ansible总结
ansible
ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于Python开发,分布式,无需客户端,轻量级,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能,ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。基于python开发,分布式,无需客户端,轻量级,配置语法YAML语言,更强的远程命令执行操作。
ansible特性
no agents:不需要在被管控主机上安装任何客户端,更新时,只需要在操作机上进行一次更新即可。(分布式,不需要安装客户端)
no server:无服务器端,使用时直接运行命令即可。
modules in any languages :基于模块工作,可使用任意语言开发模块。
yaml,not code :使用yaml语言定制剧本playbook
ssh by default:基于ssh工作
strong multi-tier solution: 可实现多级指挥。
connection plugins:连接插件,负责和被监控端实现通信,默认使用SSH连接
host inventory:主机清单,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机
modules : 模块,核心模块、command模块、自定义模块等
plugins : modules功能的补充,包括连接插件,邮件插件等
playbook:编排,定义 Ansible 多任务配置文件,非必需
ansible安装
环境:
机:4台 一个控制节点 三个被控制节点
在/etc/hosts里相互做解析
配置ssh公钥认证:控制节点需要发送ssh公钥给所有被控制节点。
ssh-keygen
ssh-copy-id -i 所有被控制端机器ip
安装:
配置epel网络yum源
yum -y install epel-release
安装
yum -y install ansible
查看版本
ansible --version
查看帮助
ansible --help
安装完成后有两个文件
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg #主配置文件
/etc/ansible/hosts #主机清单文件
语法:
1.添加主机或主机组
ansible-web1 单独指定主机,可以是主机名称或ip地址
2.添加主机组
[webservers] #组名
192.168.77.126
ansible-web1
3.为一个组指定变量,组内每一个主机都可以使用该变量。
[weball:vars] #设置变量,vars--照写
ansible_ssh_port=22
ansible_ssh_user=root
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=/root/.ssh/id_rsa
#ansible_ssh_pass=test #也可以定义密码,如果没有互传秘钥可以使用密码。
查看组内主机列表
ansible 组名 --list-hosts
ansible -i /opt/hostlist all -m ping -o
-i指定清单文件
-m指定模块
-o横屏显示
-a 传递给模块的参数
测试
语法:
# ansible -m -a
pattern--主机清单里定义的主机组名,主机名,IP,别名等,all表示所有的主机,支持通配符,正则
-m module_name: 模块名称,默认为command
-a arguments: 传递给模块的参数
-o 横着显示(单行显示)
**使用案例**
使用ping模块检查ansible节点的连通性:
1.指定单台机器:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1 -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
2.同时指定多台机器:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web1,ansible-web2 -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
ansible-web2 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
3.指定组名:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m ping -o
ansible-web1 | SUCCESS => {"ansible_facts": {"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"}, "changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
执行shell命令:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m shell -a 'uptime'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
23:32:47 up 5:24, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
不加 -m 默认是 command 模块
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -a 'uptime'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
23:34:01 up 5:25, 3 users, load average: 0.16, 0.05, 0.06
1.给节点增加用户:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m shell -a 'useradd tom'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m shell -a 'grep tom /etc/passwd'
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
tom:x:1000:1000::/home/tom:/bin/bash
重定向输出到本地文件中:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m shell -a 'df -Th' > /opt/a.txt
[root@ansible-server ~]# cat /opt/a.txt
ansible-web1 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 18G 1.1G 17G 6% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 226M 0 226M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 237M 0 237M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 237M 4.7M 232M 2% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 237M 0 237M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 125M 890M 13% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 48M 0 48M 0% /run/user/0
Ad-Hoc
ad hoc其实就是执行简单的命令——一条命令。对于复杂的命令则为 playbook。
帮助文档:
列出ansible支持的模块:
-l:获取列表
-s module_name:获取指定模块的使用信息
看所有模块(A10,华为,docker,EC2,aws等等广大厂商设备)
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible-doc -l
查看模块使用信息,了解其功能:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible-doc -s yum
常用模块
1.远程复制备份模块:copy
模块参数详解:
src=:指定源文件路径
dest=:目标地址(拷贝到哪里)
owner:指定属主
group:指定属组
mode:指定权限,可以以数字指定比如0644
backup:在覆盖之前将原文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息。有两个选项:yes|no
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim a.txt #创建一个测试文件
123123
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible weball -m copy -a 'src=/root/a.txt dest=/opt owner=root group=root mode=644' -o
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim a.txt #追加如下内容
123123
234234
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible weball -m copy -a 'src=/root/a.txt dest=/opt/ owner=root group=root mode=644 backup=true' -o
注释:如果文件没有变化,不会备份。只有文件内容不同,才会做备份。
登录被控制机器其中一台查看
[root@ansible-web1 ~]# cat /opt/a.txt.15301.2019-09-01\@00\:35\:18~
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible weball -m shell -a 'mv /mnt/qf.txt /tmp' -o
移动被控制节点的文件
2.软件包管理 yum模块
安装apache
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m yum -a "name=httpd state=latest" -o
state= #状态是什么,干什么
state=absent 用于remove安装包
state=latest 表示最新的
state=removed 表示卸载
卸载软件:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m yum -a "name=httpd state=removed" -o
或者
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m yum -a "name=httpd state=absent" -o
3.服务管理service模块
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started" #启动
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=stopped" #停止
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=restarted" #重启
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes" #开机启动
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=no" #开机关闭
4.文件模块file
模块参数详解:
owner:修改属主
group:修改属组
mode:修改权限
path=:要修改文件的路径
recurse:递归的设置文件的属性,只对目录有效
yes:表示使用递归设置
state:
touch:创建一个新的空文件
directory:创建一个新的目录,当目录存在时不会进行修改
#创建一个文件
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/youngfit1.txt mode=777 state=touch'
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/youngfit2.txt mode=777 owner=nginx state=touch'
#创建一个目录
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m file -a 'path=/tmp/qf mode=777 state=directory'
被控节点ansible-web2操作:
[root@ansible-web2 tmp]# cd /opt/
[root@ansible-web2 opt]# ll haha
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Sep 12 09:41 haha2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx root 0 Sep 12 09:41 haha.txt
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible ansible-web2 -m file -a "path=/opt/haha owner=nginx group=nginx state=directory recurse=yes"
被控节点查看:
[root@ansible-web2 opt]# ll haha
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx nginx 0 Sep 12 09:41 haha2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 nginx nginx 0 Sep 12 09:41 haha.txt
5.收集信息模块setup
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m setup #收集所有信息
[root@ansible-server ~]# ansible webservers1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses' #只查询ipv4的地址
filter:过滤
ansible-playbook 剧本(1)
Playbook介绍
playbook是ansible用于配置,部署,和管理被控节点的剧本。通过playbook的详细描述,执行其中的tasks,可以让远端主机达到预期的状态。playbook是由一个或多个”play”组成的列表。 当对一台机器做环境初始化的时候往往需要不止做一件事情,这时使用playbook会更加适合。通过playbook你可以一次在多台机器执行多个指令。通过这种预先设计的配置保持了机器的配置统一,并很简单的执行日常任务。
ansible通过不同的模块实现相应的管理,管理的方式通过定义的清单文件(hosts)所管理的主机包括认证的方式连接的端口等。所有的功能都是通过调用不同的模块(modules)来完成不同的功能的。不管是执行单条命令还是play-book都是基于清单文件。
playbook格式
playbook由YMAL语言编写。YMAL格式是类似于JSON的文件格式,便于人理解和阅读,同时便于书写。
一个剧本里面可以有多个play,每个play只能有一个tasks,每个tasks可以有多个name
核心元素:
Playbooks
Variables #变量元素,可传递给Tasks/Templates使用;
Tasks #任务元素,由模块定义的操作的列表,即调用模块完成任务;
Templates #模板元素,使用了模板语法的文本文件;
Handlers #处理器元素,通常指在某事件满足时触发的操作;
Roles #角色元素
playbook的基础组件:
name:
定义playbook或者task的名称(描述信息),每一个play都可以完成一个任务。
hosts:
hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机.
user:
remote_user则用于指定远程主机上的执行任务的用户
tasks:
任务列表play的主体部分是task list. task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后再开始第二个。
vars:
定义变量(如果不使用内部变量需要提前定义)
vars_files:
调用定义变量文件
notify:
任务执行结果如果是发生更改了的则触发定义在handler的任务执行
handlers:
用于当前关注的资源发生变化时采取一定指定的操作
实例一:
[root@ansible-server ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
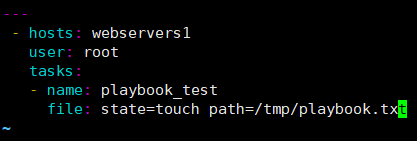
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim test.yml #创建文件必须以.yml/.yaml结尾
---
- hosts: webservers1
user: root
tasks:
- name: playbook_test
file: state=touch path=/tmp/playbook.txt
===================================================================================
参数解释:
hosts: 参数指定了对哪些主机进行操作;
user: 参数指定了使用什么用户登录远程主机操作;
tasks: 指定了一个任务.
name:参数同样是对任务的描述,在执行过程中会打印出来。
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check test.yml
playbook: test.yml
运行Playbook:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook test.yml #加剧本名称
实例二
handlers:由特定条件触发的Tasks
handlers:处理器
notify:触发器
语法:
tasks:
- name: TASK_NAME
module: arguments #1.上面任务执行成功,然后
notify: HANDLER_NAME #2.通知他
handlers:
- name: HANDLER_NAME #3.一一对应,这里的描述与notify定义的必须一样
module: arguments #4.执行这个命令
=======================================================
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim handlers.yml
- hosts: webservers1
user: root
tasks:
- name: test copy
copy: src=/root/a.txt dest=/mnt
notify: test handlers
handlers:
- name: test handlers
shell: echo "abcd" >> /mnt/a.txt
========================================================
说明:只有 copy 模块真正执行后,才会去调用下面的 handlers 相关的操作,追加内容。所以这种比较适合配置文件发生更改后,需要重启服务的操作。
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check handlers.yml
playbook: handlers.yml
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook handlers.yml
案例三
循环:迭代,需要重复执行的任务;
对迭代项的引用,固定变量名为”item”,使用with_item属性给定要迭代的元素;
基于字符串列表元素实战:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim list.yml
- hosts: webservers2
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest #相当于for循环里面的i
with_items: #取值 。但是不支持通配符
- httpd
- php
- php-mysql
- php-mbstring
- php-gd
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check list.yml
playbook: list.yml
执行:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook list.yml
案例四、自定义vars_files变量
变量调用语法:
{{ var_name }}
====================================================
创建变量目录:
[root@ansible-server ~]# mkdir /etc/ansible/vars
[root@ansible-server ~]# cd /etc/ansible/vars/
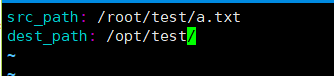
[root@ansible-server vars]# vim file.yml #创建变量文件。
src_path: /root/test/a.txt
dest_path: /opt/test/
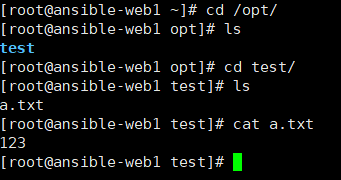
创建一个测试文件
[root@ansible-server vars]# mkdir /root/test
[root@ansible-server vars]# vim /root/test/a.txt #编辑测试文件
123
创建play-book引用变量文件:
[root@ansible-server vars]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim vars.yml
- hosts: ansible-web1
user: root
vars_files:
- /etc/ansible/vars/file.yml
tasks:
- name: create directory
file: path={{ dest_path }} mode=755 state=directory
- name: copy file
copy: src={{ src_path }} dest={{ dest_path }}
检测语法:
[root@ansible-server vars]# cd ..
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check vars.yml
playbook: vars.yml
执行:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook vars.yml
实战:通过playbook安装apache
1.准备工作:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim hosts #添加主机web3
[webservers3]
ansible-web3
2.安装apache,准备配置文件
[root@ansible-server ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@ansible-server ~]# mkdir /apache
[root@ansible-server ~]# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /apache/ #将配置文件推送到web3
3.修改端口将原来的80修改为8080
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim /apache/httpd.conf
Listen 8080
[root@ansible-server ~]# cd /etc/ansible/ #编写剧本
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim apache.yml
---
- hosts: webservers3
user: root
tasks:
- name: install apache
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: copy conf file
copy: src=/apache/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: start httpd
handlers:
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=restarted
语法检测:
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check apache.yml
playbook: apache.yml
执行play-book
[root@ansible-server ansible]# ansible-playbook apache.yml
group模块参数:
name参数:必须参数,用于指定组名称。
state参数:用于指定组的状态,两个值可选,present,absent,默认为 present,设置为absent 表示删除组。
gid参数:用于指定组的gid。如果不指定为随机
system参数:如果是yes为系统组。--可选
=========================================================================================
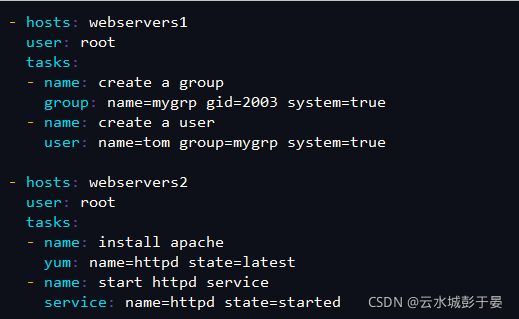
1.创建多个play
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible ansible]# vim play.yml
- hosts: webservers1
user: root
tasks:
- name: create a group
group: name=mygrp gid=2003 system=true
- name: create a user
user: name=tom group=mygrp system=true
- hosts: webservers2
user: root
tasks:
- name: install apache
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
=========================================================================================
检查并执行
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check play.yml
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook play.yml
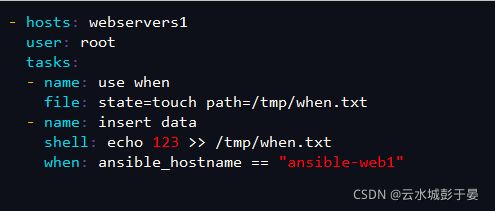
2.条件执行when模块
先判断when条件是否成立
[root@ansible ansible]# cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[webservers1]
ansible-web1
ansible-web2
[root@ansible ansible]# vim when.yml
- hosts: webservers1
user: root
tasks:
- name: use when
file: state=touch path=/tmp/when.txt
- name: insert data
shell: echo 123 >> /tmp/when.txt #2在执行这个模块命令
when: ansible_hostname == "ansible-web1" #1.先条件执行,先判断when是否成立,如果成立则执行上面命令,ansible-web1指的是被控节点上真正的主机名称
执行
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook when.yml
[root@ansible-web1 ~]# cat /tmp/when.txt
123
[root@ansible-web2 ~]# cat /tmp/when.txt
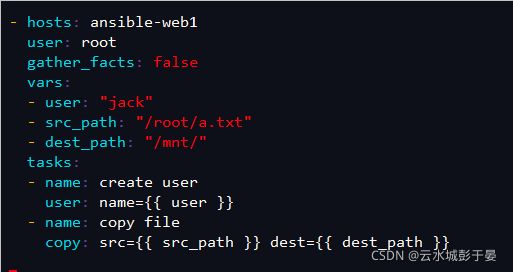
3.使用变量并不显示搜集主机相关信息
gather_facts参数:指定了在任务部分执行前,是否先执行setup模块获取主机相关信息,默认值为true,改成false之后在执行过程中不会搜集主机相关信息。
============================================================================
[root@ansible ansible]# vim create_user.yml
- hosts: ansible-web1
user: root
gather_facts: false #是否执行setup模块,搜集对方机器的信息
vars: #自定义变量
- user: "jack" #user是自定义变量名称,“jack”是变量值
- src_path: "/root/a.txt" #同上
- dest_path: "/mnt/"
tasks:
- name: create user
user: name={{ user }}
- name: copy file
copy: src={{ src_path }} dest={{ dest_path }}
[root@ansible ansible]# vim /root/a.txt #创建测试文件
123
执行:
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook create_user.yml
Role角色
roles则是在ansible中,playbooks的目录组织结构。而模块化之后,成为roles的组织结构,易读,代码可重用,层次清晰。
实战目标:通过role远程部署nginx并配置
两台机器配置本地解析
[root@ansible-server ~]# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.1.9 ansible-server
192.168.1.13 ansible-web4
[root@ansible-web4 ~]# vim /etc/hosts
192.168.1.9 ansible-server
192.168.1.13 ansible-web4
添加主机组
[root@ansible-server ansible]# pwd
/etc/ansible
[root@ansible-server ansible]# vim hosts
[webservers4]
ansible-web4
配置免密登录:
[root@ansible-server ~]# ssh-copy-id -i 192.168.1.13
目录顺序:
role_name/ ---角色名称=目录
files/:存储一些可以用copy调用的静态文件。
tasks/: 存储任务的目录,此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各task;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
handlers/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各handler;其它的文件需要由(与notify:名字相同,方便notify通知执行下一条命令)通过main.yml进行“包含”调用;
vars/:此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各variable;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
templates/:存储由template模块调用的模板文本; (也可以调用变量)
site.yml:定义哪个主机应用哪个角色
=========================================================================================
1.准备目录结构
[root@ansible-server ~]# cd /etc/ansible/roles/ #roles为自带目录,如果不存在可以创建
[root@ansible-server roles]# mkdir nginx/{files,handlers,tasks,templates,vars} -p
2.创建文件:
[root@ansible-server roles]# touch site.yml nginx/{handlers,tasks,vars}/main.yml
[root@ansible-server roles]# yum install -y tree
1.创建nginx的测试文件
[root@ansible-server roles]# echo 1234 > nginx/files/index.html
2.安装nginx并配置模板
[root@ansible-server roles]# yum install -y nginx && cp /etc/nginx/nginx.conf nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
3.编写任务
[root@ansible-server roles]# vim nginx/tasks/main.yml
---
- name: install epel
yum: name=epel-release state=latest
- name: install nginx
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: copy nginx.conf templte
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- name: copy index.html
copy: src=/etc/ansible/roles/nginx/files/index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
notify: start nginx
4.准备配置文件
[root@ansible-server roles]# vim nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
修改成如下内容。自定义变量
5.编写变量
[root@ansible-server roles]# vim nginx/vars/main.yml #添加如下内容
worker_connections: 2
6.编写handlers
[root@ansible-server roles]# vim nginx/handlers/main.yml #编写如下内容
---
- name: start nginx #和notify的名字必须一样
service: name=nginx state=started
7.编写剧本
[root@ansible-server roles]# vim site.yml
---
- hosts: webservers4
user: root
roles:
- nginx
检测语法
[root@ansible-server roles]# ansible-playbook site.yml --syntax-check
playbook: site.yml
执行剧本:
[root@ansible-server roles]# ansible-playbook site.yml
查看:
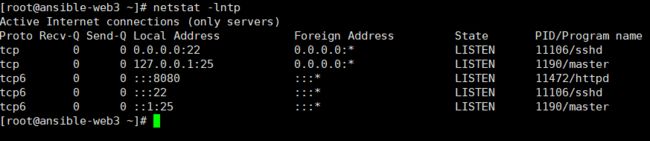
[root@ansible-web4 ~]# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3102/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 926/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1007/master
tcp6 0 0 :::80 :::* LISTEN 3102/nginx: master
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 926/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1007/master
[root@ansible-web4 ~]# cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep pro
#worker_processes auto;
worker_processes 2;
访问:
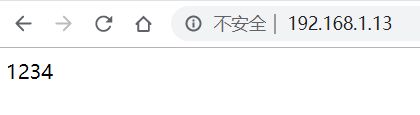
项目通过ansible上线
批量部署jdk+tomcat
[root@ansible-server src]# cat tomcat.yml
- hosts: webservers
user: root
tasks:
##配置JDK,上传jdk、tomcat的安装包到/usr/src
- name: configure Jdk1.8
copy: src=/usr/src/jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz dest=/usr/src
- name: unzip
shell: tar -xvzf /usr/src/jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
- name: rename to java
shell: mv /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_211 /usr/local/java
- name: configure envirement1
shell: echo "JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java" >> /etc/profile
- name: configure envirement2
shell: echo 'PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH' >> /etc/profile
##Tomcat
- name: copy tomcat
copy: src=/usr/src/apache-tomcat-8.5.45.tar.gz dest=/usr/src
- name: unzip tomcat
shell: tar -xvzf /usr/src/apache-tomcat-8.5.45.tar.gz -C /usr/local
- name: rename to tomcat
shell: mv /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.45 /usr/local/tomcat
- name: copy startup file
copy: src=/usr/src/startup.sh dest=/usr/local/tomcat/bin
notify: start tomcat
handlers:
- name: start tomcat
shell: nohup /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh &
[root@java-server src]# ls
apache-tomcat-8.5.45 debug kernels tomcat.retry
apache-tomcat-8.5.45.tar.gz jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz startup.sh tomcat.yml
[root@java-server src]# head -2 startup.sh
#!/bin/sh
source /etc/profile
批量部署jenkins
项目描述:
1.准备两台机器,一台作为nginx代理。一台为tomcat服务器。
2.tomcat服务器手动部署tomcat服务,并将webapps目录下面的内容提前删掉。
3.将jenkins.war包上传到nginx服务器。通过ansible将war包拷贝过去。并启动tomcat
4.配置nginx反向代理tomcat,实现访问jenkins。
操作如下:
一、tomcat服务器
1.安装jdk与tomcat略。
2.添加tomcat启动脚本中添加环境变量
[root@ansible-web2 ~]# vim /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh #需要添加如下内容
source /etc/profile
====================================
二、nginx服务器:
1.安装nginx与ansible,上传jenkins的war包略。
2.ansible配置如下:
3.定义变量:
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible ansible]# mkdir vars
[root@ansible ansible]# vim vars/path.yml
src_path: /root/jenkins.war
dest_path: /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/
4.配置playbook:
[root@ansible ansible]# vim jenkins.yml
- hosts: webserver2
user: root
vars_files:
- /etc/ansible/vars/path.yml
tasks:
- name: copy jenkins.war
copy: src={{ src_path }} dest={{ dest_path }}
- name: start tomcat
shell: nohup /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh &
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook jenkins.yml
5.配置nginx反向代理
[root@ansible ansible]# vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/jenkins.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
charset koi8-r;
access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location /jenkins {
proxy_pass http://192.168.62.181:8080;
proxy_set_header Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
6.启动nginx
7.检查nginx与tomcat是否启动成功!
8.访问nginx服务器http://ip/jenkins。
批量部署jdk+tomcat+jenkins
将Jdk、Tomcat、Jenkins的安装包上传到ansbile控制节点的/usr/src下
[root@ansible ansible]# ls /usr/src/
[root@java-server ansible]# head -2 /usr/src/startup.sh //startup.sh是tomcat的启动脚本
#!/bin/sh
source /etc/profile #加上此行,是为了启动加载到环境变量
下面是变量文件
变量文件
[root@ansible ansible]# cat /etc/ansible/vars/file.yml
[root@ansible ansible]# cat jenkins.yml
- hosts: ansible-web1
user: root
vars_files:
- /etc/ansible/vars/file.yml
tasks:
##配置JDK,上传jdk、tomcat的安装包到/usr/src
- name: configure JDK1.8
copy: src={{ src_jdk_path }} dest={{ dest_jdk_path }}
- name: unzip JDK
shell: tar -xvzf /usr/src/jdk-8u211-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
- name: rename to java
shell: mv /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_211 /usr/local/java
- name: configure JDK envirement1
shell: echo "JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java" >> /etc/profile
- name: configure JDK envirement2
shell: echo 'PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH' >> /etc/profile
##Tomcat
- name: copy tomcat
copy: src={{ src_tomcat_path }} dest={{ dest_tomcat_path }}
- name: unzip tomcat
shell: tar -xvzf /usr/src/apache-tomcat-8.5.45.tar.gz -C /usr/local
- name: rename to tomcat
shell: mv /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.45 /usr/local/tomcat
- name: copy startup file
copy: src=/usr/src/startup.sh dest=/usr/local/tomcat/bin
##Jenkins
- name: copy jenkins
copy: src=/usr/src/jenkins.war dest=/usr/local/tomcat/webapps/
notify: start jenkins
handlers:
- name: start jenkins
shell: nohup /usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh &