValue仍然保持在600单位/秒,而CurrentValue 将等于650单位/秒=600 + 50。当移动速度加成BUFF过期后,CurrentValue 将恢复成BaseValue` 600单位/秒。
通常刚接触GAS的新手会将BaseValue理解为或当作是一个属性的最大值。这是不正确的, 能够被技能或者UI使用的Attribute的最大值应该是另一个单独的Attribute。 对于硬编码的最大值和最小值,可以通过FAttributeMetaData的DataTable定义,其可以设置最大值和最小值,但Epic注意这个结构体"work in progress"。详见AttributeSet.h。 为了清除困惑,强烈建议用于技能或者UI上的最大值Attribute是一个单独的Attribute,并且FAttributeMetaData中的最大值和最小值仅用于属性值的限定(Clamping)。CurrentValue 的属性值限定将会在PreAttributeChange()谈论,BaseValue 的属性值限定将会在PostGameplayEffectExecute()讨论,其执行由GameplayEffects触发。
立即(Instant) GameplayEffects将永久改变BaseValue,而持续(Duration) 和永恒(Infinite) GameplayEffects 将改变CurrentValue。周期性(Periodic )GameplayEffects像立即(Instant) GameplayEffects一样将改变BaseValue
4.3.3 Meta Attributes
有一些Attributes会被当作仅用于与其他Attributes交互的临时值来使用,这种属性被称作元属性( Meta Attributes)。例如,我们通常定义伤害值(damage)为元属性,而不是直接在 GameplayEffect中修改生命 Attribute。这样damage的值 可以在Buffs和Debuffs的 GameplayEffectExecutionCalculation中修改,也可以在 AttributeSet中被进一步处理,例如让damage减掉当前的护甲 Attribute, 最后让生命值 Attribute减去damage即可。 这个 damage 元属性并不持久在每一次的GameplayEffects其值都会被覆盖,Meta Attributes 通常也不会被网络复制。
Meta Attributes 为伤害和治愈这种属性( “造成了多少伤害?”,“用这个伤害做什么?”)提供了一个好的逻辑分离方案。逻辑分离意味着我们的Gameplay Effects 和 Execution Calculations不需要关心目标如何处理damage。继续我们的damage 示例,Gameplay Effect 决定了damage是多少,然后AttributeSet决定了如何使用damage。并不是所有角色都有相同的Attributes,尤其是当子类化AttributeSets时。基类 AttributeSet 可能只拥有一个生命值的Attribute,但其子类AttributeSet 可能添加了一个护盾的Attribute。那么这两个AttributeSets对于damage的处理肯定不同。
Meta Attributes是一个好的设计模式,当然这并不代表一定要使用Meta Attributes。如果你仅有一个Execution Calculation 用于处理所有damage并且仅有一个 Attribute Set类用于所有角色,那么你可以直接在Exeuction Calculation中修改生命值,护盾等属性。这样做也是可行的,但会牺牲掉灵活性。
4.3.4 响应Attribute的改变
要监听 Attribute的变化以更新UI或者做其他事情,可以使用UAbilitySystemComponent::GetGameplayAttributeValueChangeDelegate(FGameplayAttribute Attribute)。这个方法会返回一个委托,可以为特定属性绑定一个回调方法,当属性改变会自动执行这个方法。这个委托会提供一个FOnAttributeChangeData参数,带有NewValue, OldValue和FGameplayEffectModCallbackData。 Note: FGameplayEffectModCallbackData 仅在服务器端有效。
AbilitySystemComponent->GetGameplayAttributeValueChangeDelegate(AttributeSetBase->GetHealthAttribute()).AddUObject(this, &AGDPlayerState::HealthChanged);
virtual void HealthChanged(const FOnAttributeChangeData& Data);
示例项目在GDPlayerState 中绑定了Attribute 值改变的委托用以更新HUD和当生命值为0时响应死亡。
在示例项目中还包含了一个使用异步任务(AsyncTask)处理Attribute委托回调的自定义蓝图节点。它被用在UI_HUD UMG Widget中用来更新生命值,法力值,体力值。异步任务AsyncTask会永远存活直到调用EndTask(), 我们会在 UMG Widget的 Destruct 事件中调用,详见AsyncTaskAttributeChanged.h/cpp。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-46I977RZ-1591700466340)(C:\Users\X\Desktop\attributechange.png)]
4.3.5 推导属性(Derived Attributes)
要使某个属性依据其他属性进行更新,可以使用永恒(Infinite)的GameplayEffect和基于属性或MMC(Custom Calculation Class)的修改器。在其他属性变化时这个属性将会自动更新。这个属性叫作推导属性(Derived Attributes)。
推导属性上所有修改器的最终公式与修改器聚合器(Modifier Aggregators)的公式相同。如果需要按一定顺序进行计算,可以在MMC内部完成所有操作。
((CurrentValue + Additive) * Multiplicitive) / Division
注意: 在PIE中运行多个客户端实例时,一定要在Editor Preferences中禁用Run Under One Process。否则除第一个客户端之外的客户端将不会更新`推导属性。
示例,我们有一个 Infinite GameplayEffect,其根据属性TestAttrB和TestAttrC推导(计算)并更新属性TestAttrA的值, 计算公式如下:
TestAttrA = (TestAttrA + TestAttrB) * ( 2 * TestAttrC)
在TestAttrB和TestAttrC发生变化时TestAttrA的属性值将根据上述公式重新计算
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-5GTWDac1-1591700466341)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/derivedattribute.png)]
4.4 属性集 Attribute Set
4.4.1 Attribute Set 定义
AttributeSet 负责定义和持有属性并且管理属性的变化。开发者可以子类化UAttributeSet。在OwnerActor的构造方法中创建的AttributeSet将会自动注册到ASC。这一步必须在C++中完成。
4.4.2 Attribute Set 设计
一个ASC可以拥有一个或多个AttributeSets。属性集的内存开销是微不足道的,因此要使用多少属性集完全由开发者决定。
在游戏中所有Actor共享一个巨大的AttributeSet也是可行的,每个Actor仅使用需要的属性即可。
或者,你也可以使用多个AttributeSet对Attributes进行分组,然后根据Actors的需要进行有选择添加。例如,可以创建一个与生命值属性有关的AttributeSet,再创建一个与法力值属性有关的AttributeSet,等等。在MOBA游戏中,英雄可能需要法力值,但小怪可能不需要。
另外,AttributeSets 可以被子类化,这也作为Actor选择拥有哪些属性的另一种方式。Attributes 在内部以AttributeSetClassName.AttributeName的方式引用。当你子类化AttributeSet后,所有父类的属性也必须通过父类作为前缀引用(ParentClassName.AttributeName)。
在一个ASC中可以有多个不同的AttributeSet,谨记因为上述的属性引用方式,所以同一个AttributeSet在一个ASC中最多只能有一个。
具有个别属性的子组件
考虑一个场景,当Pawn上有多个可被破坏的组件时(比如可被破坏的护甲),假设你已经知道了一个Pawn可拥有护甲的最大数量,那么Pawn可以有一个包含众多像DamageableCompHealth0、DamageableCompHealth1等属性的AttributeSet,然后通过一些方法(logical slots)将这些属性与护甲关联起来。在护甲组件中有个槽位数字,护甲受到伤害时可以通过这个槽位数字索引到能够被GameplayAbilities 或者Executions处理的Attribute。即使Pawns拥有的护甲少于AttributeSet中定义的属性数量也没关系,因为AttributeSet中定义的未被使用的Attribute只占用极小的内存开销。
如果你的子组件需要很多Attributes,或者子组件的数量是未知的,再或者子组件会被卸载然后被其他玩家使用(比如武器)。总之不管什么情况当上述方案并不能满足需求时,那么我建议你在组件上直接使用float并且远离Attributes。详见 物品属性。
在运行时添加和删除属性集
可以通过ASC在运行时动态添加和删除AttributeSets,当然,删除AttributeSets是非常危险的。例如,如果一个AttributeSet的删除在客户端先完成于服务器端时,恰巧AttributeSet中的一个Attribute's Value的修改被同步到客户端,Attribute将无法找到所属的AttributeSet这将导致游戏崩溃。
however, removing AttributeSets can be dangerous. For example, if an AttributeSet is removed on a client before the server and an Attribute value change is replicated to client, the Attribute won’t find its AttributeSet and crash the game.
装备武器时:
AbilitySystemComponent->SpawnedAttributes.AddUnique(WeaponAttributeSetPointer);
AbilitySystemComponent->ForceReplication();
卸载武器时:
AbilitySystemComponent->SpawnedAttributes.Remove(WeaponAttributeSetPointer);
AbilitySystemComponent->ForceReplication();
物品属性 (武器弹药)
有多种方式可以实现带有属性(武器弹药、装甲耐久等等)的可装备物品,所有这些方式都是将值直接存储在物品上,对于能够被其他玩家装备和使用的物品这是必须的。方法如下:
- 在物品上使用
floats(推荐)- 在物品上使用
AttributeSet- 在物品上使用
ASC
在物品上使用floats
代替Attributes,直接在物品实例上存储浮点值。堡垒之夜和GASShooter使用这种方式处理枪的弹药。对于一把枪,需要存储弹夹大小,弹夹弹药数量,储备弹药等可直接使用支持复制的浮点数(COND_OwnerOnly)。如果储备弹药是在武器间共享的(换句话说储备弹药属于角色而不是武器),那么你可以为Character添加一个带有储备弹药Attribute的AttributeSet。由于弹夹弹药数量没有使用Attributes,所以你需要重载几个UGameplayAbility的方法以检查和应用消耗(枪上的浮点值)。在授予Ability时,需要将枪作为GameplayAbilitySpec的SourceObject 才能在Ability中访问枪的数据(译者注:读一下示例中如何实现的射击就理解这个了)
为了防止枪在自动射击时弹药复制会搞乱本地弹药数量,所以需要在PreReplication(此方法仅在服务器执行)中判断当玩家射击时(IsFiring GameplayTag)禁止replication,也可以在这里实现你自己的本地预测。
void AGSWeapon::PreReplication(IRepChangedPropertyTracker& ChangedPropertyTracker)
{
Super::PreReplication(ChangedPropertyTracker);
DOREPLIFETIME_ACTIVE_OVERRIDE(AGSWeapon, PrimaryClipAmmo, (IsValid(AbilitySystemComponent) && !AbilitySystemComponent->HasMatchingGameplayTag(WeaponIsFiringTag)));
DOREPLIFETIME_ACTIVE_OVERRIDE(AGSWeapon, SecondaryClipAmmo, (IsValid(AbilitySystemComponent) && !AbilitySystemComponent->HasMatchingGameplayTag(WeaponIsFiringTag)));
}
优势:
- 解决了使用
AttributeSets的限制 (继续往下看)
缺陷:
- 不能使用
GameplayEffect(比如Cost GEs) - 需要手动重载
UGameplayAbility的方法才能检查和应用弹药消耗
在物品上使用AttributeSet
在物品上使用单独的AttributeSet,当玩家装备物品时将物品上的AttributeSet动态添加到玩家的ASC上是可行的,但也会带来一些问题。我在GASShooter早期的版本中为武器弹药使用这种方式。武器通过一个AttributeSet存储了一些Attributes,例如弹夹大小,弹夹弹药数量,储备弹药等。如果储备弹药是在武器间共享的,那么可以将所需属性(Reserve Ammo)转移到角色身上。当在服务器端玩家装备武器时,武器的AttributeSet将会被添加到玩家的ASC::SpawnedAttributes中,然后服务器将此复制到客户端。如果玩家卸载武器,过程同上,只是由添加变成删除。
当AttributeSet 存在于非OwnerActor(比如武器),然后在构造方法中初始化AttributeSet时将会编译错误。解决办法是将其放在BeginPlay()进行初始化,还要在武器上实现IAbilitySystemInterface 接口,在装备武器时设置ASC的指针。
void AGSWeapon::BeginPlay()
{
if (!AttributeSet)
{
AttributeSet = NewObject(this);
}
//...
}
上述示例详见older version of GASShooter.
优势:
- 可以使用
GameplayAbility和GameplayEffect的工作流(Cost GEs) - 物品少时易于设置
缺陷:
- 对于每个武器都需要一个新的
AttributeSet,因为ASC仅能有一个AttributeSetClass的实例。(如果你能够同时装备两把武器,这两把武器又有相同的AttributeSet,这个方案就无解了) - 删除
AttributeSet是非常危险的。上面解释过,不再赘述。
在物品上使用ASC
为每个物品添加一个ASC是一种极端的方案。我没有亲自实践过这种方案,也没见过。要实现这个方案可能需要大量的工程工作。
多个
ASCs拥有相同的Owner不同的Avatars是否可行(比如pawn和weapon/items/projectiles的Owner全设置为PlayerState)?第一个问题,在
Owing Actor上实现IGameplayTagAssetInterface和IAbilitySystemInterface。实现IGameplayTagAssetInterface或许可能:仅汇总所有ASCs中的标签(但请注意,HasAlMatchingGameplayTags只能通过交叉ASC聚合来满足)。但要实现IAbilitySystemInterface会更棘手:哪一个ASC才是权威的?如果要应用一个GE,哪一个ASC会接收它?也许你可以解决这些问题,但Owner拥有多个ASCs才是最难处理的。在
pawn和weapon上有单独的ASCs这很好理解。例如,区分描述weapon的标签和描述owing pawn的标签,也许应用在武器上的标签应用在拥有者上也是有意义的(例如属性和GEs是独立的,但拥有者将会聚合拥有的标签像我上面描述的)。我相信这可以解决,但相同的owner拥有多个ASCs会有很大的风险。
Dave Ratti from Epic’s answer to community questions #6
优势:
- 可以使用
GameplayAbility和GameplayEffect的工作流(Cost GEs) - 可以重用
AttributeSetClasses (因为每个武器都有自己的ASC)
缺陷:
- 未知的工作量
- 甚至于此方案的可行性?
4.4.3 定义Attributes
Attributes只能在C++ 的AttributeSet头文件中定义。强烈建议在每个AttributeSet 头文件中定义下述宏,它将会为属性自动生成Getter和Setter。
// Uses macros from AttributeSet.h
#define ATTRIBUTE_ACCESSORS(ClassName, PropertyName) \
GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_PROPERTY_GETTER(ClassName, PropertyName) \
GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_VALUE_GETTER(PropertyName) \
GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_VALUE_SETTER(PropertyName) \
GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_VALUE_INITTER(PropertyName)
可被复制(replicated)的生命值的定义:
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, Category = "Health", ReplicatedUsing = OnRep_Health)
FGameplayAttributeData Health;
ATTRIBUTE_ACCESSORS(UGDAttributeSetBase, Health)
同样需要在头文件中定义 OnRep 方法:
UFUNCTION()
virtual void OnRep_Health(const FGameplayAttributeData& OldHealth);
在AttributeSet 的.cpp文件中实现OnRep方法,调用GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_REPNOTIFY 宏才能使用预测系统
void UGDAttributeSetBase::OnRep_Health(const FGameplayAttributeData& OldHealth)
{
GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_REPNOTIFY(UGDAttributeSetBase, Health, OldHealth);
}
最后, Attribute 需要被添加到GetLifetimeReplicatedProps中:
void UGDAttributeSetBase::GetLifetimeReplicatedProps(TArray& OutLifetimeProps) const
{
Super::GetLifetimeReplicatedProps(OutLifetimeProps);
DOREPLIFETIME_CONDITION_NOTIFY(UGDAttributeSetBase, Health, COND_None, REPNOTIFY_Always);
}
REPTNOTIFY_Always 告诉 OnRep 方法在本地值和服务器下发的值即使已经相同也会触发(为了预测),默认情况下OnRep不会触发。
如果Attribute不需要复制(像Meta Attribute),那么OnRep 和GetLifetimeReplicatedProps可以被跳过。
4.4.4 初始化Attributes
有多种方法可以初始化Attributes (设置BaseValue并因此让其CurrentValue为某个初始值),Epic建议使用一个Instant GameplayEffect,这也是示例项目中使用的方法。详见示例项目中的GE_HeroAttributes蓝图(在C++中应用的这个GameplayEffect)。
当定义Attributes属性时使用了ATTRIBUTE_ACCESSORS 宏,它将会为每个属性自动生成一个初始化方法
// InitHealth(float InitialValue) is an automatically generated function for an Attribute 'Health' defined with the `ATTRIBUTE_ACCESSORS` macro
AttributeSet->InitHealth(100.0f);
更多初始化属性的方法详见AttributeSet.h。
注意: 在4.24之前,FAttributeSetInitterDiscreteLevels将不能和FGameplayAttributeData一起工作。它会在属性是原始浮点数时创建, 会抱怨FGameplayAttributeData不是Plain Old Data(POD)。4.24已经解决了这个问题 https://issues.unrealengine.com/issue/UE-76557。
4.4.5 PreAttributeChange()
PreAttributeChange(const FGameplayAttribute& Attribute, float& NewValue)是AttributeSet中一个主要的方法,当Attribute的CurrentValue被改变之前调用。对于让CurrentValue保持在正确的范围这是个理想的地方。
示例中让movespeed保持在150-1000 units/s之间:
if (Attribute == GetMoveSpeedAttribute())
{
// Cannot slow less than 150 units/s and cannot boost more than 1000 units/s
NewValue = FMath::Clamp(NewValue, 150, 1000);
}
GetMoveSpeedAttribute()是由宏创建(Defining Attributes)。
任何Attributes的改变都会调用此方法,无论是使用Attribute setters 还是使用GameplayEffects。
注意: 此处的clamping并没有永久地修改ASC的modifier,它仅改变了查询modifier返回的值。这意味着任何修改器GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations和ModifierMagnitudeCalculations对CurrentValue的重计算都要重新clamping。
注意: Epic注释,不要使用PreAttributeChange()处理游戏性事件,仅用它处理clamping(让CurrentValue处在正确的范围内)。监听Attribute的改变进行游戏性事件处理(比如角色上的血条)最好使用UAbilitySystemComponent::GetGameplayAttributeValueChangeDelegate(FGameplayAttribute Attribute) (Responding to Attribute Changes)。
4.4.6 PostGameplayEffectExecute()
PostGameplayEffectExecute(const FGameplayEffectModCallbackData & Data) 仅在instant GameplayEffect使Attribute的 BaseValue改变时触发。GameplayEffect执行后,在这里可以对Attribute做进一步处理。
比如,在示例项目中当角色受到伤害后我们在这里让Health Attribute减去最终伤害值(Final Damage Meta Attribute)。如果有护盾属性(Shield Attribute),我们可以先通过护盾抵消相对的伤害,然后让生命值减去剩余的伤害。示例项目也在这里处理击中反应动画,显示伤害跳字,给击杀者经验和金币奖励。在设计上,伤害值Meta Attribute将始终通过instant GameplayEffect进行设置,永远不会通过Attribute setter设置。
由instant GameplayEffect改变BaseValue的其他属性,像法力值和耐力值也可以通过其最大值属性(MaxMana或MaxStamina)在此处进行clamping。
注意 当PostGameplayEffectExecute()被调用时,对属性的改变已经发生 ,但还没有复制回客户端,因此在此处进行clamping不会执行两次复制,客户端只要收到clamping后的结果。
4.4.7 OnAttributeAggregatorCreated()
在属性集中当为Attribute创建聚合器(Aggregator)后将会调用OnAttributeAggregatorCreated(const FGameplayAttribute& Attribute, FAggregator* NewAggregator)。在此方法中可以设置FAggregatorEvaluateMetaData。AggregatorEvaluateMetaData被Aggregator用来基于所有应用到当前属性的Modifiers求CurrentValue的值。默认情况下,AggregatorEvaluateMetaData 仅被Aggregator 用来确定哪些Modifiers符合MostNegativeMod_AllPositiveMods ,MostNegativeMod_AllPositiveMods 允许所有正的Modifiers和最负的Modifiers。Paragon中使用此方法仅允许将最负面的减速效果应用于玩家,无论正在应用多少减速效果。没有资格的Modifiers仍然存在于ASC上,只是不会被汇总到最终的CurrentValue。当条件改变后这些Modifiers仍有可能取得资格,比如最负的Modifier已经过时,那么下一个最负的Modifier()将会取得资格。
示例中使用AggregatorEvaluateMetaData仅允许最负的Modifier和所有正的`Modifiers:
virtual void OnAttributeAggregatorCreated(const FGameplayAttribute& Attribute, FAggregator* NewAggregator) const override;
void UGSAttributeSetBase::OnAttributeAggregatorCreated(const FGameplayAttribute& Attribute, FAggregator* NewAggregator) const
{
Super::OnAttributeAggregatorCreated(Attribute, NewAggregator);
if (!NewAggregator)
{
return;
}
if (Attribute == GetMoveSpeedAttribute())
{
NewAggregator->EvaluationMetaData = &FAggregatorEvaluateMetaDataLibrary::MostNegativeMod_AllPositiveMods;
}
}
自定义的AggregatorEvaluateMetaData限定符需要以静态变量的方式添加到FAggregatorEvaluateMetaDataLibrary。(译者注:还要为其提供一个类似void QualifierFunc_MostNegativeMod_AllPositiveMods(const FAggregatorEvaluateParameters& EvalParameters, const FAggregator* Aggregator)的方法)
4.5 游戏效果 Gameplay Effects
4.5.1 Gameplay Effect定义
GameplayEffects (GE) 是Abilities改变自己或别人的Attributes 和GameplayTags的途径。GEs可以立即改变Attribute(像伤害、治疗)或者立即应用持续长时间的Buff/Debuffs(移动加速或眩晕)。UGameplayEffect是定义一个游戏效果的数据类,GameplayEffects中不能添加任何其他逻辑。通常设计者只需要创建UGameplayEffect的蓝图派生类。
GameplayEffects通过Modifiers 和Executions (GameplayEffectExecutionCalculation) 改变Attributes。
GameplayEffects有三种持续类型:立即(Instant),持续( Duration),和无限(Infinite)。
此外,GameplayEffects 也能够添加和执行GameplayCues。 Instant GameplayEffect将调用GameplayCue的Execute,Duration或Infinite GameplayEffect将在GameplayCue GameplayTags上执行添加和删除。
| 持续类型 | GameplayCue 事件 | 何时使用 |
|---|---|---|
Instant |
Execute | 用于立即永久改变Attribute的BaseValue。GameplayTags将不适用,即使一帧也不行。 |
Duration |
Add & Remove | 用于临时修改Attribute的CurrentValue,并且添加GameplayTags( 在GameplayEffect过期时将会被删除或者手动删除)。持续时间可以在UGameplayEffect的类或蓝图中指定。 |
Infinite |
Add & Remove | 用于临时修改Attribute的CurrentValue,并且添加GameplayTags(在GameplayEffect被移除时删除)。永不过时,必须通过Ability或ASC手动删除。 |
Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects有周期效果(Periodic Effects)配置项,可以通过配置Period每隔x秒周期性的执行Modifiers 和Executions。周期性效果可以看作是Instant GameplayEffects,每次修改属性的BaseValue并且执行GameplayCues。这对实现持续伤害效果非常有用。 注意: Periodic Effects 不能被预测。
如果你需要手动重新计算Duration或Infinite GameplayEffect的Modifiers(比如有一个MMC要使用的数据并不是来源于Attributes),可以通过调用UAbilitySystemComponent::ActiveGameplayEffects.SetActiveGameplayEffectLevel(FActiveGameplayEffectHandle ActiveHandle, int32 NewLevel)传递一个从UAbilitySystemComponent::ActiveGameplayEffects.GetActiveGameplayEffect(ActiveHandle).Spec.GetLevel()获取的NewLevel,Level本质并没有变化 ,只是为了调用SetActiveGameplayEffectLevel以更新Modifiers,其内部的主要实现如下:
MarkItemDirty(Effect);
Effect.Spec.CalculateModifierMagnitudes();
// Private function otherwise we'd call these three functions without needing to set the level to what it already is
UpdateAllAggregatorModMagnitudes(Effect);
GameplayEffects 的创建很特别。当Ability或ASC想要应用一个GameplayEffect时,会从GameplayEffect的ClassDefaultObject创建一个GameplayEffectSpec。然后当应用成功后将其添加到ASC的ActiveGameplayEffects(FActiveGameplayEffect)中。
4.5.2 应用Gameplay Effects
在GameplayAbilities和ASC中有多个方法可以应用GameplayEffects,通常格式是ApplyGameplayEffectTo。不同的方法其本质是相同的,都是在目标上调用UAbilitySystemComponent::ApplyGameplayEffectSpecToSelf()。
在GameplayAbility 之外应用GameplayEffects (比如炮弹),你需要获取目标的ASC然后调用其ApplyGameplayEffectToSelf方法。
你也可以通过下述方法监听在ASC上应用任何Duration或Infinite的GameplayEffects:
AbilitySystemComponent->OnActiveGameplayEffectAddedDelegateToSelf.AddUObject(this, &APACharacterBase::OnActiveGameplayEffectAddedCallback);
回调方法:
virtual void OnActiveGameplayEffectAddedCallback(UAbilitySystemComponent* Target, const FGameplayEffectSpec& SpecApplied, FActiveGameplayEffectHandle ActiveHandle);
服务器总会调用此方法无论什么复制模式。当复制模式为Full或Mixed时,自主代理会调用此方法。只有当复制模式为Full时,模拟代理才会调用此方法。
4.5.3 删除Gameplay Effects
在GameplayAbilities和ASC中有多个方法可以删除GameplayEffects,通常格式是RemoveActiveGameplayEffect。不同的方法其本质是相同的,都是在目标上调用FActiveGameplayEffectsContainer::RemoveActiveEffects()。
在GameplayAbility 之外删除GameplayEffects,你需要获取目标的ASC然后调用其RemoveActiveGameplayEffect方法。
你也可以通过下述方法监听在ASC上删除任何Duration或Infinite的GameplayEffects:
AbilitySystemComponent->OnAnyGameplayEffectRemovedDelegate().AddUObject(this, &APACharacterBase::OnRemoveGameplayEffectCallback);
回调方法:
virtual void OnRemoveGameplayEffectCallback(const FActiveGameplayEffect& EffectRemoved);
服务器总会调用此方法无论什么复制模式。当复制模式为Full或Mixed时,自主代理会调用此方法。只有当复制模式为Full时,模拟代理才会调用此方法。
4.5.4 Gameplay Effect修改器
修改器(Modifiers)用于修改属性并且是属性修改预测的仅有方式。一个GameplayEffect 可以有0个或多个Modifiers。每一个修改器只能通过下述方式修改一个属性:
| 操作 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Add |
加 |
Multiply |
乘 |
Divide |
除 |
Override |
覆盖 |
Attribute 的CurrentValue 是一系列Modifiers添加到BaseValue的聚合结果。聚合Modifiers的公式如下所示(FAggregatorModChannel::EvaluateWithBase):
((InlineBaseValue + Additive) * Multiplicitive) / Division
任何Override Modifiers都会优先使用最后应用的Modifier覆盖最终值。
注意: 百分比的修改要使用Multiply(在Additive之后执行)
注意: 百分比的修改Prediction会有问题。
一共有四种Modifiers:Scalable Float, Attribute Based, Custom Calculation Class, and Set By Caller。这些全部通过浮点值和操作符改变Modifier的Attribute。
| 修改器类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Scalable Float |
FScalableFloats是一种能够指向Data Table(行表示变量,列表示等级)的结构。 Scalable Floats将根据当前技能等级(或者是在GameplayEffectSpec覆盖的等级)自动读取值。这个值可以根据系数进一步处理。如果没有指定数据表,值会被当作是1,需要硬编码系数作为实际的值(忽略等级)。[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-F6d0oFbK-1591700466343)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/scalablefloats.png)] |
Attribute Based |
Attribute Based Modifiers 基于源(GameplayEffectSpec创建者)或目标(GameplayEffectSpec接收者)的支持属性的CurrentValue 或BaseValue并且可通过系数、Pre/Post Multiply Additive Value进一步处理。快照(Snapshot)意味着取GameplayEffectSpec被创建时属性的值,否则取GameplayEffectSpec被应用时属性的值。 |
Custom Calculation Class |
Custom Calculation Class 是最灵活和最复杂的Modifiers。这个Modifier需要创建一个ModifierMagnitudeCalculation类并且可通过系数、Pre/Post Multiply Additive Value进一步处理。 |
Set By Caller |
SetByCaller Modifiers是在GameplayEffect之外由Ability在运行时设置或者由GameplayEffectSpec的创建者设置。 例如,当你想根据按钮按下的时间决定伤害大小时可以使用SetByCaller。SetByCallers本质是存在于GameplayEffectSpec上的TMap,Modifier仅仅是告诉聚合器通过GameplayTag去检索值。 SetByCallers仅能使用GameplayTag不能使用FName。如果没有在GameplayEffectSpec中找到GameplayTag对应的值,游戏将会抛出一个运行时错误并且返回0。如果运算是除法你就悲剧了。 具体使用详见SetByCallers。 |
4.5.5 叠加Gameplay Effects
GameplayEffects 默认会无视已存在的GameplayEffectSpec实例,在应用GameplayEffectSpec 时会直接创建新的实例。GameplayEffects 也能够设置在新增效果时使用叠加替代创建新实例,这将只会改变当前已存在GameplayEffectSpec的叠加数量。叠加仅能用于Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects。
有两种类型的叠加:源聚合和目标聚合。
| 叠加类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 源聚合 | 目标上的每一个不同源的ASC都有一个单独的栈实例。每一个源能够应用X个栈。 |
| 目标聚合 | 在目标上仅有一个栈实例无论源有多少。每一个源能够应用栈的上限不能超过共享栈限制。 |
叠加也有一些相应的策略:过期、持续时间刷新、定期刷新。在GameplayEffect蓝图上有对应的悬停提示。
示例项目包含了一个自定义的蓝图节点用于监听GameplayEffect 栈的变化。UI界面使用这个监听更新玩家拥有的被动护甲叠加数量。我们将在UMG的Destruct中调用AsyncTask的EndTask(),否则AsyncTask将调用存在。详见AsyncTaskEffectStackChanged.h/cpp。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-gAeBqGDA-1591700466344)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/gestackchange.png)]
4.5.6 赋予Abilities
GameplayEffects能够赋予ASCs新的GameplayAbilities。仅有 Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects 才能赋予Abilities。
一个常见的用例是当你想要强制其他玩家做一些事情(例如让他们击退或拉近)。你可以给他们应用一个GameplayEffect然后自动激活能够完成上述事情的Ability(详见当赋予Ability时如何自动激活(被动技能) Passive Abilities)。
设计者可以选择GameplayEffect将赋予哪些Abiltities,设置Ability的等级,绑定输入ID,设置Ability的移除策略。
| 移除策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Cancel Ability Immediately | 当GameplayEffect从目标移除时立即取消并移除Ability |
| Remove Ability on End | 当Ability执行完成后移除 |
| Do Nothing | 除非手动移除,否则永久存在 |
4.5.7 游戏效果标签 Gameplay Effect Tags
GameplayEffects 带有多个标签容器( GameplayTagContainers)。对于每个类别设计者可以编辑GameplayTagContainers的Added和Removed结果将会呈现在Combined Tags 中。Added用于向父中添加标签。Removed 删除父中已有的标签。
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Gameplay Effect Asset Tags | GameplayEffect具有的标签。 它们本身不执行任何功能,仅用于描述GameplayEffect |
| Granted Tags | 存在于GameplayEffect的标签,但也会给到GameplayEffect应用到的ASC。当GameplayEffect被移除时这些标签也会从ASC移除。仅用于Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects |
| Ongoing Tag Requirements | 一旦应用,这些标签将决定GameplayEffect是开启还是关闭。这也说明了GameplayEffect在应用时可以被关闭。如果GameplayEffect不满足Ongoing Tag Requirements其将会被关闭,直到条件满足GameplayEffect会被再次打开并重新应用Modifiers。仅用于Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects |
| Application Tag Requirements | 目标上的标签决定GameplayEffect是否能够被应用 |
| Remove Gameplay Effects with Tags | 当前GameplayEffect被成功应用时,如果目标上的GameplayEffects的Asset Tags或Granted Tags中有这些标签,那么对应的GameplayEffect将被移除 |
4.5.8 免疫游戏效果
GameplayEffects能够获得免疫,用于通过 GameplayTags高效的阻止其他GameplayEffects的应用。免疫也可以通过其他方式实现,比如Application Tag Requirements,但此方法将提供一个委托(UAbilitySystemComponent::OnImmunityBlockGameplayEffectDelegate)可以监听GameplayEffects的免疫阻止。
GrantedApplicationImmunityTags将检查源ASC(也包括源的Ability中的AbilityTags如果有的话)是否有指定的标签。这提供了一种根据某些角色或者源所拥有的标签决定是否免疫GameplayEffects的方式。
Granted Application Immunity Query将检查要应用的GameplayEffectSpec如果满足标签匹配则阻止应用,否则允许。
通过GameplayEffect蓝图的悬停提示了解更多关于Queries的使用。
4.5.9 游戏效果细则 Gameplay Effect Spec
(GESpec) 可以相像成是GameplayEffects的实例化。GESpec包括一个GameplayEffect类的引用,创建时的等级,由谁创建。这些可以在运行时(被应用前)自由的创建和修改,不像GameplayEffects是由设计师在运行前创建。在应用一个GameplayEffect时,将会由GameplayEffect创建出GameplayEffectSpec,然后将其应用给目标。
GameplayEffectSpecs是通过可被蓝图调用的UAbilitySystemComponent::MakeOutgoingSpec()创建(需要以GameplayEffects类作为参数),GameplayEffectSpecs 不会被立即应用。通常将其传递给由技能创建的炮弹,然后当炮弹击中目标时将其应用给目标。当GameplayEffectSpecs被成功应用将返回一个新的结构体FActiveGameplayEffect。
GameplayEffectSpec主要内容:
GameplayEffec类,由设计师在运行前创建GameplayEffectSpec的等级,通常和创建GameplayEffectSpec的技能等级相同,但也可以不同GameplayEffectSpec的持续时间,默认是GameplayEffect的持续时间,但也可以不同- 用于周期效果时,
GameplayEffectSpec的周期时间,默认是GameplayEffect的周期时间,但也可以不同 GameplayEffectSpec的当前堆叠数量,堆叠数量限制在GameplayEffect上GameplayEffectContextHandle表示谁创建的这个GameplayEffectSpecGameplayEffectSpec创建时的属性快照DynamicGrantedTags是对应GameplayEffect中的GrantedTags的额外标签DynamicAssetTags是对应GameplayEffect中的AssetTags的额外标签SetByCallerTMaps
SetByCallers
SetByCallers允许GameplayEffectSpec以GameplayTag 或FName关联浮点值,具体存储在GameplayEffectSpec的TMap和TMap中。使用方式和GameplayEffect的Modifiers类似,也可以通过SetByCallers将Ability中生成的数据传递给GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations 或ModifierMagnitudeCalculations。
SetByCaller 使用 |
描述 |
|---|---|
Modifiers |
必须在GameplayEffect类中提前定义。仅能使用GameplayTag版本。如果在GameplayEffect中被定义,在GameplayEffectSpec找不到对应的值,游戏将会运行时错误并且返回0。小心除法,详见Modifiers |
| Elsewhere | 不需要被提前定义。 如果在GameplayEffectSpec找不到对应的值时将会返回一个开发者定义的默认值并且可选是否要给出警告 |
要在蓝图中设置SetByCaller的值,可以使用对应的蓝图节点(GameplayTag 或 FName)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1ao6XdWY-1591700466345)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/setbycaller.png)]
要在蓝图中读取SetByCaller的值,需要在自己的Blueprint Library中实现蓝图节点
要在C++中设置SetByCaller的值,可以使用对应的方法(GameplayTag 或 FName)
void FGameplayEffectSpec::SetSetByCallerMagnitude(FName DataName, float Magnitude);
void FGameplayEffectSpec::SetSetByCallerMagnitude(FGameplayTag DataTag, float Magnitude);
要在C++中读取SetByCaller的值,可以使用对应的方法(GameplayTag 或 FName)
float GetSetByCallerMagnitude(FName DataName, bool WarnIfNotFound = true, float DefaultIfNotFound = 0.f) const;
float GetSetByCallerMagnitude(FGameplayTag DataTag, bool WarnIfNotFound = true, float DefaultIfNotFound = 0.f) const;
建议使用GameplayTag而不是FName版本的SetByCaller。GameplayTags 可以阻止在蓝图中的拼写错误,而且在网络同步过程中会更高效。
4.5.10 游戏效果上下文 Gameplay Effect Context
包含了GameplayEffectSpec 的创建者(Instigator)和应用的目标(TargetData)。可以通过派生GameplayEffectSpec用来在ModifierMagnitudeCalculations / GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations,AttributeSets和GameplayCues之间传递任意数据。
派生GameplayEffectContext的过程:
- 重载
FGameplayEffectContext::GetScriptStruct() - 重载
FGameplayEffectContext::Duplicate() - 需要复制新数据时需要重载
FGameplayEffectContext::NetSerialize() - 像
FGameplayEffectContext一样实现派生类的TStructOpsTypeTraits - 在你的
AbilitySystemGlobals中重载AllocGameplayEffectContext()返回FGameplayEffectContext派生类的对象
GASShooter 在GameplayEffectContext 的派生类中添加TargetData用于在GameplayCues中访问,比如霰弹枪可以击中多个目标。
4.5.11 修改器量计算 Modifier Magnitude Calculation
ModifierMagnitudeCalculations(简称ModMagcCalc 或MMC)用于GameplayEffects中的Modifiers。 其作用和GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations类似但不同的是MMC可以被预测(Predicted)。MMC唯一的作用是通过CalculateBaseMagnitude_Implementation()返回一个浮点值,可以通过蓝图或C++进行MMC的派生并重载此方法。
MMCs 可以被任何类型的GameplayEffects(Instant, Duration, Infinite, 或Periodic)使用。
MMC的优势在于可以获取GameplayEffect的目标和源的任何属性并且能够读取GameplayEffectSpec 中的GameplayTags和SetByCallers。Attributes可以是快照也可以不是,属性快照将在GameplayEffectSpec创建时获取,属性非快照将在应用时自动获取。通过已存在于ASC的Modes捕获Attributes 重计算他们的CurrentValue,重计算并不会执行AbilitySet中的PreAttributeChange()因此需要在此处完成Clamping。
| Snapshot | Source or Target | Captured on GameplayEffectSpec |
Automatically updates when Attribute changes for Infinite or Duration GE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Source | Creation | No |
| Yes | Target | Application | No |
| No | Source | Application | Yes |
| No | Target | Application | Yes |
MMC的结果浮点值可以被GameplayEffect's Modifier的coefficient、pre coefficient和post coefficient进一步处理。
下面是一个MMC的示例,Dota2中被敌法师打一下,计算法力损耗:
UPAMMC_PoisonMana::UPAMMC_PoisonMana()
{
//ManaDef defined in header FGameplayEffectAttributeCaptureDefinition ManaDef;
ManaDef.AttributeToCapture = UPAAttributeSetBase::GetManaAttribute();
ManaDef.AttributeSource = EGameplayEffectAttributeCaptureSource::Target;
ManaDef.bSnapshot = false;
//MaxManaDef defined in header FGameplayEffectAttributeCaptureDefinition MaxManaDef;
MaxManaDef.AttributeToCapture = UPAAttributeSetBase::GetMaxManaAttribute();
MaxManaDef.AttributeSource = EGameplayEffectAttributeCaptureSource::Target;
MaxManaDef.bSnapshot = false;
RelevantAttributesToCapture.Add(ManaDef);
RelevantAttributesToCapture.Add(MaxManaDef);
}
float UPAMMC_PoisonMana::CalculateBaseMagnitude_Implementation(const FGameplayEffectSpec & Spec) const
{
// Gather the tags from the source and target as that can affect which buffs should be used
const FGameplayTagContainer* SourceTags = Spec.CapturedSourceTags.GetAggregatedTags();
const FGameplayTagContainer* TargetTags = Spec.CapturedTargetTags.GetAggregatedTags();
FAggregatorEvaluateParameters EvaluationParameters;
EvaluationParameters.SourceTags = SourceTags;
EvaluationParameters.TargetTags = TargetTags;
float Mana = 0.f;
GetCapturedAttributeMagnitude(ManaDef, Spec, EvaluationParameters, Mana);
Mana = FMath::Max(Mana, 0.0f);
float MaxMana = 0.f;
GetCapturedAttributeMagnitude(MaxManaDef, Spec, EvaluationParameters, MaxMana);
MaxMana = FMath::Max(MaxMana, 1.0f); // Avoid divide by zero
float Reduction = -20.0f;
if (Mana / MaxMana > 0.5f)
{
// Double the effect if the target has more than half their mana
Reduction *= 2;
}
if (TargetTags->HasTagExact(FGameplayTag::RequestGameplayTag(FName("Status.WeakToPoisonMana"))))
{
// Double the effect if the target is weak to PoisonMana
Reduction *= 2;
}
return Reduction;
}
如果你没有在MMC的构建方法中将FGameplayEffectAttributeCaptureDefinition 添加到RelevantAttributesToCapture中,在获取Attributes时将会得到一个missing Spec的错误。除非在计算过程中你不需要获取任何Attributes。
4.5.12 游戏效果执行计算 Gameplay Effect Execution Calculation
GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations (ExecutionCalculation, Execution(在插件代码中经常会看到这个术语), or ExecCalc) 是GameplayEffects改变ASC的一种最有力的方式。与ModifierMagnitudeCalculations类似,ExecCalc可以获取Attributes,可选的是否快照。 与MMCs不同的是,ExecCalc可以改变多个属性并且高效的处理任何事情。强大和灵活之下,ExecCalc不支持Predicted,且必须在C++中实现(4.25已经可以在蓝图中实现)。
ExecutionCalculations仅能用于Instant 和Periodic GameplayEffects。通常情况下带有Execute的环境中只能使用这两种GameplayEffects。
属性是否快照同4.5.11 修改器量计算 Modifier Magnitude Calculation,这里不再赘述
| Snapshot | Source or Target | Captured on GameplayEffectSpec |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | Source | Creation |
| Yes | Target | Application |
| No | Source | Application |
| No | Target | Application |
可以按照Epic的ActionRPG示例项目中的方式设置Attribute的获取,通过一个自定义的结构体定义要获取的Attributes。
对于Local Predicted, Server Only, 和Server Initiated的 GameplayAbilities,ExecCalc仅在服务器端执行。
ExecCalc最常用于伤害计算,从Source和Target读取一系列属性值,然后进行复杂的计算。示例项目中也使用ExecCalc完成伤害计算,读取由GameplayEffectSpec's SetByCaller设置的伤害值,再通过Target中的护甲属性缓解伤害。详见GDDamageExecCalculation.cpp/.h。
4.5.13 自定义应用条件 Custom Application Requirement
CustomApplicationRequirement (CAR) 类给设计者提供了是否能够应用GameplayEffect的高级控制手段(有别于简单的标签控制)。 可以通过在蓝图中重载CanApplyGameplayEffect()或者在C++中重载CanApplyGameplayEffect_Implementation()实现。
何时需要使用CARs?比如:
Target需要有一定数量的属性时Target需要GameplayEffect堆叠到一定数量时
除此之外CARs还能够做更多事情,比如检查Target是否应用了一个GameplayEffect 的实例,在应用一个新实例时如果同类型的实例已存在则只改变其持续时间(CanApplyGameplayEffect()要返回false)。
4.5.14 技能消耗 Cost Gameplay Effect
GameplayAbilities 可以指定一个处理技能消耗的GameplayEffect。如果无法满足消耗,则技能不会被激活。Cost GE必须是一个Instant GameplayEffect其中可以有一个或多个Modifiers用于减去技能所需的属性消耗。默认情况下,Cost GEs是支持预测的,所以最好不要使用ExecutionCalculations,建议只使用MMCs完成消耗计算。
刚开始,你可能会为每一个带有消耗的GA创建一个对应的Cost GE。高阶方法是,对于多个GAs复用一个Cost GE,仅通过GA的消耗数据(消耗值定义在GA上)修改从Cost GE创建出的GameplayEffectSpec。仅能用于Instanced Abilities。
两种使用Cost GE的方法:
- Use an
MMC,这是最简单的方法。 创建一个MMC从GameplayAbility实例中读取消耗值:
float UPGMMC_HeroAbilityCost::CalculateBaseMagnitude_Implementation(const FGameplayEffectSpec & Spec) const
{
const UPGGameplayAbility* Ability = Cast(Spec.GetContext().GetAbilityInstance_NotReplicated());
if (!Ability)
{
return 0.0f;
}
return Ability->Cost.GetValueAtLevel(Ability->GetAbilityLevel());
}
在这个示例中,通过在派生的GameplayAbility 中添加FScalableFloat保存GA的消耗:
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, EditAnywhere, Category = "Cost")
FScalableFloat Cost;
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-yC21FWgU-1591700466346)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/costmmc.png)]
- 重载
UGameplayAbility::GetCostGameplayEffect(),在运行时创建GameplayEffect,读取GameplayAbility中的消耗值。
4.5.15 技能冷却 Cooldown Gameplay Effect
GameplayAbilities 可以指定一个处理技能冷却的GameplayEffect。冷却决定了技能多长时间能够被再次施放,处在冷却中的技能无法被施放。Cooldown GE必须是一个Duration GameplayEffect,不带Modifiers,在GameplayEffect的GrantedTags (“Cooldown Tag”)中配置代表每个GameplayAbility 或Ability Slot(槽位装备技能)的唯一的GameplayTag。实际上是由GA检查Cooldown Tag而不是Cooldown GE。默认情况下,Cooldown GEs是支持预测的,所以最好不要使用ExecutionCalculations,建议只使用MMCs完成冷却计算。
刚开始,你可能会为每一个带有冷却的GA创建一个对应的Cooldown GE。高阶方法是,对于多个GAs复用一个Cooldown GE,仅通过GA的冷却数据(冷却时间和Cooldown Tag定义在GA上)修改从Cooldown GE创建出的GameplayEffectSpec。仅能用于Instanced Abilities。
两种使用Cooldown GE的方法:
- Use a
SetByCaller,这是最简单的方法,通过带有GameplayTag的SetByCaller设置Cooldown GE的持续时间,在你的GameplayAbility子类中定义一个FScalableFloat的持续时间,一个FGameplayTagContainer用于唯一的Cooldown Tag,再有一个临时的FGameplayTagContainer用于返回Cooldown Tag和Cooldown GE's Tags的合并。
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, EditAnywhere, Category = "Cooldown")
FScalableFloat CooldownDuration;
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, EditAnywhere, Category = "Cooldown")
FGameplayTagContainer CooldownTags;
// Temp container that we will return the pointer to in GetCooldownTags().
// This will be a union of our CooldownTags and the Cooldown GE's cooldown tags.
UPROPERTY()
FGameplayTagContainer TempCooldownTags;
接下来重载UGameplayAbility::GetCooldownTags()并返回Cooldown Tag和Cooldown GE's Tags的合并:
const FGameplayTagContainer * UPGGameplayAbility::GetCooldownTags() const
{
FGameplayTagContainer* MutableTags = const_cast(&TempCooldownTags);
const FGameplayTagContainer* ParentTags = Super::GetCooldownTags();
if (ParentTags)
{
MutableTags->AppendTags(*ParentTags);
}
MutableTags->AppendTags(CooldownTags);
return MutableTags;
}
最后,重载UGameplayAbility::ApplyCooldown()注入上述的Cooldown Tags并且通过GameplayEffectSpec的SetByCaller写入冷却持续时间:
void UPGGameplayAbility::ApplyCooldown(const FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle Handle, const FGameplayAbilityActorInfo * ActorInfo, const FGameplayAbilityActivationInfo ActivationInfo) const
{
UGameplayEffect* CooldownGE = GetCooldownGameplayEffect();
if (CooldownGE)
{
FGameplayEffectSpecHandle SpecHandle = MakeOutgoingGameplayEffectSpec(CooldownGE->GetClass(), GetAbilityLevel());
SpecHandle.Data.Get()->DynamicGrantedTags.AppendTags(CooldownTags);
SpecHandle.Data.Get()->SetSetByCallerMagnitude(FGameplayTag::RequestGameplayTag(FName( OurSetByCallerTag )), CooldownDuration.GetValueAtLevel(GetAbilityLevel()));
ApplyGameplayEffectSpecToOwner(Handle, ActorInfo, ActivationInfo, SpecHandle);
}
}
在下图中,冷却持续时间的Modifier是由SetByCaller通过Data.Cooldown设置。 Data.Cooldown是上述代码中OurSetByCallerTag的值:
- Use an
MMC,这种方法基本和上述相同,除了设置Cooldown GE冷却持续时间的方式从SetByCaller改变成了使用Custom Calculation Class:
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, EditAnywhere, Category = "Cooldown")
FScalableFloat CooldownDuration;
UPROPERTY(BlueprintReadOnly, EditAnywhere, Category = "Cooldown")
FGameplayTagContainer CooldownTags;
// Temp container that we will return the pointer to in GetCooldownTags().
// This will be a union of our CooldownTags and the Cooldown GE's cooldown tags.
UPROPERTY()
FGameplayTagContainer TempCooldownTags;
const FGameplayTagContainer * UPGGameplayAbility::GetCooldownTags() const
{
FGameplayTagContainer* MutableTags = const_cast(&TempCooldownTags);
const FGameplayTagContainer* ParentTags = Super::GetCooldownTags();
if (ParentTags)
{
MutableTags->AppendTags(*ParentTags);
}
MutableTags->AppendTags(CooldownTags);
return MutableTags;
}
void UPGGameplayAbility::ApplyCooldown(const FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle Handle, const FGameplayAbilityActorInfo * ActorInfo, const FGameplayAbilityActivationInfo ActivationInfo) const
{
UGameplayEffect* CooldownGE = GetCooldownGameplayEffect();
if (CooldownGE)
{
FGameplayEffectSpecHandle SpecHandle = MakeOutgoingGameplayEffectSpec(CooldownGE->GetClass(), GetAbilityLevel());
SpecHandle.Data.Get()->DynamicGrantedTags.AppendTags(CooldownTags);
ApplyGameplayEffectSpecToOwner(Handle, ActorInfo, ActivationInfo, SpecHandle);
}
}
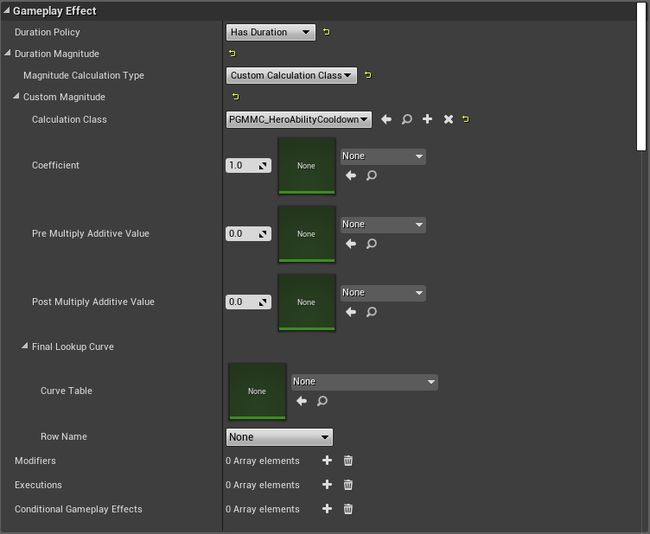
float UPGMMC_HeroAbilityCooldown::CalculateBaseMagnitude_Implementation(const FGameplayEffectSpec & Spec) const
{
const UPGGameplayAbility* Ability = Cast(Spec.GetContext().GetAbilityInstance_NotReplicated());
if (!Ability)
{
return 0.0f;
}
return Ability->CooldownDuration.GetValueAtLevel(Ability->GetAbilityLevel());
}
获取冷却剩余时间
bool APGPlayerState::GetCooldownRemainingForTag(FGameplayTagContainer CooldownTags, float & TimeRemaining, float & CooldownDuration)
{
if (AbilitySystemComponent && CooldownTags.Num() > 0)
{
TimeRemaining = 0.f;
CooldownDuration = 0.f;
FGameplayEffectQuery const Query = FGameplayEffectQuery::MakeQuery_MatchAnyOwningTags(CooldownTags);
TArray< TPair > DurationAndTimeRemaining = AbilitySystemComponent->GetActiveEffectsTimeRemainingAndDuration(Query);
if (DurationAndTimeRemaining.Num() > 0)
{
int32 BestIdx = 0;
float LongestTime = DurationAndTimeRemaining[0].Key;
for (int32 Idx = 1; Idx < DurationAndTimeRemaining.Num(); ++Idx)
{
if (DurationAndTimeRemaining[Idx].Key > LongestTime)
{
LongestTime = DurationAndTimeRemaining[Idx].Key;
BestIdx = Idx;
}
}
TimeRemaining = DurationAndTimeRemaining[BestIdx].Key;
CooldownDuration = DurationAndTimeRemaining[BestIdx].Value;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
**注意:**要在客户端中查询剩余冷却时间,客户端必须能够收到GameplayEffects的复制,这将依赖ASC的Replication Mode。
监听冷却的开始和结束
要监听冷却开始,可以通过绑定AbilitySystemComponent->OnActiveGameplayEffectAddedDelegateToSelf判断是否应用了Cooldown GE或者通过绑定AbilitySystemComponent->RegisterGameplayTagEvent(CooldownTag, EGameplayTagEventType::NewOrRemoved)判断是否新增了Cooldown Tag。建议使用监听Cooldown GE添加的方式,因为FOnGameplayEffectAppliedDelegate可以访问GameplayEffectSpec用以区分Cooldown GE是本地预测还是服务器校正。
要监听冷却结束,可以通过绑定AbilitySystemComponent->OnAnyGameplayEffectRemovedDelegate判断是否删除了Cooldown GE或者通过绑定AbilitySystemComponent->RegisterGameplayTagEvent(CooldownTag, EGameplayTagEventType::NewOrRemoved)判断是否删除了Cooldown Tag。建议使用监听Cooldown Tag删除的方式,因为当服务器校正的Cooldown GE到达时,本地预测的Cooldown GE将会被删除这将会触发OnAnyGameplayEffectRemovedDelegate()即使我们仍处于冷却状态。而Cooldown Tag 在删除本地预测的Cooldown GE ,应用服务器校正的Cooldown GE过程中将不会发生变化。
**注意:**监听GameplayEffect在客户端的添加或删除,客户端必须能够收到GameplayEffects的复制,这将依赖ASC的Replication Mode。
示例工程包含了一个自定义的蓝图节点用来监听冷却的开始和结束,用以在UI上显示和更新陨石技能的剩余冷却时间。需要在UMG Widget的 Destruct 事件中调用EndTask()以结束AsyncTask。详见AsyncTaskEffectCooldownChanged.h/cpp。
冷却预测
当前,冷却并不能正真的被预测。当本地预测的Cooldown GE被应用时我们可以开始启动UI冷却的计数器,但GameplayAbility的实际冷却束缚于服务器的冷却剩余时间。根据玩家的延迟,本地预测的冷却已经结束但在服务器端GameplayAbility仍处于冷却中,这将阻止技能的施放直到服务器冷却结束。
示例工程解决上述问题的方式是,在本地预测冷却开始时将陨石技能UI图标置灰,然后当服务器校正的Cooldown GE到达时启动UI冷却的计数器。
这样的游戏结果是,与较低延迟的玩家相比,具有较高延迟的玩家在短冷却时间的射击率较低。堡垒之夜解决此问题的方式是在武器中使用自定义统计而不是使用Cooldown GE。
真正的可预测冷却(在GameplayAbility本地冷却已结结束服务器仍在冷却中玩家依然可以激活GameplayAbility)Epic会在后续GAS的迭代中实现。
4.5.16 修改活动游戏效果的持续时间
要修改Cooldown GE或任何Duration GameplayEffect的剩余持续时间,我们需要修改GameplayEffectSpec的Duration,更新StartServerWorldTime、CachedStartServerWorldTime、StartWorldTime并且使用CheckDuration()重新检查持续时间。在服务器完成上述步骤并将FActiveGameplayEffect标记为Dirty将会把修改复制到客户端。
注意: 这将需要一个const_cast转换并且也不是Epic官方给出的方式,但目前为止工作正常:
bool UPAAbilitySystemComponent::SetGameplayEffectDurationHandle(FActiveGameplayEffectHandle Handle, float NewDuration)
{
if (!Handle.IsValid())
{
return false;
}
const FActiveGameplayEffect* ActiveGameplayEffect = GetActiveGameplayEffect(Handle);
if (!ActiveGameplayEffect)
{
return false;
}
FActiveGameplayEffect* AGE = const_cast(ActiveGameplayEffect);
if (NewDuration > 0)
{
AGE->Spec.Duration = NewDuration;
}
else
{
AGE->Spec.Duration = 0.01f;
}
AGE->StartServerWorldTime = ActiveGameplayEffects.GetServerWorldTime();
AGE->CachedStartServerWorldTime = AGE->StartServerWorldTime;
AGE->StartWorldTime = ActiveGameplayEffects.GetWorldTime();
ActiveGameplayEffects.MarkItemDirty(*AGE);
ActiveGameplayEffects.CheckDuration(Handle);
AGE->EventSet.OnTimeChanged.Broadcast(AGE->Handle, AGE->StartWorldTime, AGE->GetDuration());
OnGameplayEffectDurationChange(*AGE);
return true;
}
4.5.17 在运行时创建动态游戏效果
在运行时动态创建GameplayEffects是一个高级主题。这种用法不能过于频繁。
仅有Instant GameplayEffects能够在C++中被运行时创建。示例工程动态创建了一个GameplayEffects,用于当一个角色受到致命一击时(在其AttributeSet中处理),将金币和经验奖励发送给他的击杀者。
// Create a dynamic instant Gameplay Effect to give the bounties
UGameplayEffect* GEBounty = NewObject(GetTransientPackage(), FName(TEXT("Bounty")));
GEBounty->DurationPolicy = EGameplayEffectDurationType::Instant;
int32 Idx = GEBounty->Modifiers.Num();
GEBounty->Modifiers.SetNum(Idx + 2);
FGameplayModifierInfo& InfoXP = GEBounty->Modifiers[Idx];
InfoXP.ModifierMagnitude = FScalableFloat(GetXPBounty());
InfoXP.ModifierOp = EGameplayModOp::Additive;
InfoXP.Attribute = UGDAttributeSetBase::GetXPAttribute();
FGameplayModifierInfo& InfoGold = GEBounty->Modifiers[Idx + 1];
InfoGold.ModifierMagnitude = FScalableFloat(GetGoldBounty());
InfoGold.ModifierOp = EGameplayModOp::Additive;
InfoGold.Attribute = UGDAttributeSetBase::GetGoldAttribute();
Source->ApplyGameplayEffectToSelf(GEBounty, 1.0f, Source->MakeEffectContext());
Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects不能在运行时动态创建,因为在他们复制时会查找GameplayEffect类定义,结果没有。为了实现此功能,你应该像通常在编辑器中那样制作GameplayEffect原型类,然后根据需要在运行时自定义GameplayEffectSpec实例。
4.5.18 游戏效果容器 Gameplay Effect Containers
Epic官方的Action RPG 示例项目实现了一个叫FGameplayEffectContainer的结构,对于包含GameplayEffects 和TargetData极为方便。它自动化了一些工作,像根据GameplayEffects 创建GameplayEffectSpecs,设置GameplayEffectContext的默认值。在GameplayAbility中创建一个GameplayEffectContainer并且将它传递给生成的炮弹是非常简单和直接的。我并没有在示例项目中实现GameplayEffectContainers,但还是强烈建议了解这个并考虑将其添加到你的项目中。
要访问GameplayEffectContainers中的GESpecs,需要展开FGameplayEffectContainer然后通过索引GESpecs可以得到具体的GESpec。这需要在刚开始就知道你想访问的GESpec索引是多少。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EUkFtmi1-1591700466348)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/gecontainersetbycaller.png)]
GameplayEffectContainers还包括可选的目标选取方式。
4.6 游戏技能 Gameplay Abilities
4.6.1 Gameplay Ability定义
GameplayAbilities (GA)是在游戏中Actor能做的行为或技能。在同一时间可以激活多个GameplayAbility,例如冲刺的同时射击。GA可以通过Blueprint或C++制作。
GameplayAbilities的示例:
- 跳跃
- 冲刺
- 射击
- 每隔几秒被动的阻挡一次攻击
- 使用一个药瓶
- 开门
- 收集资源
- 建造建筑
不能通过GameplayAbilities实现的示例:
- 基本的移动输入
- 一些UI交互 - 不要使用
GameplayAbility处理从商店购买物品
这些不是规则,只是我的建议。
GameplayAbilities默认带有一个等级(技能等级)用于定义修改属性时的修改量,或是改变GameplayAbility的功能。
GameplayAbilities会在Owning Client上执行,根据 Net Execution Policy设置的策略决定是否在服务器端也要执行。Net Execution Policy决定一个GameplayAbility是否将会进行本地预测。对于可选的cost and cooldown GameplayEffects它们包含了一些默认的行为。 在GameplayAbilities持续过程中会使用AbilityTasks处理一些行为比如等待一个事件、等待一个属性改变、等待玩家选择目标或者通过Root Motion Source移动一个角色。模拟的客户端将不会执行GameplayAbilities。取而代之的是,当服务器执行技能时,任何需要在simulated proxies呈现的表现(像播放动画)都将通过Replicated或者通过AbilityTasks执行的RPC或者是GameplayCues(播放声音和特效)来实现。
所有的GameplayAbilities都需要重载ActivateAbility()方法以实现自己的游戏逻辑。在GameplayAbility 完成或取消时可以通过EndAbility实现一些额外的逻辑。
复杂一些的GameplayAbility流程图:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3gLmT8ic-1591700466349)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/abilityflowchartcomplex.png)]
复杂的Ability也可以通过多个彼此交互的GameplayAbilities实现。
复制策略 Replication Policy
不要使用这个选项。这个名字有误导性你并不需要这个。GameplayAbilitySpecs默认会从服务器复制到Owning Client。就像上面说过的,GameplayAbilities 不会在simulated proxies上执行。Epic的Dave Ratti说过他希望 在将来删除这个选项。
服务器端远程技能取消 Server Respects Remote Ability Cancellation
这个选项常常引发问题。这意味着如果客户端的GameplayAbility由于取消或自然完成而终止,将强制服务器的版本结束(无论其是否完成)。 后一个问题很重要,尤其是对于高延迟玩家使用的本地预测的GameplayAbilities。 通常要禁用此选项。
直接输入复制 Replicate Input Directly
开启此项将总是将输入的按下和释放事件传递到服务器。
Epic官方建议不要使用此选项,取而代之的应该使用已存在的输入相关的AbilityTasks内置的Generic Replicated Events:
/** Direct Input state replication. These will be called if bReplicateInputDirectly is true on the ability and is generally not a good thing to use. (Instead, prefer to use Generic Replicated Events). */
UAbilitySystemComponent::ServerSetInputPressed()
4.6.2 输入绑定
ASC允许直接绑定输入操作并且在获得技能时指定这些输入到GameplayAbilities 。当输入绑定后,触发事件时如果GameplayTag 满足则会自动施放这些GameplayAbilities 。要想使用内置的AbilityTasks响应输入必须分配输入操作。
除了分配的输入操作可以激活GameplayAbilities之外,ASC也能够接受确认(Confirm)和取消(Cancel)输入。这些特别的输入被AbilityTasks用于确定目标或取消目标。
要为ASC绑定输入,必须先创建一个枚举将输入操作名转换为一个字节。枚举中的每一项必须与项目设置中输入操作匹配(DisplayName无所谓)。
示例:
UENUM(BlueprintType)
enum class EGDAbilityInputID : uint8
{
// 0 None
None UMETA(DisplayName = "None"),
// 1 Confirm
Confirm UMETA(DisplayName = "Confirm"),
// 2 Cancel
Cancel UMETA(DisplayName = "Cancel"),
// 3 LMB
Ability1 UMETA(DisplayName = "Ability1"),
// 4 RMB
Ability2 UMETA(DisplayName = "Ability2"),
// 5 Q
Ability3 UMETA(DisplayName = "Ability3"),
// 6 E
Ability4 UMETA(DisplayName = "Ability4"),
// 7 R
Ability5 UMETA(DisplayName = "Ability5"),
// 8 Sprint
Sprint UMETA(DisplayName = "Sprint"),
// 9 Jump
Jump UMETA(DisplayName = "Jump")
};
如果你的ASC在Character上,那么可在以SetupPlayerInputComponent()进行绑定:
// Bind to AbilitySystemComponent
AbilitySystemComponent->BindAbilityActivationToInputComponent(PlayerInputComponent, FGameplayAbilityInputBinds(FString("ConfirmTarget"), FString("CancelTarget"), FString("EGDAbilityInputID"), static_cast(EGDAbilityInputID::Confirm), static_cast(EGDAbilityInputID::Cancel)));
如果你的ASC在PlayerState上,SetupPlayerInputComponent()内部可能存在潜在的竞态条件,PlayerState可能还没有复制到客户端。因此,建议在SetupPlayerInputComponent() 和OnRep_PlayerState()都尝试进行绑定。只在OnRep_PlayerState()中进行绑定也不够充分,在PlayerState被复制到客户端时 Actor的 InputComponent也可能是空的(PlayerController通知客户端调用ClientRestart()以创建InputComponent,当这一步晚于OnRep_PlayerState())。示例项目尝试在这两个地方尝试进行绑定且通过一个布尔变量控制真正的绑定只会进行一次。
注意: 在示例项目中枚举中的Confirm 和Cancel与项目设置中输入操作名并不匹配 (ConfirmTarget 和CancelTarget)。但是我们可以通过BindAbilityActivationToInputComponent完成它们的映射。枚举中的其他输入都与项目设置中的输入操作名匹配。
对于只会通过一个输入激活的GameplayAbilities(比如MOBA中有些技能可以使用相同的槽),建议为UGameplayAbility子类添加一个变量用于定义输入,然后在赋予技能时从ClassDefaultObject中读取这个变量。
4.6.3 赋予技能 Granting Abilities
为ASC赋予一个GameplayAbility 会将其加入到ASC的ActivatableAbilities列表中,并允许GameplayAbility在满足GameplayTag requirements时可以被激活,只能在C++。
我们在服务器端赋予GameplayAbilities,对应的GameplayAbilitySpec会被自动复制到Owning Client。其他客户端(Simulated Proxies)将不会收到GameplayAbilitySpec。
示例项目在Character类中存储了一个TArray,这些技能在游戏开始时将被自动赋予角色:
void AGDCharacterBase::AddCharacterAbilities()
{
// Grant abilities, but only on the server
if (Role != ROLE_Authority || !AbilitySystemComponent.IsValid() || AbilitySystemComponent->CharacterAbilitiesGiven)
{
return;
}
for (TSubclassOf& StartupAbility : CharacterAbilities)
{
AbilitySystemComponent->GiveAbility(
FGameplayAbilitySpec(StartupAbility, GetAbilityLevel(StartupAbility.GetDefaultObject()->AbilityID), static_cast(StartupAbility.GetDefaultObject()->AbilityInputID), this));
}
AbilitySystemComponent->CharacterAbilitiesGiven = true;
}
当赋予这些GameplayAbilities时,我们会创建带有UGameplayAbility类、技能等级、绑定的输入、SourceObject(谁将GameplayAbility给了ASC)的GameplayAbilitySpecs。
4.6.4 激活技能 Activating Abilities
如果为一个GameplayAbility分配了输入操作,当输入按下并且GameplayTag 满足技能就会被释放。这并不总是期望的GameplayAbility激活方式,ASC还提供了其他四种激活GameplayAbilities的方法:通过GameplayTag,GameplayAbility类,GameplayAbilitySpec句柄(Handle)和事件。通过事件激活一个GameplayAbility允许你传递一些事件数据(Payload)。
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Abilities")
bool TryActivateAbilitiesByTag(const FGameplayTagContainer& GameplayTagContainer, bool bAllowRemoteActivation = true);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Abilities")
bool TryActivateAbilityByClass(TSubclassOf InAbilityToActivate, bool bAllowRemoteActivation = true);
bool TryActivateAbility(FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle AbilityToActivate, bool bAllowRemoteActivation = true);
bool TriggerAbilityFromGameplayEvent(FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle AbilityToTrigger, FGameplayAbilityActorInfo* ActorInfo, FGameplayTag Tag, const FGameplayEventData* Payload, UAbilitySystemComponent& Component);
FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle GiveAbilityAndActivateOnce(const FGameplayAbilitySpec& AbilitySpec);
要通过事件激活一个GameplayAbility,需要在GameplayAbility中添加一个Triggers,分配一个GameplayTag,选择GameplayEvent。然后通过UAbilitySystemBlueprintLibrary::SendGameplayEventToActor(AActor* Actor, FGameplayTag EventTag, FGameplayEventData Payload)发送事件。通过事件激活一个GameplayAbility允许你传递一些事件数据(Payload)。
GameplayAbility Trigger也可以在GameplayTag添加或删除时激活GameplayAbility。
注意: 当通过事件激活一个GameplayAbility,你必须在技能蓝图中使用ActivateAbilityFromEvent节点,并且ActivateAbility节点不能存在于你的蓝图中。如果技能蓝图中ActivateAbility节点存在,它将始终被调用,ActivateAbilityFromEvent则不会被调用。
注意: 不要忘记在GameplayAbility结束时调用EndAbility(),除非你想要一个一直运行的被动技能。
本地预测GameplayAbilities的激活序列过程:
- Owning client 调用
TryActivateAbility() - 调用
InternalTryActivateAbility() - 调用
CanActivateAbility()检查GameplayTag、消耗、冷却等决定是否能够释放技能 - 调用
CallServerTryActivateAbility()并且传递生成好的Prediction Key - 调用
CallActivateAbility() - 调用
PreActivate() - 调用
ActivateAbility()最终施放技能
Server receives CallServerTryActivateAbility()
- 调用
ServerTryActivateAbility() - 调用
InternalServerTryActivateAbility() - 调用
InternalTryActivateAbility() - 调用
CanActivateAbility() - 调用
ClientActivateAbilitySucceed()在服务器确定激活成功时更新ActivationInfo并且广播OnConfirmDelegate委托(这不同于输入确认) - 调用
CallActivateAbility() - 调用
PreActivate() - 调用
ActivateAbility()最终施放技能
如果服务器激活技能失败,将会调用ClientActivateAbilityFailed()并立即终止客户端的GameplayAbility并回退任何可预测的修改。
被动技能 Passive Abilities
要自动激活执行运行的被动GameplayAbilities,可以重写UGameplayAbility::OnAvatarSet()(它将在赋予GameplayAbility并且设置AvatarActor时自动执行)调用TryActivateAbility()。
建议为自定义的UGameplayAbility类添加一个bool变量用以控制GameplayAbility在被赋予时是否自动激活。示例工程这样实现的被动护甲技能。
通常被动GameplayAbilitites 的Net Execution Policy设置为Server Only。
void UGDGameplayAbility::OnAvatarSet(const FGameplayAbilityActorInfo * ActorInfo, const FGameplayAbilitySpec & Spec)
{
Super::OnAvatarSet(ActorInfo, Spec);
if (ActivateAbilityOnGranted)
{
bool ActivatedAbility = ActorInfo->AbilitySystemComponent->TryActivateAbility(Spec.Handle, false);
}
}
4.6.5 取消技能 Canceling Abilities
要从内部取消一个GameplayAbility,可以调用CancelAbility(),它将调用EndAbility()并且设置WasCancelled为true。
要从外部取消一个GameplayAbility,ASC提供了几个方法:
/** Cancels the specified ability CDO. */
void CancelAbility(UGameplayAbility* Ability);
/** Cancels the ability indicated by passed in spec handle. If handle is not found among reactivated abilities nothing happens. */
void CancelAbilityHandle(const FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle& AbilityHandle);
/** Cancel all abilities with the specified tags. Will not cancel the Ignore instance */
void CancelAbilities(const FGameplayTagContainer* WithTags=nullptr, const FGameplayTagContainer* WithoutTags=nullptr, UGameplayAbility* Ignore=nullptr);
/** Cancels all abilities regardless of tags. Will not cancel the ignore instance */
void CancelAllAbilities(UGameplayAbility* Ignore=nullptr);
/** Cancels all abilities and kills any remaining instanced abilities */
virtual void DestroyActiveState();
注意: 我发现CancelAllAbilities可能无法正确工作,当存在Non-Instanced GameplayAbilities的时候。它似乎在遇到Non-Instanced GameplayAbility时会放弃取消。CancelAbilities会更好的处理Non-Instanced GameplayAbilities,示例项目就是用的这个 (Jump 是一个Non-Instanced GameplayAbility)。
4.6.6 获取当前活动的技能 Getting Active Abilities
新手经常会问“怎样获得激活的技能?”。由于可以同时激活多个技能,因此需要在ASC的ActivatableAbilities(可激活技能)列表中查找匹配Asset或Granted GameplayTag的技能。
UAbilitySystemComponent::GetActivatableAbilities()返回一个可被迭代的TArray。
ASC提供了另一个帮助方法,可以带有一个GameplayTagContainer参数(比上述方法方便很多),还有一个bOnlyAbilitiesThatSatisfyTagRequirements仅返回当前能够被激活的GameplayAbilitySpecs。
例如,你可能有两种基本的攻击技能,一个是带武器,一个是赤手空拳。可以根据装备武器的GameplayTag区分两者以激活正确的一个。详见Epic对此方法的注释。
UAbilitySystemComponent::GetActivatableGameplayAbilitySpecsByAllMatchingTags(const FGameplayTagContainer& GameplayTagContainer, TArray < struct FGameplayAbilitySpec* >& MatchingGameplayAbilities, bool bOnlyAbilitiesThatSatisfyTagRequirements = true)
获取FGameplayAbilitySpec后可以通过IsActive()方法判断技能当前是否激活中。
4.6.7 实例化策略 Instancing Policy
GameplayAbility的实例化策略决定当激活GameplayAbility时是否以及如何实例化GameplayAbility。
Instancing Policy |
描述 | 何时使用 |
|---|---|---|
| Instanced Per Actor | 每一个ASC仅有一个GameplayAbility的实例,激活时复用 |
通常这是使用最多的实例化策略,设计师需要在激活时手动重置所有变量 |
| Instanced Per Execution | 每一次GameplayAbility的激活都会创建一个新的实例 |
优势是每一次GameplayAbilitites激活变量都是已经重置的。问题是性能开销较大。示例工程并没有使用过这个 |
| Non-Instanced | 使用GameplayAbility的 ClassDefaultObject,没有实例被创建 |
三者之中性能最好的,但使用也是最苛刻的。Non-Instanced GameplayAbilities不能存储任何状态,不能有动态变量,不能绑定AbilityTask的委托。最佳用途是频繁使用的简单技能,比如MOBA或RTS中小怪的普攻。示例项目中的Jump Ability是Non-Instanced |
4.6.8 网络执行策略 Net Execution Policy
GameplayAbility的网络执行策略决定谁以什么顺序运行GameplayAbility
Net Execution Policy |
描述 |
|---|---|
Local Only |
GameplayAbility仅运行于Owning Client,当技能仅用于本地修饰时有用。单人游戏应使用Server Only |
Local Predicted |
Local Predicted GameplayAbilities将在Owning Client先执行,然后在Server执行。服务器版本将修正客户端所有的预测错误 |
Server Only |
GameplayAbility仅运行于Server,被动GameplayAbilities通常使用Server Only。单人游戏应使用Server Only |
Server Initiated |
Server Initiated GameplayAbilities先在Server执行,然后在Owning Client执行。个人没怎么用过 |
4.6.9 技能标签 Ability Tags
GameplayAbilities有一系列的GameplayTagContainers用以处理内部逻辑。所有`GameplayTags均未复制。
GameplayTag Container |
Description |
|---|---|
Ability Tags |
用以描述GameplayAbility |
Cancel Abilities with Tag |
当此技能激活时会用此取消其他GameplayAbilities |
Block Abilities with Tag |
当此技能激活时会用此阻止其他GameplayAbilities的激活 |
Activation Owned Tags |
当GameplayAbility激活时将GameplayTags给GameplayAbility的Owner。记住不会被复制 |
Activation Required Tags |
仅当Owner拥有所有这些GameplayTags,GameplayAbility才能被激活 |
Activation Blocked Tags |
Owner拥有任一个这里的GameplayTags,GameplayAbility都不能被激活 |
Source Required Tags |
仅当Source拥有所有这些GameplayTags,GameplayAbility才能被激活。仅在由事件触发的GameplayAbility设置 |
Source Blocked Tags |
Source拥有任一个这里的GameplayTags,GameplayAbility都不能被激活。仅在由事件触发的GameplayAbility设置 |
Target Required Tags |
仅当Target拥有所有这些GameplayTags,GameplayAbility才能被激活。仅在由事件触发的GameplayAbility设置 |
Target Blocked Tags |
Target拥有任一个这里的GameplayTags,GameplayAbility都不能被激活。仅在由事件触发的GameplayAbility设置 |
4.6.10 游戏技能细则 Gameplay Ability Spec
在赋予GameplayAbility后,ASC上会存在一个GameplayAbilitySpec,其定义了可被激活的GameplayAbility(其中包括GameplayAbility类,等级,输入绑定,运行时状态)。
当在Server赋予了一个GameplayAbility,Server将会把GameplayAbilitySpec复制给Owning Client(才可被激活)。
激活一个GameplayAbilitySpec是否会创建一个GameplayAbility的实例由Instancing Policy决定。
4.6.11 为技能传递数据 Passing Data to Abilities
GameplayAbilities的通常范例是激活->生成数据->应用->结束。有时需要将外部的数据传递给GameplayAbilities,为此GAS提供了下述方式:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
Activate GameplayAbility by Event |
通过事件激活一个GameplayAbility带有一个Payload。对于本地预测的GameplayAbilities,事件的Payload将会从Client传递至Server。Payload除了包含一些变量外,还可以使用两个可选的Objects或者一个TargetData。问题是不能使用输入绑定激活技能。要使用此项必须在GameplayAbility中设置Triggers,上面介绍过这里不再赘述 |
Use WaitGameplayEvent AbilityTask |
在技能激活后,可以使用WaitGameplayEvent AbilityTask告诉GameplayAbility监听带有Payload(格式同上)的事件。WaitGameplayEvent的问题是将不会被网络复制仅能用于Local Only 或Server Only 的GameplayAbilities。你可以自己编写支持Replicated复制Payload的AbilityTask |
Use TargetData |
使用一个自定义的TargetData结构体是在客户端和服务器端之间传递数据的好方式,详见FGameplayAbilityTargetData |
Store Data on the OwnerActor or AvatarActor |
使用OwnerActor或AvatarActor存储可被复制的变量,或者任何能获得引用的其他对象。这种方法是最灵活的并且也可以与事件绑定激活的GameplayAbilities一起工作。但并不能保证在需要时,同步的数据一定到达。要使用这种方法必须要能够确保数据复制已提前完成,这意味着如果设置Replicated Variable后马上激活一个GameplayAbility将不能保证由于潜在的数据包丢失而在接收器上发生的顺序。 |
4.6.12 技能的消耗与冷却
GameplayAbilities带有可选的消耗和冷却功能。Cost GEs和Cooldown GEs上面已经介绍过这里不再赘述。
在一个GameplayAbility调用UGameplayAbility::Activate()之前,首先会调用UGameplayAbility::CanActivateAbility(),此方法中会检查ASC是否能够负担技能开销(UGameplayAbility::CheckCost()) 并且确保技能没有处在冷却中(UGameplayAbility::CheckCooldown())。
在GameplayAbility 调用Activate()之后,技能激活的任何时间内都可以通过UGameplayAbility::CommitAbility()提交Cost和Cooldown。设计者也可以根据需要使用UGameplayAbility::CommitCost()和UGameplayAbility::CommitCooldown()单独提交Cost或Cooldown。 提交Cost和Cooldown时会再次调用CheckCost()和CheckCooldown,因为在激活GameplayAbility之后Owning ASC的Attributes可能被修改,导致提交消耗时可能无法满足。如果提交时prediction key是有效的则消耗和冷却是可以被本地预测的(locally predicted)。
对于实现细节详见CostGE和CooldownGE。
4.6.13 技能升级
升级技能有两种常用的方法:
| 技能升级方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 基于新的等级重新赋予技能 | 先从ASC中删除GameplayAbility然后在服务器端基于新的等级重新赋予GameplayAbility。如果技能此时处于激活状态会被终止 |
增加GameplayAbilitySpec 的Level |
在服务器端,找到GameplayAbilitySpec,增加它的Level,标记它为Dirty以复制到Owning Client。如果技能此时处于激活状态不会被终止 |
两种方法的主要区别是在技能升级时当前激活的技能是否会被终止。使用哪种方法依赖于你的 GameplayAbilities,建议为你的UGameplayAbility子类添加一个bool变量控制使用哪种方式。
4.6.14 技能集 Ability Sets
GameplayAbilitySets是一个便利的UDataAsset类,用于将其持有的带有输入绑定的GameplayAbilities赋予给Characters 。GameplayAbilitySets子类化可以添加额外的逻辑和属性。Paragon对于每一个英雄都会有一个与之对应的GameplayAbilitySet。
这个类并不是必须要使用。示例工程在GDCharacterBase和它的子类中完成了和GameplayAbilitySets类似的功能。
4.6.15 技能批处理 Ability Batching
传统的Gameplay Ability生命周期涉及到最小两到三次的客户端到服务器端的RPC调用。
CallServerTryActivateAbility()ServerSetReplicatedTargetData()(可选)ServerEndAbility()
如果一个GameplayAbility可以在一帧内原子性的执行完上述步骤,那么我们可以通过Batch(Combine)优化这个工作流,将两到三个RPCs合并到一个RPC。GAS提供了这种优化叫作Ability Batching。使用Ability Batching通常的示例是基于命中检测的枪(hitscan guns),射击、射线检测、将命中结果(TargetData)发送给服务器、结束一气呵成。GASShooter提供了一个这样的示例。
半自动的枪(按一下射一发)是最佳示例,将CallServerTryActivateAbility(),ServerSetReplicatedTargetData() (the bullet hit result)和ServerEndAbility()从三个RPCs合并到一个RPC。
全自动或连发的枪对第一发子弹将CallServerTryActivateAbility() 和ServerSetReplicatedTargetData()这两个RPCs合并到一个RPC。随后的每一发子弹只有一个ServerSetReplicatedTargetData() RPC。最终,当停止射击时发送一个单独的RPC ServerEndAbility()。这是糟糕示例,我们仅将第一发子弹从两个RPCs优化成了一个RPC。这种情况也可以通过Gameplay Event来触发技能,使用EventPayload将子弹的TargetData从客户端发送到服务器,这种方法的缺点是必须在Ability的外部生成TargetData ,而Ability Batching方式是在Ability的内部生成。
Ability Batching 在ASC中默认是被禁用的。要启用Ability Batching需要重载ShouldDoServerAbilityRPCBatch()并且返回true:
virtual bool ShouldDoServerAbilityRPCBatch() const override { return true; }
现在Ability Batching已经启用,接下来在激活要批处理的技能之前,必须预先创建一个FScopedServerAbilityRPCBatcher结构体。在其后的且在其作用域内的任何Abilities都将尝试Ability Batching。FScopedServerAbilityRPCBatcher的工作原理是在每个可批处理的函数中都有特殊的代码,这些特殊代码可拦截发送RPC的调用,并将消息打包为批处理结构。当FScopedServerAbilityRPCBatcher超出作用域时,将在UAbilitySystemComponent::EndServerAbilityRPCBatch()中自动把这个批处理结构发送到服务器,服务器会在UAbilitySystemComponent::ServerAbilityRPCBatch_Internal(FServerAbilityRPCBatch& BatchInfo)中接收到这个Batch RPC,BatchInfo参数包含了一些标记:技能是否结束,激活技能时是否有输入按下,是否有TargetData。调试Ability Batching是否工作正确时可以在这里设置断点。也可以使用AbilitySystem.ServerRPCBatching.Log 1开启Ability Batching的日志。
这个机制只能在C++中使用并且仅能通过FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle激活技能。
bool UGSAbilitySystemComponent::BatchRPCTryActivateAbility(FGameplayAbilitySpecHandle InAbilityHandle, bool EndAbilityImmediately)
{
bool AbilityActivated = false;
if (InAbilityHandle.IsValid())
{
FScopedServerAbilityRPCBatcher GSAbilityRPCBatcher(this, InAbilityHandle);
AbilityActivated = TryActivateAbility(InAbilityHandle, true);
if (EndAbilityImmediately)
{
FGameplayAbilitySpec* AbilitySpec = FindAbilitySpecFromHandle(InAbilityHandle);
if (AbilitySpec)
{
UGSGameplayAbility* GSAbility = Cast(AbilitySpec->GetPrimaryInstance());
GSAbility->ExternalEndAbility();
}
}
return AbilityActivated;
}
return AbilityActivated;
}
GASShooter为半自动和全自动的射击复用了相同的支持批处理的GameplayAbility并且永远不会直接调用EndAbility() (整个射击一共由两个技能实现:一个是仅本地执行用于根据玩家输入和当前射击模式激活批处理射击的一个技能,其也会负责调用批处理射击的EndAbility()。第二个是真正完成射击逻辑的技能,也就是这里的支持批处理GameplayAbility)。由于所有的RPCs必须发生在FScopedServerAbilityRPCBatcher作用域之内,我提供了一个参数EndAbilityImmediately用以控制是否将EndAbility()纳入批处理,用以区分半自动射击和全自动射击。
GASShooter暴露了一个蓝图节点用以在仅本地执行的技能中激活批处理技能。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-eLK1rupZ-1591700466350)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/batchabilityactivate.png)]
4.6.15 网络安全策略 Net Security Policy
一个GameplayAbility的网络安全策略决定技能在网络上何处执行,这可以防止客户端尝试执行受限功能。
| 网络安全策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ClientOrServer |
没有安全要求,客户端和服务器可以自由的执行和终止技能 |
ServerOnlyExecution |
客户端发送的执行请求会被服务器端忽略。客户端仅能请求取消或结束技能 |
ServerOnlyTermination |
客户端发送的取消或结束技能的请求会被服务器端忽略。客户端仅能请求技能的执行 |
ServerOnly |
服务器控制技能的执行和终止。客户端的任何请求都会被忽略 |
4.7 技能任务 Ability Tasks
4.7.1 Ability Task定义
GameplayAbilities仅能执行一帧,其本身并没有太大的灵活性。要在技能的持续过程中做一些事情或者在稍后响应委托回调,我们可以使用AbilityTasks。
GAS带了很多拆箱即用的AbilityTasks:
- 基于
RootMotionSource的角色移动任务 - 播放动画蒙太奇的任务
- 响应属性修改的任务
- 响应游戏效果修改的任务
- 响应玩家输入的任务
- 等等
同时最多只能运行1000个并行的AbilityTasks(见UAbilityTask的构建方法)。在设计GameplayAbilities 时需要谨记这一点,一个RTS游戏在同一时间可能有几百个角色。
4.7.2 自定义Ability Tasks
通常你将在C++中创建自定义的AbilityTasks。示例项目有两个自定义的AbilityTasks:
PlayMontageAndWaitForEvent组合了默认的PlayMontageAndWait和WaitGameplayEventAbilityTasks。这将允许动画蒙太奇通过AnimNotifies给播放它的技能发送事件,使用这个在指定的动画播放节点触发行为。WaitReceiveDamage监听OwnerActor受到伤害,被动护甲技能在英雄受到伤害时删除一层护甲。
AbilityTasks的构成:
- 一个用于创建
AbilityTask的静态方法 - 在
AbilityTask完成任务时广播的委托 Activate()方法,开始主要任务,绑定外部委托等OnDestroy()方法,执行清理工作,包括清理已经绑定的委托- 绑定到外部委托的回调方法
- 成员变量和内部的帮助方法
注意: AbilityTasks仅能定义一种类型的输出委托,所有的输出委托都必须是这种类型,无论它们是否使用参数,对于未使用参数的委托传递默认值。
AbilityTasks仅在拥有GameplayAbility的客户端或服务器上执行。不过,AbilityTasks能够通过在构造方法中设置bSimulatedTask = true,重载virtual void InitSimulatedTask(UGameplayTasksComponent& InGameplayTasksComponent);使其运行在Simulated Clients上。也可以复制任意数量的成员变量。这仅用于极少的情况,比如模拟整个移动的AbilityTasks,你肯定不想复制每一次的移动变化。所有的RootMotionSource AbilityTasks都是这么做的。 详见AbilityTask_MoveToLocation.h/.cpp。
AbilityTasks也可以通过在AbilityTask的构造方法设置bTickingTask = true开启Tick,还需要重载virtual void TickTask(float DeltaTime)。这在需要流畅的插值时将非常有用。 详见AbilityTask_MoveToLocation.h/.cpp。
4.7.3 使用Ability Tasks
在C++中创建和激活一个AbilityTask(来自GDGA_FireGun.cpp):
UGDAT_PlayMontageAndWaitForEvent* Task = UGDAT_PlayMontageAndWaitForEvent::PlayMontageAndWaitForEvent(this, NAME_None, MontageToPlay, FGameplayTagContainer(), 1.0f, NAME_None, false, 1.0f);
Task->OnBlendOut.AddDynamic(this, &UGDGA_FireGun::OnCompleted);
Task->OnCompleted.AddDynamic(this, &UGDGA_FireGun::OnCompleted);
Task->OnInterrupted.AddDynamic(this, &UGDGA_FireGun::OnCancelled);
Task->OnCancelled.AddDynamic(this, &UGDGA_FireGun::OnCancelled);
Task->EventReceived.AddDynamic(this, &UGDGA_FireGun::EventReceived);
Task->ReadyForActivation();
在蓝图中, 仅用一个创建AbilityTask的蓝图节点即可,并不需要调用ReadyForActivate(),它将被Engine/Source/Editor/GameplayTasksEditor/Private/K2Node_LatentGameplayTaskCall.cpp自动调用。 K2Node_LatentGameplayTaskCall也会自动调用BeginSpawningActor() 和FinishSpawningActor()如果你的AbilityTask类中存在的话(详见AbilityTask_WaitTargetData)。再次重审,K2Node_LatentGameplayTaskCall仅对蓝图完成这些。在C++中,需要手动调用ReadyForActivation(), BeginSpawningActor(), 和 FinishSpawningActor()。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-hX04e0NF-1591700466351)(C:\Users\X\Desktop\abilitytask.png)]
要取消AbilityTask,可以在蓝图或C++通过AbilityTaskProxy对象调用EndTask()。
有些AbilityTasks不会在GameplayAbility结束时自动结束比如WaitTargetData,这些需要在GameplayAbility的OnEndAbility中手动结束(WaitTargetData 在用户输入Confirm 或Cancel时将自然结束)。
4.7.4 Root Motion Source Ability Tasks
GAS带有一些能够处理角色移动的AbilityTasks,比如对于角色击退、复杂的跳跃、拉、冲撞。其本质是使用连接到CharacterMovementComponent的Root Motion Sources。
注意: 可预测的RootMotionSource AbilityTasks在4.19和4.25+版本能够正常工作,在4.20-4.24有BUG(如果要使用这些版本,可以自行修正详见prediction fix)。
4.8 游戏表现 Gameplay Cues
4.8.1 Gameplay Cue定义
GameplayCues (GC) 执行非游戏性相关的事情,比如音效,粒子特效,震屏等。GameplayCues通常会被复制和预测(除非设置Executed, Added或Removed是本地的)。
我们通过发送必须以GameplayCue开始的GameplayTag触发GameplayCues并且通过ASC向GameplayCueManager指定事件类型(Executed, Added或Removed)。
GameplayCueNotify对象和其他实现了IGameplayCueInterface 接口的Actors能够订阅基于 GameplayCueTag的事件。
注意: 再次重审,GameplayCue GameplayTags必须要以GameplayCue开始。一个正确的示例:GameplayCue.A.B.C。
有两种类型的GameplayCueNotifies,Static 和Actor。他们响应不同的事件,并且需要不同类型的GameplayEffects来触发。使用时根据你的需要重载对应的事件即可。
GameplayCue Class |
事件 | GameplayEffect 类型 |
描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
GameplayCueNotify_Static |
Execute |
Instant or Periodic |
静态GameplayCueNotifies将使用ClassDefaultObject(意味着没有实例),主要用于一次性的效果比如击中效果 |
GameplayCueNotify_Actor |
Add or Remove |
Duration or Infinite |
Actor GameplayCueNotifies当被Added时将创建一个新的实例。这些实例能在持续时间内一直工作直到他们被Removed。主要用于在Duration 或Infinite GameplayEffect的持续期间循环播放音效或粒子特效,当然也可以手动删除他们。他们也带有一个选项用来管理能Added多少个相同的GameplayCueNotify_Actor,因此对同一个目标多次应用相同的效果比如音效和粒子可以使其只执行一次 |
从技术上讲,GameplayCueNotify可以响应任何事件,但上述内容通常是我们使用它们的方式。
注意: 当使用GameplayCueNotify_Actor时要勾选Auto Destroy on Remove否则后续通过GameplayCueTag调用Add将不能工作。
当ASC的Replication Mode不是Full时,在服务器玩家(Listen Server)上Add and Remove GC的事件将会触发两次,一次是应用GE,另一次是通过NetMultiCast广播给客户端,然而,WhileActive 事件仅会触发一次。所有事件在客户端仅触发一次。
示例项目使用GameplayCueNotify_Actor实现了一个眩晕和一个冲刺效果。还使用了一个GameplayCueNotify_Static实现子弹击中效果。这些GC能够通过本地触发进一步优化,而不是通过GE复制它们,详见示例项目。
4.8.2 触发Gameplay Cues
当GameplayEffect 被成功应用时,配置在GameplayTags的所有GameplayCues都会被触发。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0irxy9Io-1591700466352)(C:\Users\X\Desktop\gcfromge.png)]
UGameplayAbility提供了相应的蓝图节点用于Execute, Add或Remove GameplayCues。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ADZ0WB9O-1591700466352)(C:\Users\X\Desktop\gcfromga.png)]
在C++中,可以直接调用ASC中的这些方法 (或者在你ASC的子类中将这些方法暴露给蓝图):
/** GameplayCues can also come on their own. These take an optional effect context to pass through hit result, etc */
void ExecuteGameplayCue(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, FGameplayEffectContextHandle EffectContext = FGameplayEffectContextHandle());
void ExecuteGameplayCue(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters& GameplayCueParameters);
/** Add a persistent gameplay cue */
void AddGameplayCue(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, FGameplayEffectContextHandle EffectContext = FGameplayEffectContextHandle());
void AddGameplayCue(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters& GameplayCueParameters);
/** Remove a persistent gameplay cue */
void RemoveGameplayCue(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag);
/** Removes any GameplayCue added on its own, i.e. not as part of a GameplayEffect. */
void RemoveAllGameplayCues();
4.8.3 本地游戏表现 Local Gameplay Cues
从GameplayAbilities和ASC暴露的用于触发GameplayCues的方法默认会复制。每一个GameplayCue事件都是一个多播RPC,这将导致大量的RPCs。GAS也强制每次网络更新相同的GameplayCue RPCs最大只有两个,我们可以使用本地GameplayCues解决此问题,Local GameplayCues仅能在每个客户端独立的执行Execute, Add 或Remove。
什么情况下会使用Local GameplayCues:
- 炮弹击中效果
- 近战击中效果
- 从动画蒙太奇触发
GameplayCues
Local GameplayCue相关方法可以添加到ASC的子类中:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "GameplayCue", Meta = (AutoCreateRefTerm = "GameplayCueParameters", GameplayTagFilter = "GameplayCue"))
void ExecuteGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters& GameplayCueParameters);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "GameplayCue", Meta = (AutoCreateRefTerm = "GameplayCueParameters", GameplayTagFilter = "GameplayCue"))
void AddGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters& GameplayCueParameters);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "GameplayCue", Meta = (AutoCreateRefTerm = "GameplayCueParameters", GameplayTagFilter = "GameplayCue"))
void RemoveGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters& GameplayCueParameters);
void UPAAbilitySystemComponent::ExecuteGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters & GameplayCueParameters)
{
UAbilitySystemGlobals::Get().GetGameplayCueManager()->HandleGameplayCue(GetOwner(), GameplayCueTag, EGameplayCueEvent::Type::Executed, GameplayCueParameters);
}
void UPAAbilitySystemComponent::AddGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters & GameplayCueParameters)
{
UAbilitySystemGlobals::Get().GetGameplayCueManager()->HandleGameplayCue(GetOwner(), GameplayCueTag, EGameplayCueEvent::Type::OnActive, GameplayCueParameters);
}
void UPAAbilitySystemComponent::RemoveGameplayCueLocal(const FGameplayTag GameplayCueTag, const FGameplayCueParameters & GameplayCueParameters)
{
UAbilitySystemGlobals::Get().GetGameplayCueManager()->HandleGameplayCue(GetOwner(), GameplayCueTag, EGameplayCueEvent::Type::Removed, GameplayCueParameters);
}
如果一个GameplayCue是本地添加的,它也会被本地删除。如果它是由Replication添加的,也会被Replication删除。
4.8.4 游戏表现参数 Gameplay Cue Parameters
GameplayCues 接收一个FGameplayCueParameters 结构体作为其参数其中包含了一些额外的信息。如果你通过GameplayAbility或者 ASC中的方法手动激活一个GameplayCue,那么你也必须手动填充一个GameplayCueParameters用以传递给GameplayCue。如果GameplayCue是被GameplayEffect触发,那么GameplayCueParameters将会被自动填充。
- AggregatedSourceTags
- AggregatedTargetTags
- GameplayEffectLevel
- AbilityLevel
- EffectContext
- Magnitude (if the
GameplayEffecthas anAttributefor magnitude selected in the dropdown above theGameplayCuetag container and a correspondingModifierthat affects thatAttribute)
在GameplayCueParameters结构体中的SourceObject变量可能是当手动激活GameplayCue时向其传递任意数据的好地方。
**注意:**在参数结构体中的一些变量像Instigator可能已经存在于EffectContext之中。EffectContext也包含一个FHitResult用于指定GameplayCue在世界中生成的位置。通过子类化EffectContext向GameplayCues传递更多数据可能是一种好的方式,尤其是当GameplayCues是由GameplayEffect触发时。
下面UAbilitySystemGlobals中的三个方法用于自动填充GameplayCueParameters结构,这些是可以被重载的virtual方法。
/** Initialize GameplayCue Parameters */
virtual void InitGameplayCueParameters(FGameplayCueParameters& CueParameters, const FGameplayEffectSpecForRPC &Spec);
virtual void InitGameplayCueParameters_GESpec(FGameplayCueParameters& CueParameters, const FGameplayEffectSpec &Spec);
virtual void InitGameplayCueParameters(FGameplayCueParameters& CueParameters, const FGameplayEffectContextHandle& EffectContext);
4.8.5 游戏表现管理器 Gameplay Cue Manager
默认情况下,GameplayCueManager将会搜索整个游戏目录寻找GameplayCueNotifies并且在游戏时将它们加载到内存。我们可以通过DefaultGame.ini改变GameplayCueManager搜索的目录:
[/Script/GameplayAbilities.AbilitySystemGlobals]
GameplayCueNotifyPaths="/Game/GASDocumentation/Characters"
我们想要GameplayCueManager检索到所有的GameplayCueNotifies,但并不希望它在游戏开始的时候异步加载所有的GameplayCueNotifies。因为这将导致其引用的所有声音和粒子特效等资源也会被加载到内存中,无论当前关卡是否需要。在大体量的游戏中比如Paragaon,这将会导致在内存中存在几百兆不需要的资源并且可能还会导致在游戏开始时的冻结。对于在开始游戏时就加载每一个GameplayCue,另一个方案是在游戏中真正使用GameplayCue时才进行异步加载,用哪个加载哪个。这将会缓解不必要的内存开销,加载GameplayCue时的游戏冻结会变成小的游戏卡顿,在游戏过程中GameplayCue第一次被触发时其效果也可能会延迟。到目前为止,这是我推荐的解决方案,直到我们发现更好的方法。
首先必须要子类化UGameplayCueManager,然后在DefaultGame.ini中配置我们的UGameplayCueManager子类:
[/Script/GameplayAbilities.AbilitySystemGlobals]
GlobalGameplayCueManagerClass="/Script/ParagonAssets.PBGameplayCueManager"
在 UGameplayCueManager子类中重载ShouldAsyncLoadRuntimeObjectLibraries():
virtual bool ShouldAsyncLoadRuntimeObjectLibraries() const override
{
return false;
}
4.8.6 阻止触发游戏表现 Prevent Gameplay Cues from Firing
有些时候我们不希望GameplayCues被触发,比如当我们格档了一次攻击时不希望播放Damage GameplayEffect上的受击效果或者希望换一个效果。这时我们可以在GameplayEffectExecutionCalculations中调用OutExecutionOutput.MarkGameplayCuesHandledManually()并且手动发送我们想要的GameplayCue事件给Target或 Source的 ASC即可。
如果在特定的ASC上不想触发任何GameplayCues,可以设置AbilitySystemComponent->bSuppressGameplayCues = true。
4.8.7 游戏表现批处理
每一个GameplayCue的触发都是一次不可靠的广播RPC,当我们同时触发多个GCs时,有几种优化的方法将他们压缩到一个RPC中或是发送少量的数据以节省带宽。
手动RPC
假设你有一把霰弹枪能够同时发射8发弹丸,有8个射线检测和8个GameplayCues。GASShooter使用了一种懒方法,通过将射线检测信息以TargetData的形式保存到EffectContext中将其组合到一个RPC中。当然这种作法只是将RPCs从8个减少到1个,但还是会在这个RPC中通过网络发送大量的数据(大概是500字节)。一种更好的方法是,发送一个自定义结构体的RPC,将击中的位置信息或者一个能在接收端重建位置信息的随机种子编码到这个结构体中,在客户端通过这个自定义的结构体触发 locally executed GameplayCues即可。
具体步骤:
- 声明一个
FScopedGameplayCueSendContext,它将阻止UGameplayCueManager::FlushPendingCues()直到超出其作用域。这意味着所有在其作用域内的GameplayCues都将进行排队。 - 重载
UGameplayCueManager::FlushPendingCues(),根据GameplayTag将能够合并到一个批次的GameplayCues保存到自定义结构体中,调用RPC将其发送到客户端。 - 客户端接收到自定义结体体并将其解压到本地执行的
GameplayCues中。
这种方法还能将一些特定的参数传递给GameplayCues,这些参数并不在GameplayCueParameters中并且你也不想将它们添加到EffectContext中,比如伤害数字,是否暴击,是否破盾,是否致使一击等。
https://forums.unrealengine.com/development-discussion/c-gameplay-programming/1711546-fscopedgameplaycuesendcontext-gameplaycuemanager
一个游戏技能上的多个游戏表现
在一个GameplayEffect上的所有GameplayCues已经通过一个RPC发送。默认情况下,UGameplayCueManager::InvokeGameplayCueAddedAndWhileActive_FromSpec()将会通过不可靠的多播发送整个GameplayEffectSpec(但会转换成FGameplayEffectSpecForRPC)而无论ASC的Replication Mode是什么。根据GameplayEffectSpec中包含的内容这有可能需要大量的带宽,不过可以通过设置cvar AbilitySystem.AlwaysConvertGESpecToGCParams 1尝试进行优化。开启这个选项后将会在RPC的过程中把GameplayEffectSpecs转换成FGameplayCueParameter这样就不用发送整个FGameplayEffectSpecForRPC了。这将可能会节省带宽但也会少了一些信息,这依赖于GESpec是如何转换成GameplayCueParameters的,且必须知晓你的GCs需要哪些信息。
4.9 技能系统全局数据
AbilitySystemGlobals类持有GAS的全局信息。其中的大多数变量可以通过DefaultGame.ini设置。通常并不需要与这个类进行交互,但需要知道它的存在。如果需要子类化GameplayCueManager或GameplayEffectContext,则需要通过派生AbilitySystemGlobals完成。
派生AbilitySystemGlobals后需要在DefaultGame.ini中进行设置:
[/Script/GameplayAbilities.AbilitySystemGlobals]
AbilitySystemGlobalsClassName="/Script/ParagonAssets.PAAbilitySystemGlobals"
4.9.1 InitGlobalData()
从UE4.24开始,要使用TargetData必须要调用UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData(),否则你会遇到ScriptStructCache相关的错误且客户端将从服务器断开连接。在项目中这个方法只需要调用一次。堡垒之夜是在AssetManager类的开始初始加载方法调用,帕拉贡是在UEngine::Init()中调用。示例项目在UEngineSubsystem::Initialize()中调用,建议将这个直接拷贝到你的项目中以解决TargetData相关的问题。
如果在使用AbilitySystemGlobals GlobalAttributeSetDefaultsTableNames时崩溃,则需要将UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData()的调用置后一些,将其放到AssetManager或GameInstance中而不是UEngineSubsystem::Initialize()中。崩溃的原因是因为子系统的初始化顺序导致,GlobalAttributeDefaultsTables需要EditorSubsystem已被加载以绑定UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData()里的一个委托。
4.10 预测 Prediction
GAS支持拆箱即用的客户端预测(预判)功能,然而它并不能预测所有事情。GAS中的客户端预测意味着客户端不必等待服务器的许可就可以激活一个GameplayAbility并应用GameplayEffects。它也能预测做这件事需要的服务器许可和应用GameplayEffects的目标。在客户端激活后,服务器将在网络延迟时间后执行GameplayAbility并且告诉客户端它的预测执行是否正确。如果客户端的预测是错误的,它将从错误的预测中回滚它的修改匹配到服务器。
GAS预测相关代码在插件的GameplayPrediction.h文件中。
Epic的倾向是仅预测可以回滚的,例如Paragon和Fortnite都不预测伤害,这两个游戏很可能使用ExecutionCalculations(不支持预测)做伤害计算。这并不是说你一定不能预测这些事情,只要符合需求并且能够工作。
我们也不是“无缝地,自动地预测一切”的解决方案。 我们仍然认为,将玩家的预测最好保持在最低限度。
摘自Epic的Dave Ratti新的网络预测插件Network Prediction Plugin
什么是可以预测的:
- 技能激活
- 触发事件
GameplayEffect的应用:
Attribute修改 (注意:Executions当前不能被预测,只有只有属性Modifiers才可以被预测)GameplayTag修改Gameplay Cue事件- 动画蒙太奇
- 移动 (
UCharacterMovement)
什么是不可预测的:
GameplayEffect移除GameplayEffect周期效果
来自GameplayPrediction.h(译者注:一个注释比代码多的头文件,如果要使用客户端预测强烈建议读此文件)
我们可以预测GameplayEffect的应用,却不能预测GameplayEffect的移除。解决这个问题的一种方式是预测我们想要移除的GameplayEffect的反效果。比如说我们预测一个移动速度减缓40%的效果,我们可以通过应用一个移动速度加速40%的效果来当作删除它,最后同时删除这两个GameplayEffects。当然这并不能满足所有GameplayEffect移除的情况。Epic的Dave Ratti表示希望在GAS后续的迭代中支持这个。
因为我们不能预测GameplayEffects的移除,我们不能完整的预测GameplayAbility的冷却,并没有与之对应的反效果。服务器复制的Cooldown GE将存在于客户上,并且任何绕过此操作的尝试将被服务器拒绝。 这意味着高延迟的客户端需要花费更长的时间告诉服务器进行冷却并接受服务器的Cooldown GE的移除。这将导致高延迟的玩家射击频率会低于低延迟的玩家,低延迟的玩家比高延迟的玩家有优势。Fortnight使用自定义的统计替代了Cooldown GEs以解决此问题。
就预测伤害而论,我个人并不推荐,尽管它是大多数人开始使用GAS时首先尝试的事情之一。我也强烈建议不要预测死亡。虽然你可以预测伤害,但这很棘手。如果你错误的预测了应用伤害,玩家会看到敌人的生命值跳回。如果要预测死亡,这可能会更加奇葩。假设你误预测了角色的死亡刚开始了布娃娃模拟,当服务器校正后这个角色突然停止了布娃娃模拟并且开始朝你射击,这种体验太奇怪了。
注意: Instant GameplayEffects (像Cost GEs) 预测修改你自己的属性是无缝的, 预测Instant Attribute对其他角色的修改将会在他们的属性上表现短暂的异常。可预测的Instant GameplayEffects预测失败时,可以想像成是Infinite GameplayEffects的回滚。当服务器的GameplayEffect被应用时,可能存在两个相同的GameplayEffect,这将导致短时间内Modifier被应用两次或根本不应用。最终它会自行修正,但有时玩家会注意到此问题。
GAS的预测实现尝试解决的问题:
- “我可以这样做吗?” 预测的基本协议
- “Undo”当预测失败时如何撤消副作用
- “Redo”如何避免重播我们在本地预测但也会从服务器复制的副作用
- “完整性”如何确定我们预测了所有副作用
- “依赖性”如何管理依赖性预测和预测事件链
- “覆盖”如何预测性地覆盖服务器原本已复制/拥有的状态。
来自GameplayPrediction.h
4.10.1 预测键 Prediction Key
GAS的预测机制基于一个叫作预测键(Prediction Key)的概念,它是一个当客户端激活一个GameplayAbility时在客户端生成的整型标识符。
- 客户端激活一个
GameplayAbility时生成一个预测键(Activation Prediction Key) - 客户端调用
CallServerTryActivateAbility()将这个预测键发送给服务器 - 当预测键有效时,客户端将这个预测键添加给所有它应用的
GameplayEffects - 客户端预测键超出范围,在相同的
GameplayAbility中进一步预测效果需要一个新的 Scoped Prediction Window - 服务器接收到来自客户端的预测键
- 服务器将这个预测键添加给所有它应用的
GameplayEffects - 服务器将这个预测键复制(Replicates)回客户端
- 客户端接收到从服务器复制回的
GameplayEffects,如果复制回的GameplayEffects与客户端应用的GameplayEffects有相同的预测键,则预测正确。此时在目标上将有两个GameplayEffect直到客户端删除它预测的那一个 - 客户端接收到从服务器返回的预测键(
Replicated Prediction Key),这个预测键现在被标记为阵旧的 - 客户端删除所有它创建带有阵旧预测键的
GameplayEffects,服务器复制回的GameplayEffects将被保持。任何客户端添加的且没有接收到匹配的服务器返回版本的GameplayEffects都是预测失败的
预测键在通过Activation Prediction Key激活的GameplayAbilities的原子指令组(也叫作Window)中保证是有效的。你也可以想像成仅在一帧有效。任何AbilityTasks中的回调将不再有一个有效的预测键除非AbilityTask中有内建的同步点生成一个新的Scoped Prediction Window。
4.10.2 在技能中创建新的预测窗口
要在AbilityTasks的回调中预测更多行为,我们需要使用一个新的Scoped Prediction Key创建一个新的Scoped Prediction Window。这有时也被称作在客户端和服务器间的一个同步点(Synch Point)。一些AbilityTasks,比如所有输入相关的AbilityTasks内建了创建新的Scoped Prediction Window的功能,意味着在AbilityTasks的回调方法中的原子性代码可以使用一个有效的Scoped Prediction Key。其他任务,像WaitDelay则没有内置的代码为它的回调方法创建新的Scoped Prediction Window。如果你需要为一个没有内置代码创建新的Scoped Prediction Window的AbilityTask预测行为(像上述的WaitDelay),我们可以通过手动调用OnlyServerWait选择的WaitNetSync完成。当客户端遇到带有OnlyServerWait的WaitNetSync它将基于GameplayAbility的Activation Prediction Key生成一个新的Scoped Prediction Key,通过RPC将其传递给服务器,然后将其添加给它应用的新的GameplayEffects。当服务器端遇到带有OnlyServerWait的WaitNetSync,它将等待直到它从客户端收到新的Scoped Prediction Window才会继续。接下来Scoped Prediction Key要做的和Activation Prediction Key一样。Scoped Prediction Key超出作用域时失效,意味着Scoped Prediction Windows已经关闭。再讲一次,仅不能延迟的原子操作才可以使用Scoped Prediction Key。
你可以根据需要创建Scoped Prediction Windows。
如果你想在自定义的AbilityTasks中加入同步点功能,可以参考WaitNetSync。
**注意:**当使用 WaitNetSync时,其会阻塞服务器上GameplayAbility的执行直到收到客户端的消息。这可能会被恶意的玩家滥用,他们会攻击游戏故意延迟发送新的Scoped Prediction Key。Epic很少使用WaitNetSync,如果你有这种困扰,建议你创建一个新版本的可以延迟自动继续的AbilityTask(指定时间内收不到客户端的消息就跳过等待)。
示例项目在冲刺技能中使用了WaitNetSync创建了一个新的Scoped Prediction Windows,这使得每次应用耐力消耗都能够进行预测。理想情况下,在应用消耗和冷却时我们想要一个有效的Prediction Key。
如果你有一个预测的 GameplayEffect在其所属客户端上播放了两次,你的预测密钥已过期并且遇到了"Redo"问题。这通常可以在应用GameplayEffect之前放一个带有OnlyServerWait的WaitNetSync以创建一个新的Scoped Prediction Key解决。
4.10.3 可预测的生产Actor
在客户端可预测的生产Actors是一个高级主题,GAS没有提供拆箱即用的功能(SpawnActor AbilityTask仅在服务器端生产Actor)。核心点是在客户端和服务器端都生产一个复制的Actor。
如果Actor仅用于视觉表现或者不是任何游戏性相关的目的,有一个简单的方案可以满足此需求。重载Actor的 IsNetRelevantFor() 方法阻止从服务器将其复制到所属客户端。所属客户端仅需要本地生产的版本,服务器和其他客户端使用服务器的已复制版本。
bool APAReplicatedActorExceptOwner::IsNetRelevantFor(const AActor * RealViewer, const AActor * ViewTarget, const FVector & SrcLocation) const
{
return !IsOwnedBy(ViewTarget);
}
如果生产的Actor会影响到游戏性(比如子弹,需要预测伤害),那么你需要更高级的方案这超出了此文档的范围。可以在Epic Games的GitHub中找到UnrealTournament项目参考其中如何实现的可预测生产子弹。它们仅在所属客户端上生成一个虚拟子弹,该虚拟子弹与服务器的复制子弹同步。
4.10.4 GAS预测机制的开发计划
将来官方可能会在GameplayPrediction.h中加入GameplayEffect的移除预测和周期性GameplayEffects的预测。
来自Epic的Dave Ratti表达了有兴趣解决冷却预测导致的低延迟玩家比高延迟玩家有优势的问题。
预计由Epic开发的新插件Network Prediction将能与GAS完全互用就像CharacterMovementComponent一样。
4.10.5 网络预测插件
Epic最近发起了一项计划,用新的Network Prediction插件替换CharacterMovementComponent。 该插件仍处于早期阶段,但仍可以在Unreal Engine GitHub上提早访问。现在还不确定此插件在未来哪个版本的引擎亮相。
4.11 技能目标
4.11.1 目标数据
FGameplayAbilityTargetData是一个能在网络上传递用于描述目标数据的通用结构体。TargetData通常将持有AActor或UObject的引用以及FHitResults和位置/朝向/原点信息。不过,你也可以通过子类化在其中加入任何你需要的东西,这是一种通过GameplayAbilities在客户端和服务器端之间传递数据的简单方法。不要直接使用FGameplayAbilityTargetData 结构体而应使用它的子类。在GAS的GameplayAbilityTargetTypes.h中包含了几个能够被直接使用的FGameplayAbilityTargetData派生类。
TargetData 通常是由Target Actors产生或者是手动创建,它会被AbilityTasks和GameplayEffects(通过EffectContext)消耗。TargetData作为EffectContext的结果时,Executions, MMCs, GameplayCues和AttributeSet的[Pre|Post]GameplayEffectExecute方法都可以访问它。
通常我们不会直接传递FGameplayAbilityTargetData,而是使用一个FGameplayAbilityTargetDataHandle,其内部保存了一个FGameplayAbilityTargetData指针的TArray。
4.11.2 目标Actor
GameplayAbilities使用WaitTargetData AbilityTask生产TargetActors,其作用是呈现和捕获世界中的目标信息。TargetActors可以使用可选的GameplayAbilityWorldReticles显示当前的目标。在目标选择确认之后,目标信息将会以TargetData的形式返回,然后将其传递给GameplayEffects。TargetActors本质是AActor因此他们可以有任何的显示组件(static meshes 或者 decals)用以呈现在哪以及如何选择目标。Static Meshes被用来显示你的角色将要构建的一个对象(堡垒之夜的建造模式)。Decals用来显示地面上的作用区域。示例项目使用带有一个Decal的AGameplayAbilityTargetActor_GroundTrace呈现陨石技能的伤害区域。TargetActors也可以不显示任何东西,比如GASShooter中的霰弹枪会直接使用射线检测目标而不需要显示任何东西。
TargetActors使用基本的射线检测或者碰撞检测获得目标信息并根据TargetActor的实现方式将结果转换成FHitResults或AActor的数组保存到TargetData。WaitTargetData AbilityTask通过TEnumAsByte参数决定目标何时被确定。当参数不是TEnumAsByteTargetActor通常会在Tick()中执行trace/overlap并且根据它的实现更新FHitResult的位置。要注意它使用了Tick()并且复杂的TargetActors可能会做很多的事情,比如GASShooter中的火箭筒的第二技能。当在Tick()上追踪时对客户端是非常敏感的,如果消耗了太多性能你可能要考虑降低TargetActor的Tick频率。当参数是TEnumAsByteTargetActor会立即产生,并生产TargetData,然后销毁(Tick()将不会被调用)。
EGameplayTargetingConfirmation::Type |
何时确定目标 |
|---|---|
Instant |
触发目标选取时立即确定,不需要额外逻辑或者用户输入决定 |
UserConfirmed |
当技能绑定了Confirm目标选取由用户确定或者是通过调用UAbilitySystemComponent::TargetConfirm()确定。取消同理可以绑定Cancel或者调用UAbilitySystemComponent::TargetCancel() |
Custom |
通过技能的UGameplayAbility::ConfirmTaskByInstanceName()确定选取,通过技能的UGameplayAbility::CancelTaskByInstanceName()取消选取 |
CustomMulti |
要使用的方法同上,只是在数据产生时不结束AbilityTask,可用于选取多个目标 |
并不是每个TargetActor都会支持上述所有EGameplayTargetingConfirmation::Type。例如AGameplayAbilityTargetActor_GroundTrace不支持Instant。
WaitTargetData AbilityTask带有一个AGameplayAbilityTargetActor的参数,在每一次AbilityTask 激活时创建TargetActor的实例,AbilityTask 结束时销毁这个实例。WaitTargetDataUsingActor AbilityTask则可以利用一个已存在的TargetActor,且在AbilityTask结束时并不会销毁它。这两种AbilityTasks效率都很低,它们都会生产或请求生产一个新的TargetActor。对于制作游戏原型它们很方便,但在生产中当需要不断的产生TargetData时(比如自动步枪)则需要对此进行优化。GASShooter中有一个自定义AGameplayAbilityTargetActor子类和一个新的WaitTargetDataWithReusableActorAbilityTask,它们可以复用一个TargetActor而不会进行销毁。
TargetActors默认情况下不会被复制,但是当在你的游戏中需要将本地玩家的目标选择过程显示给其他玩家时也可以将TargetActors改为被复制。WaitTargetData AbilityTask中包含了通过RPCs与服务器通讯的默认功能。如果TargetActor 的ShouldProduceTargetDataOnServer为false,在确定选择目标时会通过在UAbilityTask_WaitTargetData::OnTargetDataReadyCallback()方法中调用CallServerSetReplicatedTargetData()使客户端把TargetData通过RPC传递给服务器。当ShouldProduceTargetDataOnServer为true,客户端将发送一个确定事件(EAbilityGenericReplicatedEvent::GenericConfirm),通过在UAbilityTask_WaitTargetData::OnTargetDataReadyCallback中调用RPC方法ServerSetReplicatedEvent() 传递给服务器,然后服务器基于接收到的RPC将会执行射线或碰撞检测并产生TargetData。如果客户端取消了选取目标,将会发送一个取消事件(EAbilityGenericReplicatedEvent::GenericCancel),在UAbilityTask_WaitTargetData::OnTargetDataCancelledCallback中执行上述类似过程,这里不再赘述。就像你所见,TargetActor 和 WaitTargetData AbilityTask包含了大量的委托。TargetActor响应输入产生并且广播 TargetData 就绪,确定,取消的委托。WaitTargetData 则监听TargetActor的TargetData就绪,确定和取消的委托并且将结果返回给GameplayAbility和服务器。如果是客户端将TargetData发送给服务器,还需要进行反作弊处理。如果直接在服务器产生TargetData 会解决上述问题,但可能会导致所属客户端的误判。
根据使用的AGameplayAbilityTargetActor的派生类,在WaitTargetData AbilityTask节点将会暴露不同的ExposeOnSpawn参数。包含的一些公共参数:
Common TargetActor Parameters |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Debug | 为true时,在非Shipping构建中将会绘制TargetActor的射线或碰撞检测的信息 |
| Filter | [可选]用于过滤检测到的结果,常用于过滤玩家角色,只检测特定类型的目标,或是通过子类化FGameplayTargetDataFilter做更复杂的检测(比如团队) |
| Reticle Class | [可选] TargetActor会创建的AGameplayAbilityWorldReticle的子类 |
| Reticle Parameters | [可选] Reticles的配置 |
| Start Location | 追踪的起始位置,通常是玩家的视点,武器的枪口或者是玩家的位置 |
对于默认的TargetActor ,当Actors处于追踪或碰撞时它们才是有效目标,一旦离开追踪或碰撞(它们移开了或者你转移了目光)它们将不再有效。如果你想让TargetActor记住最近的有效目标,可以将这个功能添加到自定义的TargetActor类中。我将这些称为永久目标,它们将一直有效直到收到目标的确定和取消事件,或者是TargetActor找到了新目标,再或者是目标本身已经无效(比如Actor已销毁)。GASShooter为火箭筒的第二技能使用了永久目标。
4.11.3 游戏技能的标线
(Reticles)显示了TargetActors(必须是非Instant)已确定的目标。TargetActors负责所有Reticles的创建和销毁。 Reticles是AActors因此它们可以使用任何可视化组件。GASShooter中常见的实现是使用WidgetComponent在屏幕空间显示了一个UMG Widget(总是朝向玩家摄相机)。Reticles并不知道哪一个AActor是他们的目标(但是你可以在自定义的TargetActor中实现此功能),通常由TargetActors在Tick()中根据目标位置更新Reticle的位置。
GASShooter使用Reticles显示被火箭筒二技能锁定的目标,在下图中敌人身上的红色标识就是Reticle。白色的是火箭筒的准星。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-bl0yzoX1-1591700466353)(C:\Users\X\Desktop\gameplayabilityworldreticle.png)]
Reticles提供给设计师一些有用的蓝图事件:
/** Called whenever bIsTargetValid changes value. */
UFUNCTION(BlueprintImplementableEvent, Category = Reticle)
void OnValidTargetChanged(bool bNewValue);
/** Called whenever bIsTargetAnActor changes value. */
UFUNCTION(BlueprintImplementableEvent, Category = Reticle)
void OnTargetingAnActor(bool bNewValue);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintImplementableEvent, Category = Reticle)
void OnParametersInitialized();
UFUNCTION(BlueprintImplementableEvent, Category = Reticle)
void SetReticleMaterialParamFloat(FName ParamName, float value);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintImplementableEvent, Category = Reticle)
void SetReticleMaterialParamVector(FName ParamName, FVector value);
Reticles可以使用由TargetActor提供的FWorldReticleParameters进行配置。默认的结构体仅提供了一个变量FVector AOEScale,当需要更多的变量时可以派生FWorldReticleParameters,当然也需要同时派生对应的TargetActor(原本的TargetActor仅能接受基类)。
Reticles默认不会被复制,但当你的游戏需要将本地玩家的目标显示给其他玩家时可以打开复制。
默认的TargetActors仅当存在有效目标时Reticles才会显示,例如,你使用AGameplayAbilityTargetActor_SingleLineTrace追踪一个目标,当敌人在追踪路径上时Reticle才会显示出来如果你转移目光,当你转移目光敌人不再有效时Reticle将会消失。如果想要Reticle保持在最后一个有效目标上,你需要定制自己的TargetActor用来记住最后的有效目标并且将Reticle保持在目标上。
4.11.4 游戏效果容器
GameplayEffectContainers带有TargetType和GameplayEffects,当EffectContainer在客户端和服务器端被应用时立即获得目标并应用GameplayEffects。这样比TargetActors高效,因为它是运行在目标选取对象的CDO上(不需要创建和销毁Actors),但它会缺失玩家输入,只能被立即触发不能确认和取消选取,并且不能从客户端向服务器发送数据(因为它将同时在两端执行)。对于立即触发的射线或碰撞检测这将非常有效。Epic的ActionRPG示例工程中在Containers里包含了两种不同的目标选择类型,一个是选择技能施放者,一个是从事件中取得的TargetData。它还在蓝图中实现了一个功能,可以在玩家特定的偏移(可以在子蓝图中设置)位置立即触发球体追踪。你也可以通过在C++或蓝图中子类化URPGTargetType实现自己的目标选取类型。
5. 常用的技能和效果
5.1 眩晕
眩晕可以打断一个角色正在施放的技能,阻止他施放新的技能,在整个眩晕的过程中阻止其移动。示例项目的陨石技能在击中的目标上应用了眩晕。
取消目标正在施放的技能,可以在stun GameplayTag添加时调用AbilitySystemComponent->CancelAbilities()。
在眩晕时阻止施放技能,可以在GameplayAbilities的 Activation Blocked Tags GameplayTagContainer中添加stun GameplayTag。
在眩晕时阻止角色移动,可以重载CharacterMovementComponent的GetMaxSpeed()方法,在其拥有者有stun GameplayTag时返回0。
5.2 冲刺
示例项目提供了冲刺技能-按住Left Shift键角色会加速跑。
加速跑是可预测的,由CharacterMovementComponent向服务器发送一个标记实现。详见GDCharacterMovementComponent.h/cpp
GA处理Left Shift的输入事件,通知CharacterMovementComponent开始和停止加速,当Left Shift按下后同时预测耐力。详见GA_Sprint_BP
5.3 瞄准
示例项目处理瞄准和冲刺相似,但瞄准会降低移动速度。
可预测的降低移动速度,详见GDCharacterMovementComponent.h/cpp。
处理输入详见GA_AimDownSight_BP ,瞄准时不会消耗耐力值。
5.4 生命偷取
我在伤害计算的ExecutionCalculation中处理生命偷取。GameplayEffect将有一个GameplayTag比如Effect.CanLifesteal。ExecutionCalculation检查如果GameplayEffectSpec有Effect.CanLifesteal这个标签则动态创建一个动态的Instant GameplayEffect,并且给它一个增加生命值的Modifer将其应用给Source的ASC。
if (SpecAssetTags.HasTag(FGameplayTag::RequestGameplayTag(FName("Effect.Damage.CanLifesteal"))))
{
float Lifesteal = Damage * LifestealPercent;
UGameplayEffect* GELifesteal = NewObject(GetTransientPackage(), FName(TEXT("Lifesteal")));
GELifesteal->DurationPolicy = EGameplayEffectDurationType::Instant;
int32 Idx = GELifesteal->Modifiers.Num();
GELifesteal->Modifiers.SetNum(Idx + 1);
FGameplayModifierInfo& Info = GELifesteal->Modifiers[Idx];
Info.ModifierMagnitude = FScalableFloat(Lifesteal);
Info.ModifierOp = EGameplayModOp::Additive;
Info.Attribute = UPAAttributeSetBase::GetHealthAttribute();
SourceAbilitySystemComponent->ApplyGameplayEffectToSelf(GELifesteal, 1.0f, SourceAbilitySystemComponent->MakeEffectContext());
}
5.5 服务器和客户端的随机数生成
有时你需要在GameplayAbility 中生成随机数比如用作射击的后座力或子弹扩散。为了要在客户端和服务器端要生成相同的随机数,我们需要在激活GameplayAbility时设置相同的Random Seed。每次激活GameplayAbility时,都需要设置Random Seed以防止客户端错误地预测了激活并且其随机数序列与服务器的序列不同步。
| Seed Setting Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Use the activation prediction key | GameplayAbility的activation prediction key是一个int16且保证在客户端和服务器的Activation()中是同步的和可用的。可以把它当作客户端和服务器的Random Seed。问题是在每次游戏开始时prediction key从0开始,在生成keys的过程中持续增加。这意味着每次都是相同的随机数序列,这可能不足以满足你的需求 |
Send a seed through an event payload when you activate the GameplayAbility |
使用事件激活GameplayAbility并且通过可复制的Event Payload将随机生成种子从客户端发送到服务器。此方法会有更大的随机性,但客户端容易被破解每次都发送相同的种子值,而且通过事件激活的GameplayAbilities也将无法再使用输入绑定激活 |
如果你的随机偏差很小,大部分玩家不会注意到每次游戏时序列是相同的,此时使用Activation Prediction Key作为Random Seed是可行的。如果你需要做一些复杂的事情,可能使用Server Initiated GameplayAbility在服务器创建Prediction Key或生成随机种子然后通过事件Payload发送是更好的选择。
5.6 致命一击
我在伤害ExecutionCalculation中处理致命一击。在ExecutionCalculation检查GameplayEffect是否带有Effect.CanCrit标签,如果有会根据暴击率(Source中的属性)生成一个随机数并将其加到暴击伤害中(同样来源于Source)。因此我并没有预测伤害,也不需要担心随机数在客户端和服务器的同步问题因为ExecutionCalculation仅在服务器上运行。如果你要使用支持预测的MMC完成这个伤害计算,可以通过GameplayEffectSpec->GameplayEffectContext->GameplayAbilityInstance获取Random Seed。
查看GASShooter如何实现的爆头,本质和上述相同,只不过没有使用暴击率而是检查FHitResult中的骨骼名字。
5.7 减速效果
Paragon中的减速效果不会叠加,但每一个应用的减速效果都会像平常一样追踪自己的生命周期,不过只会应用最大的减速效果给角色。GAS提供了AggregatorEvaluateMetaData用于解决此问题。详见AggregatorEvaluateMetaData()
5.8 暂停游戏时生成目标数据
如果玩家在WaitTargetData AbilityTask中等待生成TargetData时需要暂停游戏,建议使用slomo 0替代pause。
6. GAS调试
通常在调试GAS相关问题时,需要了解如下事情:
- “我的属性值是什么?”
- “我有哪些游戏标签?”
- “我当前有哪些游戏效果?”
- “我有哪些技能, 哪些正在施放, 哪些不允许施放?”.
GAS有两种方式在运行时回答上述问题: showdebug abilitysystem 和挂钩(hooks in)到GameplayDebugger.
提示: UE4会优化C++代码,这将会调试一些方法变得困难。可以设置VS Solution配置为DebugGame Editor阻止代码优化。也可以通过PRAGMA_DISABLE_OPTIMIZATION_ACTUAL 和PRAGMA_ENABLE_OPTIMIZATION_ACTUAL两个宏阻止特定方法的优化。
PRAGMA_DISABLE_OPTIMIZATION_ACTUAL
void MyClass::MyFunction(int32 MyIntParameter)
{
// My code
}
PRAGMA_ENABLE_OPTIMIZATION_ACTUAL
6.1 showdebug abilitysystem
在游戏控制台输入showdebug abilitysystem。一共三页,每一页都会显示你当前拥有的 GameplayTags。输入AbilitySystem.Debug.NextCategory切换下一页。
第一页显示你所有属性的当前值:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-AqGn1dTd-1591700466354)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/showdebugpage1.png)]
第二页显示所有的BUFF(Duration 和Infinite GameplayEffects),它们的叠加数,给了哪些GameplayTags,给了哪些Modifiers :[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IblFZ9w0-1591700466354)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/showdebugpage2.png)]
第三页显示所有的拥有的 GameplayAbilities,无论它们当前是否运行,无论它们是否被阻止施放。还有当前执行的AbilityTasks的状态:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aBVviosN-1591700466355)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/showdebugpage3.png)]
当使用PageUp和PageDown在目标间切换时,当前的页面只显示本地控制角色的ASC。使用AbilitySystem.Debug.NextTarget和 AbilitySystem.Debug.PrevTarget切换目标将显示正确的ASCs的数据,但表示当前选中目标的绿色框并没有随之更新。BUG已报告 https://issues.unrealengine.com/issue/UE-90437。
6.2 Gameplay Debugger
GAS添加了一些功能给Gameplay Debugger。可以通过单引号(')开启Gameplay Debugger。按小键盘上的数字3开启Abilities Category。
当你想查看其他角色的GameplayTags, GameplayEffects和GameplayAbilities时可以使用Gameplay Debugger。可惜的是它不能显示目标属性的当前值。它将会选取屏幕中间的角色,要切换角色可以再次按下单引号(')。
当前目标角色会有一个大红圈标识:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-N2X7C3HD-1591700466355)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/gameplaydebugger.png)]
6.3 GAS 日志
GAS源代码中针对不同的日志级别包含了大量的日志语句,这些日志通过ABILITY_LOG()进行打印,默认日志级别是Display,然后高于这个级别的日志不会打印。
通过下述方法改变要打印的日志级别:
log [category] [verbosity]
例如要打开 ABILITY_LOG():
log LogAbilitySystem VeryVerbose
重置回默认状态:
log LogAbilitySystem Display
显示全部日志类别:
log list
GAS相关的日志类别:
| Logging Category | Default Verbosity Level |
|---|---|
| LogAbilitySystem | Display |
| LogAbilitySystemComponent | Log |
| LogGameplayCueDetails | Log |
| LogGameplayCueTranslator | Display |
| LogGameplayEffectDetails | Log |
| LogGameplayEffects | Display |
| LogGameplayTags | Log |
| LogGameplayTasks | Log |
| VLogAbilitySystem | Display |
详见Wiki on Logging。
7. 优化
7.1 技能批处理
GameplayAbilities的激活,发送TargetData到服务器(可选),结束所有这些事情如果在一帧完成可以使用Ability Batching将两到三个RPCs优化到一个RPC。这种类型的Abilities常用于霰弹枪。
7.2 游戏表现批处理
如果你在同时发送了多个GameplayCues,也可以考虑将他们合并到一个RPC中。这可以减少RPCs的数量并且使发送的数据量尽可能的小。
7.3 AbilitySystemComponent 复制模式
默认情况下,ASC处于Full Replication Mode模式。这将会把所有的GameplayEffects 复制到每一个客户端(这对于单人游戏没问题)。在多人游戏中,将玩家拥有的 ASCs设置为 Mixed Replication Mode,将AI控制的角色设置为Minimal Replication Mode。这将会把玩家角色上应用的GEs只复制给其角色的拥有者,AI控制的角色上的GEs将不会复制到客户端。GameplayTags将会被复制,GameplayCues将会被不可靠的广播发送给所有客户端,不管Replication Mode是什么。当所有客户端不需要看到它们时,这将减少复制GEs的网络数据。
7.4 属性代理复制
在有大量玩家的游戏中比如Fortnite Battle Royale (FNBR),将有大量的ASCs存在于对应的PlayerStates中且会复制大量属性。要优化这个瓶颈,Fortnite禁用了ASC和它的AttributeSets在PlayerState::ReplicateSubobjects()中一起同步给Simulated Player-controlled Proxies。Autonomous Proxies和AI Controlled角色仍然根据其Replication Mode进行全同步。取而代之的当要同步PlayerStates中的ASC中的Attributes时,FNBR使用一个玩家角色上的复制代理结构体。当服务器端的ASC的属性改变时,上述代理结构体也与之改变,客户端接收到改变的代理结构体并将其包含的属性修改同步至本地的ASC中。这将允许属性复制使用Pawn的相关性机制(Relevancy)和其网络更新频率(NetUpdateFrequency)。这个代理结构体也可以使用位掩码同步白名单的GameplayTags。这个优化大大降低了网络带宽,体现了Relevancy的优势。AI控制的Pawns的ASC在Pawn上,其原本就会使用Relevancy因为不需要为它额外优化。
详见community questions #3*
7.5 ASC 延迟加载
Fortnite Battle Royale (FNBR)的世界中有大量可被破坏的AActors(树,建筑等),每一个都带有一个ASC。这将增加内存的消耗。FNBR使用延迟加载ASCs的方案解决此问题,仅当需要时才加载ASCs(当这些AActors第一次被玩家伤害时)。一场游戏中很多AActors可能从未被伤害,这将减少整体内存的开销。
8. 建议
8.1 Gameplay Effect Containers
GameplayEffectContainers combine GameplayEffectSpecs, TargetData, simple targeting, and related functionality into easy to use structures. These are great for transfering GameplayEffectSpecs to projectiles spawned from an ability that will then apply them on collision at a later time.
Blueprint AsyncTasks to Bind to ASC Delegates
To increase designer-friendly iteration times, especially when designing UMG Widgets for UI, create Blueprint AsyncTasks (in C++) to bind to the common change delegates on the ASC directly from your UMG Blueprint graphs. The only caveat is that they must be manually destroyed (like when the widget is destroyed) otherwise they will live in memory forever. The Sample Project includes three Blueprint AsyncTasks.
Listen for Attribute changes:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-a7LC1UTa-1591700466356)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/attributeschange.png)]
Listen for cooldown changes:
Listen for GE stack changes:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jywAbnNS-1591700466357)(https://github.com/tranek/GASDocumentation/raw/master/Images/gestackchange.png)]
9. 疑难解答
LogAbilitySystem: Warning: Can't activate LocalOnly or LocalPredicted ability %s when not local!
You need to initialize the ASC on the client.
ScriptStructCache errors
You need to call UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData().
10. GAS名词缩写
| Name | Acronyms |
|---|---|
| AbilitySystemComponent | ASC |
| AbilityTask | AT |
| Action RPG Sample Project by Epic | ARPG, ARPG Sample |
| CharacterMovementComponent | CMC |
| GameplayAbility | GA |
| GameplayAbilitySystem | GAS |
| GameplayCue | GC |
| GameplayEffect | GE |
| GameplayEffectExecutionCalculation | ExecCalc, Execution |
| GameplayTag | Tag, GT |
| ModiferMagnitudeCalculation | ModMagCalc, MMC |
11. 其他资源
- Official Documentation
- Source Code!
- Especially
GameplayPrediction.h
- Especially
- Action RPG Sample Project by Epic
- Dave Ratti from Epic’s responses to community questions about GAS
- Unreal Slackers Discord has a text channel dedicated to GAS
#gameplay-abilities-plugin- Check pinned messages
- GitHub repository of resources by Dan ‘Pan’
- YouTube Videos by SabreDartStudios
12. GAS 更新日志
This is a list of notable changes (fixes, changes, and new features) to GAS compiled from the official Unreal Engine upgrade changelog and from undocumented changes that I’ve encountered. If you’ve found something that isn’t listed here, please make an issue or pull request.
4.25
- Fixed prediction of
RootMotionSourceAbilityTasks GAMEPLAYATTRIBUTE_REPNOTIFY()now additionally takes in the oldAttributevalue. We must supply that as the optional parameter to ourOnRepfunctions. Previously, it was reading the attribute value to try to get the old value. However, if called from a replication function, the old value had already been discarded before reaching SetBaseAttributeValueFromReplication so we’d get the new value instead.- Added
NetSecurityPolicytoUGameplayAbility. - Crash Fix: Fixed a crash when adding a gameplay tag without a valid tag source selection.
- Crash Fix: Removed a few ways for attackers to crash a server through the ability system.
- Crash Fix: We now make sure we have a GamplayEffect definition before checking tag requirements.
- Bug Fix: Fixed an issue with gameplay tag categories not applying to function parameters in Blueprints if they were part of a function terminator node.
- Bug Fix: Fixed an issue with gameplay effects’ tags not being replicated with multiple viewports.
- Bug Fix: Fixed a bug where a gameplay ability spec could be invalidated by the InternalTryActivateAbility function while looping through triggered abilities.
- Bug Fix: Changed how we handle updating gameplay tags inside of tag count containers. When deferring the update of parent tags while removing gameplay tags, we will now call the change-related delegates after the parent tags have updated. This ensures that the tag table is in a consistent state when the delegates broadcast.
- Bug Fix: We now make a copy of the spawned target actor array before iterating over it inside when confirming targets because some callbacks may modify the array.
- Bug Fix: Fixed a bug where stacking GamplayEffects that did not reset the duration on additional instances of the effect being applied and with set by caller durations would only have the duration correctly set for the first instance on the stack. All other GE specs in the stack would have a duration of 1 second. Added automation tests to detect this case.
- Bug Fix: Fixed a bug that could occur if handling gameplay event delegates modified the list of gameplay event delegates.
- Bug Fix: Fixed a bug causing GiveAbilityAndActivateOnce to behave inconsistently.
- Bug Fix: Reordered some operations inside FGameplayEffectSpec::Initialize to deal with a potential ordering dependency.
- New: UGameplayAbility now has an OnRemoveAbility function. It follows the same pattern as OnGiveAbility and is only called on the primary instance of the ability or the class default object.
- New: When displaying blocked ability tags, the debug text now includes the total number of blocked tags.
- New: Renamed UAbilitySystemComponent::InternalServerTryActiveAbility to UAbilitySystemComponent::InternalServerTryActivateAbility.Code that was calling InternalServerTryActiveAbility should now call InternalServerTryActivateAbility.
- New: Continue to use the filter text for displaying gameplay tags when a tag is added or deleted. The previous behaviour cleared the filter.
- New: Don’t reset the tag source when we add a new tag in the editor.
- New: Added the ability to query an ability system component for all active gameplay effects that have a specified set of tags. The new function is called GetActiveEffectsWithAllTags and can be accessed through code or blueprints.
- New: When root motion movement related ability tasks end they now return the movement component’s movement mode to the movement mode it was in before the task started.
- New: Made SpawnedAttributes transient so it won’t save data that can become stale and incorrect. Added null checks to prevent any currently saved stale data from propagating. This prevents problems related to bad data getting stored in SpawnedAttributes.
- API Change: AddDefaultSubobjectSet has been deprecated. AddAttributeSetSubobject should be used instead.
- New: Gameplay Abilities can now specify the Anim Instance on which to play a montage.
4.24
- Fixed blueprint node
Attributevariables resetting toNoneon compile. - Need to call
UAbilitySystemGlobals::InitGlobalData()to useTargetDataotherwise you will getScriptStructCacheerrors and clients will be disconnected from the server. My advice is to always call this in every project now whereas before 4.24 it was optional. - Fixed crash when copying a
GameplayTagsetter to a blueprint that didn’t have the variable previously defined. UGameplayAbility::MontageStop()function now properly uses theOverrideBlendOutTimeparameter.- Fixed
GameplayTagquery variables on components not being modified when edited. - Added the ability for
GameplayEffectExecutionCalculationsto support scoped modifiers against “temporary variables” that aren’t required to be backed by an attribute capture.- Implementation basically enables
GameplayTag-identified aggregators to be created as a means for an execution to expose a temporary value to be manipulated with scoped modifiers; you can now build formulas that want manipulatable values that don’t need to be captured from a source or target. - To use, an execution has to add a tag to the new member variable
ValidTransientAggregatorIdentifiers; those tags will show up in the calculation modifier array of scoped mods at the bottom, marked as temporary variables—with updated details customizations accordingly to support feature
- Implementation basically enables
- Added restricted tag quality-of-life improvements. Removed the default option for restricted
GameplayTagsource. We no longer reset the source when adding restricted tags to make it easier to add several in a row. APawn::PossessedBy()now sets the owner of thePawnto the newController. Useful because Mixed Replication Mode expects the owner of thePawnto be theControllerif theASClives on thePawn.- Fixed bug with POD (Plain Old Data) in
FAttributeSetInittterDiscreteLevels.