Modbus入门
Modbus入门
- Modbus
-
- Modbus模拟工具
-
- 模拟工具使用
-
- 配置Slave
- 配置Poll
- C#使用ModBus通讯
Modbus
modbus使用范围广泛,广泛应用于各类仪表,PLC等。它属于应用层协议,底层硬件基于485/以太网。
Modbus的存储区有:输入线圈(布尔,只读,代号1区),输入寄存器(寄存器,只读,代号3区),输出线圈(读写,布尔,代号0区),输出寄存器(寄存器,读写,代号4区)
Modbus是典型的半双工模式,有且只有一个master,请求由master发出,slave响应。slave之间不能通讯,只能通过master转达。相当于master是客户端,slave都是服务器。
Modbus模拟工具
模拟工具使用Modbus Slave 以及 Modbus Poll 。其中 Slave相当于服务器(Modbus Slave),Poll相当于客户端(Modbus Master)。
模拟工具使用
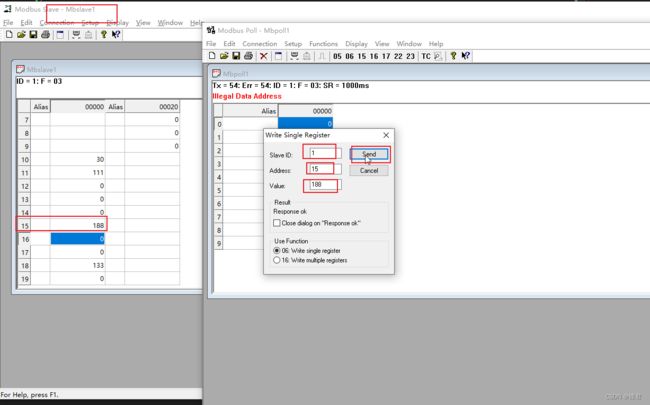
配置Slave
配置Slave

基本配置,配置完选择ok,接下来只要配置要使用的接口方式(网卡,串口等)


选择接口方式,选择串口,初始化波特率、数据位、校验位、停止位,然后选择ok即可打开链接。

配置Poll
C#使用ModBus通讯
使用NuGet中的NModbus4通讯库,进行ModBus RTU(串口)通讯
namespace ModusCommunication
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ModuleHandle moduleHandle = new ModuleHandle();
// NuGet 安装 NModbus4 库
// 确定通讯方式 这边是串口
SerialPort port = new SerialPort("COM2");
// 波特率
port.BaudRate = 9600;
// 数据位
port.DataBits= 8;
// 停止位
port.StopBits = StopBits.One;
// 校验位
port.Parity = Parity.None;
port.Open();
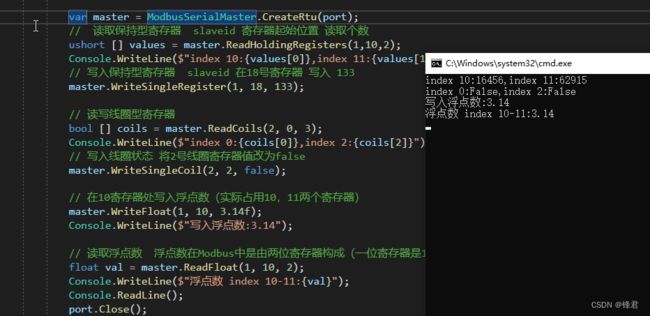
var master = ModbusSerialMaster.CreateRtu(port);
// 读取保持型寄存器 slaveid 寄存器起始位置 读取个数
ushort [] values = master.ReadHoldingRegisters(1,10,2);
Console.WriteLine($"index 10:{values[0]},index 11:{values[1]}");
// 写入保持型寄存器 slaveid 在18号寄存器 写入 133
master.WriteSingleRegister(1, 18, 133);
// 读写线圈型寄存器
bool [] coils = master.ReadCoils(2, 0, 3);
Console.WriteLine($"index 0:{coils[0]},index 2:{coils[2]}");
// 写入线圈状态 将2号线圈寄存器值改为false
master.WriteSingleCoil(2, 2, false);
// 在10寄存器处写入浮点数(实际占用10,11两个寄存器)
master.WriteFloat(1, 10, 3.14f);
Console.WriteLine($"写入浮点数:3.14");
// 读取浮点数 浮点数在Modbus中是由两位寄存器构成(一位寄存器是16bit)
float val = master.ReadFloat(1, 10, 2);
Console.WriteLine($"浮点数 index 10-11:{val}");
Console.ReadLine();
port.Close();
}
}
}
public static class NModbusExtensions
{
///