leetcode链表

这几天手的骨裂稍微好一点了,但是还是很疼,最近学校的课是真多,我都没时间做自己的事,但是好在今天下午是没有课的,我也终于可以做自己的事情了。
今天分享几道题目
移除链表元素
这道题我们将以两种方法开解决,但是我觉得从总体思路上来讲,都可以称为双指针,第一个就是我们在我们原链表上进行修改,我们和之前顺序表的一个题目很是相似,就是我们遇到val就删除,那因为是链表,我们可以理解为释放它这个当前的空间,然后进行当前位置的前一个和后以一个位置的链接就行。
我们给两个指针,然后cur的作用就是进行遍历,我们的prev这个指针就是找到它当前位置的前一个位置,因为我们要删除当前的位置,如果没有前面这个前驱指针,我们删除当前位置之后,前一个和后一个就链接不上了。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
if(prev == NULL)
{
head = head->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
struct ListNode* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
prev->next = cur;
}
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
这个就是我们这道题的一个解决方法,还有就是利用单链表的尾插思想,我们重新搞一个链表,然后进行前后链接。
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL, *tail = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val == val)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = cur;
tail = newhead;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = tail ->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
}
if(tail)
tail->next = NULL;
return newhead;
}
这个就是我们的另一种方法,其实就是一个尾插,大家仔细画图就能解决。

就是我们如果没遇到val,就拿下来,上面一个cur指针来遍历原来的链表,下面的指针来遍历新的链表,这里我觉得大家不理解的地方,可能是为什么我们的tail还要指向空,这里我来解释一下,如果我们的链表尾节点的值也是val,这个时候如果我们不进行处理的话,tail的next是尾节点,所以要判断一下。
反转链表
这个题目我们也有两种做法,第一种就是我们把箭头方向换一下就行了。
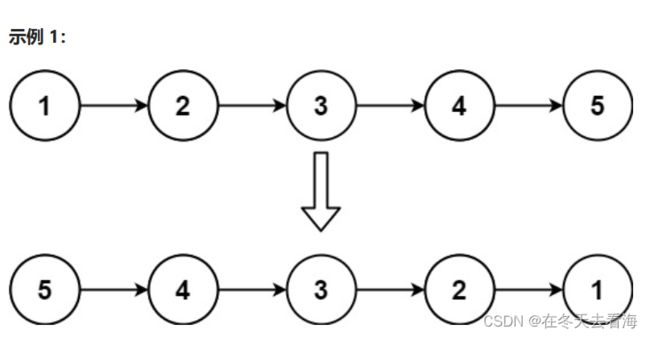
我们可以个三个指针。

可以看到我们给三个指针,第一指针n1的作用就是让n2指向它,这样我们的箭头方向就是已经换过,但是不仅仅是这样,假设我们换第一个n2指向空的时候,n2后面节点的位置就是不知道的,所以我们这里不能这样做,我们的先用一个next的指针来保存后面的位置,这里才能找到写一个地址的节点。
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode* n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode* n2 = head;
while(n2)
{
struct ListNode* n3 = n2->next;
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
这个就是我们这道题目的答案,我么这里其实需要注意两点,这两点leetcode会提示,第一就是如果一进来就是空的,就需要我们进行判断,第二个就是我们的n3会为空,什么时候为空,大家可以画图加上走读代码来看。

这里就是我们n3为空的时候,我们加上判断就可以解决了,我们这里还有一个方法就是和单链表是一样,那就是头插。
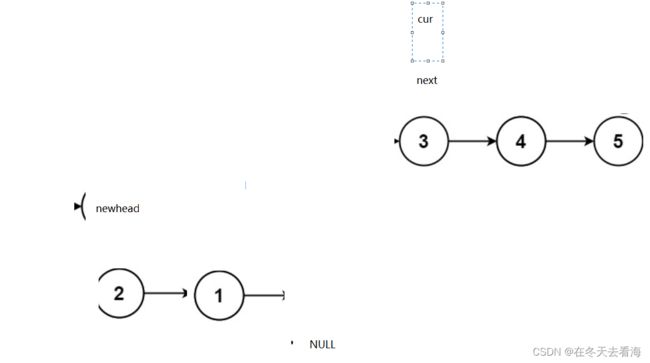
感觉下次得搞个录屏的才行,这个样子的动图总是整不上,会有点问题,大家也不好理解我的意思,如果有人看我的文章,觉得这个题目还是有问题,请私聊我
下面是代码
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
if(newhead == NULL)
{
cur->next = NULL;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
else
{
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
return newhead;
}
链表中间节点
这个题目的思路其实就是快慢指针,一个指针走的快一点,一个指针走的慢一点就可以解决
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head) {
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
这里我们需要注意的最重要的一点其实就是我们要注意奇数和偶数项,虽然都可以找到中间项,但是偶数项的时候fast会为空,所以while加个条件就可以了。
寻找第K个节点
这和我们快慢指针其实是一样的,最重要的就是注意有没有越界就OK了
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode*slow=pListHead;
struct ListNode*fast=pListHead;
while((k--))
{
if(fast==NULL)
return NULL;
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
.合并两个有序链表
这个题目我觉得其实就是仔细一点就能解决,还是那句话,我们得多画图,因为这其实就是一个尾插,我们就把两个链表各给一个指针,比较大小,小的拿出来,然后进行尾插到新链表就可以了。
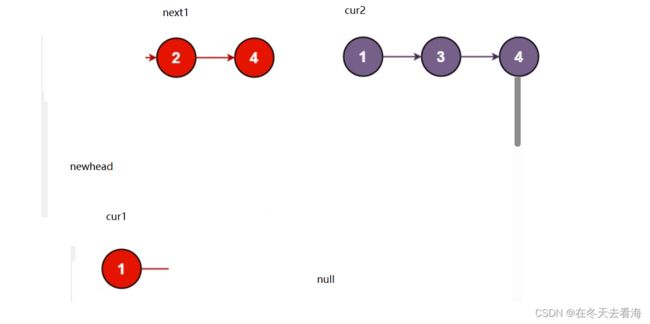
反正大家就先画图,自己先走一遍,然后再来过就可以很好的解决了,代码我给大家看看。
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {
if(list1 == NULL && list2 == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* cur1 = list1;
struct ListNode* cur2 = list2;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
struct ListNode* tail =NULL;
while(cur1 && cur2)
{
if(cur1->val < cur2->val)
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead = tail = cur1;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur1;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
else
{
if(newhead==NULL)
{
newhead = tail = cur2;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur2;
tail = tail->next;
}
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
if(tail == NULL)
{
if(list1)
return list1;
else
return list2;
}
while(cur1)
{
tail->next = cur1;
tail = tail->next;
cur1 = cur1->next;
}
while(cur2)
{
tail->next = cur2;
tail = tail->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
return newhead;
}
我觉得我的代码最大的问题就是看起来有点繁琐,但是也都是根据测试用例一个一个去尝试,leetcode用起来个测试用例是真舒服。
那今天的分享就到这里,我们下次再见。

