链式二叉树的基本操作和相关OJ题训练(建议收藏!!!)
博主csdn个人主页:小小unicorn
⏩专栏分类:数据结构&C++
代码仓库:小小unicorn的代码仓库
关注我带你学习编程知识
链式二叉树基本操作
- 二叉树节点设置
- 二叉树的深度优先遍历(DFS)
-
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 二叉树的广度优先遍历(BFS)
-
- 层序遍历:
- 节点的个数
- 叶子节点个数
- 树中第K层节点的个数
- 查找值为X的节点
- 树的高度
- 翻转二叉树
- 判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
- 判断二叉树是否为对称二叉树
- 判断二叉树是否为平衡二叉树
- 判断二叉树是否为单值二叉树
- 判断二叉树是另一棵树的子树
- 判断两颗二叉树是否相同
-
- 解题思路:
- 二叉树的销毁
- 二叉树的深度遍历(接口型题目)
-
- 前序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 左叶子之和
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 二叉树遍历(牛客)
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 完全二叉树的节点个数
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 求二叉树的最大深度:
-
- 解决思路:
- 代码解决:
- 求n叉树的最大深度:
-
- 代码解决:
- 二叉树的最小深度
-
- 解题思路:
- 整体代码解决:
- 路径总和
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 找树左下角的值:
-
- 代码解决:
- 合并二叉树
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 最大二叉树
-
- 解题思路:
- 代码解决:
- 总结:
-
- 头文件.h
- 源文件1(Queue.c)
- 源文件2(BinaryTree.c)
二叉树节点设置
链式二叉树,那必须得有自己的结点类型,以下是链式二叉树结点类型的定义,为了避免过多重复的代码,下面的问题都统一使用该结点类型。
typedef char BTDataType;//结点中存储的元素类型(以char为例)
typedef struct BTNode
{
BTDataType val;//结点中存储的元素类型
struct BTNode* left;//左指针域(指向左孩子)
struct BTNode* right;//右指针域(指向右孩子)
}BTNode;
二叉树的深度优先遍历(DFS)
学习二叉树结构,最简单的方式就是遍历。
所谓二叉树遍历(Traversal)是按照某种特定的规则,依次对二叉树中的节点进行相应的操作,并且每个节点只操作一次。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题。
遍历是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础。
按照规则,二叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
- 前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
- 中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
- 后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right subtree)又可解释为根、根的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
![]()
而深度优先遍历,前中后遍历多算,严格来说偏前序。深度优先遍历一般要借助队列实现。
前序遍历
前序遍历,又叫先根遍历。
遍历顺序:根 -> 左子树 -> 右子树
//前序遍历
void BinaryPrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//根->左子树->右子树
printf("%c ", root->val);
BinaryPrevOrder(root->left);
BinaryPrevOrder(root->right);
}
中序遍历
中序遍历,又叫中根遍历。
遍历顺序:左子树 -> 根 -> 右子树
void BinaryInOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//左子树->根->右子树
BinaryInOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->val);
BinaryInOrder(root->right);
}
后序遍历
后序遍历,又叫后根遍历。
遍历顺序:左子树 -> 右子树 -> 根
//后序遍历
void BinaryPostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
//左子树->右子树->根
BinaryPostOrder(root->left);
BinaryPostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->val);
}
![]()
二叉树的广度优先遍历(BFS)
一般情况。广度优先遍历都是借助队列实现。
层序遍历:
层序遍历,自上而下,从左往右逐层访问树的结点的过程就是层序遍历。
![]()
思路(借助一个队列):
1.先把根入队列,然后开始从队头出数据。
2.出队头的数据,把它的左孩子和右孩子依次从队尾入队列(NULL不入队列)。
3.重复进行步骤2,直到队列为空为止。
![]()
//层序遍历
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);//初始化队列
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
//队列不为空。循环继续
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//获取队头元素
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%d ", front->val);
//出队元素的左孩子入队列
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
//出队元素的右孩子入队列
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
QueuePop(&q);
}
printf("\n");
//销毁队列
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
节点的个数
求解树的结点总数时,可以将问题拆解成子问题:
1.若为空,则结点个数为0。
2.若不为空,则结点个数 = 左子树结点个数 + 右子树结点个数 + 1(自己)。
//结点的个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
//结点个数 = 左子树的结点个数 + 右子树的结点个数 + 自己
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
叶子节点个数
继续将子问题拆解:
1.若为空,则叶子结点个数为0。
2.若结点的左指针和右指针均为空,则叶子结点个数为1。
3.除上述两种情况外,说明该树存在子树,其叶子结点个数 = 左子树的叶子结点个数 + 右子树的叶子结点个数。
//叶子结点的个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//空树无叶子结点
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL&&root->right == NULL)//是叶子结点
return 1;
//叶子结点的个数 = 左子树的叶子结点个数 + 右子树的叶子结点个数
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
树中第K层节点的个数
思路:
相对于根结点的第k层结点的个数 = 相对于以其左孩子为根的第k-1层结点的个数 + 相对于以其右孩子为根的第k-1层结点的个数。
![]()
//第k层结点的个数
int BinaryTreeKLevelSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (k < 1 || root == NULL)//空树或输入k值不合法
return 0;
if (k == 1)//第一层结点个数
return 1;
//相对于父结点的第k层的结点个数 = 相对于两个孩子结点的第k-1层的结点个数之和
return BinaryTreeKLevelSize(root->left, k - 1) + BinaryTreeKLevelSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
查找值为X的节点
子问题:
1.先判断根结点是否是目标结点。
2.再去左子树中寻找。
3.最后去右子树中寻找。
// 二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, int x)
{
//空树
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
//先判断根节点
if (root->val == x)
return root;
//在左孩子中找
BTNode* ret = NULL;
ret = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
//在右孩子中找
ret = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret)
return ret;
//根节点和左右子树节点中均未找到
return NULL;
}
树的高度
解决思路:
拆分成子问题:
1.若为空,则深度为0。
2.若不为空,则树的最大深度 = 左右子树中深度较大的值 + 1。
//树的高度:左右子树高的那颗树的高度在加1
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftHeight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightHeight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;
}
翻转二叉树
题目来源:Leetcode226.翻转二叉树
![]()
![]()
思路:
1.翻转左子树。
2.翻转右子树。
3.交换左右子树的位置。
//翻转二叉树
BTNode* invertTree(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//根为空,直接返回
return NULL;
BTNode* left = invertTree(root->left);//翻转左子树
BTNode* right = invertTree(root->right);//翻转右子树
//左右子树位置交换
root->left = right;
root->right = left;
return root;
}
判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
思路(借助一个队列):
1.先把根入队列,然后开始从队头出数据。
2.出队头的数据,把它的左孩子和右孩子依次从队尾入队列(NULL也入队列)。
3.重复进行步骤2,直到读取到的队头数据为NULL时停止入队列。
4.检查队列中剩余数据,若全为NULL,则是完全二叉树;若其中有一个非空的数据,则不是完全二叉树。
![]()
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int TreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);//初始化队列
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
//当队列不为空时,继续
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
//读取队头元素
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
//当读取到空指针时,停止入队操作
if (front == NULL)
break;
//出队元素的左孩子入队列
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
//出队元素的右孩子入队列
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
QueuePop(&q);
}
// 已经遇到空节点,如果队列中后面的节点还有非空,就不是完全二叉树
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//若队列中存在非空指针,则不是完全二叉树
if (front != NULL)
{
//销毁队列
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
//若队列中全是空指针,则是完全二叉树
return true;
}
判断二叉树是否为对称二叉树
题目来源:101.对称二叉树
题目描述:
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称
对称二叉树就是镜像对称。
![]()
要判断某二叉树是否是对称二叉树,则判断其根结点的左子树和右子树是否是镜像对称即可。
因为是镜像对称,所以左子树的遍历方式和右子树的遍历方式是不同的,准确来说,左子树和右子树的遍历是反方向进行的。
//对称二叉树:
bool isSameTree2(BTNode* p, BTNode* q)
{
//都为空
if (p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
//其中一个为空
if (p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//都不为空
if (p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree2(p->left, q->right) && isSameTree2(p->right, q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return isSameTree2(root->left, root->right);
}
判断二叉树是否为平衡二叉树
若一棵二叉树的每个结点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,则称该树为平衡二叉树。
![]()
思路一:
继续拆分子问题:
1.求出左子树的深度。
2.求出右子树的深度。
3.若左子树与右子树的深度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右子树也是平衡二叉树,则该树是平衡二叉树。
时间复杂度O(N2)
//判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
bool isBalanced(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)//空树是平衡二叉树
return true;
int leftDepth = BinaryTreeMaxDepth(root->left);//求左子树的深度
int rightDepth = BinaryTreeMaxDepth(root->right);//求右子树的深度
//左右子树高度差的绝对值不超过1 && 其左子树是平衡二叉树 && 其右子树是平衡二叉树
return abs(leftDepth - rightDepth) < 2 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
思路二:
我们可以采用后序遍历:
1.从叶子结点处开始计算每课子树的高度。(每棵子树的高度 = 左右子树中高度的较大值 + 1)
2.先判断左子树是否是平衡二叉树。
3.再判断右子树是否是平衡二叉树。
4.若左右子树均为平衡二叉树,则返回当前子树的高度给上一层,继续判断上一层的子树是否是平衡二叉树,直到判断到根为止。(若判断过程中,某一棵子树不是平衡二叉树,则该树也就不是平衡二叉树了)
bool _isBalanced(BTNode* root, int* ph)
{
if (root == NULL)//空树是平衡二叉树
{
*ph = 0;//空树返回高度为0
return true;
}
//先判断左子树
int leftHight = 0;
if (_isBalanced(root->left, &leftHight) == false)
return false;
//再判断右子树
int rightHight = 0;
if (_isBalanced(root->right, &rightHight) == false)
return false;
//把左右子树的高度中的较大值+1作为当前树的高度返回给上一层
*ph = Max(leftHight, rightHight) + 1;
return abs(leftHight - rightHight) < 2;//平衡二叉树的条件
}
//判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
bool isBalanced(BTNode* root)
{
int hight = 0;
return _isBalanced(root, &hight);
}
判断二叉树是否为单值二叉树
题目来源:Leetcode965.单值二叉树
这个题我们可以通过判断二叉树的根与叶子是否相等来解决这个问题,注意要分三种情况:
1.如果是空树,那也是符合情况的,直接返回true。
2.首先满足左子树不为空的条件下,判断左子树的值是否与根相同,相同返回true,不相同返回false.
3.首先满足右子树不为空的条件下,判断右子树的值是否与根相同,相同返回true,不相同返回false.
//单值二叉树
bool isUnivalTree(BTNode* root)
{
//空树符合情况,返回true
if (root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
//首先满足左子树不为空的条件下,判断左子树的值是否与根相同
if (root->left && root->left->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
//首先满足右子树不为空的条件下,判断左子树的值是否与根相同
if (root->right && root->right->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
判断二叉树是另一棵树的子树
题目来源:Leetcode572.另一颗树的子树
判断 subRoot 是否是二叉树 root 的子树,即检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和结点值的子树,其中 root 和 subRoot 均为非空二叉树。
![]()
思路:
依次判断以 root 中某一个结点为根的子树是否与subRoot相同。
![]()
发现 root 中的某一个子树与 subRoot 相匹配时,便不再继续比较其他子树,所以图中只会比较到序号2就结束比较。
//比较以root和subRoot为根结点的两棵树是否相等
bool Compare(BTNode* root, BTNode* subRoot)
{
if (root == NULL&&subRoot == NULL)//均为空树,相等
return true;
if (root == NULL || subRoot == NULL)//一个为空另一个不为空,不相等
return false;
if (root->val != subRoot->val)//结点的值不同,不相等
return false;
//比较两棵树的子结点
return Compare(root->left, subRoot->left) && Compare(root->right, subRoot->right);
}
//另一个树的子树
bool isSubtree(BTNode* root, BTNode* subRoot)
{
if (root == NULL)//空树,不可能是与subRoot相同(subRoot非空)
return false;
if (Compare(root, subRoot))//以root和subRoot为根,开始比较两棵树是否相同
return true;
//判断root的左孩子和右孩子中是否有某一棵子树与subRoot相同
return isSubtree(root->left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
判断两颗二叉树是否相同
题目来源:leetcode100.相同的树
题目描述:
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
解题思路:
判断两棵二叉树是否相同,也可以将其分解为子问题:
1.比较两棵树的根是否相同。
2.比较两根的左子树是否相同。
3.比较两根的右子树是否相同。
代码如下:
bool isSameTree(BTNode* p, BTNode* q)
{
//都为空
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
//其中一个为空
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)
return false;
//都不为空
if(p->val!=q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&
isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
二叉树的销毁
二叉树的销毁,与其他数据结构的销毁类似,都是一边遍历一边销毁。但是二叉树需要注意销毁结点的顺序,遍历时我们应该选用后序遍历,也就是说,销毁顺序应该为:左子树->右子树->根。
我们必须先将左右子树销毁,最后再销毁根结点,若先销毁根结点,那么其左右子树就无法找到,也就无法销毁了。
//二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestroy(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->left);//销毁左子树
BinaryTreeDestroy(root->right);//销毁右子树
free(root);//释放根结点
}
二叉树的深度遍历(接口型题目)
接下来所要说的深度遍历与前面会有所不同,我们前面说到的深度遍历是将一棵二叉树遍历,并将遍历结果打印屏幕上(较简单)。
而下面说到的深度遍历是将一棵二叉树进行遍历,并将遍历结果存储到一个动态开辟的数组中,将数组作为函数返回值进行返回。
思路:
1.首先计算二叉树中结点的个数,便于确定动态开辟的数组的大小。
2.遍历二叉树,将遍历结果存储到数组中。
3.返回数组。
前序遍历
题目来源:144.二叉树的前序遍历
代码:
//求树的结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//将树中结点的值放入数组
void preorder(BTNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if (root == NULL)//根结点为空,直接返回
return;
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;//先将根结点的值放入数组
preorder(root->left, a, pi);//再将左子树中结点的值放入数组
preorder(root->right, a, pi);//最后将右子树中结点的值放入数组
}
//前序遍历
int* preorderTraversal(BTNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);//值的个数等于结点的个数
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int i = 0;
preorder(root, a, &i);//将树中结点的值放入数组
return arr;
}
中序遍历
题目来源:94.二叉树的中序遍历
//求树的结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//将树中结点的值放入数组
void inorder(BTNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if (root == NULL)//根结点为空,直接返回
return;
inorder(root->left, a, pi);//先将左子树中结点的值放入数组
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;//再将根结点的值放入数组
inorder(root->right, a, pi);//最后将右子树中结点的值放入数组
}
//中序遍历
int* inorderTraversal(BTNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);//值的个数等于结点的个数
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int i = 0;
inorder(root, a, &i);//将树中结点的值放入数组
return arr;
}
后序遍历
题目来源:145.二叉树的后序遍历
//求树的结点个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//将树中结点的值放入数组
void postorder(BTNode* root, int* a, int* pi)
{
if (root == NULL)//根结点为空,直接返回
return;
postorder(root->left, a, pi);//先将左子树中结点的值放入数组
postorder(root->right, a, pi);//再将右子树中结点的值放入数组
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;//最后将根结点的值放入数组
}
//后序遍历
int* postorderTraversal(BTNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);//值的个数等于结点的个数
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(*returnSize));
int i = 0;
postorder(root, a, &i);//将树中结点的值放入数组
return arr;
}
左叶子之和
题目描述:
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
![]()
题目来源:leetcode404.左叶子之和
牛客:NC248.左叶子之和
解题思路:
在解决这个问题之前,我们首先要知道什么是叶子节点:
叶子节点:当前节点没有左孩子也没有右孩子
具体解题思路如下:
首先:
判断是否为空树,
如果是空树,返回0;
如果不是空树,判断左孩子节点是否为左叶子节点
然后继续遍历左子树和右子树中的孩子节点,并把结果累加起来。
代码解决:
int sumOfLeftLeaves(struct TreeNode* root )
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int sum=0;
if(root->left&&root->left->left==NULL&&root->left->right==NULL)
{
sum=root->left->val;
}
return sum+sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left)+sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right);
}
结果如下:
![]()
![]()
二叉树遍历(牛客)
题目来源:KY11.二叉树遍历(牛客网)
题目描述:
编一个程序,读入用户输入的一串先序遍历字符串,根据此字符串建立一个二叉树(以指针方式存储)。 例如如下的先序遍历字符串: ABC##DE#G##F### 其中“#”表示的是空格,空格字符代表空树。建立起此二叉树以后,再对二叉树进行中序遍历,输出遍历结果。
输入描述:
输入包括1行字符串,长度不超过100。
输出描述:
可能有多组测试数据,对于每组数据, 输出将输入字符串建立二叉树后中序遍历的序列,每个字符后面都有一个空格。 每个输出结果占一行。
![]()
解题思路:
根据前序遍历所得到的字符串,我们可以很容易地将其对应的二叉树画出来。
![]()
其实很容易发现其中的规律,我们可以依次从字符串读取字符:
1.若该字符不是#,则我们先构建该值的结点,然后递归构建其左子树和右子树。
2.若该字符是#,则说明该位置之下不能再构建结点了,返回即可。
构建完树后,使用中序遍历打印二叉树的数据即可。
代码解决:
#include 测试结果:
![]()
完全二叉树的节点个数
题目来源:Leetcode222.完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述:
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
解题思路:
先拿到左子树的节点个数,在拿到有子树节点的个数,最后加1,。
返回条件:如果碰到空树,则返回0;
代码解决:
//完全二叉树的节点个数
int countNodes(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//拿到左子树的个数
int lson=countNodes(root->left);
//拿到右子树的个数
int rson=countNodes(root->right);
//在加上自己
return 1+lson+rson;
}
求二叉树的最大深度:
题目来源:Leetcode104.二叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
解决思路:
递归法:
本题可以使用前序(中左右),也可以使用后序遍历(左右中),使用前序求的就是深度,使用后序求的是高度。
二叉树节点的深度:指从根节点到该节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于深度从0开始还是从1开始)
二叉树节点的高度:指从该节点到叶子节点的最长简单路径边的条数或者节点数(取决于高度从0开始还是从1开始)
而根节点的高度就是二叉树的最大深度,所以本题中我们通过后序求的根节点高度来求的二叉树最大深度。
我先用后序遍历(左右中)来计算树的高度。
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:参数就是传入树的根节点,返回就返回这棵树的深度,所以返回值为int类型。
int getdepth(BTNode* node)
2.确定终止条件:如果为空节点的话,就返回0,表示高度为0。
if (node == NULL) return 0;
3.确定单层递归的逻辑:先求它的左子树的深度,再求右子树的深度,最后取左右深度最大的数值 再+1 (加1是因为算上当前中间节点)就是目前节点为根节点的树的深度。
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
代码解决:
//求较大值
int max(int a, int b)
{
return a > b ? a : b;
}
int getdepth(struct TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
int leftdepth = getdepth(node->left); // 左
int rightdepth = getdepth(node->right); // 右
int depth = 1 + max(leftdepth, rightdepth); // 中
return depth;
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return getdepth(root);
}
//精简版版本:
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode*root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return fmax(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right))+1;
}
精简之后的代码根本看不出是哪种遍历方式,也看不出递归三部曲的步骤,所以如果对二叉树的操作还不熟练,尽量不要直接照着精简代码来学。
求n叉树的最大深度:
题目来源:Leetcode559.N叉树的最大深度
题目描述:
给定一个 N 叉树,找到其最大深度。
最大深度是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点总数。
N 叉树输入按层序遍历序列化表示,每组子节点由空值分隔(请参见示例)
代码解决:
思路是和二叉树思路一样的,直接给出代码如下
int maxDepth(struct Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int depth = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < root->numChildren; i++)
{
depth = fmax (depth, maxDepth(root->children[i]));
}
return depth + 1;
}
二叉树的最小深度
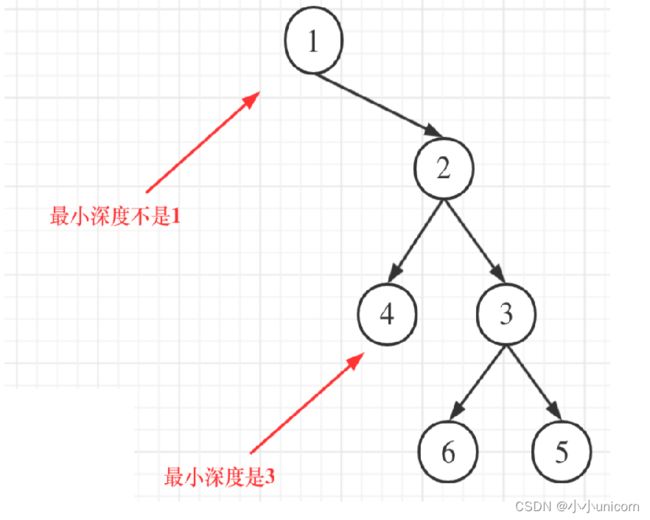
题目描述:Leetcode111.二叉树的最小深度
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
解题思路:
仔细审题:
题目中说的是:最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。,注意是叶子节点。
什么是叶子节点,左右孩子都为空的节点才是叶子节点!
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值
参数为要传入的二叉树根节点,返回的是int类型的深度。
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
2.确定终止条件
终止条件也是遇到空节点返回0,表示当前节点的高度为0。
if (node == NULL) return 0;
3.确定单层递归的逻辑
这块和求最大深度可就不一样了,如果左子树为空,右子树不为空,说明最小深度是 1 + 右子树的深度。
反之,右子树为空,左子树不为空,最小深度是 1 + 左子树的深度。 最后如果左右子树都不为空,返回左右子树深度最小值 + 1 。
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL) {
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL) {
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
int result = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
可以看出:求二叉树的最小深度和求二叉树的最大深度的差别主要在于处理左右孩子不为空的逻辑。
整体代码解决:
int getDepth(TreeNode* node)
{
if (node == NULL) return 0;
int leftDepth = getDepth(node->left); // 左
int rightDepth = getDepth(node->right); // 右
// 中
// 当一个左子树为空,右不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL)
{
return 1 + rightDepth;
}
// 当一个右子树为空,左不为空,这时并不是最低点
if (node->left != NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
return 1 + leftDepth;
}
//都不为空时:左子树和右子树小的那个的深度+1;
int result = 1 + fmin(leftDepth, rightDepth);
return result;
}
int minDepth(TreeNode* root)
{
return getDepth(root);
}
//精简后:
int minDepth(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//左子树为空,右子树不为空
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right!=NULL)
{
return 1+minDepth(root->right);
}
//左子树不为空,右子树为空
if(root->left!=NULL&&root->right==NULL)
{
return 1+minDepth(root->left);
}
//都不为空:
return fmin(minDepth(root->left),minDepth(root->right))+1;
}
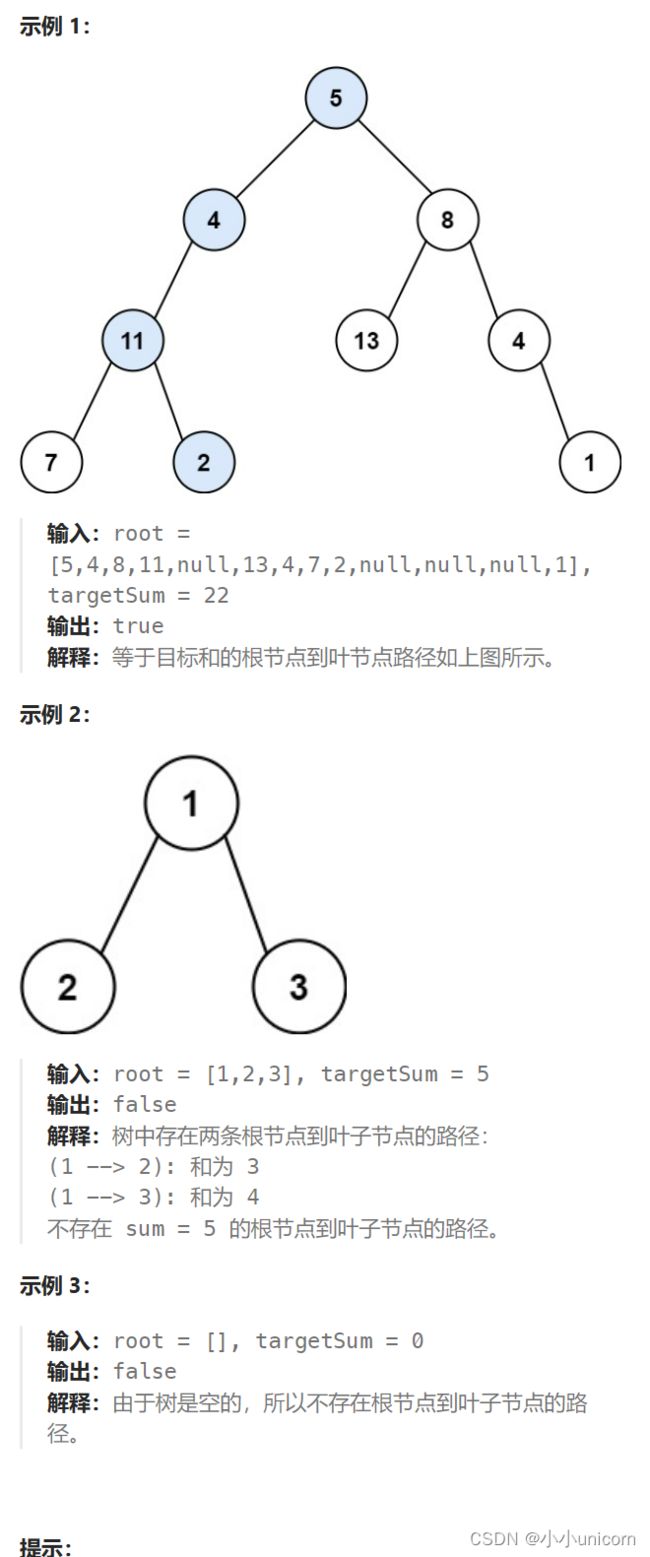
路径总和
题目来源:Leetcode112.路径总和
题目描述:
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
解题思路:
1.题中已说明叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。即左右节点均为 NULL 时,满足叶子节点要求。
2.每经过 1 个节点,在路径和上减去该节点 val 值,当 sum 为 0 时,满足目标和要求。
3.综合以上两条,即为返回 true 的条件,简单递归左右子树即可。
代码解决:
bool hasPathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum)
{
//空树时,不存在
if(root==NULL)
{
return false;
}
targetSum=targetSum-root->val;
//左右节点均为空时,且targetSum为0时,满足条件
if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL&&targetSum==0)
{
return true;
}
//
return hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum)||hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum);
}
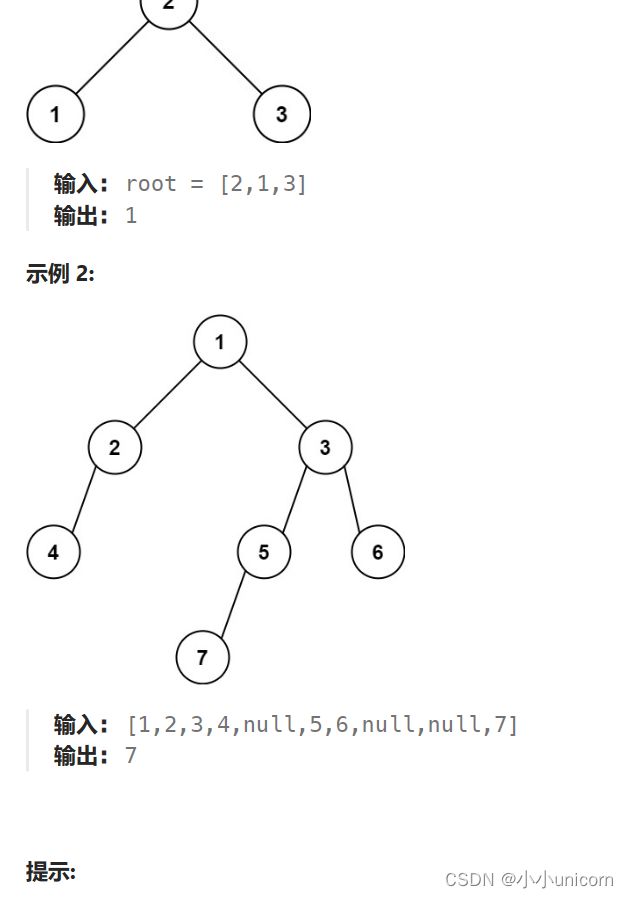
找树左下角的值:
题目来源:Leetcode513.找树左下角的值
题目描述:
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
代码解决:
void dfs(struct TreeNode* root, int *max_depth, int depth, int *value)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
if (*max_depth < depth)
{
*value = root->val;
*max_depth = depth;
}
/* 保证深度最深的第一个点是左子树节点 */
dfs(root->left, max_depth, depth + 1, value);
dfs(root->right, max_depth, depth + 1, value);
}
int findBottomLeftValue(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if (root->right == NULL && root->left == NULL)
{
return root->val;
}
int value = 0;
/* 记录最大深度 */
int max_depth = 0;
dfs(root, &max_depth, 0, &value);
return value;
}
合并二叉树
题目来源:Leetcode617.合并二叉树
题目描述:
给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。
想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。
返回合并后的二叉树。
解题思路:
1.确定递归函数的参数和返回值:
首先要合入两个二叉树,那么参数至少是要传入两个二叉树的根节点,返回值就是合并之后二叉树的根节点。
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2)
2.确定终止条件:
因为是传入了两个树,那么就有两个树遍历的节点t1 和 t2,如果t1 == NULL 了,两个树合并就应该是 t2 了(如果t2也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
反过来如果t2 == NULL,那么两个数合并就是t1(如果t1也为NULL也无所谓,合并之后就是NULL)。
if (t1 == NULL) return t2; // 如果t1为空,合并之后就应该是t2
if (t2 == NULL) return t1; // 如果t2为空,合并之后就应该是t1
3.确定单层递归的逻辑:
单层递归的逻辑就比较好写了,这里我们重复利用一下t1这个树,t1就是合并之后树的根节点(就是修改了原来树的结构)。
那么单层递归中,就要把两棵树的元素加到一起。
t1->val += t2->val;
接下来t1 的左子树是:合并 t1左子树 t2左子树之后的左子树。
t1 的右子树:是 合并 t1右子树 t2右子树之后的右子树。
最终t1就是合并之后的根节点。
t1->left = mergeTrees(t1->left, t2->left);
t1->right = mergeTrees(t1->right, t2->right);
return t1;
整体代码:
struct TreeNode* mergeTrees(struct TreeNode* t1, struct TreeNode* t2)
{
if (t1 == NULL) return t2; // 如果t1为空,合并之后就应该是t2
if (t2 == NULL) return t1; // 如果t2为空,合并之后就应该是t1
// 修改了t1的数值和结构
t1->val += t2->val; // 中
t1->left = mergeTrees(t1->left, t2->left); // 左
t1->right = mergeTrees(t1->right, t2->right); // 右
return t1;
}
代码解决:
咱们还可以不修改输入树的结构,使用前序遍历,代码如下:
struct TreeNode* mergeTrees(struct TreeNode* t1, struct TreeNode* t2)
{
if (t1 == NULL)
return t2;
if (t2 == NULL)
return t1;
// 重新定义新的节点,不修改原有两个树的结构
struct TreeNode* root = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->val = t1->val + t2->val;
root->left = mergeTrees(t1->left, t2->left);
root->right = mergeTrees(t1->right, t2->right);
return root;
}
最大二叉树
题目来源:Leetcode654.最大二叉树
题目描述:
给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
1.递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
2.递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
3.返回 nums 构建的 最大二叉树 。
解题思路:
1、以左闭右开为区间递归构造二叉树,区间内至少得有一个元素,
若left >= right则表示无节点,需返回NULL
2、找到当前区间中最大的元素,记录下标maxValueIndex
3、以[left, maxIndex) 和 [maxIndex + 1, right)为区间构造左右子树
代码解决:
struct TreeNode* traversal(int* nums, int left, int right)
{
//若左边界大于右边界,返回NULL
if(left >= right)
return NULL;
//找出数组中最大数坐标
int maxIndex = left;
int i;
for(i = left + 1; i < right; i++)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[maxIndex])
maxIndex = i;
}
//开辟结点
struct TreeNode* node = (struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
//将结点的值设为最大数组数组元素
node->val = nums[maxIndex];
node->left=NULL;
node->right=NULL;
//递归定义左孩子结点和右孩子结点
node->left = traversal(nums, left, maxIndex);
node->right = traversal(nums, maxIndex + 1, right);
return node;
}
struct TreeNode* constructMaximumBinaryTree(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
return traversal(nums, 0, numsSize);
}
总结:
费尽千辛万苦,咱们链式二叉树已经圆满结束了,希望本篇文章能对你有所帮助。
以下是测试所用的代码:
头文件.h
#include源文件1(Queue.c)
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
源文件2(BinaryTree.c)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include