Java NIO操作
内容:Java NIO
Java NIO介绍
Java NIO缓存区
通道和内存映射
文件锁
Selecto
一、Java NIO介绍
1.Java传统的IO是面向Stream-Oriented,而NIO是面向Block-Oriented,也就是说NIO的操作正常情况下是相对比较大的Block快为单位的,而不是像Java IO一样是针对字节或字符进行操作;
2.NIO提供与平台无关的Non-Blocking I/O,这种模式可以更加有效的处理大量链接的情况;
3.NIO在原有IO基本功能的基础上,提供一些全新的功能:
多路选择的非封锁式I/O设施;
支持强大的内存映射
支持文件锁
支持译码器
支持使用正则表达式来进行设施匹配
4.在NIO所有的操作都是使用缓存区来处理的,也就是说NIO的读写操作就是基于缓存区完成的;
二:NIO下的缓存
1.Buffer本身是一个线性的数据集(数据集中只能容纳某种特定类型的数据);
2.Buffer中有三个关键的值来表示Buffer的状态:
a)Position:表示下一个缓冲区读取或者写入的操作的指针;
b)Limit:表示还有多上数据要存储或者读取;
c)Capacity:表示缓冲区的最大容量;
3.直接缓冲区:在每次调用OS的I/O操作的时候,JVM都会尽量避免将缓存区的内容复制到中间缓存区;
//代码示例
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.IntBuffer;
/**
* FileName: JavaNIO
* Author: hadoop
* Email: [email protected]
* Date: 18-10-3 上午10:39
* Description:
*
*/
public class JavaNIO {
public static void main(String[] args){
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(100);//开辟容量大小为100的IntBuffer
ByteBuffer.allocate(5);//直接开辟缓冲区
//ByteBuffer,CharBuffer,ShortBuffer,LongBuffer,FloatBuffer,DoubleBuffer
System.out.println("Position: "+intBuffer.position()+ " ,Limit: "+intBuffer.limit()+" Capacity: "+intBuffer.capacity());
int[] data = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0}; //定义整型数组
intBuffer.put(100); //向缓存区写入整数100
intBuffer.put(data);//直接把数组放入缓存区
System.out.println("Position: "+intBuffer.position()+ " ,Limit: "+intBuffer.limit()+" Capacity: "+intBuffer.capacity());
intBuffer.flip(); //重设缓冲区,
System.out.println("Position: "+intBuffer.position()+ " ,Limit: "+intBuffer.limit()+" Capacity: "+intBuffer.capacity());
while(intBuffer.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(intBuffer.get());
}
intBuffer.position(2);
intBuffer.limit(4);
IntBuffer sliced = intBuffer.slice();
for (int i = 0; i < sliced.capacity();i++){
System.out.println(sliced.get(i));
int item = sliced.get(i);
sliced.put(item-100);
}
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++");
sliced.flip();
while(sliced.hasRemaining()){
System.out.println(sliced.get());
}
}
}
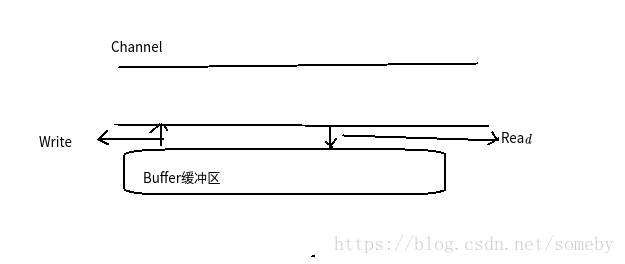
三:Channel
1.Channel是基于缓存区来读取和写入数据;
2.Channel是双向的,既可以完成输入也可以完成输出
3.FileChannel对文件进行读写,其中map操作是将文件区域映射到内存中;
4.Channel中读数据是指将内容读入到缓存区中,而写数据是指将内容从缓存区写到通道中;
private static void channelNIOReadData() {
File fileInput = new File("/home/hadoop/learnJava/nio.txt");
File fileOutput = new File("/home/hadoop/learnJava/nioout.txt");
FileInputStream input = null;
FileOutputStream output = null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(fileInput);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
output = new FileOutputStream(fileOutput);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
FileChannel fileChannelInput = null;
FileChannel fileChannelOutput = null;
fileChannelInput = input.getChannel();
fileChannelOutput = output.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int tmp = 0;
try{
while ((tmp = fileChannelInput.read(buffer))!= -1){
buffer.flip();
fileChannelOutput.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
input.close();
output.close();
fileChannelInput.close();
fileChannelOutput.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void channelNIOWriteData() {
String[] data = {"Scala","Spark","Java","Hadoop"};
File file = new File("/home/hadoop/learnJava/nio.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
FileChannel fileChannel = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
fileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
for (String item:data){
buffer.put(item.getBytes());
}
buffer.flip();
try {
fileChannel.write(buffer);
fileChannel.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
四:内存映射
1.内存映射是指把文件映射到内存中,这样就可以通过操作内存的指令来操作文件中的数据,采用内存映射的方式读取文件速度是最快的!
2.Java中读文件的操作速度比较:
a)最慢的是RandomAccessFile,支持随机读写数据;
b)第二慢的是FileInputStream,采用流的方式读取数据;
c)采用BufferReader等方式进行缓存读取是相对比较快的方式;
d)最快的是采用内存映射MappedByteBuffer的方式读取文件数据;
3.内存映射模式有三中:READ_ONLY、READ_WRITE、PRIVATE(写入时复制模式);
4.一般情况下使用内存映射主要用于最快速的读取文件!
private static void channelMap() {
File file = new File("/usr/local/spark/README.md");
FileInputStream input = null;
try {
input =new FileInputStream(file);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
FileChannel fileChannelInput = null;
fileChannelInput = input.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffer map = null;
try {
map = fileChannelInput.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,0,file.length()); //将文件映射到内存中去
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
byte[] data = new byte[(int) file.length()];
int index = 0;
while (map.hasRemaining()){
data[index++] = map.get();
}
System.out.println(new String(data));
try {
fileChannelInput.close();
input.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
五:文件锁
1.FileLock基于FileChannel对文件提供锁的功能;
2.FileLock有共享锁和独占锁两种类型;
六:Charset
1.一般采用UTF-8的方式
七:Selector
1.可以基于Selector来构建非阻塞的网络服务;