yolov8-seg 训练自己的数据集(Linux)--详细步骤
1、源码地址:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
2、环境准备:
有直接能用的镜像:docker pull ultralytics/ultralytics:latest
镜像拉下来就有源码
3、准备数据集(labelme标注)
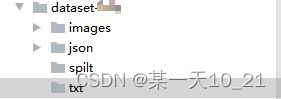
- 数据集结构:images为存放的原图,json文件夹下为labelme的标注文件,txt用来存放转化后的txt标注文件,spilt存放划分好,用来训练的的数据集
- 将json转化为txt,运行labelme2txt.py,将最后一行的class_list,需改成自己的数据集类型
import json import os import glob import os.path as osp from shutil import copy, rmtree def mk_file(file_path: str): if os.path.exists(file_path): # 如果文件夹存在,则先删除原文件夹在重新创建 rmtree(file_path) os.makedirs(file_path) def labelme2txt(jsonfilePath="", resultDirPath="", classList=["YiBiao", "ZhiZhen"]): """ 此函数用来将labelme软件标注好的数据集转换为yolov5_7.0sege中使用的数据集 :param jsonfilePath: labelme标注好的*.json文件所在文件夹 :param resultDirPath: 转换好后的*.txt保存文件夹 :param classList: 数据集中的类别标签 :return: """ # 0.创建保存转换结果的文件夹 mk_file(resultDirPath) # 1.获取目录下所有的labelme标注好的Json文件,存入列表中 jsonfileList = glob.glob(osp.join(jsonfilePath, "*.json")) #print(jsonfileList) # 打印文件夹下的文件名称 # 2.遍历json文件,进行转换 for jsonfile in jsonfileList: # 3. 打开json文件 with open(jsonfile, "r") as f: file_in = json.load(f) # 4. 读取文件中记录的所有标注目标 shapes = file_in["shapes"] # 5. 使用图像名称创建一个txt文件,用来保存数据 with open(resultDirPath + "/" + jsonfile.split("/")[-1].replace(".json", ".txt"), "w") as file_handle: # 6. 遍历shapes中的每个目标的轮廓 for shape in shapes: # 7.根据json中目标的类别标签,从classList中寻找类别的ID,然后写入txt文件中 file_handle.writelines(str(classList.index(shape["label"])) + " ") # 8. 遍历shape轮廓中的每个点,每个点要进行图像尺寸的缩放,即x/width, y/height for point in shape["points"]: x = point[0]/file_in["imageWidth"] # mask轮廓中一点的X坐标 y = point[1]/file_in["imageHeight"] # mask轮廓中一点的Y坐标 file_handle.writelines(str(x) + " " + str(y) + " ") # 写入mask轮廓点 # 9.每个物体一行数据,一个物体遍历完成后需要换行 file_handle.writelines("\n") # 10.所有物体都遍历完,需要关闭文件 file_handle.close() # 10.所有物体都遍历完,需要关闭文件 f.close() print("运行完成") if __name__ == "__main__": jsonfilePath = "/workspace/dataset/json" # 要转换的json文件所在目录 resultDirPath = "/workspace/dataset/txt" # 要生成的txt文件夹 labelme2txt(jsonfilePath=jsonfilePath, resultDirPath=resultDirPath, classList=["people", "car"]) - 划分数据集,运行split.py,修改 train_percent 调整数据集划分比例。
# 将图片和标注数据按比例切分为 训练集和测试集
import shutil
import random
import os
import argparse
from shutil import copy, rmtree
# 检查文件夹是否存在
def mk_file(file_path: str):
if os.path.exists(file_path):
# 如果文件夹存在,则先删除原文件夹在重新创建
rmtree(file_path)
os.makedirs(file_path)
def main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir):
# 创建文件夹
mk_file(save_dir)
images_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'images')
labels_dir = os.path.join(save_dir, 'labels')
img_train_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'train')
img_test_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'test')
img_val_path = os.path.join(images_dir, 'val')
label_train_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'train')
label_test_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'test')
label_val_path = os.path.join(labels_dir, 'val')
mk_file(images_dir);
mk_file(labels_dir);
mk_file(img_train_path);
mk_file(img_test_path);
mk_file(img_val_path);
mk_file(label_train_path);
mk_file(label_test_path);
mk_file(label_val_path);
# 数据集划分比例,训练集75%,验证集15%,测试集15%,按需修改
train_percent = 0.8
val_percent = 0.2
test_percent = 0
total_txt = os.listdir(txt_dir)
num_txt = len(total_txt)
list_all_txt = range(num_txt) # 范围 range(0, num)
num_train = int(num_txt * train_percent)
num_val = int(num_txt * val_percent)
num_test = num_txt - num_train - num_val
train = random.sample(list_all_txt, num_train)
# 在全部数据集中取出train
val_test = [i for i in list_all_txt if not i in train]
# 再从val_test取出num_val个元素,val_test剩下的元素就是test
val = random.sample(val_test, num_val)
print("训练集数目:{}, 验证集数目:{},测试集数目:{}".format(len(train), len(val), len(val_test) - len(val)))
for i in list_all_txt:
name = total_txt[i][:-4]
srcImage = os.path.join(image_dir, name + '.jpg')
srcLabel = os.path.join(txt_dir, name + '.txt')
if i in train:
dst_train_Image = os.path.join(img_train_path, name + '.jpg')
dst_train_Label = os.path.join(label_train_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_train_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_train_Label)
elif i in val:
dst_val_Image = os.path.join(img_val_path, name + '.jpg')
dst_val_Label = os.path.join(label_val_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_val_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_val_Label)
else:
dst_test_Image = os.path.join(img_test_path, name + '.jpg')
dst_test_Label = os.path.join(label_test_path, name + '.txt')
shutil.copyfile(srcImage, dst_test_Image)
shutil.copyfile(srcLabel, dst_test_Label)
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
python split_datasets.py --image-dir my_datasets/color_rings/imgs --txt-dir my_datasets/color_rings/txts --save-dir my_datasets/color_rings/train_data
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='split datasets to train,val,test params')
parser.add_argument('--image-dir', type=str, default='/workspace/dataset/images', help='image path dir')
parser.add_argument('--txt-dir', type=str, default='/workspace/dataset/txt', help='txt path dir')
parser.add_argument('--save-dir', default='/workspace/dataset/split', type=str, help='save dir')
args = parser.parse_args()
image_dir = args.image_dir
txt_dir = args.txt_dir
save_dir = args.save_dir
main(image_dir, txt_dir, save_dir)
print("运行完成")到这里数据集准备完成
4、修改源码的配置文件
- ultralytics\datasets\coco128-seg.yaml
将path和class修改为自己数据集,可以将coco128-seg.yaml 另存为自己项目的名字。
path: /workspace/dataset/split # dataset root dir
train: /workspace/dataset/split/images/train # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images
val: /workspace/dataset/split/images/val # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images
test: # test images (optional)
names:
0: people
1: car
- ultralytics\models\v8\yolov8-seg.yaml ,修改nc的值,我这里只有两个类别。
- ultralytics\yolo\cfg\default.yaml ,修改配置文件,预训练权重的路径,训练次数等
model: /workspace/ultralytics/models/v8/yolov8-seg.yaml # path to model file, i.e. yolov8n.pt, yolov8n.yaml
data: ultralytics\datasets\coco128-seg.yaml 5、 开始训练:ultralytics\yolo\v8\segment\train.py
6、预测:ultralytics\yolo\v8\segment\predict.py
预测相关的参数测试也在ultralytics\yolo\cfg\default.yaml 里面,可以设置图片路径,置信度,保存预测结果等。
我不想修改default.py,就改了predict.py文件的源码。
将model和source注释掉,修改成自己的权重文件和自己要预测的文件夹或图片的路径。
加一行:cfg.mode='predict',预测的结果就保存在 ultralytics\yolo\cfg\default.yaml里面设置的project的路径/predict 下面,不加也不影响,运行完会提示保存路径的。
def predict(cfg=DEFAULT_CFG, use_python=False):
"""Runs YOLO object detection on an image or video source."""
#model = cfg.model or 'yolov8m-seg.pt'
#source = cfg.source if cfg.source is not None else ROOT / 'assets' if (ROOT / 'assets').exists() \
# else 'https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
model = "/workspace/runs/train/weights/best.pt"
source = '/workspace/test/'
args = dict(model=model, source=source)
cfg.mode='predict'
if use_python:
from ultralytics import YOLO
YOLO(model)(**args)
else:
predictor = SegmentationPredictor(overrides=args)
predictor.predict_cli()