算法与数据结构——算法基础——二叉树(java)(b站左程云课程笔记整理)
二叉树
了解一个二叉树的递归序、先序、中序、后序
递归序:每个数会被打印三次(可以理解为前中后)
先序:头左右
中序:左头右
后序:左右头
public static class Node {
public int value;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int data) {
this.value = data;
}
}
//先序
public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
preOrderRecur(head.left);
preOrderRecur(head.right);
}
//中序
public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
inOrderRecur(head.left);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
inOrderRecur(head.right);
}
//后序
public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
posOrderRecur(head.left);
posOrderRecur(head.right);
System.out.print(head.value + " ");
}
补充:任何递归都可以改成非递归(通过自己压栈的方式)
先序:
先将头节点入栈
从栈中弹出一个节点
打印(处理)
先把右节点压入栈,再压左节点
循环
//先序
public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head!=null){
Stack<Node> stack=new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
head=stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value+" ");
if(head.right!=null){
stack.push(head.right);
}
if(head.left!=null){
stack.push(head.left);
}
}
}
}
后序:
在前序的基础上做修改:先压左栈再压右栈,则此时顺序为:头右左
准备一个辅助栈
在弹出的时候压入辅助栈
等全部节点都进入辅助栈后,最后一次性弹出并打印辅助栈中所有的节点
顺序即为左右头(后序)
//后序
public static void posOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head!=null){
Stack<Node> stack1=new Stack<>();
Stack<Node> stack2=new Stack<>();
stack1.push(head);
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
head=s1.pop();
s2.push(head);
if(head.left!=null){
s1.push(head.left);
}
if(head.right!=null){
s1.push(head.right);
}
}
while(!s2.isEmpty()){
System.out.print(s2.pop().value+" ");
}
}
}
//后序2
public static void posOrderUnRecur2(Node head){
if(head!=null){
Stack<Node> stack=new Stack<>();
stack.push(head);
Node help=null;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
help=stack.peek();//查看栈顶对象 不删除
if(help.left!=null&&head!=help.left&&head!=help.right){
stack.push(head.left);
}else if(help.right!=null&&head!=help.right){
stack.push(help.right);
}else{
System.out.print(stack.pop().value+" ");
head=help;
}
}
}
}
中序
每棵子树,整棵树左边界依次进栈(一直left),依次弹出的过程中打印并且对弹出节点的右树重复该过程
每一颗树都可以被左边界划分
而左边界的顺序是头到左
主要按照这个顺序入栈,得到的顺序就是左头
而我们操作的过程是每弹出一个节点就压右节点
右节点所对应的那颗子树又是可以被左边界划分(顺序为头左,压栈出栈的顺序为左头)
因此操作的过程就是中序遍历
//中序
public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head){
if(head!=null){
Stack<Node> stack=new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty()||head!=null){
if(head!=null){//这里的处理条件很妙
stack.push(head);
head=head.left;
}else{
head=stack.pop();
System.out.print(head.value+" ");
head=head.right;
}
}
}
}
二叉树的宽度优先遍历(层序遍历)
深度优先遍历其实就是先序遍历
宽度优先遍历使用 队列 头+打印+左+右
public static void widthPrint(Node head){
if(head==null){
return;
}
Queue<Node> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(head);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
head=queue.poll();
System.out.println(head.value);
if(head.left!=null){
queue.add(head.left);
}
if(head.right!=null){
queue.add(head.right);
}
}
}
求一颗二叉树的最大宽度
给定一个二叉树,编写一个函数来获取这个树的最大宽度。树的宽度是所有层中的最大宽度。这个二叉树与满二叉树(full binary tree)结构相同,但一些节点为空。
每一层的宽度被定义为两个端点(该层最左和最右的非空节点,两端点间的null节点也计入长度)之间的长度。
keypoint:记录每一层的最左边的位置
宽度优先搜索
宽度优先搜索顺序遍历每个节点的过程中,我们记录节点的 position 信息,对于每一个深度,第一个遇到的节点是最左边的节点,最后一个到达的节点是最右边的节点。
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
Queue<AnnotatedNode> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(root, 0, 0));
int curDepth = 0, left = 0, ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
AnnotatedNode a = queue.poll();
if (a.node != null) {
queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(a.node.left, a.depth + 1, a.pos * 2));
queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(a.node.right, a.depth + 1, a.pos * 2 + 1));
//第一次到达下一层,记录左节点的pos值
if (curDepth != a.depth) {
curDepth = a.depth;
left = a.pos;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, a.pos - left + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
class AnnotatedNode {
TreeNode node;
int depth, pos;
AnnotatedNode(TreeNode n, int d, int p) {
node = n;
depth = d;
pos = p;
}
}
深度优先搜索
按照深度优先的顺序,我们记录每个节点的 position 。对于每一个深度,第一个到达的位置会被记录在 left[depth] 中。
然后对于每一个节点,它对应这一层的可能宽度是 pos - left[depth] + 1 。我们将每一层这些可能的宽度去一个最大值就是答案。
class Solution {
int ans;
Map<Integer, Integer> left;
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
ans = 0;
left = new HashMap();
dfs(root, 0, 0);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, int pos) {
if (root == null) return;
left.computeIfAbsent(depth, x-> pos);
ans = Math.max(ans, pos - left.get(depth) + 1);
dfs(root.left, depth + 1, 2 * pos);
dfs(root.right, depth + 1, 2 * pos + 1);
}
}
左神 有些用例通过不了 因为力扣上的题目要求两端点间的null节点也计入长度
他的题目是整颗二叉树每一层中最多有几个节点
class Solution {
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int max=0;
Map<TreeNode,Integer> hashmap=new HashMap<>();
int curlevel=1;
int curlevelnodes=0;
hashmap.put(root,curlevel);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
int level=hashmap.get(node);
if(level==curlevel){
curlevelnodes++;
}else{
max=Math.max(max,curlevelnodes);
curlevel++;
curlevelnodes=1;
}
if(node.left!=null){
hashmap.put(node.left,level+1);
queue.add(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
hashmap.put(node.right,level+1);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
//最后需要再做一次比较保存最后一层的结果
max=Math.max(max,curlevelnodes);
return max;
}
}
如何判断一颗二叉树是搜索二叉树
搜索二叉树:每一棵子树,左树的节点比父节点小,右树的节点比父节点大
中序遍历 中序遍历的顺序是升序的二叉树就是搜索二叉树
左神 力扣上通过不了 应该是help变量static的问题以及int的问题
public static int help=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public static boolean isBST(Node head){
if(head==null){
return true;
}
boolean leftRes=isBST(head.left);
if(!leftRes){
return false;
}
if(head.value<=help){//这里等号的使用还要是否有重复值
return false;
}else{
help=head.value;
}
return isBST(head.right);
}
力扣上可以通过的版本
class Solution {
long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; // 记录上一个节点的值,初始值为Long的最小值
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
boolean l=isValidBST(root.left);
if(root.val<=pre){
return false;
}else{
pre=root.val;
}
return l&&isValidBST(root.right);
}
}
非递归的方式
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root!=null){
long help=Long.MIN_VALUE;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty()||root!=null){
if(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}else{
root=stack.pop();
if(root.val<=help){
return false;
}else{
help=root.val;
}
root=root.right;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
另一种递归方式
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return isValidBST(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode node, long lower, long upper) {
if (node == null) {
return true;
}
if (node.val <= lower || node.val >= upper) {
return false;
}
return isValidBST(node.left, lower, node.val) && isValidBST(node.right, node.val, upper);
}
}
如何判断一棵树是完全二叉树
完全二叉树:堆:只有最后一层可能不是满的,即使最后一层不满,也是从左往右是满的
宽度优先遍历
两个条件返回false
1.任一节点有右节点没有左节点
2.在1的条件下,如果遇到了第一个左右孩子不全的情况,后续节点都应该为叶子节点——》需设置触发器
class Solution {
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return true;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
boolean isOpen=false;
TreeNode l=null;
TreeNode r=null;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
root=queue.poll();
l=root.left;
r=root.right;
if((l==null&&r!=null)||(isOpen&&(l!=null||r!=null))){
return false;
}
if(l!=null){
queue.add(l);
}
if(r!=null){
queue.add(r);
}
//触发器
if(l==null||r==null){
isOpen=true;
}
}
return true;
}
}
如何判断一棵树是满二叉树
思路一:
先得到二叉树的最大深度以及节点数
如果满足2^n-1的关系则是满二叉树
二:二叉树递归套路
class Solution{
public boolean isFullTree(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return true;
}
ReturnType res=process(root);
return res.nodes==((1>>res.depth)-1);//这里注意逻辑右移的优先级很低
}
public class ReturnType{
int depth;
int nodes;
ReturnType(int d,int n){
this.depth=d;
this.nodes=n;
}
}
public ReturnType process(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return new ReturnType(0,0);
}
ReturnType leftData=process(node.left);
ReturnType rightData=process(node.right);
int depth=Math.max(leftData.depth,rightData.depth)+1;
int nodes=leftData.nodes+rightData.nodes+1;
return new ReturnType(depth,nodes);
}
}
如何判断一棵树是平衡二叉树
二叉树递归套路
从左子树和右子树上获取信息
分析题目:需要什么信息
比如平衡二叉树:三个条件同时成立才是平衡二叉树
1.左子树是平衡二叉树
2.右子树是平衡二叉树
3.左右子树高度差不超过1
因此需要从左右子树上获取的信息都是两个:是否是平衡的、高度
整个过程是设置黑盒和拆解黑盒的过程
如果能把黑盒完美的拆掉 那递归过程就连起来了
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return process(root).isBal;
}
public ReturnType process(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return new ReturnType(true,0);//base case
}
ReturnType left=process(node.left);
ReturnType right=process(node.right);
int height=Math.max(left.height,right.height)+1;
boolean isBal=left.isBal&&right.isBal&&Math.abs(left.height-right.height)<2;
return new ReturnType(isBal,height);
}
public class ReturnType{
int height;
boolean isBal;
ReturnType(boolean ib,int h){
this.isBal=ib;
this.height=h;
}
}
}
递归套路 能解决二叉树的一切树形DP问题(动态规划)
黑盒+拆黑盒+root==null的情况+可能性罗列
代码结构:类+主方法+辅助方法
给定两个二叉树的节点node1和node2,找到他们的最低公共祖先节点
思路一:准备一个HashMap把整颗树的每一个节点以及他的父节点存进去
准备一个HashSet把node1节点到整棵树的父节点的路上的点全都加到HashSet中
遍历node2节点到整棵树的父节点的路上是否有点存在HashSet中
返回找到的第一个点
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
HashMap<TreeNode,TreeNode> hashmap=new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put(root,root);
HashSet<TreeNode> hashset=new HashSet<>();
hashset.add(root);
process(root,hashmap);
while(p!=hashmap.get(p)){//注意退出while的条件
hashset.add(p);
p=hashmap.get(p);
}
while(q!=hashmap.get(q)){
if(hashset.contains(q)){
break;
}else{
q=hashmap.get(q);
}
}
return q;
}
public void process(TreeNode node,HashMap hashmap){
if(node==null){
return;
}
if(node.left!=null){
hashmap.put(node.left,node);
}
if(node.right!=null){
hashmap.put(node.right,node);
}
process(node.left,hashmap);
process(node.right,hashmap);
}
}
思路二:题目默认node1和node2有最低公共祖先
情况可以分为两大类
1.node1是node2的最低公共祖先或者node2是node1的最低公共祖先
2.node1与node2通过汇聚才能找到最低公共祖先
一个子树上如果没有node1也没有node2则返回空
有node1则返回node1,有node2则返回node2
一个子树上的左右子树都有返回值则返回当前节点
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null||root==p||root==q){
return root;
}
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
//两棵子树都不为空返回当前节点
if(left!=null&&right!=null){
return root;
}
//左右两棵子树有一个不为空则返回不为空的那个
return left!=null?left:right;
}
}
在二叉树中找到一个节点的后继节点
后继节点是指每个节点的中序遍历的下一个节点
前驱节点是指每个节点的中序遍历的前一个节点
按照普通的二叉树要找到一个节点的后继节点的话需要遍历整颗二叉树
时间复杂度是O(N)
现在通过新的一种二叉树结构(加了一个parent指向自己的父节点)
在时间复杂度上做优化
优化成O(k)
k是指每个节点到下一个节点的真实距离
要求x节点的后继节点
分情况讨论:
1.x有右树,后继节点为右树上的最左节点2.x无右树,从x往上看,x是不是父亲的左孩子,不是就再往上看,直到该节点是父亲的左孩子,后继节点为父亲
3.整棵树总有一个节点是最右边的,它的后继节点是null(通过第二种情况找不到是父亲的左孩子节点,返回null)
public TreeNode getSuccessorNode(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return node;
}
if(node.right!=null){
return getLeftMost(node.right);
}else{
TreeNode parent=node.parent;
while(parent!=null&&parent.left!=node){
node=parent;
parent=node.parent;
}
return parent;//头节点的pare
}
}
public TreeNode getLeftMost(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return node;
}
while(node.left!=null){
node=node.left;
}
return node;
}
二叉树的序列化和反序列化
内存里的一棵树如何变成字符串形式,又如何冲字符串形式变成内存里的树
只能存在一对一关系
先序
下划线表示一个值的结束
#表示空
反序列化过程就是用下划线分割字符串形成一个字符数组还原二叉树
public String serialByPre(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return "#_";
}
String res=root.value+"_";
res+=serialByPre(root.left);
res+=serialByPre(root.right);
return res;
}
public TreeNode reconByPreString(String preStr){
String[] values=preStr.split("_");
Queue<String> queue=new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i!=values.length;i++){
queue.offer(values[i]);
}
return reconPreOrder(queue);
}
public TreeNode reconPreOrder(Queue queue){
String value=queue.poll();
if(value.equals("#")){
return null;
}
TreeNode head=new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(value));
head.left=reconPreOrder(queue);
head.right=reconPreOrder(queue);
return head;
}
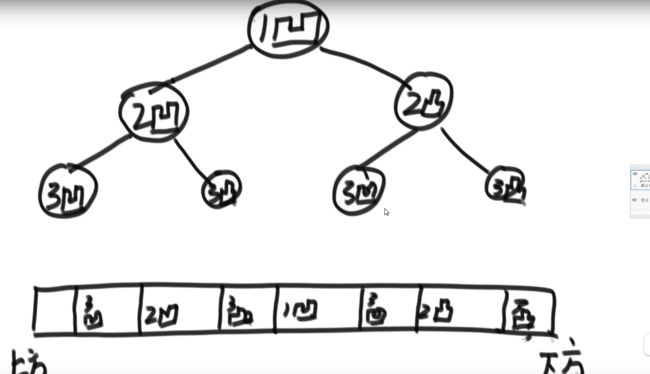
纸条对折问题
每次折纸条,在原来的痕迹的上下分别多一条凹和一条凸
打印所有折叠方向就是这颗二叉树的中序遍历
//模拟了一颗实际上并不存在的二叉树
//i是指当前节点的层数 N是指一共的层数 down==true:凹 down==false:凸
public void printProcess(int i,int N,boolean down){
if(i>N){
return;
}
printProcess(i+1,N,true);
System.out.println(down?"凹":"凸");
printProcess(i+1,N,false);
}