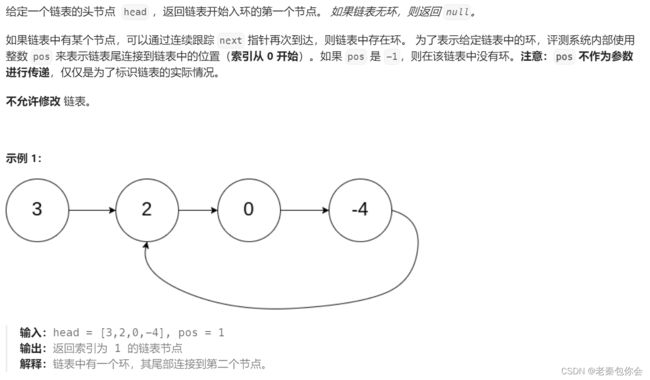
链表练习题
作者前言
✨✨✨✨✨✨
作者介绍:
作者id:老秦包你会,
简单介绍:
喜欢学习C语言和python等编程语言,是一位爱分享的博主,有兴趣的小可爱可以来互讨
个人主页::小小页面
gitee页面:秦大大
一个爱分享的小博主 欢迎小可爱们前来借鉴
练习
- **作者前言**
- 移除链表元素
- 分割链表
- 反向链表
- 链表中倒数第k个结点
- 相交链表
- 环形链表
- 环形链表 II
- 合并两个有序链表
- 链表的回文结构
- 随机链表的复制
移除链表元素
移除链表元素

这道题有多种思路,双指针法
思路:遍历一遍,在中途中我们要找出要删除的节点,并把要删除的节点进行free,我们要注意的就是
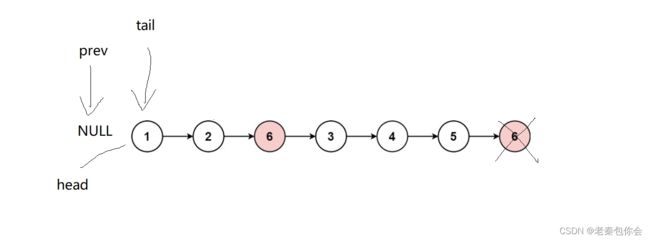
我们通过判断tail->val是否为要删除的值,如果不是就prev = tail, tail = tail->next,如果是的话,我们就要删除, 然后tail存储下一个节点的地址,而prev不变,
我们要考虑一些情况,当我们删除的是第一个节点,那head存储的地址就要改变,
循环结束的条件就是
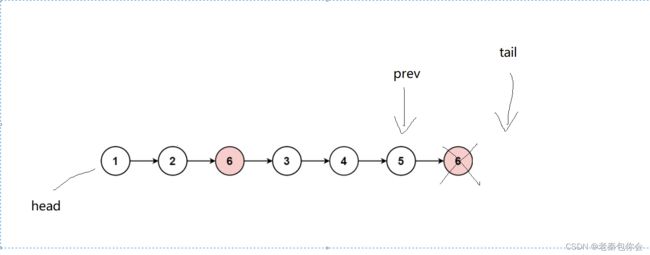
tail的值为NULL,就是循环停止的时候
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* prev = NULL;
//遍历一遍
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val == val)
{
struct ListNode* nex = cur->next;
if (prev)
{
prev->next = nex;
}
//判断是否要删除第一个节点
else
{
head = nex;
}
free(cur);
cur = nex;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
cur去判断该节点是否符合,引用新的newhead指向符合条件的节点,符合就添加到newhead,不是就free,然后cur指向下一个节点,tail不动,有两种特殊情况,一种的head=NULL,一种是free最后一个节点,前一个节点的next没有NULL
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* tail = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val != val)
{
if (tail == NULL)
{
newnode = cur;
tail = cur;
}
else
{
tail->next = cur;
tail = cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
//保存下一个节点
struct ListNode* p = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = p;
}
}
//假设head为NULL
if (tail)
tail->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
哨兵位方法

这里的头节点不是d1而是head也称哨兵位头节点
这个带哨兵位的链表的好处就是头节点一定存在,地址不为空,

struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
//创建哨兵位
struct ListNode* newnode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* tail = newnode;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val != val)
{
tail->next = cur;
cur = cur->next;
tail = tail->next;
}
else
{
//保存下一个节点
struct ListNode* p = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = p;
}
}
//假设head为NULL
tail->next = NULL;
//释放哨兵
struct ListNode*p = newnode->next;
free(newnode);
return p;
}
分割链表
分割链表
方法1:创建两个空链表 链表1存储小于X的所有节点,链表2存储大于等于x的所有节点,然后两个链表链接起来,

ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
//小
struct ListNode *head1 = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode *tail1 = head1;
//大
struct ListNode *head2 = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode *tail2 = head2;
struct ListNode *cur = pHead;
while (cur)
{
if(cur->val < x)
{
tail1->next = cur;
tail1 = tail1->next;
}
else
{
tail2->next = cur;
tail2 = tail2->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
//防止head2最后一个节点的next不为NULL
tail2->next = NULL;
tail1->next = head2->next;
struct ListNode *ph = head1->next;
free(head1);
free(head2);
return ph;
}
我们需要注意的是head2的最后一个节点的next可能指向野指针,也可能形成环状链表,
反向链表
反向链表
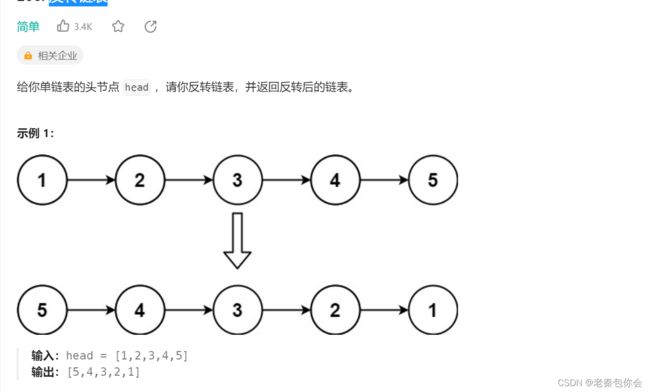
方法1
三指针反转

主要进行交换的是n1和n2这两个指针,n3指针是辅助n2能找到下一个节点的地址
循环结束就是

当n2 = NULL或者是n1->next = NULL循环结束
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return head;
struct ListNode *n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode *n2 = head;
struct ListNode *n3 = head->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
return n1;
}
方法二:创建空链表,头插

思路:把旧链表的节点取下来,然后头插到新链表中
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* newnode = NULL;
struct ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct ListNode* pn = cur->next;
cur->next = newnode;
newnode = cur;
cur = pn;
}
return newnode;
}
链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点

方法1暴力法
先求出链表的长度,然后长度减去倒数的个数,再遍历一遍
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode* tail = pListHead;
if (tail) {
int size = 1;
while (tail->next) {
tail = tail->next;
size++;
}
tail = pListHead;
if (k > size) {
return NULL;
}
while (size > k) {
tail = tail->next;
size--;
}
return tail;
}
else {
return NULL;
}
}
时间复杂度是O(n)
但是不够高效
方法二
双指针距离差
创建两个指针,指向头节点,然后一个一个节点也走k步,然后两个指针一起走,当走k步的那个指针为NULL就结束

struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k ) {
struct ListNode* fast = pListHead, *slow = pListHead;
//fast先走k步
while(k--)
{
//防止为空
if(fast ==NULL)
return NULL;
fast = fast->next;
}
//一起走
while (fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
相交链表
相交链表

方法1:暴力法
A中的每个节点的地址在B链表都找一遍,然后比较,时间复杂度是O(n^2)
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
struct ListNode* taila = headA;
while(taila)
{
struct ListNode* tailb = headB;
while(tailb)
{
if(taila == tailb)
{
return tailb;
}
tailb = tailb->next;
}
taila = taila->next;
}
return NULL;
}
方法2
两个链表遍历一遍,然后找出尾节点进行比较地址,相同则继续计算长度,长度大的先走,走到剩下的长度和另外一个链表的长度一样,然后一起走,然后一一比较节点的地址

struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
if(!(headA && headB))
return NULL;
struct ListNode* tail1 = headA;
struct ListNode* tail2 = headB;
int conut1 =1;
int conut2 =1;
//找出尾节点,随便算出cah
while(tail1->next)
{
tail1 = tail1->next;
conut1++;
}
while(tail2->next)
{
tail2 = tail2->next;
conut2++;
}
if(!(tail1 == tail2))
return NULL;
struct ListNode* maxh = (conut1 >= conut2 ? headA : headB);
struct ListNode* minh = (conut1 >= conut2 ? headB : headA);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <abs(conut1 -conut2);i++)
{
maxh = maxh->next;
}
while(minh)
{
if(maxh == minh)
{
return maxh;
}
maxh = maxh->next;
minh = minh->next;
}
return NULL;
}
环形链表
环形链表
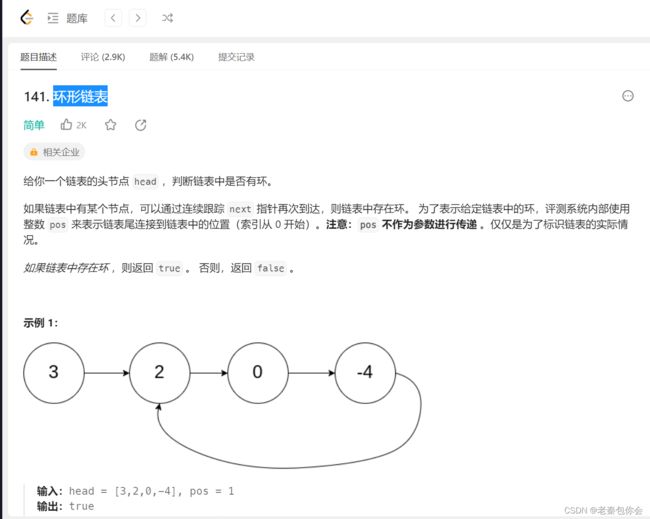
这里考察带环链表
代环链表:尾节点的next指向链表的任意节点
看到这里可能会想到遍历一遍,找出尾节点,这样很容易陷入死循环,或者有人想到找节点比较,怎么找,因为节点是不确定的,无法这样
这个题可以使用漏洞法
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode*tail = head;
int a = 10002;
while(tail)
{
if(a==0)
return true;
a--;
tail = tail->next;
}
return false;
}

可以判断如果循环次数超出节点数就可以判断是有环的,否则就是无环的这种方法不推荐
方法2:快慢指针速度差法
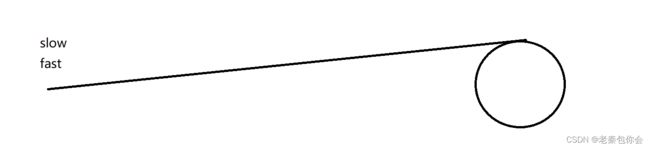
slow一次走一步,fast一次走两步,当slow刚刚进入到环里面时

fast和slow的距离就是X,转换成fast追逐slow
v1 t - v2t = X, t = x/(v1 - v2)
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
return true;
}
return false;
}
环形链表 II
slow一次走一步,fast一次走两步,当slow刚刚进入到环里面时,fast和slow的距离就是X,转换成slow和fast在入环点的经过x的长度相遇,c为环的长度
写成 2(L+x) = n*c + L +x
化简成L = (n-1)*c + c - x

所以我们求出入环点可以这样,一个指针在fast和slow相遇的节点开始循环,一个指针从头节点开始走,最终一定会在入环点相遇
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode*tail = head;
struct ListNode*prev = head;
//找出相遇点
while (prev && prev->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
prev = prev->next ->next;
//找出相遇点
if(tail == prev)
{ //开始两个指针走
tail = head;
while(tail != prev)
{
tail = tail->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
return tail;
}
}
return NULL;
}
转换相交链表解决
先找出相遇点,然后一个指针指向相遇点的下一个节点,把相遇点的next =NULL,然后一个指针从head开始走,变成找两链表找交点
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
if(!(headA && headB))
return NULL;
struct ListNode* tail1 = headA;
struct ListNode* tail2 = headB;
int conut1 =1;
int conut2 =1;
//找出尾节点,随便算出cah
while(tail1->next)
{
tail1 = tail1->next;
conut1++;
}
while(tail2->next)
{
tail2 = tail2->next;
conut2++;
}
if(!(tail1 == tail2))
return NULL;
struct ListNode* maxh = (conut1 >= conut2 ? headA : headB);
struct ListNode* minh = (conut1 >= conut2 ? headB : headA);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i <abs(conut1 -conut2);i++)
{
maxh = maxh->next;
}
while(minh)
{
if(maxh == minh)
{
return maxh;
}
maxh = maxh->next;
minh = minh->next;
}
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct ListNode*tail = head;
struct ListNode*prev = head;
//找出相遇点
while (prev && prev->next)
{
tail = tail->next;
prev = prev->next ->next;
//找出相遇点
if(tail == prev)
{ //开始两个指针走
tail = head;
struct ListNode*p = prev->next;
prev->next = NULL;
p = getIntersectionNode(tail, p);
if(p)
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
合并两个有序链表
合并两个有序链表
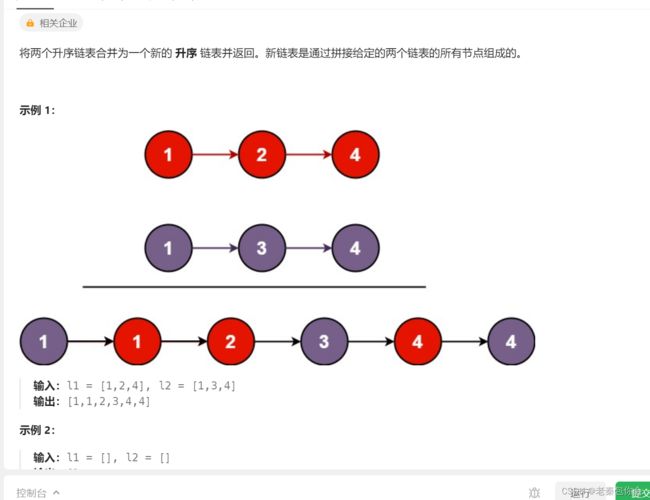
思路:这里的思路和顺序表的(两顺序表合成一个顺序表)很像,创建两个指针分别指向l1和l2的头节点,创建一个空链表和一个指针,l1和l2的链表的节点进行判断,然后放入到空链表中,然后把剩下的节点一并插入到链表中
这里的空链表可以是带哨兵位的也可以不要
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2)
{
if(list1 == NULL)
return list2;
if(list2 == NULL)
return list1;
struct ListNode*newnode =NULL;
struct ListNode*prev =NULL;
struct ListNode* tail1 = list1;
struct ListNode* tail2 = list2;
while(tail1 && tail2)
{
if(tail1->val < tail2->val)
{
if(prev == NULL)
{
newnode = tail1;
prev = tail1;
tail1 = tail1->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = tail1;
prev = prev->next;
tail1 = tail1->next;
}
}
else
{
if(prev == NULL)
{
newnode = tail2;
prev = tail2;
tail2 = tail2->next;
}
else
{
prev->next = tail2;
prev = prev->next;
tail2 = tail2->next;
}
}
}
if(tail1)
prev->next = tail1;
if(tail2)
prev->next = tail2;
return newnode;
// if(list1 == NULL)
// return list2;
// if(list2 == NULL)
// return list1;
// //哨兵位
// struct ListNode *newnode = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
// struct ListNode* tail1 = list1;
// struct ListNode* tail2 = list2;
// struct ListNode* prev = newnode;
// while(tail1 && tail2)
// {
// if(tail1->val > tail2->val)
// {
// prev->next = tail2;
// tail2 = tail2->next;
// }
// else
// {
// prev->next = tail1;
// tail1 = tail1->next;
// }
// prev = prev->next;
// }
// if(tail1)
// prev->next = tail1;
// if(tail2)
// prev->next = tail2;
// struct ListNode *ph = newnode->next;
// free(newnode);
// return ph;
}
链表的回文结构
链表的回文结构
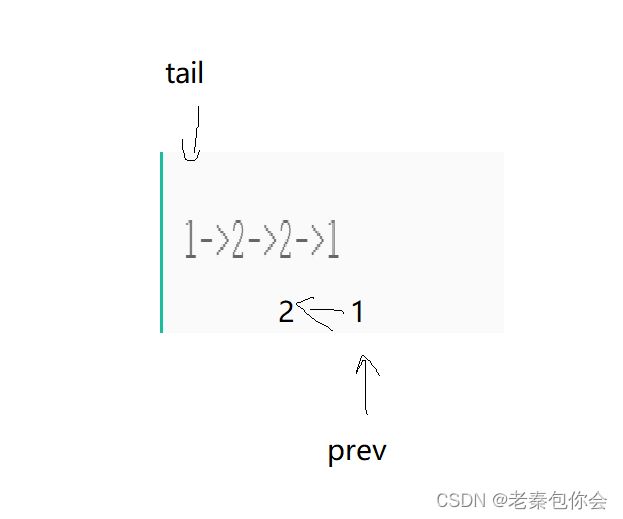
思路:我们可以先找到这个链表的中间节点,然后把后半段的链表逆置过来,然后转换成两个链表(节点数一样的)对应的节点一一比较
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == NULL)
return true;
//双指针速度差法
struct ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast ->next ->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
//slow为中间节点
//后部分反转
struct ListNode *n1 = NULL;
struct ListNode *n2 = slow;
struct ListNode *n3 = slow->next;
while(n2)
{
n2->next = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = n3;
if(n3)
n3 = n3->next;
}
//fast为第二个链表头节点地址
fast = n1;
slow = head;
while(slow && fast)
{
if(slow->val != fast->val)
{
return false;
}
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return true;
//双指针比较
}
};
随机链表的复制
随机链表的复制

思路:
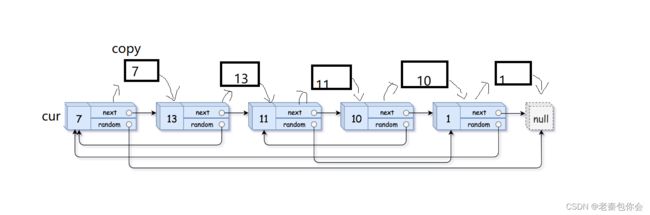
我们可以像上图一样,往每个原节点的后面插入一个和该节点相同值的节点,然后我们在原节点的找到random, 每个原节点的后一个节点就是复制的节点,我们可以通过这种特性把复制的节点的random进行连接,然后创建一个空链表,把复制的节点进行连接,
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
struct Node *cur = head;
while(cur)
{
//创建节点
struct Node *copy = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
struct Node *cp = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
copy->next = cp;
cur = cp;
}
//开始指向random
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node *cp = cur->next;
if(cur->random)
cp->random = cur->random->next;
else
cp->random = NULL;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
//创建空链表,然后尾插
//创建哨兵位
struct Node *newnode = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node *tail = newnode;
//开始尾插
cur = head;
while(cur)
{
struct Node *new = cur->next;
tail->next = new;
tail = tail->next;
cur = new->next;
}
struct Node *p = newnode->next;
free(newnode);
return p;
}