Qsort函数实现对各类型数组中元素的排序
目录
函数介绍
函数使用案例:
(一)对int型数组的排序
(二)对char型数组的排序
(三)对浮点型数组的排序
(四)对结构体类型的排序
(五) 模仿qsort的功能实现一个通用的冒泡排序
函数介绍
作用:对指向的数组中的数组元素进行快速排序
头文件: stdlib.h
函数原型:void qsort (void* base, size_t num, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void*,const void*));
参数解释:
base: 指向需要排序的数组首元素的指针num: 数组中元素个数size: 每个元素大小(以字节为单位)compar: 比较函数,用于确定两个元素之间的顺序关系
比较函数需要满足以下条件:
- 第一个参数小于第二个参数,返回负数
- 两个参数相等,返回零
- 第一个参数大于第二个参数,返回正数
Void*类型的指针是通用指针,可以接受任意类型的地址
函数使用案例:
(一)对int型数组的排序
#include
#include
#include
//排序整型数组
int my_cmp(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
int main()
{
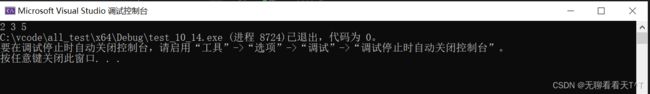
int num[3] = { 2,5,3 };
qsort(num, 3, sizeof(num[0]), my_cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("%d ", num[i]);
}
return 0;
} (二)对char型数组的排序
#include
#include
#include
//排序char型数组
int my_cmp(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(char*)a - *(char*)b);
}
int main()
{
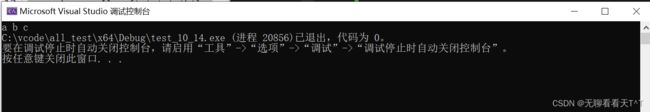
char num[] = { 'a','c','b' };
qsort(num, 3, sizeof(num[0]), my_cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("%c ", num[i]);
}
return 0;
}
(三)对浮点型数组的排序
注意事项:由于浮点数存在精度问题,在计算机内部表示时可能会出现舍入误差,所以如果还是在上面的基础上进行简单修改的化就会导致数组中的3.14>3.20的情况发生,所以需要更加严谨的
#include
#include
#include
//排序浮点型型数组
int my_cmp(const void* a, const void* b)
{
double num1 = *(const double*)a;
double num2 = *(const double*)b;
if (num1 < num2)
return -1;
else if (num1 > num2)
return 1;
return 0; // 相等情况
}
int main()
{
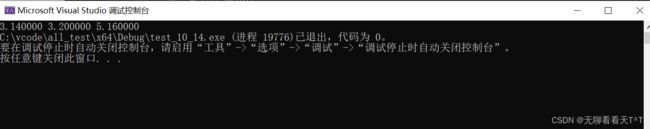
double arr[] = { 3.14, 5.16, 3.20 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
qsort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), my_cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%lf ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
} (四)对结构体类型的排序
同时包含了对字符串数组的排序
#include
#include
#include
//按单个字节交换位置
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, size_t width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
//模拟qsort函数
void bubble_sort(void* base, size_t sz, size_t width, int (*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
}
}
}
}
//声明结构体(以后会写到,现在先用着)
struct Stu {
char name[20];
int age;
};
//计算年龄差值与0的关系
int cmp_stu_by_age(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return ((struct Stu*)e1)->age - ((struct Stu*)e2)->age;
}
//利用strcmp函数比较字符的ASCII码
int cmp_stu_by_name(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return strcmp(((struct Stu*)e1)->name, ((struct Stu*)e2)->name);
}
//测试bubble_sort排序结构体数据
void test2()
{
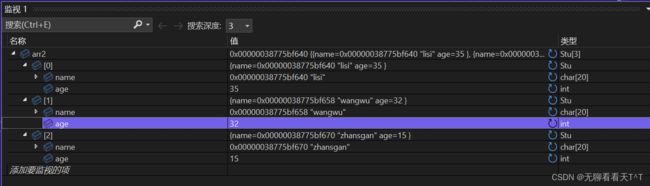
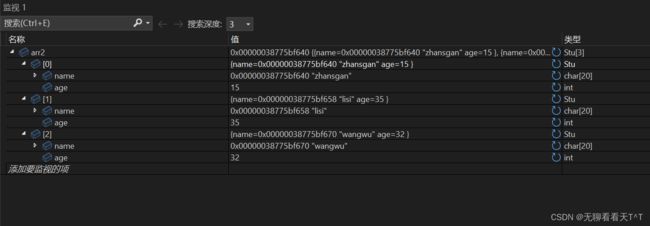
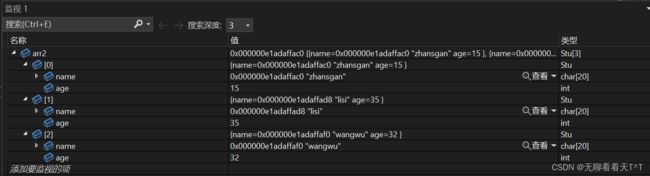
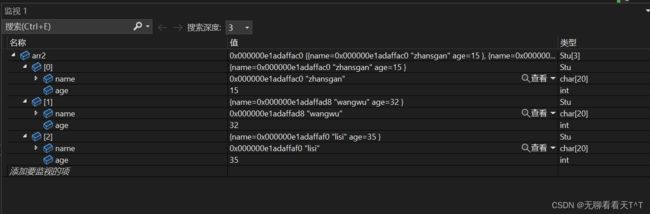
struct Stu arr2[] = { {"zhansgan", 15}, {"lisi", 35},{"wangwu", 32} };
int sz = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(arr2[0]); //sz = 3 , sizeof(arr2[0]) = 24
//bubble_sort(arr2, sz, sizeof(arr2[0]), cmp_stu_by_age);
bubble_sort(arr2, sz, sizeof(arr2[0]), cmp_stu_by_name);
}
int main()
{
test2();
return 0;
} 对于名字的排序结果:
对于年龄的排序结果:
(五) 模仿qsort的功能实现一个通用的冒泡排序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include
#include
#include
void Swap(char* buf1, char* buf2, size_t width)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < width; i++)
{
char tmp = *buf1;
*buf1 = *buf2;
*buf2 = tmp;
buf1++;
buf2++;
}
}
void bubble_sort(void* base, size_t sz, size_t width, int (*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2))
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz - 1; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < sz - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (cmp((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width) > 0)
{
Swap((char*)base + j * width, (char*)base + (j + 1) * width, width);
}
}
}
}
int cmp_int(const void* e1, const void* e2)
{
return *(int*)e1 - *(int*)e2;
}
void print_arr(int arr[], int sz)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
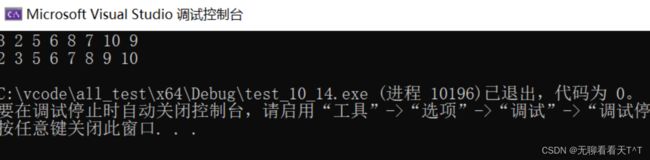
void test1()
{
int arr[] = { 3,2,5,6,8,7,10,9 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
print_arr(arr, sz);
bubble_sort(arr, sz, sizeof(arr[0]), cmp_int);
print_arr(arr, sz);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
} ~over~