顺序表的实现
CSDN主页:醋溜马桶圈_C语言进阶,初始C语言,数据结构-CSDN博客
Gitee主页:mnxcc (mnxcc) - Gitee.com
专栏:数据结构_醋溜马桶圈的博客-CSDN博客
之前我们学习了顺序表的有关知识
这篇文章我们学习一下顺序表的接口实现
同样我们创建SeqList.h SeqList.c test.c三个文件来实现功能
1.创建顺序表
2.基本的增删查改接口
2.1顺序表初始化
顺序表的初始化我们只需要讲指针置为空指针
然后将当前数据元素个数和最大数据元素个数置为0
到插入时我们便会动态开辟空间给指针a
//顺序表的初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;//置为空指针
ps->size = 0;//数据个数为0
ps->capacity = 0;//空间大小置为0
}2.2顺序表的销毁
//顺序表的销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->a != NULL)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}2.3检查顺序表的容量
//检查顺序表的容量
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity = 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}2.4打印顺序表
//打印顺序表
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}2.5顺序表的尾插
//顺序表的尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}2.6顺序表的头插
//顺序表的头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}2.7顺序表的尾删
//顺序表的尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
//ps->a[ps->size - 1] = -1;
ps->size--;
}2.8顺序表的头删
//顺序表的头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
//for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
//{
// ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
//}
//ps->size--;
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}2.9任意位置的插入
//任意位置的插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}2.10任意位置的删除
//任意位置的删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
int begin = pos;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin+1];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}2.11顺序表的查找
//顺序表的查找
//找到返回下标,找不到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}3.总代码
SeqList.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
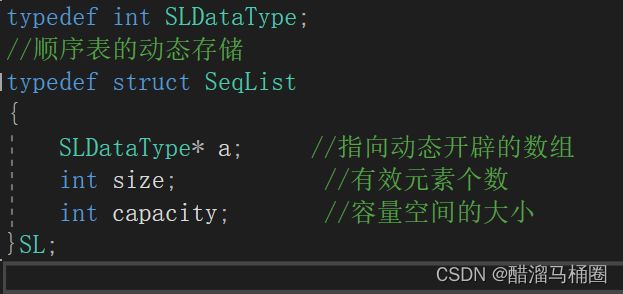
typedef int SLDataType;
//顺序表的动态存储
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a; //指向动态开辟的数组
int size; //有效元素个数
int capacity; //容量空间的大小
}SL;
//顺序表的初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps);
//顺序表的销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);
//检查顺序表的容量
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
//打印顺序表
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
//顺序表的尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//顺序表的头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//顺序表的尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//顺序表的头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);
//任意位置的插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//任意位置的删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//顺序表的查找
//找到返回下标,找不到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
SeqList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
//顺序表的初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;//置为空指针
ps->size = 0;//数据个数为0
ps->capacity = 0;//空间大小置为0
}
//顺序表的销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->a != NULL)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
}
//检查顺序表的容量
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(SLDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
//打印顺序表
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//顺序表的尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//顺序表的头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//顺序表的尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
//ps->a[ps->size - 1] = -1;
ps->size--;
}
//顺序表的头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
//for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
//{
// ps->a[i] = ps->a[i + 1];
//}
//ps->size--;
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size > 0);
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
//任意位置的插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//任意位置的删除
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= ps->size);
int begin = pos;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin] = ps->a[begin+1];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
//顺序表的查找
//找到返回下标,找不到返回-1
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqList.h"
int main()
{
SL sl;
SLInit(&sl);
SLPushBack(&sl, 10);
SLPushBack(&sl, 20);
SLPushBack(&sl, 30);
SLPushBack(&sl, 40);
SLPrint(&sl);
SLPopBack(&sl);
SLPrint(&sl);
SLPopFront(&sl);
SLPrint(&sl);
SLPushFront(&sl, 10);
SLPrint(&sl);
SLInsert(&sl, 1, 15);
SLPrint(&sl);
SLErase(&sl, 2);
SLPrint(&sl);
int ret1 = SLFind(&sl, 15);
printf("%d\n", ret1);
int ret2 = SLFind(&sl, 20);
printf("%d\n", ret2);
SLDestroy(&sl);
return 0;
}欢迎各位大佬指正!