Spring bean的生命周期
1 bean的作用域
singleton : 单例模式,在整个Spring IOC容器中,所有的bean默认都是singleton。
prototype : 原型模式,每次通过容器的getBean方法获取prototype定义的Bean时,都将产生一个新的Bean实例。
request : 请求作用域,每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP request 内有效。
session : 会话作用域,每一次 HTTP 请求都会产生一个新的 bean,该 bean 仅在当前 HTTP session 内有效。
application: 全局作用域,bean是ServletContext级别的就是说是整个web项目全局有效。
普通的java对象的生命周期:
- 实例化
- 该对象不再被使用时通过垃圾回收机制进行回收
而对于 Spring Bean 的生命周期来说:
- 实例化 Instantiation
- 属性赋值 Populate
- 初始化 Initialize
- 销毁 Destroy
2 bean的生命周期
简单来说就四个阶段:
实例化 -> 属性赋值 -> 初始化 -> 销毁四个阶段

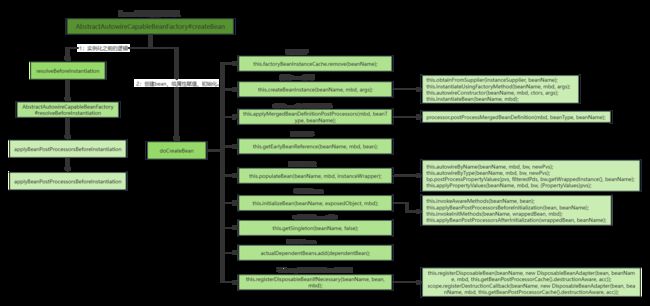
2.1 执行AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean
此方法主要做了两件事:
- 实例化之前的操作:
this.resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse); - 调用实例化方法:
this.doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);

2.1.1 this.resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);源码解析
/**
* Apply before-instantiation post-processors, resolving whether there is a
* 在实例化后处理器之前应用,解决是否存在
* before-instantiation shortcut for the specified bean.
* 在实例化指定bean的快捷方式之前。
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @return the shortcut-determined bean instance, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// synthetic表示合成,如果某些Bean式合成的,那么则不会经过BeanPostProcessor的处理
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation源码:
/**
* Apply InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors to the specified bean definition
* (by class and name), invoking their {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} methods.
* Any returned object will be used as the bean instead of actually instantiating
* the target bean. A {@code null} return value from the post-processor will
* result in the target bean being instantiated.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to use instead of a default instance of the target bean, or {@code null}
* @see InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
@Nullable
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
Object result = bp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
return null;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization源码:
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
2.2.2 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean源码解析
- 创建Bean实例:
createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
- 属性赋值:
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
- 初始化:
initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
- 注册bean:
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);这个不重要,主要是将写入缓存map并进行了bean的销毁逻辑的注册
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* 实际创建指定的bean。已进行预创建处理
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* 区分默认bean实例化和使用工厂方法,并自动连接构造函数。
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// 实例化bean
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 有可能在本Bean创建之前,就有其他Bean把当前Bean给创建出来了(比如依赖注入过程中)
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 创建Bean实例
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// 后置处理合并后的BeanDefinition
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// 为了解决循环依赖提前缓存单例创建工厂
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
// 循环依赖-添加到三级缓存
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 属性填充
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
// beanName被哪些bean依赖了,现在发现beanName所对应的bean对象发生了改变,那么则会报错
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}