嵌入式Linux C进程间通信(三)——消息队列
文章目录
- 前述
- 一、消息队列的创建和删除
-
- 1.1 消息的组成
- 1.2 创建
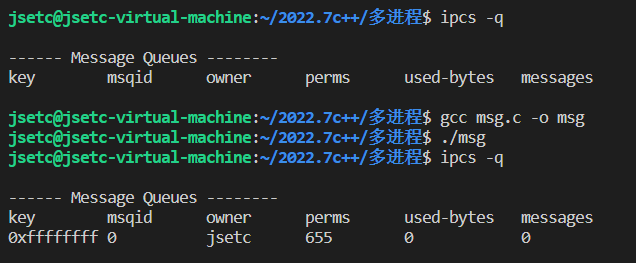
- 1.2 查看系统的消息队列
- 1.3 消息队列的创建
- 1.4 获取属性及删除
- 二、消息队列的发送和接收
-
- 2.1 发送
- 2.2 接收
- 三、任意进程通信及特点
-
- 3.1 msg_read.c
- 3.2 msg_write.c
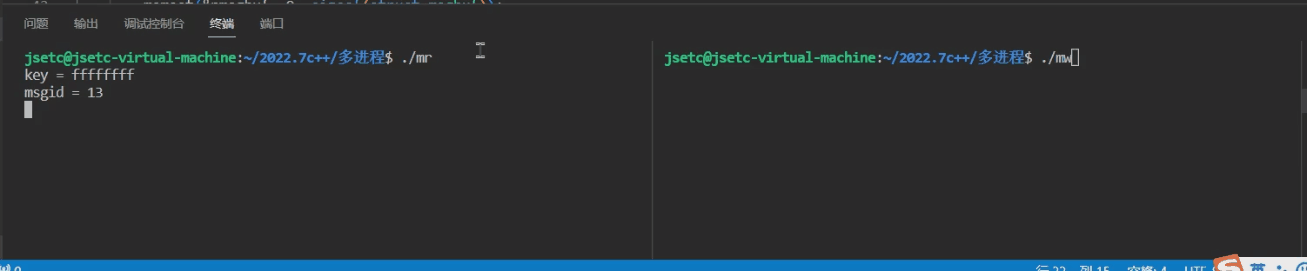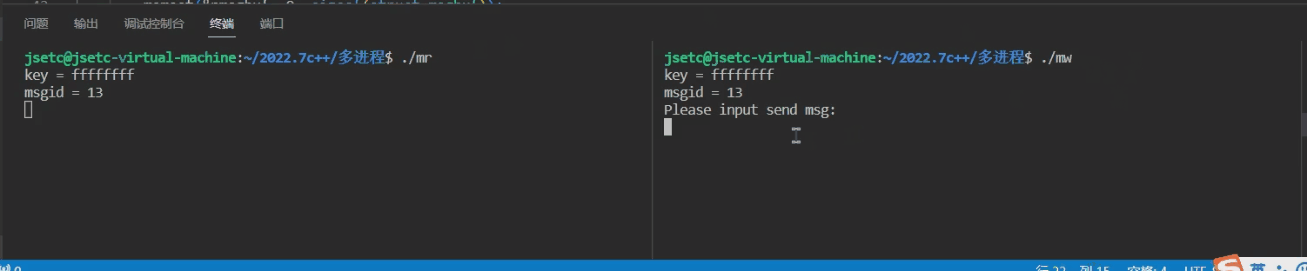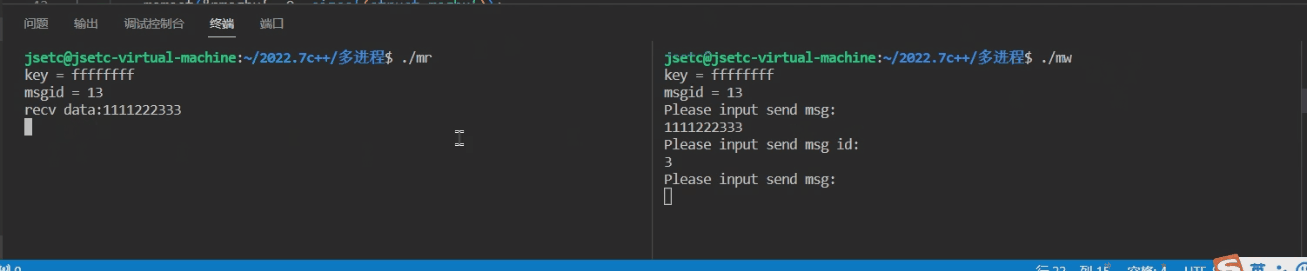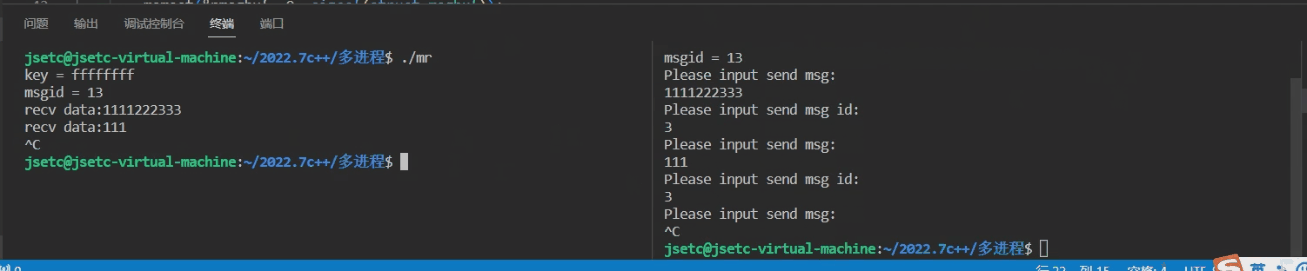
- 3.3 成果展示
前述
System V IPC

特点:
与管道有所不同,它完全使用了不同的实现机制,与文件没任何的关系,也就是说内核不再以文件的形式来管理System V IPC
System V IPC不再以文件的形式存在,因此没有文件描述符这个东西,但是它有类似的“标识符”
任何进程之间通信时,都可以使用System V IPC来通信
POSIX也可以支持消息队列、共享内存、信号量能在unix下运行
一、消息队列的创建和删除
消息队列的本质就是由内核创建的用于存放消息的链表,由于是存放消息的,所以我们就把这个链表称为消息队列。
1.1 消息的组成
1.2 创建
int msgget(key_t key, int msgflg);

1.2 查看系统的消息队列
1.3 消息队列的创建
#include 1.4 获取属性及删除
进程结束时,system v ipc不会自动删除,进程结束后,使用ipcs依然能够查看到
长方形
重启OS
使用ipcrm命令删除
int msgctl 参数:int mspid,int cmd,struct mspid_ds *buf
ipcrm -Q msgkey移除用msqkey创建的消息队列
ipcrm -q msqid移除用msqid标识的消息队列
#include 二、消息队列的发送和接收
2.1 发送
int msgsnd(int msqid,const void *msgp, size_t msgsz,int msgflg);

2.2 接收
ssize_ t msgrcv(int msqid, void *msgp, size_ t msgsz, long msgtyp, int msgflg);

#include 三、任意进程通信及特点
多个进程是如何共享到同一个消息队列?
- fork前创建
- 创建者把ID保存到某文件,共享进程读出ID即可+
- 使用ftok函数,利用与创建者相同的“路径名”和8位整形数,生成相同的key值
消息队列的特点
- 传送有格式的消息流
- 多进程网状旁叉通信时,消息队列是上上之选
- 能实现大规模数据的通信
3.1 msg_read.c
#include 3.2 msg_write.c
#include