C++ 手动实现双向链表(作业版)
双向链表,并实现增删查改等功能
首先定义节点类,类成员包含当前节点的值, 指向下一个节点的指针和指向上一个节点的指针
//节点定义
template
class Node {
public:
Node* prior;
T value;
Node* next;
Node():value(0),prior(nullptr),next(nullptr) {}
Node(T n):prior(nullptr),value(n),next(nullptr) {}
}; 然后是链表类的定义,主要包含了增删查改等功能
//双向链表定义
template
class LinkList_doubly {
public:
Node* firstNode;
Node* lastNode;
LinkList_doubly();
LinkList_doubly(int n, const T* arr);
LinkList_doubly(const LinkList_doubly& link);
~LinkList_doubly();
LinkList_doubly& push_back(T n);
LinkList_doubly& push_front(T n);
LinkList_doubly& insert(int pos, int n, T* arr);
LinkList_doubly& pop_front();
LinkList_doubly& pop_back();
LinkList_doubly& remove(int pos, int num);
LinkList_doubly& reverse();
T& operator[](int n);
T& at(int n);
LinkList_doubly& replace(int pos, int n, T* arr);
int getLen() {return len;}
void clear() {this->~LinkList_doubly();}
void display();
private:
int len = 0;
Node* getNode_next(int n);
}; 各个函数解释:
LinkList_doubly(); 默认构造函数
LinkList_doubly(const T* arr, int len); 一般构造函数
LinkList_doubly(const LinkList
~LinkList_doubly(); 析构函数
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
LinkList_doubly
T& operator[](int n); 重载[ ]运算符,返回第n个节点的值
T& at(int n); 与[ ]一样,只不过会检查索引是否越界
LinkList_doubly
int getLen() {return len;} 返回长度,因为len是private
void clear() {this->~LinkList();} 清除链表
void display(); 显示链表所有元素
Node
#include
using namespace std;
template
class Node {
public:
Node* prior;
T value;
Node* next;
Node():value(0),prior(nullptr),next(nullptr) {}
Node(T n):prior(nullptr),value(n),next(nullptr) {}
};
template
class LinkList_doubly {
public:
Node* firstNode;
Node* lastNode;
LinkList_doubly();
LinkList_doubly(int n, const T* arr);
LinkList_doubly(const LinkList_doubly& link);
~LinkList_doubly();
LinkList_doubly& push_back(T n);
LinkList_doubly& push_front(T n);
LinkList_doubly& insert(int pos, int n, T* arr);
LinkList_doubly& pop_front();
LinkList_doubly& pop_back();
LinkList_doubly& remove(int pos, int num);
LinkList_doubly& reverse();
T& operator[](int n);
T& at(int n);
LinkList_doubly& replace(int pos, int n, T* arr);
int getLen() {return len;}
void clear() {this->~LinkList_doubly();}
void display();
private:
int len = 0;
Node* getNode_next(int n);
};
//默认构造函数
template
LinkList_doubly::LinkList_doubly() {
firstNode = nullptr;
lastNode = nullptr;
len = 0;
}
//一般构造函数,用数组进行初始化
template
LinkList_doubly::LinkList_doubly(int n, const T* arr) {
Node* temp1 = nullptr;
Node* temp2 = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
temp1 = new Node (arr[i]);
if ( i == 0 )
firstNode = temp1;
if ( i == n-1 )
lastNode = temp1;
temp1->prior = temp2;
if ( i > 0 )
temp2->next = temp1;
temp2 = temp1;
}
this->len = n;
}
//拷贝构造函数
template
LinkList_doubly::LinkList_doubly(const LinkList_doubly& link) {
this->firstNode = link.firstNode;
this->lastNode = link.lastNode;
this->len = link.getLen();
}
//析构函数
template
LinkList_doubly::~LinkList_doubly() {
this->len = 0;
Node* temp = firstNode;
lastNode = nullptr;
while ( firstNode ) {
temp = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
delete temp;
temp = nullptr;
}
}
//在尾部添加一个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::push_back(T n) {
Node* newNode = new Node (n);
newNode->prior = lastNode;
lastNode->next = newNode;
lastNode = newNode;
len++;
return *this;
}
//在头部添加一个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::push_front(T n) {
Node* newNode = new Node (n);
newNode->next = firstNode;
firstNode->prior = newNode;
firstNode = newNode;
len++;
return *this;
}
//在position位置插入n个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::insert(int pos, int n, T* arr) {
if ( pos < 0 || pos > len-1 ) {
cout << "[error]: illegal insert index, please check" << endl;
exit(0);
}
if ( pos == 0 ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ )
this->push_front(arr[n-1-i]); //push_front自带len++
return *this;
}
Node* temp_end = getNode_next(pos);
Node* temp_front = getNode_next(pos-1);
Node* temp_new = nullptr;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) {
temp_new = new Node (arr[i]);
temp_front->next = temp_new;
temp_new->prior = temp_front;
temp_front = temp_front->next;
}
temp_front->next = temp_end;
temp_end->prior = temp_front;
len += n;
return *this;
}
//删除第一个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::pop_front() {
if ( len == 0 ) {
cout << "[warning]: linkedlist is empty" << endl;
return *this;
}
Node* temp = firstNode;
firstNode = firstNode->next;
firstNode->prior = nullptr;
delete temp;
len--;
return *this;
}
//删除最后一个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::pop_back() {
if ( len == 0 ) {
cout << "[warning]: linkedlist is empty" << endl;
return *this;
}
Node* temp = lastNode;
lastNode = lastNode->prior;
lastNode->next = nullptr;
delete temp;
len--;
return *this;
}
//删除position开始的num个元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::remove(int pos, int num) {
if ( pos > len-1 || len < 0 || pos < 0 || pos > len-1) {
cout << "[error]: illegal remove position, please check again" << endl;
exit(0);
} else if ( pos + num - 1 > len-1) {
cout << "[error]: remove index out of range" << endl;
exit(0);
}
//如果删除了首元节点或者尾节点,要考虑firstNode和lastNode的指向,用pop比较方便
if ( pos == 0 ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < num; i++ )
this->pop_front();
return *this;
}
if ( pos + num == len ) {
for ( int i = 0; i < num; i++ )
this->pop_back();
return *this;
}
Node* temp_front = getNode_next(pos-1);
Node* temp_end = getNode_next(pos+num);
Node* temp = getNode_next(pos);
while ( 1 ) {
Node* node = temp;
temp = temp->next;
delete node;
if ( temp == temp_end ) {
break;
}
}
temp_front->next = temp_end;
temp_end->prior = temp_front;
len -= num;
return *this;
}
//替换元素
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::replace(int pos, int n, T* arr) {
Node* temp = getNode_next(pos);
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) {
temp->value = arr[i];
temp = temp->next;
}
return *this;
}
//反转链表,终极偷懒写法,实在不想动脑子了
template
LinkList_doubly& LinkList_doubly::reverse() {
const int num = len;
T arr[num];
Node* temp = firstNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < this->len; i++ ) {
arr[i] = temp->value;
temp = temp->next;
}
temp = lastNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < this->len; i++ ) {
temp->value = arr[i];
temp = temp->prior;
}
return *this;
}
//访问第n个元素
template
T& LinkList_doubly::operator[](int n){
Node* temp = nullptr;
if ( n <= len/2 ) {
temp = firstNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) {
temp = temp->next;
}
} else {
temp = lastNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < len-1-n; i++ ) {
temp = temp->prior;
}
}
return temp->value;
}
//访问第n个元素,增加索引检查
template
T& LinkList_doubly::at(int n){
if ( n < 0 || n > len-1 ) {
cout << "[error]:index out of range" << endl;
exit(0);
}
return (*this)[n];
}
//获取第n个Node的next指针
template
Node* LinkList_doubly::getNode_next(int n) {
if ( n > len-1 ) {
cout << "[error]: illegal index" << endl;
}
Node* temp = firstNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) {
temp = temp->next;
}
return temp;
}
//显示链表所有元素,会对链表正反向一致性进行检查
template
void LinkList_doubly::display() {
const int num = len;
T arr1[num];
T arr2[num];
Node* temp = firstNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < this->len; i++ ) {
arr1[i] = temp->value;
temp = temp->next;
}
temp = lastNode;
for ( int i = 0; i < this->len; i++ ) {
arr2[i] = temp->value;
temp = temp->prior;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < this->len; i++ ) {
if ( arr1[i] != arr2[len-1-i] ) {
cout << "第"<len; i++ ) {
cout << temp->value << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
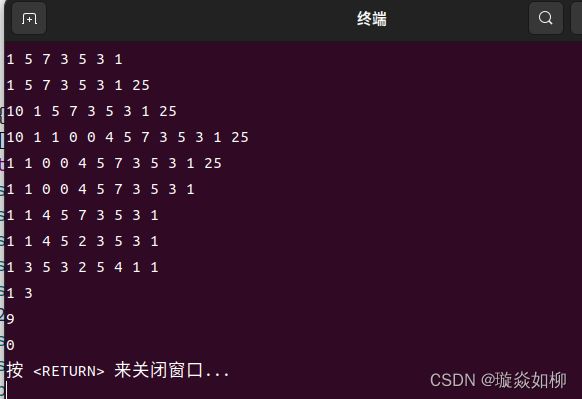
int main() {
int arr[] = {1,5,7,3,5,3,1};
LinkList_doubly link(sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int), arr);
link.display();
link.push_back(25);
link.display();
link.push_front(10);
link.display();
int arr2[] = {1,0,0,4};
link.insert(0,sizeof(arr2)/sizeof(int), arr2);
link.display();
link.pop_front();
link.display();
link.pop_back();
link.display();
link.remove(7,2);
link.display();
int arr3[] = {2,3,5};
link.replace(4, sizeof(arr3)/sizeof(int), arr3);
link.display();
link.reverse();
link.display();
cout << link[8] << " " << link.at(3) << endl;
cout << link.getLen() << endl;
link.~LinkList_doubly();
cout << link.getLen() << endl;
}