pytest框架(1)
安装
pip install -U pytest
测试demo
# content of test_sample.py
def func(x):
return x + 1
def test_answer():
assert func(3) == 5
执行结果
$ pytest
=========================== test session starts ============================
platform linux -- Python 3.x.y, pytest-6.x.y, py-1.x.y, pluggy-0.x.y
cachedir: $PYTHON_PREFIX/.pytest_cache
rootdir: $REGENDOC_TMPDIR
collected 1 item
test_sample.py F [100%]
================================= FAILURES =================================
_______________________________ test_answer ________________________________
def test_answer():
> assert func(3) == 5
E assert 4 == 5
E + where 4 = func(3)
test_sample.py:6: AssertionError
========================= short test summary info ==========================
FAILED test_sample.py::test_answer - assert 4 == 5
============================ 1 failed in 0.12s =============================
Python测试发现的约定
- 如果未指定参数,则集合从开始 testpaths (如果配置)或当前目录。或者,命令行参数可以用于目录、文件名或节点ID的任意组合。递归到目录中,除非它们匹配 norecursedirs .
- 在这些目录中,搜索 test_*.py 或 *_test.py 文件,由其导入 test package name .
- 从这些文件中收集测试项:
- test 在类之外加前缀的测试函数或方法
- test 内置前缀测试函数或方法 Test 带前缀的测试类(不带 init 方法)
例如以下
tests/
|-- example
| |-- test_example_01.py
| |-- test_example_02.py
| '-- test_example_03.py
|-- foobar
| |-- test_foobar_01.py
| |-- test_foobar_02.py
| '-- test_foobar_03.py
'-- hello
'-- world
|-- test_world_01.py
|-- test_world_02.py
'-- test_world_03.py
执行结果
=========================== test session starts ============================
platform linux -- Python 3.x.y, pytest-5.x.y, py-1.x.y, pluggy-0.x.y
rootdir: $REGENDOC_TMPDIR, inifile:
collected 5 items
tests/example/test_example_01.py . [ 20%]
tests/example/test_example_02.py . [ 40%]
tests/example/test_example_03.py . [ 60%]
tests/foobar/test_foobar_01.py . [ 80%]
tests/foobar/test_foobar_02.py . [100%]
========================= 5 passed in 0.02 seconds =========================
运行方式
1.Pycharm 界面运行,设置默认使用pytest运行
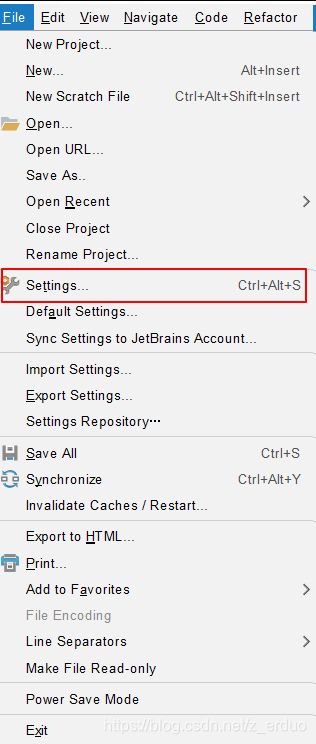
(1)在菜单栏点击【File】>【Settings】
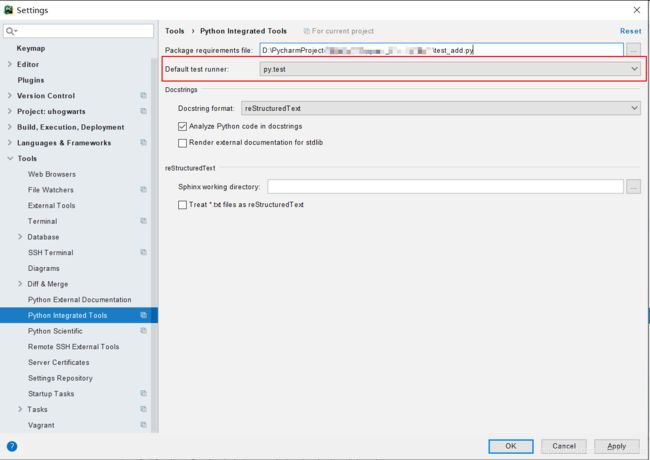
(2)【Settings】>【Tools】>【Python Integrated Tools】>【Default test runner】下拉菜单中勾选【py.test】,点击【apply】应用设置,点击【ok】关闭窗口
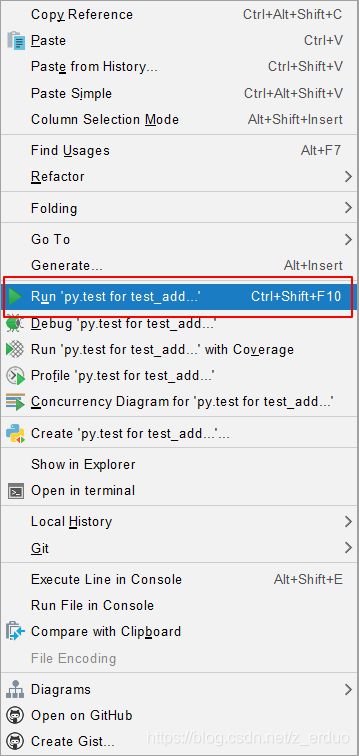
(3)右键,如下图,pytest已成为PyCharm脚本的默认执行方式
2.命令行执行
pytest
pytest test_add.py
pytest test_add.py::test_func
pytest 常用的命令行参数
常用参数
pytest --collect-only 只收集用例
pytest -k “add ” 匹配所有名称中包含add的用例(‘add or div’ ‘TestClass’)
pytest -m mark标签名 标记
pytest - - junitxml=./result.xml 生成执行结果文件
pytest --setup-show 回溯fixture的执行过程
更多的用法使用pytest —help查看帮助文档
pytest 框架结构
● 类似的setup,teardown同样更灵活,
● 模块级(setup_module/teardown_module)模块始末,全局的(优先最高)
● 函数级(setup_function/teardown_function)只对函数用例生效(不在类中)
● 类级**(setup_class/teardown_class)**只在类中前后运行一次(在类中)
● 方法级(setup_method/teardown_methond)开始于方法始末(在类中)
● **类里面的(setup/teardown)**运行在调用方法的前后
参数化
@pytest.mark.parametrize进⾏参数化
import pytest
def add(a,b):
return a+b
class TestAdd:
def setup(self):
print("开始计算".center(30,"*"))
def teardown(self):
print("结束计算".center(30,"*"))
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect',[[1,2,3],[2,3,5]])
def test_add(self, a,b,expect):
print("{}+{}={}".format(str(a),str(b),str(expect)))
assert expect == add(a, b)
使用YAML参数化
安装
python3.X使用以下命令安装
pip install pyyaml
python2.X 使用以下命令安装
pip install yaml
语法
大小写敏感
使用缩进表示层级关系
缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
'#'表示注释
数组
“-” 后面要有空格
- A
- B
- C
字典
":"冒号后面要有空格
child-key: value
混合
companies:
-
id: 1
name: company1
price: 200W
-
id: 2
name: company2
price: 500W
相当于
companies: [{id: 1,name: company1,price: 200W},{id: 2,name: company2,price: 500W}]
YAML读取
cases_datas.yaml
ids:
- 正数和正数相加
- 0和0相加
datas:
# -
# - a
# - b
# - expect
-
- 1
- 2
- 3
-
- 0
- 0
- 0
读取yaml文件内容
#do_yaml.py
# pip install pyyaml
import yaml
class Do_YAML:
def read_yaml(self,file_path):
with open(file_path,encoding='utf-8') as f:
datas = yaml.safe_load(f)
return datas
if __name__ == '__main__':
t = Do_YAML()
datas = t.read_yaml(file_path='./cases_datas.yaml')
print(datas)
打印结果
{'ids': ['正数和正数相加', '0和0相加'], 'datas': [[1, 2, 3], [0, 0, 0]]}
pytest demo
Calculator.py
#Calculator.py
class Calculator:
def add(self,a,b):
return a+b
def div(self,a,b):
return a/b
def multi(self,a,b):
return a*b
def sub(self,a,b):
return a-b
test_add.py
#test_add.py
# pip install pytest
import pytest
# pip install pyyaml
from do_yaml import Do_YAML
from Calculator import Calculator
calc = Calculator()
do_yaml = Do_YAML()
case_datas = do_yaml.read_yaml(file_path="./add_cases.yaml")
class TestAdd:
def setup(self):
print("开始计算".center(30,"*"))
def teardown(self):
print("结束计算".center(30,"*"))
@pytest.mark.parametrize('a,b,expect',case_datas["datas"], ids=case_datas["ids"])
def test_add(self, a,b,expect):
print("{}+{}={}".format(str(a),str(b),str(expect)))
assert expect == calc.add(a, b)
参考资料:
英文文档
https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/getting-started.html#create-your-first-test
中文文档:
https://www.osgeo.cn/pytest/contents.html
yaml文档
https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation