【入门Flink】- 11Flink实现动态TopN
基本处理函数(ProcessFunction)
stream.process(new MyProcessFunction())
方法需要传入一个 ProcessFunction 作为参数,ProcessFunction 不是接口 , 而是一个抽象类 ,继承了AbstractRichFunction,所有的处理函数,都是富函数(RichFunction),拥有富函数所有功能。
// 泛型:
// Type parameters: – Type of the input elements. 输入类型
// – Type of the output elements. 输出类型
public abstract class ProcessFunction<I, O> extends AbstractRichFunction {
public abstract void processElement(I value, Context ctx, Collector<O> out) throws Exception;
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<O> out) throws Exception {}
}
1)抽象方法.processElement()
“处理元素”,定义了处理的核心逻辑。这个方法对于流中的每个元素都会调用一次,参数包括三个:输入数据值 value,上下文 ctx,以及“收集器”(Collector)out。
value:当前流中的输入元素ctx:类型是 ProcessFunction 中定义的内部抽象类 Context,表示当前运行的上下文,可以获取到当前的时间戳,并提供了用于查询时间和注册定时器的“定时服务”(TimerService),以及可以将数据发送到“侧输出流”(side output)的方法.output()。out:“收集器”(类型为 Collector),用于返回输出数据。调用 out.collect()方法就可以向下游发出一个数据。这个方法可以多次调用,也可以不调用。
ProcessFunction 可以轻松实现flatMap、map、filter 这样的基本转换功能;而通过富函数提供的获取上下文方法.getRuntimeContext(),也可以自定义状态(state)进行处理。
2)非抽象方法.onTimer()
只有在注册好的定时器触发的时候才会调用,而定时器是通过“定时服务”TimerService 来注册的。
三个参数:时间戳(timestamp),上下文(ctx),以及收集器(out)。
-
timestamp:指设定好的触发时间,事件时间语义下是水位线 -
ctx:同样可以调用定时服务(TimerService)
-
采集器:任意输出处理之后的数据
.onTimer()方法定时触发,因此ProcessFunction可以自定义数据按照时间分组 、 定时触发计算输出结果;这 就实现了**窗口(window )**的功能。所以说
ProcessFunction 可以实现一切功能。
注意:在 Flink 中,只有**“按键分区流”KeyedStream 才支持设置定时器的操作**。
处理函数的分类(8大处理函数)
1)ProcessFunction
最基本的处理函数,基于 DataStream 直接调用.process()时作为参数传入。
2)KeyedProcessFunction
对流按键分区后的处理函数,基于 KeyedStream 调用.process()时作为参数传入。要想使用定时器,必须基于 KeyedStream。
3)ProcessWindowFunction
开窗之后的处理函数,也是全窗口函数的代表。基于 WindowedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。
4)ProcessAllWindowFunction
同样是开窗之后的处理函数,基于 AllWindowedStream 调用.process()时作为参数传入
5)CoProcessFunction
合并(connect)两条流之后的处理函数,基于 ConnectedStreams 调用.process()时作为参数传入
6)ProcessJoinFunction
间隔连接(interval join)两条流之后的处理函数,基于 IntervalJoined 调用.process()时作为参数传入。
7)BroadcastProcessFunction
广播连接流处理函数,基于 BroadcastConnectedStream 调用.process()时作为参数传入。
“广播连接流”BroadcastConnectedStream,是一个未 keyBy 的普通DataStream与一个广播流(BroadcastStream)做连接(conncet)之后的产物。
8)KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction
按键分区的广播连接流处理函数,同样是基于 BroadcastConnectedStream调用.process()时作为参数传 入 。 一个KeyedStream 与广播流(BroadcastStream)做连接之后的产物。
按键分区处理函数(KeyedProcessFunction)
定时器(Timer)和定时服务(TimerService)
ProcessFunction 的上下文(Context)中提供了.timerService()方法,可以直接返回一个 TimerService 对象。
TimerService包含以下六个方法:
// 获取当前的处理时间
long currentProcessingTime();
// 获取当前的水位线(事件时间)
long currentWatermark();
// 注册处理时间定时器,当处理时间超过 time 时触发
void registerProcessingTimeTimer(long time);
// 注册事件时间定时器,当水位线超过 time 时触发
void registerEventTimeTimer(long time);
// 删除触发时间为 time 的处理时间定时器
void deleteProcessingTimeTimer(long time);
// 删除触发时间为 time 的处理时间定时器
void deleteEventTimeTimer(long time);
六个方法可以分成两大类:基于处理时间和基于事件时间。
TimerService 会以键(key)和时间戳为标准,对定时器进行去重;
每个key和时间戳,最多只有一个定时器,如果注册了多次,onTimer()方法也将只被调用一次。
案例
public class KeyedProcessTimerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("124.222.253.33", 7777)
.map(new WaterSensorMapFunction())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((element, ts) -> element.getTs() * 1000L)
);
// 传感器Id keyBy
KeyedStream<WaterSensor, String> sensorKS = sensorDS.keyBy(WaterSensor::getId);
sensorKS.process(new KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, String>() {
/**
* 来一条数据调用一次
*/
@Override
public void processElement(WaterSensor value, KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
// 获取当前数据的 key
String currentKey = ctx.getCurrentKey();
// TODO 1.定时器注册
TimerService timerService = ctx.timerService();
// 1、事件时间的案例
Long currentEventTime = ctx.timestamp();//数据中提取出来的事件时间
timerService.registerEventTimeTimer(5000L);
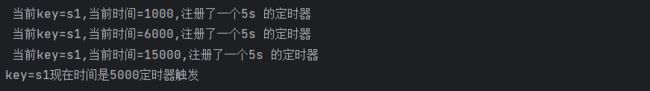
System.out.println(" 当前key=" + currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentEventTime + ",注册了一个5s 的定时器");
// 2、处理时间的案例
// long currentTs = timerService.currentProcessingTime();
// timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer(currentTs + 5000L);
// System.out.println(" 当前key="+currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentTs + ",注册了一个5s 后的定时器");
// 3、获取 process 的 当前watermark
// long currentWatermark = timerService.currentWatermark();
// System.out.println("当前数据=" +value+",当前 watermark=" + currentWatermark);
// 注册定时器: 处理时间、事件时间
// timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer();
// timerService.registerEventTimeTimer();
// 删除定时器: 处理时间、事件时间
// timerService.deleteEventTimeTimer();
// timerService.deleteProcessingTimeTimer();
// 获取当前时间进展: 处理时间-当前系统时间,事件时间-当前 watermark
// long currentTs = timerService.currentProcessingTime();
}
/**
* .时间进展到定时器注册的时间,调用该方法
* @param timestamp 当前时间进展,就是定时器被触发时的时间
*/
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, String>.OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
super.onTimer(timestamp, ctx, out);
String currentKey = ctx.getCurrentKey();
System.out.println("key=" + currentKey + "现在时间是" + timestamp + "定时器触发");
}
}).print();
env.execute();
}
}
测试结果:
注册多个定时器,但是时间到了只触发一次。
窗口处理函数
ProcessWindowFunction 和 ProcessAllWindowFunction(ProcessAllWindowFunction,没有 keyBy 的数据流直接开窗并调用.process()方法)
stream.keyBy( t -> t.f0 )
.window( TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10)))
.process(new MyProcessWindowFunction())
/* 泛型
* Type parameters:
* – The type of the input value. 输入类型
* – The type of the output value. 输出类型
* – The type of the key. key类型
* – The type of Window that this window function can be applied on. 窗口类型
*/
public abstract class ProcessWindowFunction<IN, OUT, KEY, W extends Window>
extends AbstractRichFunction {
public abstract void process(
KEY key, Context context, Iterable<IN> elements, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception;
public void clear(Context context) throws Exception {}
}
抽象方法process
- key:窗口做统计计算基于的键,也就是之前 keyBy 用来分区的字段。
- context:当前窗口进行计算的上下文,它的类型就是ProcessWindowFunction内部定义的抽象类 Context。
- elements:窗口收集到用来计算的所有数据,这是一个可迭代的集合类型。
- out:收集器
上下文调用函数:
public abstract class Context implements java.io.Serializable {
public abstract W window();
public abstract long currentProcessingTime();
public abstract long currentWatermark();
// 窗口状态
public abstract KeyedStateStore windowState();
// 全局状态
public abstract KeyedStateStore globalState();
// 定义侧输出流
public abstract <X> void output(OutputTag<X> outputTag, X value);
}
TopN
需求:实时统计一段时间内的出现次数最多的水位。例如,统计最近10 秒钟内出现次数最多的两个水位,并且每 5 秒钟更新一次。
创建实体类:
public class WaterSensor {
/**
* 传感器Id
*/
public String id;
/**
* 时间戳
*/
public Long ts;
/**
* 水位
*/
public Integer vc;
}
方法一:使用 ProcessAllWindowFunction
public class ProcessAllWindowTopNDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("124.222.253.33", 7777)
.map(new WaterSensorMapFunction())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((element, ts) -> element.getTs() * 1000L)
);
// 滑动窗口
sensorDS.windowAll(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5)))
.process(new MyTopNPAWF())
.print();
}
}
// 抽取窗口函数
public class MyTopNPAWF extends ProcessAllWindowFunction<WaterSensor, String, TimeWindow> {
@Override
public void process(ProcessAllWindowFunction<WaterSensor, String, TimeWindow>.Context context, Iterable<WaterSensor> elements, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
Map<Integer, Integer> vcCountMap = new HashMap<>();
for (WaterSensor element : elements) {
// 统计不同水位出现次数
vcCountMap.put(element.getVc(), vcCountMap.getOrDefault(element.getVc(), 0) + 1);
}
// 对 count 值进行排序: 利用 List 来实现排序
List<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>> datas = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer vc : vcCountMap.keySet()) {
datas.add(Tuple2.of(vc, vcCountMap.get(vc)));
}
// 对 List 进行排序,根据 count 值 降序
datas.sort(new Comparator<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Tuple2<Integer, Integer> o1, Tuple2<Integer, Integer> o2) {
// 降序, 后 减 前
return o2.f1 - o1.f1;
}
});
StringBuilder outStr = new StringBuilder();
outStr.append("================================\n");
// 遍历 排序后的 List,取出前 2 个, 考虑可能List 不够2个的情况==》 List 中元素的个数 和 2 取最小值
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(2, datas.size()); i++) {
Tuple2<Integer, Integer> vcCount = datas.get(i);
outStr.append("Top").append(i + 1).append("\n");
outStr.append("vc=").append(vcCount.f0).append("\n");
outStr.append("count=").append(vcCount.f1).append("\n");
outStr.append(" 窗 口 结束时间=").append(DateFormatUtils.format(context.window().getEnd(), "yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss.SSS")).append("\n");
outStr.append("================================\n");
}
out.collect(outStr.toString());
}
}
无论并行度如何设置,并行度只为1。效率不高
方法二:使用 KeyedProcessFunction ☆
从两个方面去做优化:一是对数据进行按键分区,分别统计vc 的出现次数;二是进行增量聚合,得到结果最后再做排序输出。
public class KeyedProcessFunctionTopNDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("124.222.253.33", 7777)
.map(new WaterSensorMapFunction())
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((element, ts) -> element.getTs() * 1000L)
);
// 【水位分组】
KeyedStream<WaterSensor, Integer> keyedStream = sensorDS.keyBy(WaterSensor::getVc);
/*
思路二: 使用 KeyedProcessFunction 实现
1、按照 vc 做 keyby,开窗,分别 count
==》 增量聚合,计算 count
==》 全窗口,对计算结果 count 值封装,带上窗口结束时间的标签
==》 为了让同一个窗口时间范围的计算结果到一起去
2、对同一个窗口范围的 count 值进行处理:排序、取前N 个
=》 按照 windowEnd 做 keyby
=》 使用 process, 来一条调用一次,需要先存,分开存,用HashMap,key=windowEnd,value=List
=》 使用定时器,对 存起来的结果 进行排序、取前N个
*/
// 1. 按照 vc 分组、开窗、聚合(增量计算+全量打标签)
// 开窗聚合后,就是普通的流,没有了窗口信息,需要自己打上窗口的标记windowEnd
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> windowAgg = keyedStream
.window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5)))
.aggregate(
new VcCountAgg(),
new WindowResult()
);
// 2. 按照窗口标签(窗口结束时间)keyby,保证同一个窗口时间范围的结果,到一起去。排序、取 TopN
windowAgg.keyBy(r -> r.f2)
.process(new TopN(2))
.print();
env.execute();
}
// 【同水位累加】
public static class VcCountAgg implements AggregateFunction<WaterSensor, Integer, Integer>{
@Override
public Integer createAccumulator() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Integer add(WaterSensor value, Integer accumulator) {
return accumulator + 1;
}
@Override
public Integer getResult(Integer accumulator) {
return accumulator;
}
@Override
public Integer merge(Integer a, Integer b) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 【打时间标签】
* 泛型如下:
* 第一个:输入类型 = 增量函数的输出 count 值,Integer
* 第二个:输出类型 = Tuple3(vc,count,windowEnd) ,带上窗口结束时间的标签
* 第三个:key 类型 , vc,Integer
* 第四个:窗口类型
*/
public static class WindowResult extends ProcessWindowFunction<Integer, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, Integer, TimeWindow> {
@Override
public void process(Integer key, Context context, Iterable<Integer> elements, Collector<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> out) throws Exception {
// 迭代器里面只有一条数据,next 一次即可
Integer count = elements.iterator().next();
long windowEnd = context.window().getEnd();
out.collect(Tuple3.of(key, count, windowEnd));
}
}
public static class TopN extends KeyedProcessFunction<Long, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, String> {
// 存不同窗口的 统计结果,key=windowEnd,value=list 数据
private Map<Long, List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>>> dataListMap;
// 要取的 Top 数量
private int threshold;
public TopN(int threshold) {
this.threshold = threshold;
dataListMap = new HashMap<>();
}
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
// 进入这个方法,只是一条数据,要排序,得到齐才行===》存起来,不同窗口分开存
// 1. 存到 HashMap 中
Long windowEnd = value.f2;
if (dataListMap.containsKey(windowEnd)) {
// 1.1 包含 vc,不是该 vc 的第一条,直接添加到List中
List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = dataListMap.get(windowEnd);
dataList.add(value);
} else {
// 1.1 不包含 vc,是该 vc 的第一条,需要初始化list
List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
dataList.add(value);
dataListMap.put(windowEnd, dataList);
}
// 2. 注册一个定时器, windowEnd+1ms 即可 延迟1ms 触发即可,及时性
ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(windowEnd + 1);
}
@Override
public void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
super.onTimer(timestamp, ctx, out);
// 定时器触发,同一个窗口范围的计算结果攒齐了,开始排序、取TopN
Long windowEnd = ctx.getCurrentKey();
// 1. 排序
List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = dataListMap.get(windowEnd);
dataList.sort(new Comparator<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> o1, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> o2) {
return o2.f1 - o1.f1;
}
});
// 2. 取 TopN
StringBuilder outStr = new StringBuilder();
outStr.append("================================\n");
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(threshold, dataList.size()); i++) {
Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> vcCount = dataList.get(i);
outStr.append("Top").append(i + 1).append("\n");
outStr.append("vc=").append(vcCount.f0).append("\n");
outStr.append("count=").append(vcCount.f1).append("\n");
outStr.append("窗口结束时间=").append(vcCount.f2).append("\n");
outStr.append("================================\n");
}
// 用完的 List,及时清理,节省资源
dataList.clear();
out.collect(outStr.toString());
}
}
}
增量聚合、开窗处理
- 水位线分组
- 增量聚合,相同水位线数量+1
- 窗口函数打时间标签
- 按上述打的时间标签分组,排序获取topN(process)
侧输出流
process函数带侧输出流
案例:对每个传感器,水位超过 10 的输出告警信息
public class SideOutputDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("124.222.253.33", 7777)
.map(new WaterSensorMapFunction());
OutputTag<String> warnTag = new OutputTag<>("warn", Types.STRING);
// 传感器分组
SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> process = sensorDS.keyBy(WaterSensor::getId)
.process(
new KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, WaterSensor>() {
@Override
public void processElement(WaterSensor value, Context ctx, Collector<WaterSensor> out) throws Exception {
// 使用侧输出流告警
String currentKey = ctx.getCurrentKey();
if (value.getVc() > 10) {
ctx.output(warnTag, "当前传感器=" + currentKey + ",当前水位=" + value.getVc() + ",大于阈值 10!!!");
}
// 主流正常 发送数据
out.collect(value);
}
}
);
process.print("主流");
process.getSideOutput(warnTag).printToErr("warn");
env.execute();
}
}
测流输出的同时不影响主流