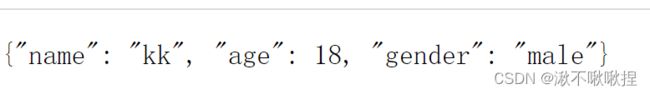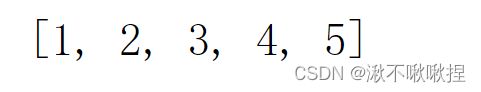Django视图层
视图层
django视图层:Django项目下的views.py文件,它的内部是一系列的函数或者是类,用来处理客户端的请求后处理并返回相应的数据
三板斧
HttpResponse # 返回字符串
render # 返回html页面,并且在返回浏览器之前还可以给html文件传值
redirect # 重定向三板斧的详情数据
class HttpResponse(HttpResponseBase):
pass
"""括号内的任意一个字符串作为响应体"""
def render(request, template_name, context=None, content_type=None, status=None, using=None)
"""参数:render:生成响应请求的对象
template_name:使用模版的完整名称,可选的参数
context : 添加到模版上下文的一个字典,默认为空字典,如果字典中有某个值可调用,那么将在视图渲染前调用它
status: 状态码
render方法就是将一个模版中页面的模板语法进行渲染,最终渲染成一个html页面作为响应体
"""
def redirect(to, *args, permanent=False, **kwargs):
"""传递一个需要重定向的硬编码URL或路由
redirect内部都是继承了HttpResponse"""
注意:用来处理视图函数的请求都需要HttpResponse对象!!!
JsonReesponse序列化对象
前后端的数据交互需要用到序列化json作为序列化方法,实现跨语言传输
混合开发项目,前端与后端的代码写在一块
前端分为一个项目,后端一个项目,后端只需写端口即可
前端序列化 后端序列化
JSON.stringify() json.dumps()
JSON.parse() json.loads()json序列化
def json_func(request):
user_dict = {'name': 'kk', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'}
#将数据发送至前段
json_str = json.dumps(user_dict)
return HttpResponse(user_dict)
#ensure_ascii 内部默认True自动转码,改为False不转码,只生成json格式,双引号JsonResponse序列化
导入模块
from django.http import JsonResponsedef json_func(request):
def json_func(request):
user_dict = {'name': 'kk', 'age': 18, 'gender': 'male'}
return JsonResponse(user_dict)
"""
本质上JsonResponse还是HttpResponse
class JsonResponse(HttpResponse):"""
使用JsonResponse序列化列表:
def index(request):
user_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
return JsonResponse(user_list)当我们直接使用JsonResponse方法时,可以发现报错了
这是我们需要看源码:
def __init__(self, data, encoder=DjangoJSONEncoder, safe=True,
json_dumps_params=None, **kwargs)把里面的safe改为False即可但是我们不能修改源码所以我们在JsonResponse中修改
def index(request):
user_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
return JsonResponse(user_list, safe=False)form表单与request对象获取文件
form请求数据方式必须是POST,
enctype="multipart/form-data"
当我们上传文件时,发现我们只得到的结果是上传文件的名称,并没有照片的数据
def index(request):
print(request.POST) #
return render(request, 'index.html') request.FILES
所以我们接受文件不能用POST,应该使用FILES
def index(request):
print(request.FILES) # ]}>
return render(request, 'index.html')
类似于一个对象,数据都在这里面:InMemoryUploadedFile 得到数据:
def index(request):
print(request.FILES) # ]}>
if request.method == "POST":
file_obj = request.FILES.get('my-fold')
file_name = file_obj.name
# 得到数据后写入文件对象中
with open(file_name, 'wb')as f:
for line in file_obj:
f.write(line)
return render(request, 'index.html')
总结:request.POST 一值都是接収的是非文件数据
request.FILES 接收的则是文件的数据,普通的数据还在POST中。
reuqest.boyd
"""request.body 接受纯原生的二进制数据,没有接受任何的处理, 所以我们要想得到数据,就必须先把它转为str---->在进行decode------->然后在进行转化为字形式"""之所以POST和FILES可以直接获取数据,是因为Django进行了封装,因为body没有进行封装所以需要我们自己来操作
request.path,request.path_info , request.get_full_path()都是与路径相关的
print(request.path)
print(request.path_info)
print(request.get_full_path())
# 1.打印结果为/index/
# 2./index/
# 3./index/?a=1&b=2CBV写法
FBV:function based view 写的是函数
CBV: class based view 写的是类
FBV
基于函数的视图
def index(request):return HttpResponse对象
CBV
基于类的视图
from django import views
class MyLoginView(views.View):
def get(self, request):
return HttpResponse('from CBV get function')
def post(self, request):
return HttpResponse('from CBV post function')
path('login/', views.MyLoginView.as_view())
会自动根据请求方法的不同自动匹配对应的方法并执行CBV源码
# 入口
url(r'^login/', views.MyLogin.as_view()),
# View类中得as_view方法的返回值是view函数名
# 当请求来的时候,会触发view函数的执行
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
# cls:Mylogin()------>self对象
self = cls(**initkwargs)
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs) # View类里的dispatch
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
return handler(request, *args, **kwargs)
from django.views import View
class MyLogin(View):
http_method_names = ['get', 'post']
def get(self, request):
print('get。。。')
self.index()
return HttpResponse("get")
def post(self, request):
return HttpResponse("hello postman!!!")
def index(self):
pass
权限、频率、jwt的源码