都快2024年了,别只使用React,需要学习一下Vue,不然没出路了
最近,我的朋友因为不熟悉 Vue.js 而未能通过面试。
她平时工作中大部分时间都在使用React,所以也懒得去了解其他前端框架。
世界上所有的前端框架我们都应该熟悉吗?
不,这是极其不合理的。
但为了生存,朋友还是要学习Vue的框架。
让我们看看如何使用 Vue 来实现 React 的一些功能。
1. v-if:如何显示和隐藏元素?
控制元素或组件的显示和隐藏是我们最常见的事情之一,在React中,我们经常这样编码。
JavaScript 中的三元表达式和“&”也可以实现同样的目标。
React
import React, { useState } from "react"
export default function Vif (){
const [ isShow, setIsShow ] = useState(true)
const onToggleShow = () => {
setIsShow(!isShow)
}
return (
{/* Of course you can also use ternary expressions */}
{/* isShow ? fatfish has shown : null */}
{
isShow && fatfish has shown
}
)
}Vue
那么在Vue中如何实现同样的功能呢?
是的,我们可以使用 v-if 指令来控制元素的显示和隐藏,这很简单,不是吗?
fatfish has shown
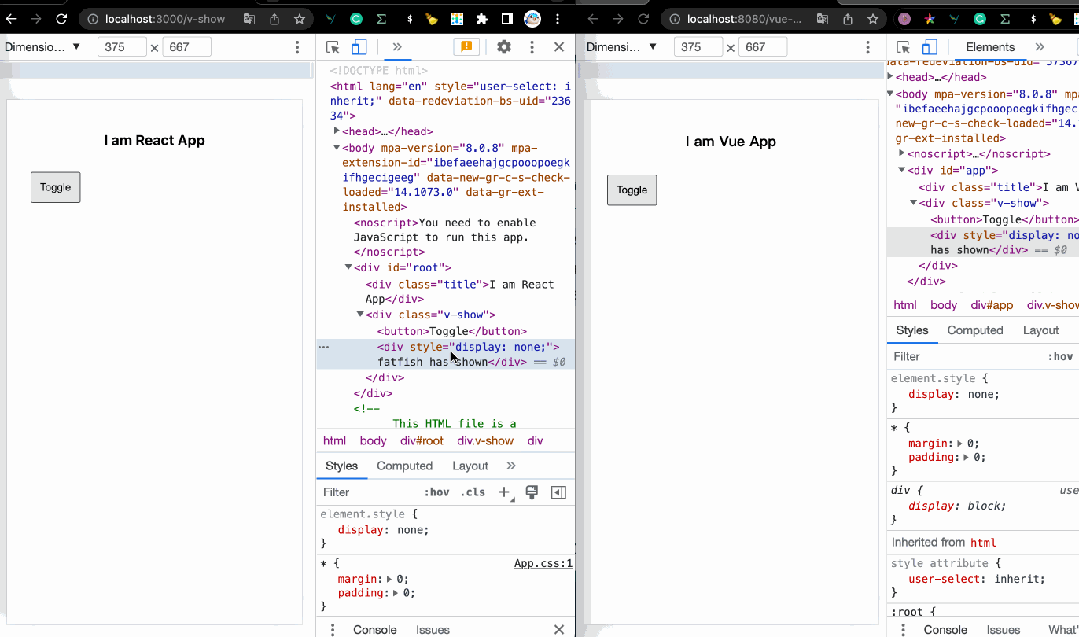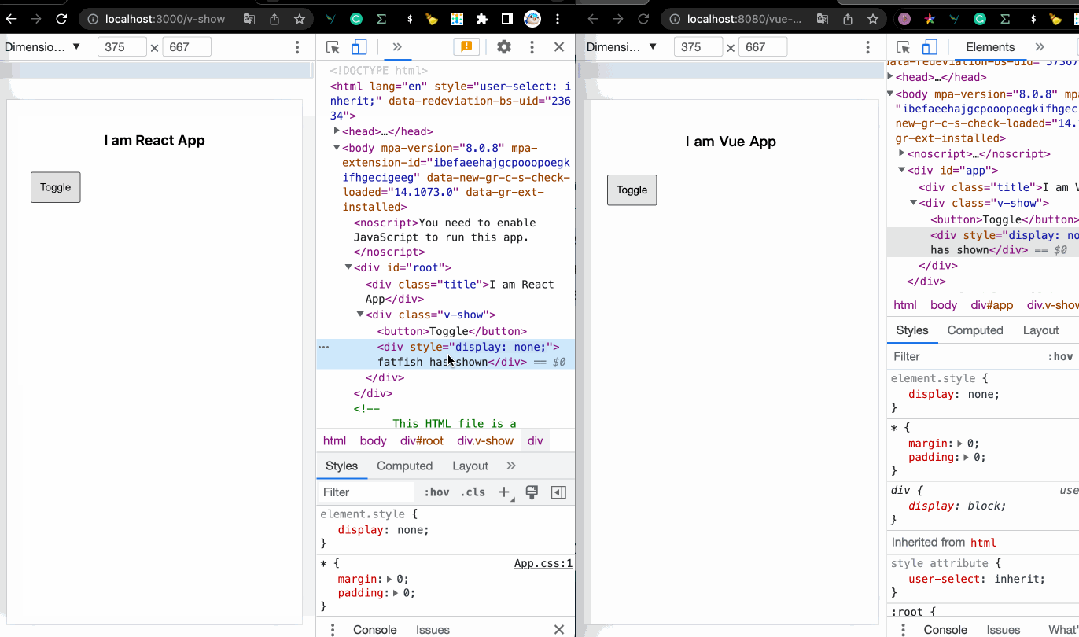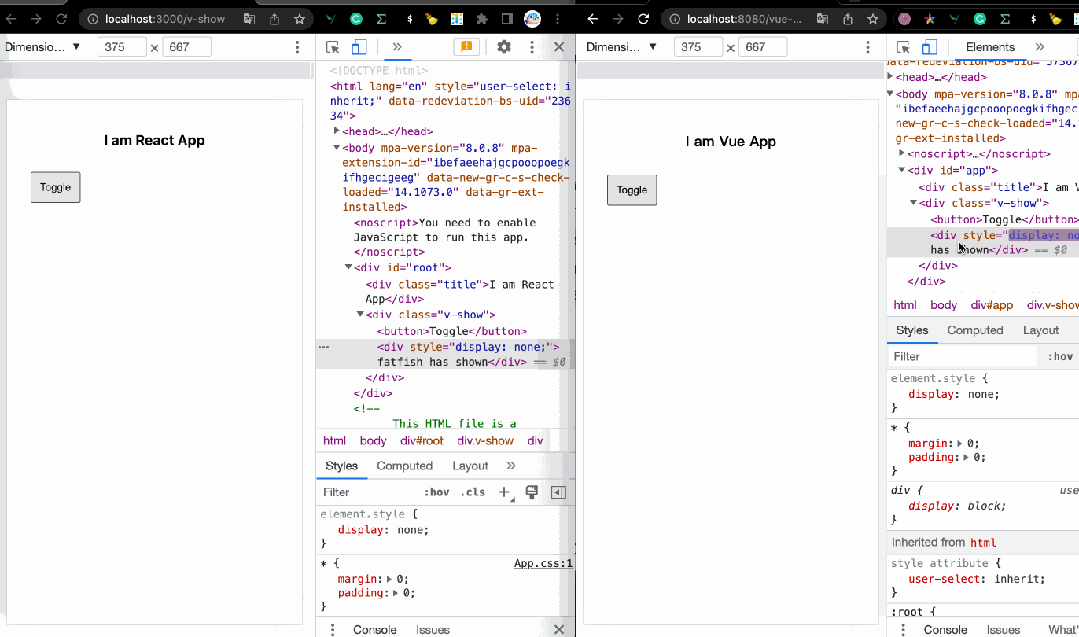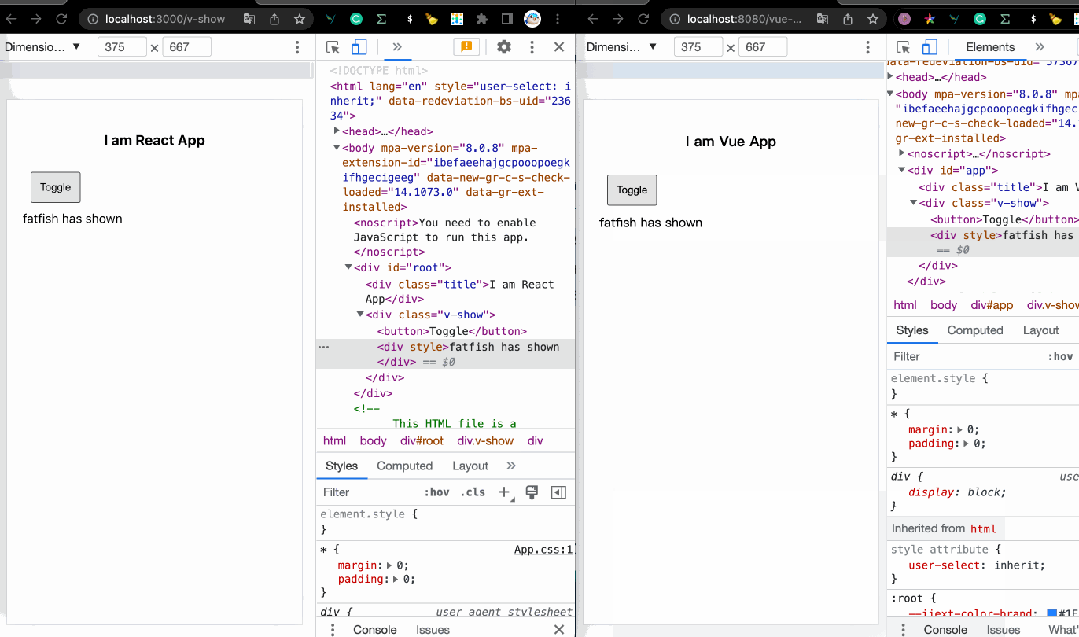
2. v-show:如何显示和隐藏元素?
v-if 导致元素或组件被重复删除和创建,如果我们只想“显示”或“隐藏”它怎么办?
也许我们可以借助 CSS 中的 display 属性来做到这一点。
React
import React, { useState } from "react"
export default function VShow (){
const [ isShow, setIsShow ] = useState(true)
const onToggleShow = () => {
setIsShow(!isShow)
}
return (
{
fatfish has shown
}
)
}Vue
你可能已经猜到了,我们可以使用 v-show 来实现与它相同的功能。看起来 Vue 更简洁,你不觉得吗?
fatfish has shown
3. v-for:渲染列表?
在React中,我们可以使用数组的map方法来创建列表,这非常简单。
看一下这段代码,它创建了三个不同职业的列表。
React
import React, { useState } from "react"
export default function VFor (){
const [ list, setList ] = useState([
{
id: 1,
name: 'Front end',
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'Android',
},
{
id: 3,
name: 'IOS',
},
])
return (
{
list.map((item) => {
return { item.name }
})
}
)
}Vue
你喜欢 Vue 中的 v-for 指令吗?
{{ item.name }}
4. 计算
如果我们想计算两个数的和,有什么好的方法吗?
我的意思是,当 num1 和 num2 发生变化时,它们的总和会自动变化,我们不需要手动处理。
React
import React, { useMemo, useState } from "react"
export default function Computed (){
const [ num1, setNum1 ] = useState(10)
const [ num2, setNum2 ] = useState(10)
const num3 = useMemo((a, b) => {
return num1 + num2
}, [ num1, num2 ])
const onAdd = () => {
setNum1(num1 + 10)
}
return (
result:{ num3 }
)
}哇,太棒了,useMemo 帮我们解决了一个问题。
Vue
那么,Vue中有没有更好的实现呢?它实际上提供了一种称为“计算”的机制,该机制更智能且更易于使用。
result:{{ num3 }}
5.watch
当我们需要监听数据变化然后执行回调函数时,可以在React中使用useEffect来完成。
让我们尝试模拟一个场景:
我们点击男孩或女孩按钮,选中时发送请求,最后显示请求结果(我们通过setTimeout模拟异步请求过程)。
React
export default function Watch() {
const [fetching, setFetching] = useState(false)
const [selects, setSelects] = useState([
'boy',
'girl'
])
const [selectValue, setSelectValue] = useState('')
const result = useMemo(() => {
return fetching ? 'requesting...' : `the result of the request: ${selectValue || '~'}`
}, [ fetching ])
const onSelect = (value) => {
setSelectValue(value)
}
const fetch = () => {
if (!fetching) {
setFetching(true)
setTimeout(() => {
setFetching(false)
}, 1000)
}
}
// Pay attention here
useEffect(() => {
fetch()
}, [ selectValue ])
return (
{
selects.map((item, i) => {
return
})
}
{ result }
)
}Vue
别担心,我们可以在 Vue 中做同样的事情,你知道它的秘密是什么吗?
是的,答案是watch。
{{ result }}
6. style
有时我们需要动态地向元素添加样式,Vue 和 React 都为我们提供了一种便捷的使用方式。
从用途上来说,它们基本上是相似的。
相同点:
CSS 属性名称可以是驼峰命名法或短横线命名法(记住将它们用引号引起来)
差异:
- 在Vue中,我们可以通过数组语法绑定多个样式对象,React主要是单个对象的形式(这一点Vue也可以)
- 在React中,对于属性的数量,它会自动给内联样式添加“px”(这一点Vue不会自动处理)后缀,其他单位需要手动指定
- 在 React 中,样式不会自动添加前缀。当 v-bind:style 使用需要浏览器引擎前缀的 CSS 属性时,例如 Transform,Vue.js 会自动检测并添加相应的前缀。
React
import React from "react"
export default function Style (){
const style = {
width: '100%',
height: '500px',
}
const style2 = {
backgroundImage: 'linear-gradient(120deg, #84fab0 0%, #8fd3f4 100%)',
borderRadius: '10px',
}
return (
)
}Vue
7.class
我们应该如何动态地为元素添加类?
在Vue中,我更喜欢使用数组语法(当然也有对象方式),在React中也可以使用一些第三方包比如classnames来起到更方便的方式来添加类的效果。
React
import React, { useMemo, useState } from "react"
import './class.css'
export default function Class (){
const [ isActive, setIsActive ] = useState(false)
const buttonText = useMemo(() => {
return isActive ? 'Selected' : 'UnSelected'
}, [ isActive ])
const buttonClass = useMemo(() => {
return [ 'button', isActive ? 'active' : '' ].join(' ')
}, [ isActive ])
const onClickActive = () => {
setIsActive(!isActive)
}
return (
{ buttonText }
)
}Vue
8. provide/inject
Vue 和 React 对于全局状态的管理都有自己很好的解决方案,比如 Vue 中的 Vuex、Redux 中的 React 和 Mobx,但是,当然,这些小项目的引入对于小用途来说有点太大了,就没有其他解决方案?
provide/inject可以在Vue中使用
React 可以使用 Context
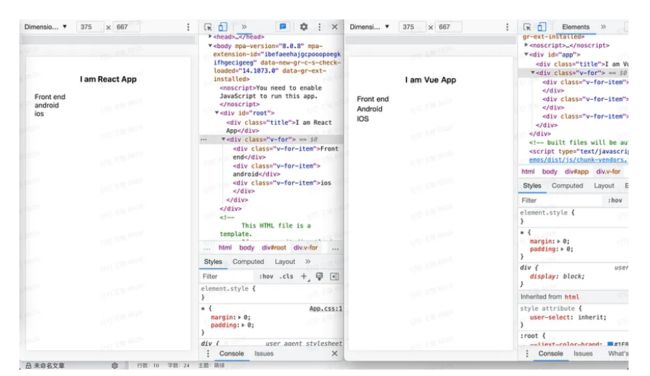
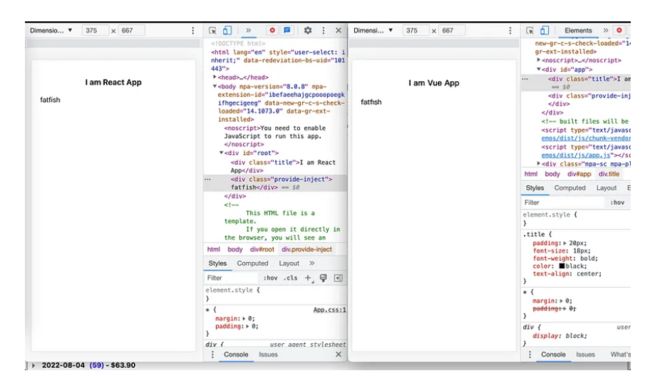
假设我们有一个用于用户信息的全局变量“userInfo”,需要在每个组件中轻松访问它,如何在Vue和React中实现它?
React
为了在 React 中实现这一点,您可以借助 Context 将全局状态共享给任何子节点。
上下文/index.js
import { createContext } from "react";
export const UserInfoContext = createContext({
userInfo: {
name: ''
}
})App.js
import { UserInfoContext } from './context/index'
function App() {
return (
// Pay attention here
I am React App
);
}provide.js
import React, { useContext } from "react"
import { UserInfoContext } from '../context/index'
export default function Provide() {
// We can use the defined "UserInfoContext" through the userContext
const { userInfo } = useContext(UserInfoContext)
return (
{ userInfo.name }
)
}Vue
在Vue中,我们可以使用“provide/inject”将顶级状态传递给任何子节点,假设我们在app.vue中声明一个“userInfo”数据。
App.vue
I am Vue App
provide.vue
{{ userInfo.name }}
9. Slots
假设我们要实现一个简单的对话组件,基本功能是标题可以作为字符串传递,内容部分可以完全自定义,我们应该如何实现呢?
React
虽然React中没有槽的概念,但是可以通过props.children获取组件内部的子元素,通过这个可以实现默认的槽。
Dialog.js
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react"
import './dialog.css'
export default function Dialog(props) {
// Forgive me for implementing this in a silly way like visible -1 first, but that's not the point
const { children, title = '', visible = -1 } = props
const [visibleInner, setVisibleInner] = useState(false)
const onHide = () => {
setVisibleInner(false)
}
useEffect(() => {
setVisibleInner(visible > 0)
}, [ visible ])
return (
{ title ? { title } : null }
{/* Note here that the default slot function is implemented via children */}
{children}
Cancel
Confirm
)
}slot.js
import React, { useState, useEffect } from "react"
import Dialog from './components/dialog'
export default function Slot() {
const [visible, setVisible] = useState(-1)
const onToggleVisible = () => {
setVisible(Math.random())
}
return (
)
}Vue
同样的功能在Vue中应该如何实现呢?
dialog.vue
{{ title }}
slot.vue