java的IO模型
IO模型
IO模型就是说用什么样的通道进行数据的发送和接收,Java共支持3种网络编程IO模式: BIO,NIO,AIO。
BIO(Blocking IO)
同步阻塞模型,一个客户端连接对应一个处理线程
BIO代码示例:
package com.tuling.bio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class SocketServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(9000);
while (true) {
System.out.println("等待连接。。");
//阻塞方法
Socket clientSocket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("有客户端连接了。。");
handler(clientSocket);
/*new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
handler(clientSocket);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();*/
}
}
private static void handler(Socket clientSocket) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.out.println("准备read。。");
//接收客户端的数据,阻塞方法,没有数据可读时就阻塞
int read = clientSocket.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println("read完毕。。");
if (read != ‐1) {
System.out.println("接收到客户端的数据:" + new String(bytes, 0, read));
}
clientSocket.getOutputStream().write("HelloClient".getBytes());
clientSocket.getOutputStream().flush();
}
}
//客户端代码
public class SocketClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 9000);
//向服务端发送数据
socket.getOutputStream().write("HelloServer".getBytes());
socket.getOutputStream().flush();
System.out.println("向服务端发送数据结束");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//接收服务端回传的数据
socket.getInputStream().read(bytes);
System.out.println("接收到服务端的数据:" + new String(bytes));
socket.close();
}
}缺点:
1、IO代码里read操作是阻塞操作,如果连接不做数据读写操作会导致线程阻塞,浪费资源
2、如果线程很多,会导致服务器线程太多,压力太大,比如C10K问题
应用场景:
BIO 方式适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构, 这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高, 但程序简单易理解。
NIO(Non Blocking IO)
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为 一个线程可以处理多个请求(连接) ,客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到 多路复用器selector 上,多路复用
器轮询到连接有IO请求就进行处理,JDK1.4开始引入。
应用场景:
NIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作) 的架构, 比如聊天服务器, 弹幕系统, 服务器间通讯,编程比较复杂
NIO非阻塞代码示例:
package com.tuling.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
public class NioServer {
// 保存客户端连接
static List channelList = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 创建NIO ServerSocketChannel,与BIO的serverSocket类似
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocket.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
// 设置ServerSocketChannel为非阻塞
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务启动成功");
while (true) {
// 非阻塞模式accept方法不会阻塞,否则会阻塞
// NIO的非阻塞是由操作系统内部实现的,底层调用了linux内核的accept函数
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocket.accept();
if (socketChannel != null) { // 如果有客户端进行连接
System.out.println("连接成功");
// 设置SocketChannel为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 保存客户端连接在List中
channelList.add(socketChannel);
}
// 遍历连接进行数据读取
Iterator iterator = channelList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SocketChannel sc = iterator.next();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
// 非阻塞模式read方法不会阻塞,否则会阻塞
int len = sc.read(byteBuffer);
// 如果有数据,把数据打印出来
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(byteBuffer.array()));
} else if (len == ‐1) { // 如果客户端断开,把socket从集合中去掉
iterator.remove();
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
}
}
}
}
} 总结:如果连接数太多的话,会有大量的无效遍历,假如有10000个连接,其中只有1000个连接有写数据,但是由于其他9000个连接并
没有断开,我们还是要每次轮询遍历一万次,其中有十分之九的遍历都是无效的,这显然不是一个让人很满意的状态。
NIO引入 多路复用器 代码示例:
package com.tuling.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
public class NioSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 创建NIO ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocket = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocket.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
// 设置ServerSocketChannel为非阻塞
serverSocket.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开Selector处理Channel,即创建epoll
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 把ServerSocketChannel注册到selector上,并且selector对客户端accept连接操作感兴趣
serverSocket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务启动成功");
while (true) {
// 阻塞等待需要处理的事件发生
selector.select();
// 获取selector中注册的全部事件的 SelectionKey 实例
Set selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
// 遍历SelectionKey对事件进行处理
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
// 如果是OP_ACCEPT事件,则进行连接获取和事件注册
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel socketChannel = server.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 这里只注册了读事件,如果需要给客户端发送数据可以注册写事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("客户端连接成功");
} else if (key.isReadable()) { // 如果是OP_READ事件,则进行读取和打印
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
int len = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
// 如果有数据,把数据打印出来
if (len > 0) {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + new String(byteBuffer.array()));
} else if (len == ‐1) { // 如果客户端断开连接,关闭Socket
System.out.println("客户端断开连接");
socketChannel.close();
}
}
//从事件集合里删除本次处理的key,防止下次select重复处理
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
} NIO 有三大核心组件: Channel(通道), Buffer(缓冲区),Selector(多路复用器)
1、channel 类似于流,每个 channel 对应一个 buffer缓冲区,buffer 底层就是个数组
2、channel 会注册到 selector 上,由 selector 根据 channel 读写事件的发生将其交由某个空闲的线程处理
3、NIO 的 Buffer 和 channel 都是既可以读也可以写
NIO底层在JDK1.4版本是用linux的内核函数select()或poll()来实现,跟上面的NioServer代码类似,selector每次都会轮询所有的
sockchannel看下哪个channel有读写事件,有的话就处理,没有就继续遍历,JDK1.5开始引入了epoll基于事件响应机制来优化NIO。
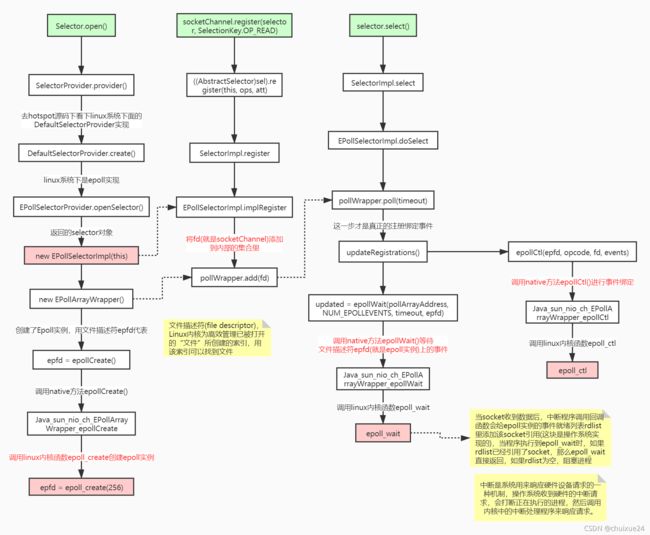
NioSelectorServer 代码里如下几个方法非常重要,我们从Hotspot与Linux内核函数级别来理解下
Selector.open() //创建多路复用器
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ) //将channel注册到多路复用器上
selector.select() //阻塞等待需要处理的事件发生 总结:NIO整个调用流程就是Java调用了操作系统的内核函数来创建Socket,获取到Socket的文件描述符,再创建一个Selector 对象,对应操作系统的Epoll描述符,将获取到的Socket连接的文件描述符的事件绑定到Selector对应的Epoll文件描述符上,进行事件的异步通知,这样就实现了使用一条线程,并且不需要太多的无效的遍历,将事件处理交给了操作系统内核(操作系统中断
程序实现),大大提高了效率。
Epoll函数详解
int epoll_create(int size);创建一个epoll实例,并返回一个非负数作为文件描述符,用于对epoll接口的所有后续调用。参数size代表可能会容纳size个描述符,但size不是一个最大值,只是提示操作系统它的数量级,现在这个参数基本上已经弃用了。
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);使用文件描述符epfd引用的epoll实例,对目标文件描述符fd执行op操作。参数epfd表示epoll对应的文件描述符,参数fd表示socket对应的文件描述符。参数op有以下几个值:
EPOLL_CTL_ADD:注册新的fd到epfd中,并关联事件event;
EPOLL_CTL_MOD:修改已经注册的fd的监听事件;
EPOLL_CTL_DEL:从epfd中移除fd,并且忽略掉绑定的event,这时event可以为null; 参数event是一个结构体
struct epoll_event {
__uint32_t events; /* Epoll events */
epoll_data_t data; /* User data variable */
};
typedef union epoll_data {
void *ptr;
int fd;
__uint32_t u32;
__uint64_t u64;
} epoll_data_t; events有很多可选值,这里只举例最常见的几个:
EPOLLIN :表示对应的文件描述符是可读的;
EPOLLOUT:表示对应的文件描述符是可写的;
EPOLLERR:表示对应的文件描述符发生了错误;成功则返回0,失败返回-1
/*
等待文件描述符epfd上的事件。
epfd是Epoll对应的文件描述符,events表示调用者所有可用事件的集合,maxevents表示最多等到多少个事件就返回,timeout是超时时间。
I/O多路复用底层主要用的Linux 内核函数(select,poll,epoll)来实现,windows不支持epoll实现,windows底层是基于winsock2的select函数实现的(不开源)
*/
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout); I/O多路复用底层主要用的Linux 内核函数(
select,poll,epoll)来实现,windows不支持epoll实现,windows底层是基于winsock2的
select函数实现的(不开源)
Redis线程模型
Redis就是典型的基于epoll的NIO线程模型(nginx也是),epoll实例收集所有事件(连接与读写事件),由一个服务端线程连续处理所有事件
命令。
Redis底层关于epoll的源码实现在redis的src源码目录的ae_epoll.c文件里,感兴趣可以自行研究。
AIO(NIO 2.0)
异步非阻塞, 由操作系统完成后回调通知服务端程序启动线程去处理, 一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用
应用场景:
AIO方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,JDK7 开始支持
AIO代码示例:
package com.tuling.aio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
public class AIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel =
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open().bind(new InetSocketAddress(9000));
serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Object attachment) {
try {
System.out.println("2‐‐"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 再此接收客户端连接,如果不写这行代码后面的客户端连接连不上服务端
serverChannel.accept(attachment, this);
System.out.println(socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
socketChannel.read(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) {
System.out.println("3‐‐"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, result));
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloClient".getBytes()));
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer buffer) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
System.out.println("1‐‐"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
} package com.tuling.aio;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
public class AIOClient {
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9000)).get();
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("HelloServer".getBytes()));
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
Integer len = socketChannel.read(buffer).get();
if (len != ‐1) {
System.out.println("客户端收到信息:" + new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));
}
}
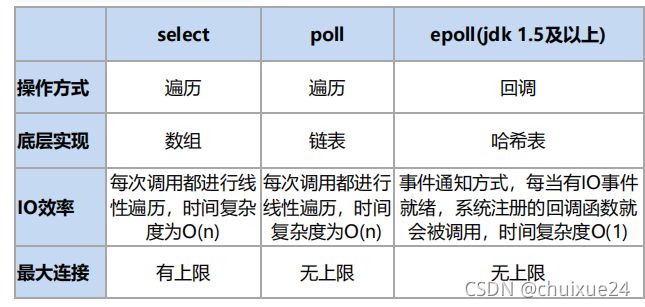
}BIO、 NIO、 AIO 对比:
为什么Netty使用NIO而不是AIO?
在Linux系统上,AIO的底层实现仍使用Epoll,没有很好实现AIO,因此在性能上没有明显的优势,而且被JDK封装了一层不容易深度优化,Linux上AIO还不够成熟。Netty是异步非阻塞 框架,Netty在NIO上做了很多异步的封装。
同步异步与阻塞非阻塞 (段子)
老张爱喝茶,废话不说,煮开水。
出场人物:老张,水壶两把(普通水壶,简称水壶;会响的水壶,简称响水壶)。
1 老张把水壶放到火上,立等水开。 (同步阻塞)
老张觉得自己有点傻
2 老张把水壶放到火上,去客厅看电视,时不时去厨房看看水开没有。 (同步非阻塞)
老张还是觉得自己有点傻,于是变高端了,买了把会响笛的那种水壶。水开之后,能大声发出嘀~~~~的噪音。
3 老张把响水壶放到火上,立等水开。 (异步阻塞)
老张觉得这样傻等意义不大
4 老张把响水壶放到火上,去客厅看电视,水壶响之前不再去看它了,响了再去拿壶。 (异步非阻塞)
老张觉得自己聪明了。
所谓同步异步,只是对于水壶而言。
普通水壶,同步;响水壶,异步。
虽然都能干活,但响水壶可以在自己完工之后,提示老张水开了。这是普通水壶所不能及的。
同步只能让调用者去轮询自己(情况2中),造成老张效率的低下。
所谓阻塞非阻塞,仅仅对于老张而言。
立等的老张,阻塞;看电视的老张,非阻塞。
阻塞:表示该线程被挂起,失去cpu操作权利,等待被唤醒。
同步:线程仍然在运行,没有被挂起,比如在一个线程中,需要调用一个本地方法或者远程方法,在本地方法或远程方法返回前,该线程不能继续向下执行