Linux设备驱动——PCI总线的初始化
目录
一、概述
二、初始化分析
2.1 pcibus_class_init
2.2 pci_driver_init
2.3 acpi_pci_init
2.3.1 基于ACPI的PCI设备枚举过程
2.4 pci_arch_init
2.5 pci_slot_init
2.6 pci_subsys_init
三、参考
一、概述
二、初始化分析
pci初始化涉及很多函数,这里根据下面的启动顺序来分析:
[root@localhost 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64]# cat System.map | grep pci | grep initcall
ffffffff81ef23a0 t __initcall_pcibus_class_init2
ffffffff81ef23a8 t __initcall_pci_driver_init2
ffffffff81ef2450 t __initcall_acpi_pci_init3
ffffffff81ef2478 t __initcall_pci_arch_init3
ffffffff81ef2580 t __initcall_pci_slot_init4
ffffffff81ef2678 t __initcall_pci_subsys_init4
ffffffff81ef27c0 t __initcall_pcibios_assign_resources5
ffffffff81ef27f8 t __initcall_pci_apply_final_quirks5s
ffffffff81ef2808 t __initcall_pci_iommu_initrootfs
ffffffff81ef2d30 t __initcall_pci_proc_init6
ffffffff81ef2d38 t __initcall_pcie_portdrv_init6
ffffffff81ef2d48 t __initcall_pcie_pme_service_init6
ffffffff81ef2d58 t __initcall_pci_hotplug_init6
ffffffff81ef2d60 t __initcall_pcied_init6
ffffffff81ef2d68 t __initcall_pci_stub_init6
ffffffff81ef2e08 t __initcall_platform_pci_module_init6
ffffffff81ef2e30 t __initcall_serial_pci_driver_init6
ffffffff81ef2ec8 t __initcall_intel_lpss_pci_driver_init6
ffffffff81ef2f28 t __initcall_ehci_pci_init6
ffffffff81ef2f38 t __initcall_ohci_pci_init6
ffffffff81ef2f50 t __initcall_xhci_pci_init6
ffffffff81ef3280 t __initcall_pci_resource_alignment_sysfs_init7
ffffffff81ef3288 t __initcall_pci_sysfs_init7
ffffffff81ef32d0 t __initcall_pci_mmcfg_late_insert_resources7
2.1 pcibus_class_init
[driver/pci/probe.c]
static struct class pcibus_class = {
.name = "pci_bus",
.dev_release = &release_pcibus_dev,
.dev_groups = pcibus_groups,
};
static int __init pcibus_class_init(void)
{
return class_register(&pcibus_class);
}2.2 pci_driver_init
[driver/pci/pci-driver.c]
static int __init pci_driver_init(void)
{
int ret;
ret = bus_register(&pci_bus_type);
if (ret)
return ret;
#ifdef CONFIG_PCIEPORTBUS
ret = bus_register(&pcie_port_bus_type);
if (ret)
return ret;
#endif
return 0;
}PCI bus的注册,不多说,基本的驱动模型,这里仅列一下pci 的bus_type:
struct bus_type pci_bus_type = {
.name = "pci",
.match = pci_bus_match,
.uevent = pci_uevent,
.probe = pci_device_probe,
.remove = pci_device_remove,
.shutdown = pci_device_shutdown,
.dev_groups = pci_dev_groups,
.bus_groups = pci_bus_groups,
.drv_groups = pci_drv_groups,
.pm = PCI_PM_OPS_PTR,
.num_vf = pci_bus_num_vf,
.force_dma = true,
};2.3 acpi_pci_init
这里有一个ACPI(Advanced Configuration and Power Interface),我的理解是ACPI提供了电源、硬件和固件的接口。这里只关注软件角度的ACPI的结构——在屏蔽了硬件细节的同时,提供了一系列系统资源,包括:
- ACPI寄存器
- ACPI BIOS
- ACPI Tables
2.3.1 基于ACPI的PCI设备枚举过程
整个ACPI的初始化在:
Bus.c (drivers\acpi):static int __init acpi_init(void)这是一个subsys_initcall(4)级别的初始化
这里关注和PCI有关的初始化acpi_init->acpi_scan_init->acpi_pci_root_init / acpi_bus_scan
static struct acpi_scan_handler pci_root_handler = {
.ids = root_device_ids,
.attach = acpi_pci_root_add,
.detach = acpi_pci_root_remove,
.hotplug = {
.enabled = true,
.scan_dependent = acpi_pci_root_scan_dependent,
},
};
void __init acpi_pci_root_init(void)
{
acpi_hest_init();
if (acpi_pci_disabled)
return;
pci_acpi_crs_quirks();
acpi_scan_add_handler_with_hotplug(&pci_root_handler, "pci_root");
}
接下来:
acpi_bus_scan(ACPI_ROOT_OBJECT)
->acpi_bus_attach(device);
->acpi_scan_attach_handler(device);static int acpi_scan_attach_handler(struct acpi_device *device)
{
struct acpi_hardware_id *hwid;
int ret = 0;
list_for_each_entry(hwid, &device->pnp.ids, list) {
const struct acpi_device_id *devid;
struct acpi_scan_handler *handler;
handler = acpi_scan_match_handler(hwid->id, &devid);
if (handler) {
if (!handler->attach) {
device->pnp.type.platform_id = 0;
continue;
}
device->handler = handler;
ret = handler->attach(device, devid);
if (ret > 0)
break;
device->handler = NULL;
if (ret < 0)
break;
}
}
return ret;
}遍历的链表就是上面注册的,可以看到先acpi_scan_match_handler,就是分别通过match和id进行匹配,如果匹配成功了就执行handler的attach函数,这就对应到了上面的acpi_pci_root_add函数,函数比较长,分段来看:
static int acpi_pci_root_add(struct acpi_device *device,
const struct acpi_device_id *not_used)
{
unsigned long long segment, bus;
acpi_status status;
int result;
struct acpi_pci_root *root;
acpi_handle handle = device->handle;
int no_aspm = 0;
bool hotadd = system_state == SYSTEM_RUNNING;
root = kzalloc(sizeof(struct acpi_pci_root), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!root)
return -ENOMEM;
segment = 0;
status = acpi_evaluate_integer(handle, METHOD_NAME__SEG, NULL,
&segment);
...
/* Check _CRS first, then _BBN. If no _BBN, default to zero. */
root->secondary.flags = IORESOURCE_BUS;
status = try_get_root_bridge_busnr(handle, &root->secondary);
...
root->device = device;
root->segment = segment & 0xFFFF;
strcpy(acpi_device_name(device), ACPI_PCI_ROOT_DEVICE_NAME);
strcpy(acpi_device_class(device), ACPI_PCI_ROOT_CLASS);
device->driver_data = root;
if (hotadd && dmar_device_add(handle)) {
result = -ENXIO;
goto end;
}
pr_info(PREFIX "%s [%s] (domain %04x %pR)\n",
acpi_device_name(device), acpi_device_bid(device),
root->segment, &root->secondary);
root->mcfg_addr = acpi_pci_root_get_mcfg_addr(handle);
negotiate_os_control(root, &no_aspm);
...
}上述过程就是分配一个acpi_pci_root,并对其进行初始化,一般情况下仅含有一个HOST桥。
struct acpi_pci_root {
struct acpi_device * device;
struct pci_bus *bus;
u16 segment;
struct resource secondary; /* downstream bus range */
u32 osc_support_set; /* _OSC state of support bits */
u32 osc_control_set; /* _OSC state of control bits */
phys_addr_t mcfg_addr;
};- 通过ACPI表获取HOST主桥的segment和bus号
看一下填充后在虚拟机上的打印信息:
[ 0.212357] ACPI: PCI Root Bridge [PCI0] (domain 0000 [bus 00-7f])来看下后半部分:
/*
* Scan the Root Bridge
* --------------------
* Must do this prior to any attempt to bind the root device, as the
* PCI namespace does not get created until this call is made (and
* thus the root bridge's pci_dev does not exist).
*/
root->bus = pci_acpi_scan_root(root);
if (no_aspm)
pcie_no_aspm();
pci_acpi_add_bus_pm_notifier(device);
device_set_wakeup_capable(root->bus->bridge, device->wakeup.flags.valid);
if (hotadd) {
pcibios_resource_survey_bus(root->bus);
pci_assign_unassigned_root_bus_resources(root->bus);
/*
* This is only called for the hotadd case. For the boot-time
* case, we need to wait until after PCI initialization in
* order to deal with IOAPICs mapped in on a PCI BAR.
*
* This is currently x86-specific, because acpi_ioapic_add()
* is an empty function without CONFIG_ACPI_HOTPLUG_IOAPIC.
* And CONFIG_ACPI_HOTPLUG_IOAPIC depends on CONFIG_X86_IO_APIC
* (see drivers/acpi/Kconfig).
*/
acpi_ioapic_add(root->device->handle);
}
pci_lock_rescan_remove();
pci_bus_add_devices(root->bus);
pci_unlock_rescan_remove();
return 1;
pci_acpi_scan_root枚举PCI设备
[arch/x86/pci/acpi.c]
struct pci_bus *pci_acpi_scan_root(struct acpi_pci_root *root)
{
int domain = root->segment;
int busnum = root->secondary.start;
int node = pci_acpi_root_get_node(root);
struct pci_bus *bus;
bus = pci_find_bus(domain, busnum);
if (bus) {
...
memcpy(bus->sysdata, &sd, sizeof(sd));
} else {
struct pci_root_info *info;
info = kzalloc_node(sizeof(*info), GFP_KERNEL, node);
if (!info)
dev_err(&root->device->dev,
"pci_bus %04x:%02x: ignored (out of memory)\n",
domain, busnum);
else {
info->sd.domain = domain;
info->sd.node = node;
info->sd.companion = root->device;
bus = acpi_pci_root_create(root, &acpi_pci_root_ops,
&info->common, &info->sd);
}
}
...
return bus;
}通过pci_find_bus查找HOST Bridge对应的segment,bus num有没有被注册,如果注册了就更新一下信息,没有注册则调用acpi_pci_root_create创建,该函数中有两个比较重要,一个是pci_create_root_bus
struct pci_bus *pci_create_root_bus(struct device *parent, int bus,
struct pci_ops *ops, void *sysdata, struct list_head *resources)
{
int error;
struct pci_host_bridge *bridge;
bridge = pci_alloc_host_bridge(0);
if (!bridge)
return NULL;
bridge->dev.parent = parent;
list_splice_init(resources, &bridge->windows);
bridge->sysdata = sysdata;
bridge->busnr = bus;
bridge->ops = ops;
error = pci_register_host_bridge(bridge);
if (error < 0)
goto err_out;
return bridge->bus;
err_out:
kfree(bridge);
return NULL;
}- 分配一个主桥结构,就是一个device,其parent为NULL,为PCI设备的顶级顶点
- 接下来注册主桥
static int pci_register_host_bridge(struct pci_host_bridge *bridge)
{
...
bus = pci_alloc_bus(NULL);
bridge->bus = bus;
/* Temporarily move resources off the list */
list_splice_init(&bridge->windows, &resources);
bus->sysdata = bridge->sysdata;
bus->msi = bridge->msi;
bus->ops = bridge->ops;
bus->number = bus->busn_res.start = bridge->busnr; //注意这
...
dev_set_name(&bridge->dev, "pci%04x:%02x", pci_domain_nr(bus),
bridge->busnr);
err = device_register(&bridge->dev);
bus->bridge = get_device(&bridge->dev);
bus->dev.class = &pcibus_class;
bus->dev.parent = bus->bridge;
dev_set_name(&bus->dev, "%04x:%02x", pci_domain_nr(bus), bus->number);
name = dev_name(&bus->dev);
err = device_register(&bus->dev);
pcibios_add_bus(bus);
/* Create legacy_io and legacy_mem files for this bus */
pci_create_legacy_files(bus);
down_write(&pci_bus_sem);
list_add_tail(&bus->node, &pci_root_buses);
up_write(&pci_bus_sem);
return 0;
unregister:
put_device(&bridge->dev);
device_unregister(&bridge->dev);
free:
kfree(bus);
return err;
}一个主桥下面新建了一个pci_bus, 其也对应一个设备,这两个设备都注册到系统中,注意他们的名字
dev_set_name(&bridge->dev, "pci%04x:%02x", pci_domain_nr(bus), bridge->busnr);
dev_set_name(&bus->dev, "%04x:%02x", pci_domain_nr(bus), bus->number);下图显示了注册后的PCI设备分级情况,其他的PCI设备都挂在主桥下
[root@localhost /]# ls /sys/devices/pci0000:00
0000:00:00.0 0000:00:07.7 0000:00:15.1 0000:00:15.6 0000:00:16.3 0000:00:17.0 0000:00:17.5 0000:00:18.2 0000:00:18.7
0000:00:01.0 0000:00:0f.0 0000:00:15.2 0000:00:15.7 0000:00:16.4 0000:00:17.1 0000:00:17.6 0000:00:18.3 firmware_node
0000:00:07.0 0000:00:10.0 0000:00:15.3 0000:00:16.0 0000:00:16.5 0000:00:17.2 0000:00:17.7 0000:00:18.4 pci_bus
0000:00:07.1 0000:00:11.0 0000:00:15.4 0000:00:16.1 0000:00:16.6 0000:00:17.3 0000:00:18.0 0000:00:18.5 power
0000:00:07.3 0000:00:15.0 0000:00:15.5 0000:00:16.2 0000:00:16.7 0000:00:17.4 0000:00:18.1 0000:00:18.6 uevent
我画了个示意图,pci桥本身也是一个设备和其下的pci device一样都挂在同一总线上:
pci_scan_child_bus包含整个的枚举过程,简单而言就是一个DFS,这个过程最终确定了每级PCI桥的bus范围:[secondary, subordinate]
pci_scan_child_bus(bus)
scan each slot on current bus
scan each function on current slot
if (function exist) //vendor id & device id
alloc pci_dev
setup pci_dev //header type:0 for PCI agent, 1 for PCI bridge. multi-function or single-function device
max = current bus start busnr
for each bridge on current bus
if bridge not scaned // secondary = subordinate = 0
set bridge PCI_PRIMARY_BUS register // primary=busnr, secondary=primary+1, subordinate=0xFF
max = pci_scan_child_bus(next(bus)) // next busnr start with max+1
set bridge PCI_SUBORDINATE_BUS register // subordinate = max
下面来看一下函数的实现:
static unsigned int pci_scan_child_bus_extend(struct pci_bus *bus,
unsigned int available_buses)
{
/* Go find them, Rover! */
for (devfn = 0; devfn < 256; devfn += 8) {
nr_devs = pci_scan_slot(bus, devfn);
...
for_each_pci_bridge(dev, bus) {
unsigned int buses = 0;
if (!hotplug_bridges && normal_bridges == 1) {
...
} else if (dev->is_hotplug_bridge) {
...
}
cmax = max;
max = pci_scan_bridge_extend(bus, dev, cmax, buses, 1);
used_buses += max - cmax;
}pci_scan_slot->pci_scan_single_device
struct pci_dev *pci_scan_single_device(struct pci_bus *bus, int devfn)
{
struct pci_dev *dev;
dev = pci_get_slot(bus, devfn);
if (dev) {
pci_dev_put(dev);
return dev;
}
dev = pci_scan_device(bus, devfn);
if (!dev)
return NULL;
pci_device_add(dev, bus);
return dev;
}- 这个函数就是分配,配置pci_dev,并将其加入设备模型
接下来就是扫描PCI桥的递归过程了:
static int pci_scan_bridge_extend(struct pci_bus *bus, struct pci_dev *dev,
int max, unsigned int available_buses,
int pass)
{
...
pci_read_config_dword(dev, PCI_PRIMARY_BUS, &buses);
primary = buses & 0xFF;
secondary = (buses >> 8) & 0xFF;
subordinate = (buses >> 16) & 0xFF;
if ((secondary || subordinate) && !pcibios_assign_all_busses() &&
!is_cardbus && !broken) {
unsigned int cmax;
...
} else {
...
/* Clear errors */
pci_write_config_word(dev, PCI_STATUS, 0xffff);
child = pci_find_bus(pci_domain_nr(bus), max+1);
if (!child) {
child = pci_add_new_bus(bus, dev, max+1);
if (!child)
goto out;
pci_bus_insert_busn_res(child, max+1,
bus->busn_res.end);
}
max++;
if (available_buses)
available_buses--;
buses = (buses & 0xff000000)
| ((unsigned int)(child->primary) << 0)
| ((unsigned int)(child->busn_res.start) << 8)
| ((unsigned int)(child->busn_res.end) << 16);
/* We need to blast all three values with a single write */
pci_write_config_dword(dev, PCI_PRIMARY_BUS, buses);
if (!is_cardbus) {
child->bridge_ctl = bctl;
max = pci_scan_child_bus_extend(child, available_buses);
} else {
...
}
/* Set subordinate bus number to its real value */
pci_bus_update_busn_res_end(child, max);
pci_write_config_byte(dev, PCI_SUBORDINATE_BUS, max);
}
...
}
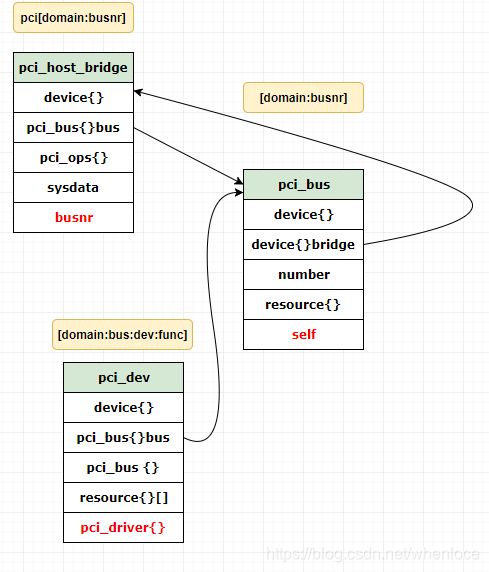
下面的图展示了一个HOST Bridge 下一个pci dev和一个pci桥的数据结构情况:
- 一个Host Bridge是一个设备(但不是PCI设备),
- 对于一个pci agent来说,使用pci_dev来描述
- 每个PCI桥对应一个pci_bus结构和一个pci_dev
2.4 pci_arch_init
[arch/x86/pci/init.c]
static __init int pci_arch_init(void)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT
int type = 0;
type = pci_direct_probe();
#endif
if (!(pci_probe & PCI_PROBE_NOEARLY))
pci_mmcfg_early_init();
if (x86_init.pci.arch_init && !x86_init.pci.arch_init())
return 0;
#ifdef CONFIG_PCI_BIOS
pci_pcbios_init();
#endif
/*
* don't check for raw_pci_ops here because we want pcbios as last
* fallback, yet it's needed to run first to set pcibios_last_bus
* in case legacy PCI probing is used. otherwise detecting peer busses
* fails.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT
pci_direct_init(type);
#endif
...
return 0;
}CONFIG_PCI_BIOS表示使用BIOS枚举结果
CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT表示由OS重新枚举
我的系统上:
[root@localhost 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64]# cat .config | grep CONFIG_PCI_BIOS
[root@localhost 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64]# cat .config | grep CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT
CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT=y
这里分析CONFIG_PCI_DIRECT
int __init pci_direct_probe(void)
{
if ((pci_probe & PCI_PROBE_CONF1) == 0)
goto type2;
if (!request_region(0xCF8, 8, "PCI conf1"))
goto type2;
if (pci_check_type1()) {
raw_pci_ops = &pci_direct_conf1;
port_cf9_safe = true;
return 1;
}
...
}这里
unsigned int pci_probe = PCI_PROBE_BIOS | PCI_PROBE_CONF1 | PCI_PROBE_CONF2 |
PCI_PROBE_MMCONF;所以使用type1,申请了0xCF8, 0xCFC两个I/O port资源,使用这种方式访问PCI配置空间:
const struct pci_raw_ops pci_direct_conf1 = {
.read = pci_conf1_read,
.write = pci_conf1_write,
};2.5 pci_slot_init
[driver/pci/slot.c]
static int pci_slot_init(void)
{
struct kset *pci_bus_kset;
pci_bus_kset = bus_get_kset(&pci_bus_type);
pci_slots_kset = kset_create_and_add("slots", NULL,
&pci_bus_kset->kobj);
if (!pci_slots_kset) {
printk(KERN_ERR "PCI: Slot initialization failure\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
return 0;
}2.6 pci_subsys_init
static int __init pci_subsys_init(void)
{
/*
* The init function returns an non zero value when
* pci_legacy_init should be invoked.
*/
if (x86_init.pci.init()) {
if (pci_legacy_init()) {
pr_info("PCI: System does not support PCI\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
}
pcibios_fixup_peer_bridges();
x86_init.pci.init_irq();
pcibios_init();
return 0;
}这里init_irq是:
Boot.c (arch\x86\kernel\acpi): x86_init.pci.init = pci_acpi_init;int __init pci_acpi_init(void)
{
struct pci_dev *dev = NULL;
if (acpi_noirq)
return -ENODEV;
printk(KERN_INFO "PCI: Using ACPI for IRQ routing\n");
acpi_irq_penalty_init();
pcibios_enable_irq = acpi_pci_irq_enable;
pcibios_disable_irq = acpi_pci_irq_disable;
x86_init.pci.init_irq = x86_init_noop;
if (pci_routeirq) {
/*
* PCI IRQ routing is set up by pci_enable_device(), but we
* also do it here in case there are still broken drivers that
* don't use pci_enable_device().
*/
printk(KERN_INFO "PCI: Routing PCI interrupts for all devices because \"pci=routeirq\" specified\n");
for_each_pci_dev(dev)
acpi_pci_irq_enable(dev);
}
return 0;
}
系统中输出“PCI: Using ACPI for IRQ routing”,因此不会执行pci_legacy_init
三、参考
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/lizuobin2/article/details/51828594