代码随想录算法训练营第二十一天 | 530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差,501. 二叉搜索树中的众数,236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
530. 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
需要领悟一下二叉树遍历上双指针操作,优先掌握递归题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:二叉搜索树中,需要掌握如何双指针遍历!| LeetCode:530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
重点:
1. 中序遍历二叉搜索树为单调递增数组。单调递增就说明了最小的差值肯定出现在相邻的数值上
2. 双指针。全局的指针变量不变,递归的指针变量被回溯到了上一个
思路:
递归法:
1. 确定参数及返回值
因为要遍历全部路径,并且不需要对递归返回值处理
private void traversal(TreeNode node)2. 确定终止条件
if (node == null) { return; }3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
中序遍历+双指针。中序遍历保证了遍历的单调递增性。指针pre记录上一个,指针node记录当前的,result不断地取min
traversal(node.left); if (pre != null) { result = Math.min(result, node.val - pre.val); } pre = node; traversal(node.right);迭代法:
1. 用栈模拟DFS中的中序遍历,中序遍历可以保证遍历的单调递增性,但需要用pre来保存上一个节点,每次更新result为最小值
TreeNode pre;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
traversal(root);
return result;
}
private void traversal(TreeNode node) {
// 终止条件
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// 左
traversal(node.left);
// 中
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, node.val - pre.val);
}
// pre肯定是node的上一个,因为递归之后node回溯到前一个了,而pre是全局变量
pre = node;
//右
traversal(node.right);
}public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
// 先走到最左边
stack.offerLast(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
// 左走完,可以开始处理中了
cur = stack.removeLast();
if (pre != null) {
result = Math.min(result, cur.val - pre.val);
}
pre = cur;
// 处理右
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return result;
} 501. 二叉搜索树中的众数
和 530差不多双指针思路,不过 这里涉及到一个很巧妙的代码技巧。可以先自己做做看,然后看我的视频讲解。
题目链接/文章讲解:代码随想录
视频讲解:不仅双指针,还有代码技巧可以惊艳到你! | LeetCode:501.二叉搜索树中的众数_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
重点:
1. 递归法为双指针+中序遍历
思路:
如果不是二叉搜索树找众数:
迭代遍历+暴力解:
1. 前/中/后/层序遍历所有节点并统计他们各自的频率
2. 把Map按照频率从大到小排序
3. 把前K个最高频的值放入到result
如果是二叉搜索树:
递归法:
1. 确定参数及返回值
private void findMode1(TreeNode cur)2. 确定终止条件
if (cur == null) { return; }3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
双指针。使用count来记录当前节点的当前频率,使用maxCount来记录当前记录到的最大频率,使用pre来记录上一个节点。每层递归都都要更新pre,如果pre和cur相等或不相等count也要更新,再把count和maxCount比较来更新result
// 左 findMode1(cur.left); // 中 // 先更新count if (pre == null) { count = 1; } else if (pre.val == cur.val) { count++; } else { count = 1; } // 更新pre pre = cur; // 根据count和maxCount来判断要不要更新result if (count == maxCount) { resList.add(cur.val); } else if (count > maxCount) { resList.clear(); resList.add(cur.val); maxCount = count; } // 右 findMode1(cur.right);迭代法:
1. 用栈来中序遍历即可,中序遍历处理中节点的时候依旧是递归时处理中节点时的逻辑
// 如果不是二叉搜索树找众数
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
List result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
// 把全部节点遍历一边并记录频率在map中
traversal(root, map);
// 把map转为存有entrySet的List,并且这个List是根据频率从大到小排序
List> mapList = map.entrySet().stream()
.sorted((c1, c2) -> c2.getValue().compareTo(c1.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 第一个肯定最大,直接加入result
result.add(mapList.get(0).getKey());
// 把其他频率高的也加入到result
for (int i = 1; i < mapList.size(); i++) {
if (mapList.get(i).getValue() == mapList.get(i - 1).getValue()) {
result.add(mapList.get(i).getKey());
} else {
break;
}
}
return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
private void traversal(TreeNode root, Map map) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
map.put(root.val, map.getOrDefault(root.val, 0) + 1);
traversal(root.left, map);
traversal(root.right,map);
} List resList;
int maxCount;
int count;
TreeNode pre;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
resList = new ArrayList<>();
maxCount = 0;
count = 0;
pre = null;
findMode1(root);
return resList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
private void findMode1(TreeNode cur) {
if (cur == null) {
return;
}
// 左
findMode1(cur.left);
// 中
// 先更新count
if (pre == null) {
count = 1;
} else if (pre.val == cur.val) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
// 更新pre
pre = cur;
// 根据count和maxCount来判断要不要更新result
if (count == maxCount) {
resList.add(cur.val);
} else if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(cur.val);
maxCount = count;
}
// 右
findMode1(cur.right);
} public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
List resList = new ArrayList<>();
int maxCount = 0;
int count = 0;
TreeNode pre = null;
Deque stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
// 左
stack.offerLast(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
// 中
cur = stack.removeLast();
// 更新count
if (pre == null) {
count = 1;
} else if (pre.val == cur.val) {
count++;
} else {
count = 1;
}
// 更新pre
pre = cur;
// 更新maxCount及result
if (count == maxCount) {
resList.add(cur.val);
} else if (count > maxCount) {
resList.clear();
resList.add(cur.val);
maxCount = count;
}
// 右
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return resList.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
} 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
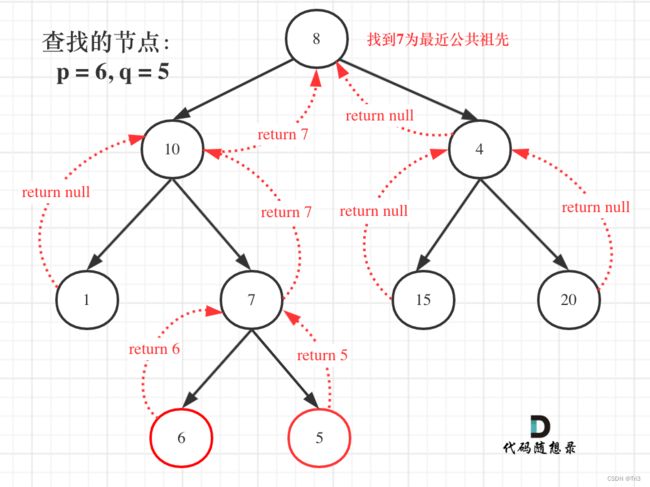
本题其实是比较难的,可以先看我的视频讲解题目链接/文章讲解: 代码随想录视频讲解:自底向上查找,有点难度! | LeetCode:236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
重点:
1. 当需要从底向上遍历的时候,只能通过后序遍历的回溯,左右中。得要先知道左右的子树的具体情况,再根据左右子树的情况来返回决定如何回溯给上一个节点
思路:
递归法:
1. 确定函数及返回值
函数必须有返回值。可能会想不是找到其中一条边就可以了嘛,但其实不是,必须遍历整棵树才能找到最近公共祖先
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q)2. 确定终止条件
不单单是遍历到了null需要返回,当遍历到了p或q的值也要直接返回,不然当前根节点怎么知道左右子树什么情况。这个终止条件也会包含了p或q本身就是公共祖先的情况,因为root == p/q都直接返回了。
if (root == null) { return null; } if (root == p || root == q) { return root; }3. 确定单层递归的逻辑
后序遍历,左右中。然后再根据左右子树的情况进行返回。
// 左 TreeNode leftResult = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); // 右 TreeNode rightResult = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); // 中 if (leftResult != null && rightResult != null) { return root; } if (leftResult == null && rightResult != null) { return rightResult; } if (leftResult != null && rightResult == null) { return leftResult; } return null;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// 终止条件
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
// 找到了与p或q相同的节点
if (root == p || root == q) {
return root;
}
// 左
TreeNode leftResult = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
// 右
TreeNode rightResult = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
// 中
// 左子树和右子树都找到对应的值了
// 说明当前节点就是最近公共祖先
if (leftResult != null && rightResult != null) {
return root;
}
// 右子树有对应的值
if (leftResult == null && rightResult != null) {
return rightResult;
}
// 左子树有对应的值
if (leftResult != null && rightResult == null) {
return leftResult;
}
return null;
}