设计模式之建造者(Builder)
用来构建复杂对象
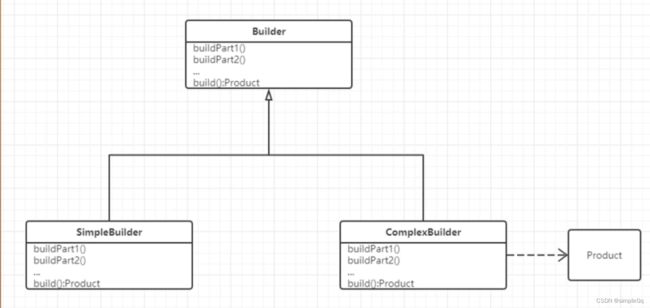
分离复杂对象的构建和表示 同样的构建过程可以创建不同的表示
当有一个复杂的对象,构建它的时候,比较复杂
例如,构建一个对象,要传入50个参数,可以先构建part1,再构建part2…最后调用build构建出整个对象
可以实现不同的构建器。不同的构建器,构造出来的对象不一样
// 地形 一个地形会非常的复杂,有 墙 暗堡 地雷
public class Terrain {
Wall w; // 墙
Fort f; // 暗堡
Mine m; // 地雷
}
// 墙 暗堡 地雷简单表示复杂
class Wall {
int x, y, w, h;
public Wall(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
}
class Fort {
int x, y, w, h;
public Fort(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
}
class Mine {
int x, y, w, h;
public Mine(int x, int y, int w, int h) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.w = w;
this.h = h;
}
}
当我们想要构建一个复杂的对象的时候,可以使用构建器
先定义一个构建器接口:
public interface TerrainBuilder {
// 先build好墙,然后暗堡,然后地雷,最后build()好
TerrainBuilder buildWall();
TerrainBuilder buildFort();
TerrainBuilder buildMine();
Terrain build();
}
实现一个地形构建器:
里面实现好各个构建器
public class ComplexTerrainBuilder implements TerrainBuilder {
Terrain terrain = new Terrain();
@Override
public TerrainBuilder buildWall() {
terrain.w = new Wall(10, 10, 50, 50);
// 返回this
return this;
}
@Override
public TerrainBuilder buildFort() {
terrain.f = new Fort(10, 10, 50, 50);
return this;
}
@Override
public TerrainBuilder buildMine() {
terrain.m = new Mine(10, 10, 50, 50);
return this;
}
@Override
public Terrain build() {
return terrain;
}
}
main函数直接用:
创建一个复杂的构建器,然后链式调用build方法,就构造好了
链式编程,构建器模式经常用这种方法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TerrainBuilder builder = new ComplexTerrainBuilder();
// 为什么这里能够链式调用? --> 因为返回的是this(TerrainBuilder)
Terrain t = builder.buildFort().buildMine().buildWall().build();
// 有必要用上面这个模式吗?直接像下面这样传参数不就好了 --> 确实可以。但是当构建复杂对象的时候,如果参数比较
// 多就需要用Builder模式 --> 这里的代码只是个演示
//new Terrain(Wall w, Fort f, Mine m)
//Effective Java
Person p = new Person.PersonBuilder()
.basicInfo(1, "zhangsan", 18)
//.score(20)
.weight(200)
//.loc("bj", "23")
.build();
}
}
上面实现的是复杂的构建器,还可以实现简单的构建器,不同的构建器构造出来的对象不同
java里面典型的用Builder模式的例子:
例如下面的Person类,属性很多,每次创建Person对象的时候,如果把所有的参数都传一遍,非常麻烦
有时候创建Person对象,可能只需要几个属性,这时候可以使用Builder模式
public class Person {
int id;
String name;
int age;
double weight;
int score;
Location loc;
private Person() {}
// 静态内部类,专门用来构建Person对象
public static class PersonBuilder {
// 创建好对象
Person p = new Person();
// 只传基本的参数构建对象
public PersonBuilder basicInfo(int id, String name, int age) {
p.id = id;
p.name = name;
p.age = age;
return this;
}
// 设置体重
public PersonBuilder weight(double weight) {
p.weight = weight;
return this;
}
// 设置score
public PersonBuilder score(int score) {
p.score = score;
return this;
}
// 设置loc
public PersonBuilder loc(String street, String roomNo) {
p.loc = new Location(street, roomNo);
return this;
}
// 返回对象
public Person build() {
return p;
}
}
}
class Location {
String street;
String roomNo;
public Location(String street, String roomNo) {
this.street = street;
this.roomNo = roomNo;
}
}
main函数里面使用:
创建Person对象的时候,可以随意选择对应的方法,创建不同的对象
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TerrainBuilder builder = new ComplexTerrainBuilder();
Terrain t = builder.buildFort().buildMine().buildWall().build();
//new Terrain(Wall w, Fort f, Mine m)
//Effective Java
Person p = new Person.PersonBuilder()
.basicInfo(1, "zhangsan", 18)
//.score(20)
.weight(200)
//.loc("bj", "23")
.build();
}
}