Python实现桌面悬浮窗(显示网速,内存,CPU)
Python实现桌面悬浮窗(显示网速,内存,CPU)
-
- 背景介绍
- 编程环境
- UI窗口设计
- 设置窗口透明与边框
-
- 重写鼠标事件,以拖动窗口
- 实现贴边收起
- 获取网速,内存,CPU信息
- 建立QThread线程,更新网速等信息
- 运行
- 效果
- 打包EXE
- 总结
- 源码链接
背景介绍
习惯了自己的电脑上火绒网速监测小工具,自己写一个,就可以在其他没装火绒的电脑上用啦。
实现的功能:
1.显示网速,CPU,内存占用;
2.贴边收起;
3.改变颜色,右键退出菜单;
编程环境
python3.9 (第三方库 pyside2 pyqt5 psutil)
本来计划使用pyside2的,但资料有点儿少,中途改到pyqt5了,不过两个库基本是兼容的
UI窗口设计
- 使用pyside2库下的qtdesigner大致画出窗口
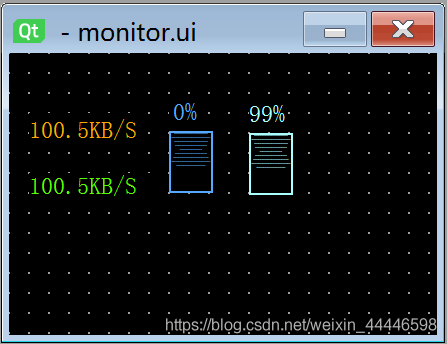
2. 将ui生成py文件便于后续修改: pyside2-uic.exe monitor.ui > monitor_ui.py
设置窗口透明与边框
# 设置窗口无边框; 设置窗口置顶;
self.setWindowFlags(Qt.FramelessWindowHint | Qt.WindowStaysOnTopHint | Qt.Tool)
# 设置窗口背景透明
# self.setAttribute(Qt.WA_TranslucentBackground)
# 设置透明度(0~1)
self.setWindowOpacity(0.9)
# 设置鼠标为手状
self.setCursor(Qt.PointingHandCursor)
重写鼠标事件,以拖动窗口
由于设置了无边框,窗口无法拖动,需要重写鼠标响应事件,让鼠标按下移动时,窗口跟随鼠标移动;此外,在mouseMoveEvent中加入了限制窗口不能移出主屏幕的代码;
#鼠标按下时,记录鼠标相对窗口的位置
def mousePressEvent(self, event: QMouseEvent):
if event.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
# event.pos() 鼠标相对窗口的位置
# event.globalPos() 鼠标在屏幕的绝对位置
self._startPos = event.pos()
# 鼠标移动时,移动窗口跟上鼠标;同时限制窗口位置,不能移除主屏幕
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event: QMouseEvent):
# event.pos()减去最初相对窗口位置,获得移动距离(x,y)
self._wmGap = event.pos() - self._startPos
# 移动窗口,保持鼠标与窗口的相对位置不变
# 检查是否移除了当前主屏幕
# 左方界限
final_pos = self.pos() + self._wmGap
if self.frameGeometry().topLeft().x() + self._wmGap.x() <= 0:
final_pos.setX(0)
# 上方界限
if self.frameGeometry().topLeft().y() + self._wmGap.y() <= 0:
final_pos.setY(0)
# 右方界限
if self.frameGeometry().bottomRight().x() + self._wmGap.x() >= self.screen_width:
final_pos.setX(self.screen_width - self.window_width)
# 下方界限
if self.frameGeometry().bottomRight().y() + self._wmGap.y() >= self.screen_height:
final_pos.setY(self.screen_height - self.window_height)
self.move(final_pos)
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event: QMouseEvent):
if event.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
self._startPos = None
self._wmGap = None
if event.button() == Qt.RightButton:
self._startPos = None
self._wmGap = None
此处参考:python百行代码自制电脑端网速悬浮窗
实现贴边收起
实现贴边收起需要重写两个鼠标响应函数,enterEvent与leaveEvent;当鼠标进入窗口时,判断是否需要将隐藏的窗口显示;当鼠标离开窗口时,判断是否需要将窗口隐藏;贴边效果借助QT的QPropertyAnimation实现;
当多屏幕时,为了不让窗口移动到另一个屏幕,贴边收起的效果做了相应调整;
def enterEvent(self, event):
self.hide_or_show('show', event)
def leaveEvent(self, event):
self.hide_or_show('hide', event)
def hide_or_show(self, mode, event):
# 获取窗口左上角x,y
pos = self.frameGeometry().topLeft()
if mode == 'show' and self.hidden:
# 窗口左上角x + 窗口宽度 大于屏幕宽度,从右侧滑出
if pos.x() + self.window_width >= self.screen_width:
# 需要留10在里边,否则边界跳动
self.startAnimation(self.screen_width - self.window_width, pos.y())
event.accept()
self.hidden = False
# 窗口左上角x 小于0, 从左侧滑出
elif pos.x() <= 0:
self.startAnimation(0, pos.y())
event.accept()
self.hidden = False
# 窗口左上角y 小于0, 从上方滑出
elif pos.y() <= 0:
self.startAnimation(pos.x(), 0)
event.accept()
self.hidden = False
elif mode == 'hide' and (not self.hidden):
if pos.x() + self.window_width >= self.screen_width:
# 留10在外面
self.startAnimation(self.screen_width - 10, pos.y(), mode, 'right')
event.accept()
self.hidden = True
elif pos.x() <= 0:
# 留10在外面
self.startAnimation(10 - self.window_width, pos.y(), mode, 'left')
event.accept()
self.hidden = True
elif pos.y() <= 0:
# 留10在外面
self.startAnimation(pos.x(), 10 - self.window_height, mode, 'up')
event.accept()
self.hidden = True
def startAnimation(self, x, y, mode='show', direction=None):
animation = QPropertyAnimation(self, b"geometry", self)
# 滑出动画时长
animation.setDuration(200)
# 隐藏时,只留10在外边,防止跨屏
# QRect限制其大小,防止跨屏
num = QApplication.desktop().screenCount()
if mode == 'hide':
if direction == 'right':
animation.setEndValue(QRect(x, y, 10, self.window_height))
elif direction == 'left':
# 多屏时采用不同的隐藏方法,防止跨屏
if num < 2:
animation.setEndValue(QRect(x, y, self.window_width, self.window_height))
else:
animation.setEndValue(QRect(0, y, 10, self.window_height))
else:
if num < 2:
animation.setEndValue(QRect(x, y, self.window_width, self.window_height))
else:
animation.setEndValue(QRect(x, 0, self.window_width, 10))
else:
animation.setEndValue(QRect(x, y, self.window_width, self.window_height))
animation.start()
此处参考:PyQt5实现仿QQ贴边隐藏功能
获取网速,内存,CPU信息
需要借助第三方库psutil;
def get_net_speed(self):
# 获取网速,当sent_pre或receive_pre为-1时,初始化窗口
if self.sent_pre == -1 or self.receive_pre == -1:
self.upload_bytes = 0
self.download_bytes = 0
try:
self.sent_pre = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
self.receive_pre = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
except RuntimeError:
# 如果获取失败,重新获取
self.sent_pre = -1
self.receive_pre = -1
else:
try:
# 长时间休眠后,会出现RuntimeError
self.upload_bytes = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent - self.sent_pre
self.download_bytes = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv - self.receive_pre
except RuntimeError:
self.sent_pre = -1
self.receive_pre = -1
self.upload_string = '↑' + '0B/S'
self.download_string = '↓' + '0B/S'
else:
self.sent_pre += self.upload_bytes
self.receive_pre += self.download_bytes
self.upload_string = '↑' + WorkThread.standard_net_speed(self.upload_bytes)
self.download_string = '↓' + WorkThread.standard_net_speed(self.download_bytes)
def get_cpu_mem(self):
self.cpu_percent = (psutil.cpu_percent(interval=0.0, percpu=False))
self.mem_percent = psutil.virtual_memory().percent
if self.cpu_percent >= 100:
self.cpu_percent = 99
if self.mem_percent >= 100:
self.mem_percent = 99
self.cpu_lines = ''.join([self.one_line + '\n' for i in range(int(self.cpu_percent) // 10)])
self.mem_lines = ''.join([self.one_line + '\n' for i in range(int(self.mem_percent) // 10)])
self.cpu_percent_string = "%d" % self.cpu_percent + '%'
self.mem_percent_string = "%d" % self.mem_percent + '%'
建立QThread线程,更新网速等信息
建立一个QThread线程,重写run方法,每隔一秒获取网速,CPU等信息,并通过pyqtSignal通知UI窗口更新;while循环会随着主线程结束自动结束;
class WorkThread(QThread):
# 实例化一个信号对象,类变量,需要定义在函数体外
trigger = pyqtSignal()
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.receive_pre = -1
self.sent_pre = -1
self.upload_bytes = 0
self.upload_string = '↑' + '0B/S'
self.download_bytes = 0
self.download_string = '↓' + '0B/S'
self.one_line = ''.join(['*' for i in range(40)])
self.cpu_percent = 0
self.cpu_percent_string = '0%'
self.mem_percent = 0
self.mem_percent_string = '0%'
self.cpu_lines = ''
self.mem_lines = ''
def run(self):
# 重写QThread 的run 函数
while True:
self.get_computer_info()
# 信号发出通知面板更新
self.trigger.emit()
time.sleep(1)
运行
运行前获取主显示器的大小,设置窗口大小,初始位置;
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 设置屏幕自适应
QtCore.QCoreApplication.setAttribute(Qt.AA_EnableHighDpiScaling)
app = QApplication([])
# 获取主显示器分辨率
screen_width = app.primaryScreen().geometry().width()
screen_height = app.primaryScreen().geometry().height()
stats = Monitor()
stats.setupUi()
stats.retranslateUi()
# 设置最初出现的位置
window_width = stats.geometry().width()
window_height = stats.geometry().height()
stats.setGeometry(screen_width - window_width - 10, screen_height//2 - 150, window_width, window_height)
# 启动QThread
stats.work_threading.start()
stats.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
效果
网速,CPU,内存显示
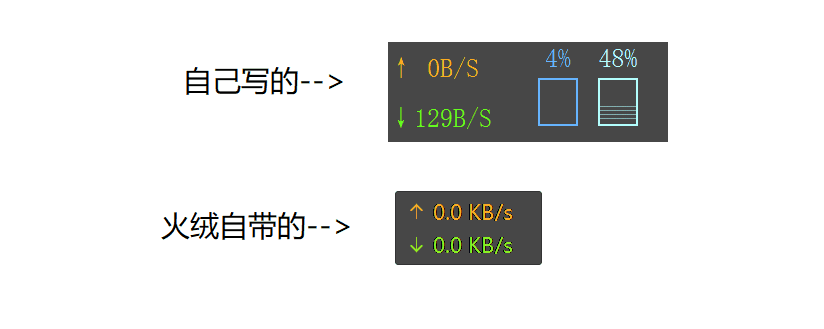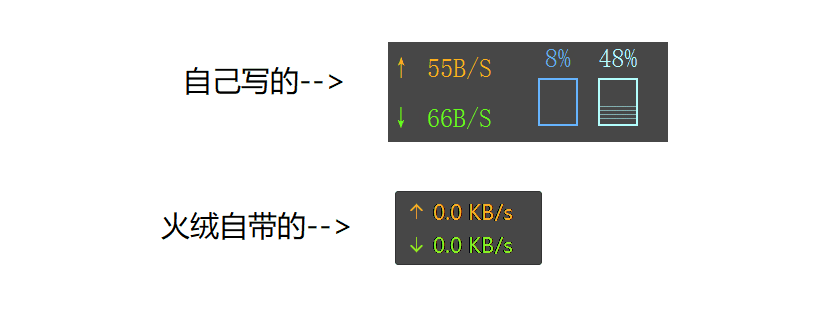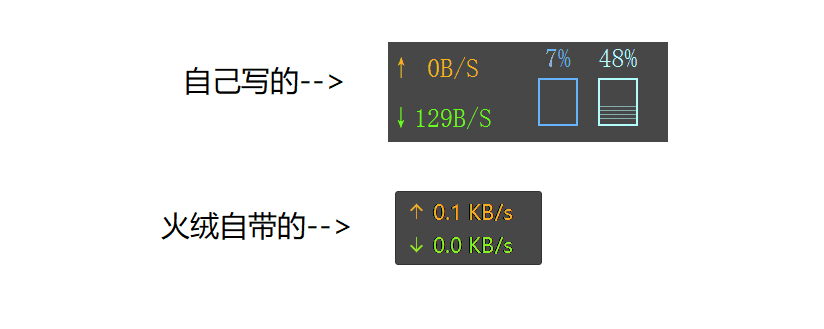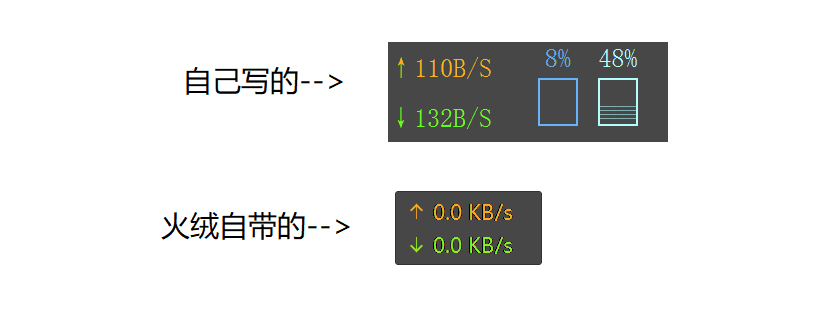
贴边收起

右键退出,改变颜色,部分显示等功能

开始运行内存占用30M左右,几乎不占用CPU;运行5天后,内存占用10M左右;

打包EXE
使用pyinstaller打包exe:
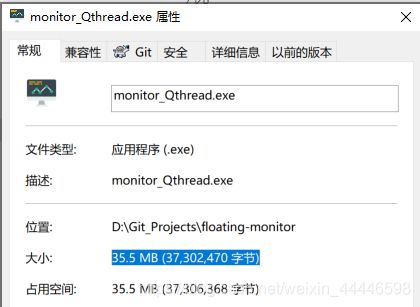
pyinstaller -F -w -i monitor.ico monitor.py
打完包一看,Python,不愧是你,近40M!尝试了虚拟纯净环境,upx压缩等,哈哈,没什么用。
总结
最开始使用的时QTimer+threading的方法,直接对窗口Label更新,发现总是运行一段时间后窗口假死,不再更新;折腾好久,后来改为QThread+qtSignal的方法,总算解决了;此外,还尝试了threading+qtSignal的方法,也能实现;
一个小教训,更新UI最好只在主线程做;
| 方法 | 线程 | 是否假死 | 资源消耗 |
|---|---|---|---|
| QTimer+threading | QTimer不会创建新的线程,阻塞主线程; | 通过threading创建的子线程更新UI,会假死 | 最大 |
| threading Timer + qtSignal | threading Timer创建新线程 | 通过qtSignal通知主线程更新UI,不会假死 | 中间 |
| QThread + qtSignal | QThread创建新的线程 | 通过qtSignal通知主线程更新UI,不会假死 | 最小 |
完整带注释的代码有400行左右,就不在这里贴了;icon图标,ui文件,三种实现方法的源码,exe已经上传github,有兴趣的可以自行下载;(monitor_Qthread.py为最稳定版本);
小白一枚,如有发现错误或有建议,还望不吝赐教 :)
源码链接
GitHub-floating-monitor