333333333333
一、Map 接口
接下来讲的都是基于 jdk8 来开展的。
1.1 特点
1、Map 与 Collection 并列存在。Map 是用于保存具有映射关系的数据,即 key-value。
2、Map 中的 key 和 value 可以是任何引用类型的数据类型。
3、Map 中的 key 不允许重复,原因和 HashSet 一样。
4、Map 中的 value 是可以重复的。
5、Map 中的 key 可以为 null,value 也可以为 null,注意 key 为 null 时只能有一个,value 为 null 时可以有多个。
6、常用 String 类作为 Map 的 key
7、key 和 value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 key 总能找到对于的 value。
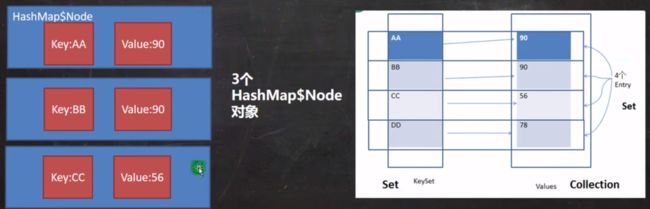
8、Map 存放数据的 key-value 示意图,一对 key-value 是放在一个 Node 中的,又因为 Node 实现了 Entry 接口,也有人说是一对 key-value 就是一个 Entry
1.2 常用实现类
HashMap、HashTable、SortedMap(接口)、TreeMap 、LinkedHashMap、Properties 等。
1.3 常用方法
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
// put 添加元素
map.put("孙悟空","唐僧");
map.put("孙悟空","猪八戒");
map.put("宋江","潘金莲");
map.put("武大郎","西门庆");
map.put("曹操",null);
map.put(null,"荀彧");
// get 根据 key 获取元素
Object o = map.get("武大郎");
// 根据 key 删除元素
map.remove("宋江");
// 判断 key 是否存在
boolean b = map.containsKey(null);
System.out.println(b);
// 获取 map 的元素个数
System.out.println(map.size());
// 判断 map 元素个数是否为 0
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
// 清除 map
map.clear();
}
}1.4 遍历方式
1.4.1 keySet 方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("孙悟空","唐僧");
map.put("武大郎","西门庆");
// 先取出所有的 key,然后再取出 value
Set keySet = map.keySet();
// (1) 使用增强 for 循环
for (Object obj :keySet) {
System.out.println(obj+"-"+map.get(obj));
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
// (2) 迭代器
Iterator iterator = keySet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next+"-"+map.get(next));
}
}1.4.2 value 值方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("孙悟空","唐僧");
map.put("武大郎","西门庆");
// 只能取出所有的 values
Collection values = map.values();
// (1) 增强 for 循环
for (Object obj :values) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
//(2)迭代器
Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();
while(iterator1.hasNext()){
Object next = iterator1.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}1.4.3 EntrySet 方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("孙悟空","唐僧");
map.put("武大郎","西门庆");
Set set = map.entrySet();
// (1) 增强 for 循环
for (Object entry :set) {
// 将 entry 转换成 Map.Entry
Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)entry;
System.out.println(m.getKey()+"-"+m.getValue());
}
System.out.println("-----------------------");
// (2) 迭代器
Iterator iterator2 = set.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry m= (Map.Entry) iterator2.next();
System.out.println(m.getKey()+"-"+m.getValue());
}
}1.5 习题练习
使用 HashMap 添加 3 个员工对象,要求:键为员工 id,值为员工对象。并遍历显示工资 > 18000 员工(遍历方式最少两种)。员工类:姓名、工资、员工 id。
class Employee{
private String id;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String id, String name, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
// setter、getter、toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", salary=" + salary +
'}';
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
Map map = new HashMap();
Employee e1 = new Employee("1","张三",20000);
Employee e2 = new Employee("2","李四",8000);
Employee e3 = new Employee("3","王五",60000);
map.put(e1.getId(),e1);
map.put(e2.getId(),e2);
map.put(e3.getId(),e3);
Set set = map.keySet();
for (Object key :set) {
Employee employee = (Employee)map.get(key);
if(employee.getSalary()>18000){
System.out.println(key+"-"+employee);
}
}
System.out.println("--------------");
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object key = iterator.next();
Employee employee = (Employee)map.get(key);
if(employee.getSalary()>18000){
System.out.println(key+"-"+employee);
}
}
System.out.println("--------------");
Set set1 = map.entrySet();
for (Object entrySet :set1) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)entrySet;
Employee employee = (Employee) entry.getValue();
if(employee.getSalary()>18000){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"-"+employee);
}
}
}