AtCoder ABC152
C - Low Elements
从前往后维护一个最长下降子序列
D - Handstand 2
设f[a][b]代表当前第一个数字为a第二个数字为b的数总个数
递推一下就可以。注意a==b的情况。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @time : 2023/6/2 13:30
# @file : atcoder.py
# @software : PyCharm
import bisect
import copy
import sys
from itertools import permutations
from sortedcontainers import SortedList
from collections import defaultdict, Counter, deque
from functools import lru_cache, cmp_to_key
import heapq
import math
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000)
def main():
items = sys.version.split()
if items[0] == '3.10.6':
fp = open("in.txt")
else:
fp = sys.stdin
n = int(fp.readline())
d = [[0] * 10 for _ in range(10)]
ans = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
s = str(i)
a, b = int(s[0]), int(s[-1])
d[a][b] += 1
if a != b:
ans += d[b][a] * 2
else:
ans += (d[a][a] - 1) * 2 + 1
print(ans)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
E - Flatten
数论题,需要分解质因数和逆元,然而python改变了一切
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @time : 2023/6/2 13:30
# @file : atcoder.py
# @software : PyCharm
import bisect
import copy
import sys
from itertools import permutations
from sortedcontainers import SortedList
from collections import defaultdict, Counter, deque
from functools import lru_cache, cmp_to_key
import heapq
import math
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000)
def main():
items = sys.version.split()
if items[0] == '3.10.6':
fp = open("in.txt")
else:
fp = sys.stdin
n = int(fp.readline())
a = list(map(int, fp.readline().split()))
def lcm(x, y):
x0, y0 = x, y
if x0 > y0:
x0, y0 = y0, x0
while x0:
x0, y0 = y0 % x0, x0
return x * y // y0
l = a[0]
for i in range(1, n):
l = lcm(l, a[i])
ans = 0
mod = 10 ** 9 + 7
for i in range(n):
ans += l // a[i]
ans %= mod
print(ans % mod)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
F - Tree and Constraints
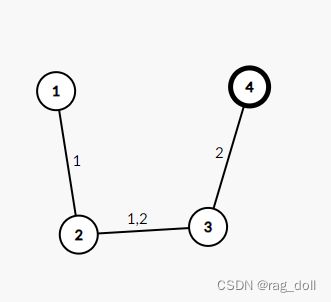
反过来考虑。比如下图中有两个constraint,原题求满足所有的限制的方案,需要枚举每种黑色放置的方案,很不好做。如果反过来求不满足限制的方案,即在某些限制路径上全填白色,求总的方案数,那么就比较好做。
由于不同的限制路径下边的集合会有交集,因此需要使用容斥原理计算。设取不同的限制路径的状态集合为 s s s,计算状态下边的并集中边数量为 x x x,不满足限制的方案数等于 a n s = ∑ s ∈ S ( − 1 ) ∣ s ∣ + 1 2 n − 1 − x ans=\sum_{s\in S}(-1)^{|s|+1}2^{n-1-x} ans=s∈S∑(−1)∣s∣+12n−1−x
如下图中按顺序对边和点0-index编号,
第一个状态集合是0b01,代表限制状态0
f(1)=2,因为边2可以取两种颜色,边0边1全取白
第二个状态集合是0b10,代表限制状态1
f(2)=2,同理
第三个状态集合0b11,代表两个限制状态都要取
在这种情况下,不满足条件的方案只有1个,就是三条边全取白
所以最终不满足任一约束的方案数是2+2-1=3个,因为三条边全取白的方案在0b01和0b10中都计数了一次,因此按照容斥原理予以减去
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @time : 2023/6/2 13:30
# @file : atcoder.py
# @software : PyCharm
import bisect
import copy
import sys
from itertools import permutations
from sortedcontainers import SortedList
from collections import defaultdict, Counter, deque
from functools import lru_cache, cmp_to_key
import heapq
import math
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000)
def main():
items = sys.version.split()
if items[0] == '3.10.6':
fp = open("in.txt")
else:
fp = sys.stdin
n = int(fp.readline())
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
fa = [-1] * n
dep = [0] * n
edge_mask = {}
for i in range(n - 1):
u, v = map(int, fp.readline().split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
edge_mask[(u, v)] = edge_mask[(v, u)] = i
def dfs0(u, f):
for v in g[u]:
if f == v:
continue
fa[v] = u
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1
dfs0(v, u)
def lca(u, v):
while u != v:
if dep[u] > dep[v]:
u = fa[u]
else:
v = fa[v]
return u
dfs0(0, -1)
m = int(fp.readline())
con = [0] * m
for i in range(m):
u, v = map(int, fp.readline().split())
u -= 1
v -= 1
l = lca(u, v)
while u != l:
fu = fa[u]
j = edge_mask[(fu, u)]
con[i] |= 1 << j
u = fu
while v != l:
fv = fa[v]
j = edge_mask[(fv, v)]
con[i] |= 1 << j
v = fv
bit_count = [0] * (1 << m)
bit = [0] * (1 << m)
for i in range(m):
bit[1 << i] = i
for i in range(1, 1 << m):
if i & 1 == 1:
bit_count[i] = bit_count[i >> 1] + 1
else:
bit_count[i] = bit_count[i >> 1]
def get_bit_count(val):
ret = 0
while val:
ret += val & 1
val >>= 1
return ret
union = [0] * (1 << m)
union[0] = 0
temp = 0
for i in range(1, 1 << m):
lb = i & -i
j = bit[lb]
union[i] = union[i - lb] | con[j]
x = get_bit_count(union[i])
t = 1 << (n - 1 - x)
if bit_count[i] & 1:
temp += t
else:
temp -= t
ans = (1 << n - 1) - temp
print(ans)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()