虚假内容检测,谣言检测,不实信息检测,事实核查;纯文本,多模态,多语言;数据集整理
本博客系博主个人理解和整理所得,包含内容无法详尽,如有补充,欢迎讨论。
这里只提供数据集相关介绍和来源出处,或者下载地址等,因版权原因不提供数据集所含的元数据。如有需要,请自行下载。
“Complete dataset cannot be distributed because of Twitter privacy policies and news publisher copy rights. Social engagements and user information are not disclosed because of Twitter Policy.”
0. 一些数据集合集及相关综述:
Fake News Detection | Papers With Code
GitHub - ICTMCG/fake-news-detection: This repo is a collection of AWESOME things about fake news detection, including papers, code, etc.
论文:Combating Fake News: A Survey on Identification and Mitigation Techniques
论文:TACL2022 A Survey on Automated Fact-Checking
论文:Fake news detection: A hybrid CNN-RNN based deep learning approach
论文:The Surprising Performance of Simple Baselines for Misinformation Detection,该论文的github项目地址GitHub - ComplexData-MILA/misinfo-baselines有本文实验所用的数据集。
一、多模态数据集
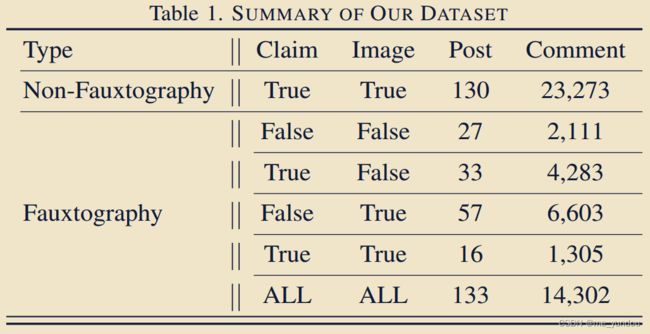
1. ExFaux数据集 [23], 2020年;
- 包含263张image和若干text;有social metadata和comments;
- 英文,来自Twitter和Reddit。
- 本文的任务除了判断一个post的真假之外,还需要判断是多模态内容中的image or claim导致的虚假(这个是别的方法没有考虑过的,也因为数据集没有提供这个标签);
- 论文中没有提供数据集的下载地址和源码,从网上也没有搜索到;
2. FauxBuster数据集 [24],2018年;
- 包含917个image及text;
- 有social metadata和comments;
- 英文,来自Twitter和Reddit网站。
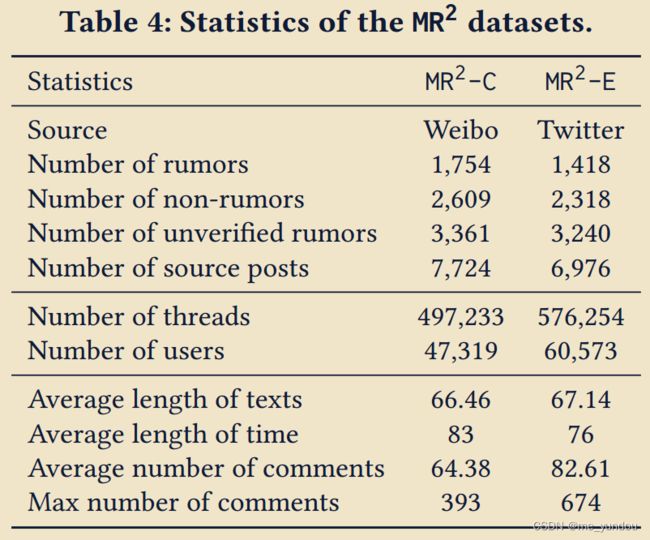
3. MR2数据集 [25];
- 包含14700个image及text,类别是rumor,non-rumor,unverified;
- 有social metadata和comments,还有从网站上检索的text和image证据;
- 中文来自weibo,英文来自Twitter。
- 数据集下载地址(在谷歌云上,weibo有24G,twitter 有22G):GitHub - THU-BPM/MR2
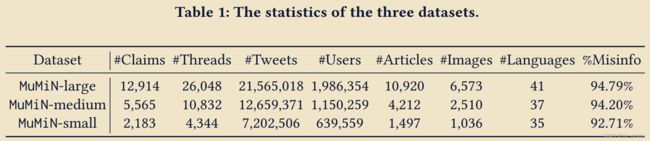
4. MuMiN数据集 [26],2022年;
- 包含984张image和text,有social metadata和comments,可以构成tweet之间的graph;
- 很多语言,来自Twitter;
- 因为来自twitter,根据twitter的规则,作者只提供了可以用来从twitter下载所有数据的爬虫代码,没有提供数据文件。数据需要大家自行下载。数据集下载地址:MuMiN - A Large-Scale Multilingual Multimodal Fact-Checked Misinformation Social Network Dataset
5. Weibo数据集 [27](来自att-RNN)
- 包含9528张image和text;
- 有social metadata(是字段型的social info,比如转发数,用户名,用户的发推数目等),没有retweet和comments;
- 中文,来自Weibo;
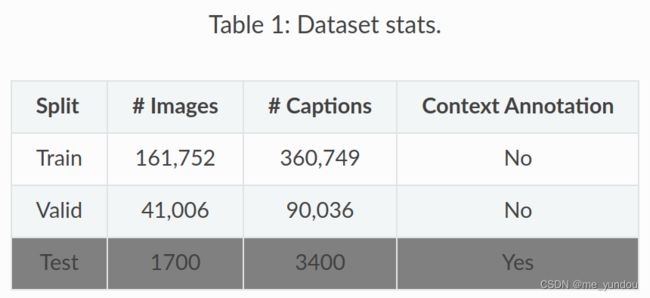
6. COSMOS数据集 [36]
- 包含image和text,是为了检测out-of-context,也就是图文不符的情况。Training (160 K images), Validation (40 K images) and Test (1700 images)。
- 没有social info;
- 每一张图片还给出了最多10个bounding box;
- 数据集地址:https://github.com/shivangi-aneja/COSMOS
- 需要先填一个表格,然后作者会给数据集的下载方式。数据集主页:COSMOS Dataset — COSMOS: Catching Out-of-Context Misinformation using Self-Supervised Learning 1.0 documentation
7. MM-COVID 数据集[37];
- 包含image,text,social info等内容,covid-19相关;
- 3981个虚假内容和 7192 个真实内容,包含 English, Spanish, Portuguese, Hindi, French and Italian, 6 种不同语言;
- 数据集地址:https://github.com/bigheiniu/MM-COVID
- 还有一个地址:GitHub - bigheiniu/MM-COVID: Cross Linugual COVID-19 Fake News Dataset
- 上述地址中只提供了news和相关tweet的id(在谷歌云上)。因为来自twitter,所以数据集中只提供了tweet的id,而tweet的text内容需要大家自行下载,数据集中提供了下载的代码。
8. FakeNewsNet [9] 数据集;
- 包含两部分:GossipCop,PolitiFact;是否包含BuzzFeed?
- 下载地址如下。作者提供了爬虫代码,可以直接运行得到所需的数据。需要twitter API:
https://github.com/KaiDMML/FakeNewsNet
- 下面也是[9]官方提出的数据集,但是数据集变成了BuzzFeed+PolitiFact,不知道为什么。这个数据集可以直接下载。
FakeNewsNet | Kaggle
- 下面是一个修改后的下载该数据集的项目,能够以更快的速度从twitter上下载tweets:
GitHub - SaschaStenger/FakeNewsNet_modified
- 下面这个论文的作者似乎能分享这个数据集的tweet和user元数据。给下面的作者发邮件,能得到谷歌云上的数据:
GitHub - hwang219/AttackFakeNews
- 使用该数据集的论文:[7],SAFE,icassp的知识蒸馏论文,spotfake or plus?,
9.Fakeddit数据集 [21],
-
有images;
-
数据集的下载地址:
GitHub - entitize/Fakeddit: r/Fakeddit New Multimodal Benchmark Dataset for Fine-grained Fake News Detection
GitHub - faiazrahman/Multimodal-Fake-News-Detection: Multi-Modal Fine-Grained Fake News Detection with Dialogue Summarization
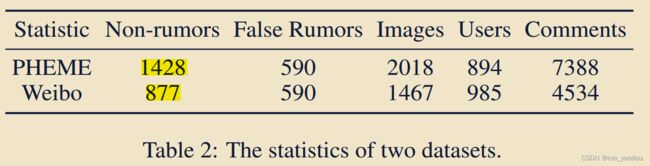
10.PHEME数据集[15];
- 这个数据集包含twitter完整的post信息,包含pic_url项,可以自己去爬对应的images。但是很多post该项为空。
- 有个人[18]爬了这个数据集的images:GitHub - drivsaf/MFAN
- 使用该数据集的文章:ICMR-2020-KMGCN, [18], HMCAN;
11. ReCOVery数据集 [38];
- 包含text,image,时间信息,传播信息(textual, visual, temporal, and network information);
- 用了三个关键词检索相关article:SARS-CoV-2,COVID-19, Coronavirus;
- 爬取每一个news的News Content,具体包括12个:Id,URL,发布者,发布时间,作者,标题和正文,图片,国家,政治偏向,真假情况NewsGuard score and MBFC factual reporting;
- 同时,作者还爬取了news在tweet上的传播情况,包括许多详细信息:the corresponding tweets with detailed information such as their IDs, text, languages of text, times of being created, statistics on retweeted/replied/liked。但是由于twitter的内容限制,数据集中没有提供这些tweet的信息,只提供了相关的tweet id,需要大家自行下载。下载的指导在数据集中有。To comply with Twitter’s Terms of Service, we only publicly release the IDs of the collected data for non-commercial research use, but provide the instructions for obtaining the tweets using the released IDs for user convenience.
- 数据集下载地址:http://coronavirus-fakenews.com
- 作者在上述地址中提供了news的url,正文text,image-url(没有image文件)。但是network信息只提供了tweet id,需要自己爬tweet的内容。(这个image和tweet都需要别人帮忙爬)
- 上面那个地址可能打不开,还有一个:GitHub - apurvamulay/ReCOVery: A Multimodal Repository for COVID-19 News Credibility Research
12.CHECKED数据集,来自 [39];
- 包含text,image,还有comment,repost等social info;
- 中文,来自weibo,关于covid-19的数据集;
- 这个数据集的地址:
https://github.com/cyang03/CHECKED
- 上面的地址中的数据集提供了所有数据的json文件,有comments和reposts(这些都有id,不知道能不能构成graph)。这些东西的text文本都有。其中包含 pic_url 和 video_url,而没有image文件。需要大家自己根据image url去下载image和video。
二、纯文本数据集
1. CW-CURE 数据集
- 来自[30],包含3266条claim text,医疗领域的;
- 只有text,没有social info,没有image。
- 英文,来自Twitter;
2. BioClaims 数据集
- 来自[31],related to COVID-19, measles, cystic fibrosis, and depression;
- 好像只有text?
- 英文,来自Twitter
4. LIAR [22] 数据集;
数据来源是从politifact网站上爬的;
数据集下载地址:
https://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~william/data/liar_dataset.zip
5. 又一个weibo数据集 [19],在[16]的基础上,数据量增加了一倍。
- 该文章的代码:
GitHub - thunlp/CED: source code for TKDE paper “CED: Credible Early Detection of Social Media Rumors”
- 该数据集所在地址及规模大小:
GitHub - thunlp/Chinese_Rumor_Dataset: 中文谣言数据
- 使用该数据集的文章有:[18];
6. CoAID 数据集 [8]:
- 包含 5,216 条新闻, 296,752 related user engagements, 958 social platform posts about COVID-19, and ground truth labels.
- 数据集地址如下:
- GitHub - cuilimeng/CoAID
- 但是github项目里面只给了news的https,以及跟news相关的tweet的id,以及retweet的id。所以数据其实还需要自己爬。而且github中没有提供爬虫代码。(这个需要别人帮忙)
- 有个论文说这个数据集包含image,应该是在爬取tweet内容的时候可以把其image也一起爬了。但是本数据集在提出的时候并没有处理image。
- 使用该数据集的论文:[7]
7. MC-Fake 数据集[40];
- 纯文本信息,针对news有 tweets, retweets, replies, retweet relations, and replying relations,可以构建post的propagation network;
- 27,155 news events, 5 million posts, 2 million users and an induced user social graph with 0.2 billion edges.
- 数据集中有五种主题: five topics: Politics, Entertainment, Health, Covid-19 and Syria War,
- 来自Twitter,又没有内容,需要自己爬,诶,人生怎么这么艰难;
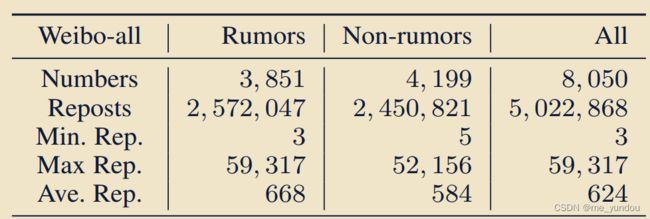
8. 又有名字一样的,Weibo和Twitter数据集,来自[16];
- 下面是原始论文提供的地址,失效了:
http://alt.qcri.org/⇠wgao/data/rumdect.zip
- 新的数据集下载地址如下:
https://www.dropbox.com/s/46r50ctrfa0ur1o/rumdect.zip?dl=0
- 推特数据集没有提供content,因为twitter的版权问题,只能自己根据id用Twitter API去爬。
- weibo提供了post的详细content。但是本数据集没有提供source images,虽然content里面有post附带的picture的url信息,而且大部分post的picture项为null。
- 该数据集规模大小:下面的图片来自[19].
- 使用该数据集的文章:[19], [2];
三、事实核查数据集
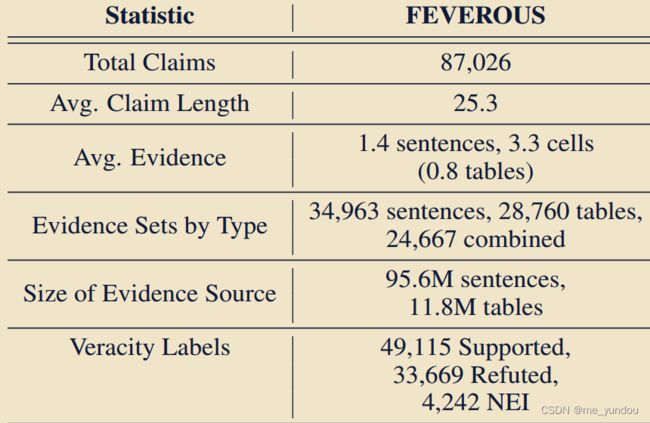
1. FEVEROUS数据集 [28];
- 包含需要验证的claim,证据是wikipedia上的pages中的sentence或者tables(其他数据集很少有用tables的);
- 数据集下载地址:https://fever.ai/dataset/feverous.html
2. CHEF数据集 [29],NAACL 2022年;
- 中文;
- 包含完整的text内容,和对应的social metadata,(e.g. author, domain, URL publication date).
- 数据集下载地址:https://github.com/THU-BPM/CHEF
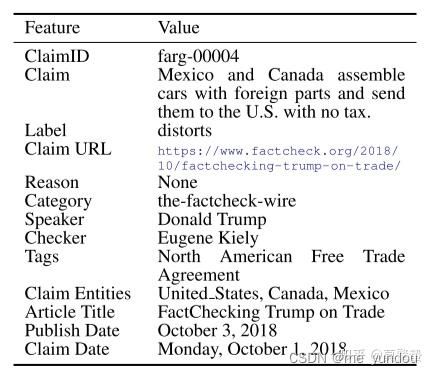
3. MultiFC数据集 [32], EMNLP 2019年;
- 有36534条claim,textual sources and rich metadata, and labelled for veracity by human expert journalists. 但是metadata如上图,是独立特征的,不是retweet;
- 英文,爬取的数据来自26个事实核查网站,非人工创造的claim;
- multi指的是claim来自多个domain,e.g., politics, sports, and entertainment。而不是多模态。
4.FEVER 数据集 [1];
dataset seeks to retrieve supporting evidence for single-sentence claims and classify the
claims as Supported, Refuted or NotEnoughInfo.
使用该数据集的论文:
三、其他(还在分析和整理中,没有分类)
1. 又一个PHEME [33],
2.PolitiFact5 is a website that manually assigns factcheck label to claims, along with the background information.
PolitiFact
使用该数据集的论文:[7]
3.Zlatkova et al. (2019) propose a dataset for fact-checking claims about images [3].
4.TabFact (Chen et al., 2019) presents semi-structural tables for fact verification [4].
5.The SemEval-2020 shared task (Da San Martino et al., 2020) centers on the detection of propaganda techniques in news articles, which is more linguistically oriented [5].
6.infosurgeon [6]通过修改news的KG或者ARM graph生成的虚假新闻:
7. Constraint 数据集[34];
跟covid-19有关的数据;
9.All-in-one: Multi-task Learning for Rumour Verifification.
10. 文章[20]提出了两个数据集Snopes和Politifact,有images。
we split the full dataset into two sub datasets called Snopes and Politifact datasets. The former one contains pairs where FC-articles are from snopes.com and the later one contains pairs where FC-articles are from politifact.com.
这是该文章的code和dataset地址(还没下载,因为在google云上):
https://github.com/nguyenvo09/EMNLP2020
11.ANTiVax 数据集[35];
跟covid-19有关,来自twitter;
12. FakeNews AMT [12]提出了该数据集
使用该数据集的论文:[10] [11]
13. Celeb [12]提出了该数据集
使用该数据集的论文:[10] [11]
14 PHEME 9 出自[13]
使用该数据集的论文:[10]
16.Sentimental-LIAR [14]提出的,对LIAR添加了情感信息和emotions。
21.又一个twitter数据集来自[17]:
https://www.dropbox.com/s/7ewzdrbelpmrnxu/rumdetect2017.zip?dl=0
由于twitter的限制,该数据集只提供了source tweet ID 及 source tweet content,还有传播树结构。
其他post相关内容需要自己根据id去爬。
这个好像就是text研究中用的很多的twitter15和twitter16,没有image内容。
参考文献:
[1] James Thorne, Andreas Vlachos, Christos Christodoulopoulos, and Arpit Mittal. 2018.
Fever: a large-scale dataset for fact extraction and verification. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, pages 809–819.
[2] F. Yu, Q. Liu, S. Wu, L. Wang, and T. Tan, “A convolutional approach for misinformation identification,” in Proceedings of IJCAI, 2017.
[3] Dimitrina Zlatkova, Preslav Nakov, and Ivan Koychev. 2019. Fact-checking meets fauxtography: Verifying claims about images. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), pages 2099–2108, Hong Kong, China. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[4] Wenhu Chen, Hongmin Wang, Jianshu Chen, Yunkai Zhang, Hong Wang, Shiyang Li, Xiyou Zhou, and William Yang Wang. 2019. Tabfact: A largescale dataset for table-based fact verification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1909.02164.
[5] Giovanni Da San Martino, Alberto Barron-Cedeno, ´Henning Wachsmuth, Rostislav Petrov, and Preslav Nakov. 2020. Semeval-2020 task 11: Detection of ropaganda techniques in news articles. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, pages 1377–1414.
[6] InfoSurgeon: Cross-Media Fine-grained Information Consistency Checking for Fake News Detection
[7] Embracing Domain Differences in Fake News: Cross-domain Fake News Detection
using Multimodal Data,AAAI 2021.
[8] Limeng Cui and Dongwon Lee. 2020. CoAID: Covid-19 healthcare misinformation dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.00885
[9] Kai Shu, Deepak Mahudeswaran, Suhang Wang, Dongwon Lee, and Huan Liu. 2020a. Fakenewsnet: A data repository with news content, social context, and spatiotemporal information for studying fake news on social media. Big data, 8(3):171–188.
[10] An Emotion-Based Multi-Task Approach to Fake News Detection (Student Abstract)
[11] Saikh, T.; De, A.; Ekbal, A.; and Bhattacharyya, P. 2020. A Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Detection of Fake News. arXiv:2005.04938.
[12] Perez-Rosas, V.; Kleinberg, B.; Lefevre, A.; and Mihalcea, R. ´ 2018. Automatic Detection of Fake News. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics,
3391–3401. Santa Fe, New Mexico, USA: ACL.
[13] Zubiaga, A.; Liakata, M.; and Procter, R. 2016. Learning Reporting Dynamics during Breaking News for Rumour Detection in Social Media. arXiv:1610.07363.
[14] Upadhayay, B.; and Behzadan, V. 2020. Sentimental LIAR: Extended Corpus and Deep Learning Models for Fake Claim Classification. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on
Intelligence and Security Informatics (ISI), 1–6. IEEE.
[15] Arkaitz Zubiaga, Maria Liakata, and Rob Procter. 2017. Exploiting context for rumour detection in social media. In International Conference on Social Informatics. Springer, 109–123.
[16] Jing Ma, Wei Gao, Prasenjit Mitra, Sejeong Kwon, Bernard J Jansen, Kam-Fai Wong, and Meeyoung Cha. Detecting rumors from microblogs with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of IJCAI 2016.
[17] Jing Ma, Wei Gao, Kam-Fai Wong. Detect Rumors in Microblog Posts Using Propagation Structure via Kernel Learning. ACL 2017.
[18] IJCAI 2022, MFAN: Multi-modal Feature-enhanced Attention Networks for Rumor Detection;
[19] Changhe Song, Cheng Yang, Huimin Chen, Cunchao Tu, Zhiyuan Liu, and Maosong Sun.
Ced: Credible early detection of social media rumors. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 33(8):3035–3047, 2019
[20] Nguyen Vo and Kyumin Lee. 2020. Where Are the Facts? Searching for Fact-checked Information to Alleviate the Spread of Fake News. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 7717–7731, Online. Association for Computational Linguistics.
[21] Kai Nakamura, Sharon Levy, and William Yang Wang. 2020. Fakeddit: A New Multimodal Benchmark Dataset for Fine-grained Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the Twelfth Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, pages 6149–6157, Marseille, France. European Language Resources Association.
[22] ACL 2017,“Liar, Liar Pants on Fire”: A New Benchmark Dataset for Fake News Detection
[23] Ziyi Kou, Daniel Yue Zhang, Lanyu Shang, and Dong Wang. 2020. ExFaux: A Weakly Supervised Approach to Explainable Fauxtography Detection. In 2020 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (IEEE BigData 2020), Atlanta, GA, USA, December 10-13, 2020, Xintao Wu, Chris Jermaine, Li Xiong, Xiaohua Hu, Olivera Kotevska, Siyuan Lu, Weija Xu, Srinivas Aluru, Chengxiang Zhai, Eyhab AlMasri, Zhiyuan Chen, and Jeff Saltz (Eds.). IEEE, 631–636. https://doi.org/10. 1109/BigData50022.2020.9378019
[24] Daniel Yue Zhang, Lanyu Shang, Biao Geng, Shuyue Lai, Ke Li, Hongmin Zhu, Md. Tanvir Al Amin, and Dong Wang. 2018. FauxBuster: A Content-free Fauxtography Detector Using Social Media Comments. In IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Big Data 2018, Seattle, WA, USA, December 10-13, 2018, Naoki Abe, Huan Liu, Calton Pu, Xiaohua Hu, Nesreen K. Ahmed, Mu Qiao, Yang Song, Donald Kossmann, Bing Liu, Kisung Lee, Jiliang Tang, Jingrui He, and Jeffrey S. Saltz (Eds.). IEEE, 891–900. https://doi.org/10.1109/BigData.2018.8622344
[25] SIGIR 2023, MR2: A Benchmark for Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Rumor Detection in Social Media
[26] Dan Saattrup Nielsen and Ryan McConville. 2022. MuMiN: A Large-Scale Multilingual Multimodal Fact-Checked Misinformation Social Network Dataset. In SIGIR ’22: The 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Madrid, Spain, July 11 - 15, 2022, Enrique Amigó, Pablo Castells, Julio Gonzalo, Ben Carterette, J. Shane Culpepper, and Gabriella Kazai (Eds.). ACM, 3141–3153. https://doi.org/10.1145/3477495.3531744
[27] Zhiwei Jin, Juan Cao, Han Guo, Yongdong Zhang, and Jiebo Luo. 2017. Multimodal fusion with recurrent neural networks for rumor detection on microblogs. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia. 795–816
[28] Rami Aly, Zhijiang Guo, Michael Sejr Schlichtkrull, James Thorne, Andreas Vlachos, Christos Christodoulopoulos, Oana Cocarascu, and Arpit Mittal. 2021. FEVEROUS: Fact Extraction and VERification Over Unstructured and Structured information. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks 1, NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks 2021, December 2021, virtual, Joaquin Vanschoren and Sai-Kit Yeung (Eds.). https://datasets-benchmarks-proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2021/hash/
68d30a9594728bc39aa24be94b319d21-Abstract-round1.html
[29] Xuming Hu, Zhijiang Guo, Guanyu Wu, Aiwei Liu, Lijie Wen, and Philip S. Yu. 2022. CHEF: A Pilot Chinese Dataset for Evidence-Based Fact-Checking. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL 2022, Seattle, WA, United States, July 10-15, 2022, Marine Carpuat, Marie-Catherine de Marneffe, and Iván Vladimir Meza Ruíz (Eds.). Association for Computational Linguistics, 3362–3376. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/2022.naacl-main.246
[30] Identifying Checkworthy CURE Claims on Twiter, www 2023;
[31] Amelie Wührl and Roman Klinger. 2021. Claim Detection in Biomedical Twitter Posts. In Proceedings of the 20th Workshop on Biomedical Language Processing. 131–142.
[32] MultiFC: A Real-World Multi-Domain Dataset for Evidence-Based Fact Checking of Claims, EMNLP 2019,
[33] Cody Buntain and Jennifer Golbeck. 2017. Automatically identifying fake news in popular twitter threads.In 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Cloud (SmartCloud), pages 208–215. IEEE.
[34] Parth Patwa, Shivam Sharma, Srinivas Pykl, Vineeth Guptha, Gitanjali Kumari, Md Shad Akhtar, Asif Ekbal, Amitava Das, and Tanmoy Chakraborty. 2021. Fighting an infodemic: Covid-19 fake news dataset. In International Workshop on Combating Online Hostile Posts in Regional Languages during Emergency Situation, pages 21–29. Springer.
[35] Kadhim Hayawi, Sakib Shahriar, Mohamed Adel Serhani, Ikbal Taleb, and Sujith Samuel Mathew. 2022. Anti-vax: a novel twitter dataset for covid-19 vaccine misinformation detection. Public health, 203:23–30.
[36] COSMOS: Catching Out-of-Context Misinformation with Self-Supervised Learning,
[37] Yichuan Li, Bohan Jiang, Kai Shu, and Huan Liu. 2020. MM-COVID: A Multilingual and Multidimensional Data Repository for CombatingCOVID-19 Fake New. arXiv e-prints (2020), arXiv–2011.
[38] X. Zhou, A. Mulay, E. Ferrara, and R. Zafarani, “Recovery: A multimodal repository for covid-19 news credibility research,” 2020.
[39] Social Network Analysis and Mining (2021), CHECKED: Chinese COVID‑19 fake news dataset;
[40] Erxue Min, Yu Rong, Yatao Bian, Tingyang Xu, Peilin Zhao, Junzhou Huang, and Sophia Ananiadou. 2022. Divide-and-Conquer: Post-User Interaction Network for Fake News Detection on Social Media. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022 (Virtual Event, Lyon, France) (WWW ’22). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 1148–1158. https://doi.org/10.1145/3485447.3512163
总结:
博主目前暂时收集和整理了这些数据集,“其他”类别中的数据集还没有进行详细分析,同时还有许多不完善的地方。
如有补充或者错漏敬请大家在评论区指正。
会持续更新,对数据集进行详细介绍,提供相应的数据集下载地址。