Spring-ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory选择cglib或jdk动态代理原理
ProxyFactory在生成代理对象之前需要决定是使用JDK动态代理还是CGLIB技术:
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable {
@Override
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
// 如果ProxyFactory的isOptimize为true,Spring认为cglib比jdk动态代理要快
// 或者isProxyTargetClass为true,
// 或者被代理对象没有实现接口,
// 或者只实现了SpringProxy这个接口
// 那么则利用Cglib进行动态代理,但如果被代理类是接口,或者被代理类已经是进行过JDK动态代理而生成的代理类了则只能进行JDK动态代理
// 其他情况都会进行JDK动态代理,比如被代理类实现了除SpringProxy接口之外的其他接口
// 是不是在GraalVM虚拟机上运行
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() &&
(config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) {
// config就是ProxyFactory对象
Class targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
// targetClass是接口,直接使用Jdk动态代理
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
// 使用Cglib
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
// 使用Jdk动态代理
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
/**
* Determine whether the supplied {@link AdvisedSupport} has only the
* {@link org.springframework.aop.SpringProxy} interface specified
* (or no proxy interfaces specified at all).
*/
private boolean hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(AdvisedSupport config) {
Class[] ifcs = config.getProxiedInterfaces();
return (ifcs.length == 0 || (ifcs.length == 1 && SpringProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(ifcs[0])));
}
}代理对象创建过程
JdkDynamicAopProxy
/**
* Construct a new JdkDynamicAopProxy for the given AOP configuration.
* @param config the AOP configuration as AdvisedSupport object
* @throws AopConfigException if the config is invalid. We try to throw an informative
* exception in this case, rather than let a mysterious failure happen later.
*/
public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null");
if (config.getAdvisorCount() == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) {
throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified");
}
this.advised = config;
// 设置JDK动态代理所要代理的接口
this.proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true);
findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(this.proxiedInterfaces);
}
// 1、在构造JdkDynamicAopProxy对象时,会先拿到被代理对象自己所实现的接口,
// 并且额外的增加SpringProxy、Advised、DecoratingProxy三个接口,组合成一个Class[],
// 并赋值给proxiedInterfaces属性
static Class[] completeProxiedInterfaces(AdvisedSupport advised, boolean decoratingProxy) {
// 被代理对象自己所实现的接口
Class[] specifiedInterfaces = advised.getProxiedInterfaces();
// 如果被代理对象没有实现接口,则判断被代理类是不是接口,或者被代理类是不是已经经过JDK动态代理之后的类从而获取想对应的接口
if (specifiedInterfaces.length == 0) {
// No user-specified interfaces: check whether target class is an interface.
Class targetClass = advised.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass != null) {
if (targetClass.isInterface()) {
advised.setInterfaces(targetClass);
}
else if (Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
advised.setInterfaces(targetClass.getInterfaces());
}
specifiedInterfaces = advised.getProxiedInterfaces();
}
}
// 添加三个Spring内置接口:SpringProxy、Advised、DecoratingProxy
List> proxiedInterfaces = new ArrayList<>(specifiedInterfaces.length + 3);
for (Class ifc : specifiedInterfaces) {
// Only non-sealed interfaces are actually eligible for JDK proxying (on JDK 17)
if (isSealedMethod == null || Boolean.FALSE.equals(ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(isSealedMethod, ifc))) {
proxiedInterfaces.add(ifc);
}
}
if (!advised.isInterfaceProxied(SpringProxy.class)) {
proxiedInterfaces.add(SpringProxy.class);
}
if (!advised.isOpaque() && !advised.isInterfaceProxied(Advised.class)) {
proxiedInterfaces.add(Advised.class);
}
if (decoratingProxy && !advised.isInterfaceProxied(DecoratingProxy.class)) {
proxiedInterfaces.add(DecoratingProxy.class);
}
return ClassUtils.toClassArray(proxiedInterfaces);
}
// 2、检查这些接口中是否定义了equals()、hashcode()方法
private void findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(Class[] proxiedInterfaces) {
// 判断被代理的接口中是否定义了equals()、hashCode()方法,
// 如果在接口中手动定义了这两个方法,则也会进行代理
// 否则这两个方法是不会走代理逻辑的
for (Class proxiedInterface : proxiedInterfaces) {
Method[] methods = proxiedInterface.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
this.equalsDefined = true;
}
if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
this.hashCodeDefined = true;
}
if (this.equalsDefined && this.hashCodeDefined) {
return;
}
}
}
}
// 3、得到代理对象,JdkDynamicAopProxy作为InvocationHandler
// 代理对象在执行某个方法时,会进入到JdkDynamicAopProxy的invoke()方法中
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
// this实现了InvocationHandler
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, this.proxiedInterfaces, this);
} ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
// 被代理的类
Class rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class proxySuperClass = rootClass;
// 0、如果被代理类本身就已经是Cglib所生成的代理类了
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
// 获取真正的被代理类
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
// 获取被代理类所实现的接口
Class[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
// 1、创建Enhancer对象
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
// 2、被代理类,代理类的父类。proxySuperClass就是ProxyFactory.setTarget()所设置的对象的类
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
// 3、代理类额外要实现的接口。通过ProxyFactory.addInterface()所添加的接口,
// 以及SpringProxy、Advised、DecoratingProxy接口
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
// 获取和被代理类所匹配的Advisor
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class[] types = new Class[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
// 4、设置Enhancer的Callbacks为DynamicAdvisedInterceptor
// 代理对象在执行某个方法时,会进入到DynamicAdvisedInterceptor的intercept()方法中
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}代理对象执行过程
1、在使用ProxyFactory创建代理对象之前,需要往ProxyFactory先添加Advisor
2、代理对象在执行某个方法时,会把ProxyFactory中的Advisor拿出来和当前正在执行的方法进行匹配筛选
3、把和方法所匹配的Advisor适配成MethodInterceptor
4、把和当前方法匹配的MethodInterceptor链,以及被代理对象、代理对象、代理类、当前Method对象、方法参数封装为MethodInvocation对象
5、调用MethodInvocation的proceed()方法,开始执行各个MethodInterceptor以及被代理对象的对应方法
6、按顺序调用每个MethodInterceptor的invoke()方法,并且会把MethodInvocation对象传入invoke()方法
7、直到执行完最后一个MethodInterceptor,就会调用invokeJoinpoint()方法,从而执行被代理对象的当前方法
各注解对应的MethodInterceptor
@Before对应的是AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice,在进行动态代理时会把AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice转成MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
-
先执行advice对应的方法
-
再执行MethodInvocation的proceed(),会执行下一个Interceptor,如果没有下一个Interceptor了,会执行target对应的方法
@After对应的是AspectJAfterAdvice,直接实现了MethodInterceptor
-
先执行MethodInvocation的proceed(),会执行下一个Interceptor,如果没有下一个Interceptor了,会执行target对应的方法
-
再执行advice对应的方法
@Around对应的是AspectJAroundAdvice,直接实现了MethodInterceptor
-
直接执行advice对应的方法,由@Around自己决定要不要继续往后面调用
@AfterThrowing对应的是AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice,直接实现了MethodInterceptor
-
先执行MethodInvocation的proceed(),会执行下一个Interceptor,如果没有下一个Interceptor了,会执行target对应的方法
-
如果上面抛了Throwable,那么则会执行advice对应的方法
@AfterReturning对应的是AspectJAfterReturningAdvice,在进行动态代理时会把AspectJAfterReturningAdvice转成AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
-
先执行MethodInvocation的proceed(),会执行下一个Interceptor,如果没有下一个Interceptor了,会执行target对应的方法
-
执行上面的方法后得到最终的方法的返回值
-
再执行advice对应的方法
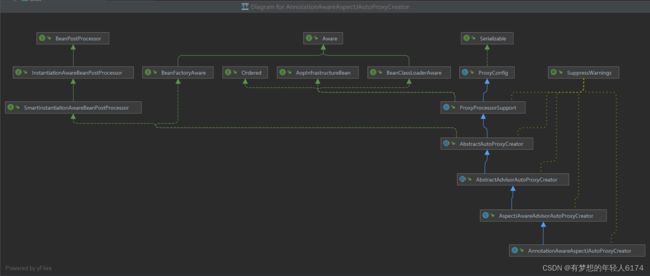
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
DefaultAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的父类是AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator。 AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator非常强大以及重要,只要Spring容器中存在这个类型的Bean,就相当于开启了AOP,AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator实际上就是一个BeanPostProcessor,所以在创建某个Bean时,就会进入到它对应的生命周期方法中。
当某个Bean初始化后,会调用wrapIfNecessary()方法进行AOP:AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator会找到所有的Advisor,然后判断当前这个Bean是否存在某个Advisor与之匹配(根据Pointcut),如果匹配就表示当前这个Bean有对应的切面逻辑,需要进行AOP,需要产生一个代理对象。
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
主要作用:往Spring容器中添加了一个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类型的Bean
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator继承了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator,重写了findCandidateAdvisors()方法。
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator只能找到所有Advisor类型的Bean对象。
AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator除了可以找到所有Advisor类型的Bean对象,还能把@Aspect注解所标注的Bean中的@Before等注解及方法进行解析,并生成对应的Advisor对象。
简单理解:@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解就是往Spring容器中添加了一个AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类型的Bean,从而开启了AOP,并且还会解析@Before等注解生成Advisor。