Elasticsearch:运用向量搜索通过图像搜索找到你的小狗
作者:ALEX SALGADO
你是否曾经遇到过这样的情况:你在街上发现了一只丢失的小狗,但不知道它是否有主人? 了解如何使用向量搜索或图像搜索来做到这一点。
通过图像搜索找到你的小狗
您是否曾经遇到过这样的情况:你在街上发现了一只丢失的小狗,但不知道它是否有主人? 在 Elasticsearch 中通过图像处理使用向量搜索,此任务可以像漫画一样简单。
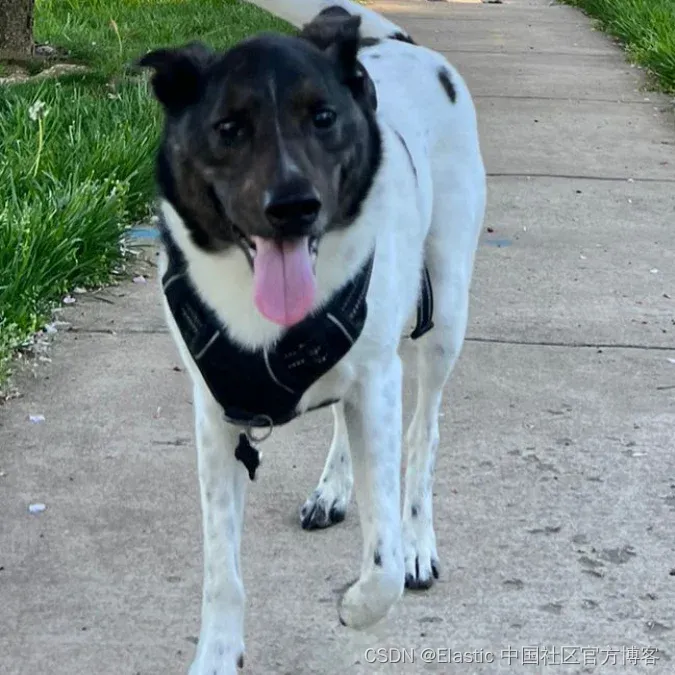
想象一下这个场景:在一个喧闹的下午,路易吉,一只活泼的小狗,在 Elastic 周围散步时不小心从皮带上滑落,发现自己独自在繁忙的街道上徘徊。 绝望的主人正在各个角落寻找他,用充满希望和焦虑的声音呼唤着他的名字。 与此同时,在城市的某个地方,一位细心的人注意到这只小狗表情茫然,决定提供帮助。 很快,他们给路易吉拍了一张照片,并利用所在公司的向量图像搜索技术,开始在数据库中进行搜索,希望能找到有关这只小逃亡者主人的线索。
如果你想在阅读时跟踪并执行代码,请访问在 Jupyter Notebook (Google Collab) 上运行的文件 Python 代码。
架构
我们将使用 Jupyter Notebook 来解决这个问题。 首先,我们下载要注册的小狗的图像,然后安装必要的软件包。
注意:要实现此示例,我们需要在使用图像数据填充向量数据库之前在 Elasticsearch 中创建索引。
- 首先部署 Elasticsearch(我们为你提供 14 天的免费试用期)。
- 在此过程中,请记住存储要在 Python 代码中使用的凭据(用户名、密码)。
- 为简单起见,我们将使用在 Jupyter Notebook (Google Colab) 上运行的 Python 代码。
下载代码 zip 文件并安装必要的软件包
!git clone https://github.com/salgado/image-search-01.git
!pip -q install Pillow sentence_transformers elasticsearch让我们创建 4 个类来帮助我们完成这项任务,它们是:
- Util 类:负责处理前期任务和 Elasticsearch 索引维护。
- Dog 类:负责存储我们小狗的属性。
- DogRepository 类:负责数据持久化任务。
- DogService 类:它将成为我们的服务层。
Util class
Util 类提供了用于管理 Elasticsearch 索引的实用方法,例如创建和删除索引。
方法:
- create_index():在 Elasticsearch 中创建一个新索引。
- delete_index():从 Elasticsearch 中删除现有索引。
### Util class
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch, exceptions as es_exceptions
import getpass
class Util:
@staticmethod
def get_index_name():
return "dog-image-index"
@staticmethod
def get_connection():
es_cloud_id = getpass.getpass('Enter Elastic Cloud ID: ')
es_user = getpass.getpass('Enter cluster username: ')
es_pass = getpass.getpass('Enter cluster password: ')
es = Elasticsearch(cloud_id=es_cloud_id,
basic_auth=(es_user, es_pass)
)
es.info() # should return cluster info
return es
@staticmethod
def create_index(es: Elasticsearch, index_name: str):
# Specify index configuration
index_config = {
"settings": {
"index.refresh_interval": "5s",
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"image_embedding": {
"type": "dense_vector",
"dims": 512,
"index": True,
"similarity": "cosine"
},
"dog_id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"breed": {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"image_path" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"owner_name" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"exif" : {
"properties" : {
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
},
"date": {
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}
}
}
# Create index
if not es.indices.exists(index=index_name):
index_creation = es.indices.create(index=index_name, ignore=400, body=index_config)
print("index created: ", index_creation)
else:
print("Index already exists.")
@staticmethod
def delete_index(es: Elasticsearch, index_name: str):
# delete index
es.indices.delete(index=index_name, ignore_unavailable=True)如果你是自构建的集群,你可以参考文章 “Elasticsearch:关于在 Python 中使用 Elasticsearch 你需要知道的一切 - 8.x” 来了解如何使用客户端来连接 Elasticsearch 集群。
Dog class
Dog 类代表一只狗及其属性,例如 ID、图像路径、品种、所有者姓名和图像嵌入。
属性:
- dog_id:狗的 ID。
- image_path:狗图像的路径。
- breed:狗的品种。
- owner_name:狗的主人的名字。
- image_embedding:狗的图像嵌入。
方法:
- __init__():初始化一个新的 Dog 对象。
- generate_embedding():生成狗的图像嵌入。
- to_dict():将 Dog 对象转换为字典。
import os
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from PIL import Image
# domain class
class Dog:
model = SentenceTransformer('clip-ViT-B-32')
def __init__(self, dog_id, image_path, breed, owner_name):
self.dog_id = dog_id
self.image_path = image_path
self.breed = breed
self.image_embedding = None
self.owner_name = owner_name
@staticmethod
def get_embedding(image_path: str):
temp_image = Image.open(image_path)
return Dog.model.encode(temp_image)
def generate_embedding(self):
self.image_embedding = Dog.get_embedding(self.image_path)
def __repr__(self):
return (f"Image(dog_id={self.dog_id}, image_path={self.image_path}, "
f"breed={self.breed}, image_embedding={self.image_embedding}, "
f"owner_name={self.owner_name})")
def to_dict(self):
return {
'dog_id': self.dog_id,
'image_path': self.image_path,
'breed': self.breed,
'image_embedding': self.image_embedding,
'owner_name': self.owner_name
}DogRepository class
DogRepository 类提供了从 Elasticsearch 保存和检索狗数据的方法。
方法:
- insert():将一条新狗插入 Elasticsearch。
- bulk_insert():将多条狗批量插入到Elasticsearch中。
- search_by_image():通过图像搜索相似的狗。
from typing import List, Dict
# persistence layer
class DogRepository:
def __init__(self, es_client: Elasticsearch, index_name: str = "dog-image-index"):
self.es_client = es_client
self._index_name = index_name
Util.create_index(es_client, index_name)
def insert(self, dog: Dog):
dog.generate_embedding()
document = dog.__dict__
self.es_client.index(index=self._index_name, document=document)
def bulk_insert(self, dogs: List[Dog]):
operations = []
for dog in dogs:
operations.append({"index": {"_index": self._index_name}})
operations.append(dog.__dict__)
self.es_client.bulk(body=operations)
def search_by_image(self, image_embedding: List[float]):
field_key = "image_embedding"
knn = {
"field": field_key,
"k": 2,
"num_candidates": 100,
"query_vector": image_embedding,
"boost": 100
}
# The fields to retrieve from the matching documents
fields = ["dog_id", "breed", "owner_name","image_path", "image_embedding"]
try:
resp = self.es_client.search(
index=self._index_name,
body={
"knn": knn,
"_source": fields
},
size=1
)
# Return the search results
return resp
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
return {}DogService Class
DogService 类提供管理狗数据的业务逻辑,例如插入和搜索狗。
方法:
- insert_dog():将一条新狗插入 Elasticsearch。
- search_dogs_by_image():通过图像搜索相似的狗。
from typing import List, Dict
# persistence layer
class DogRepository:
def __init__(self, es_client: Elasticsearch, index_name: str = "dog-image-index"):
self.es_client = es_client
self._index_name = index_name
Util.create_index(es_client, index_name)
def insert(self, dog: Dog):
dog.generate_embedding()
document = dog.__dict__
self.es_client.index(index=self._index_name, document=document)
def bulk_insert(self, dogs: List[Dog]):
operations = []
for dog in dogs:
operations.append({"index": {"_index": self._index_name}})
operations.append(dog.__dict__)
self.es_client.bulk(body=operations)
def search_by_image(self, image_embedding: List[float]):
field_key = "image_embedding"
knn = {
"field": field_key,
"k": 2,
"num_candidates": 100,
"query_vector": image_embedding,
"boost": 100
}
# The fields to retrieve from the matching documents
fields = ["dog_id", "breed", "owner_name","image_path", "image_embedding"]
try:
resp = self.es_client.search(
index=self._index_name,
body={
"knn": knn,
"_source": fields
},
size=1
)
# Return the search results
return resp
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
return {}上面介绍的类(classes)为构建狗数据管理系统奠定了坚实的基础。 Util 类提供了用于管理 Elasticsearch 索引的实用方法。 Dog 类代表狗的属性。 DogRepository 类提供了从 Elasticsearch 保存和检索狗数据的方法。 DogService 类提供了高效的狗数据管理的业务逻辑。
主要代码
我们的代码基本上有两个主要流程或阶段:
- 使用基本信息和图像注册狗。
- 使用新图像执行搜索以在向量数据库中查找狗。
第一阶段:注册小狗
为了存储有关 Luigi 和其他公司的小狗的信息,我们将使用 Dog 类。
为此,我们对序列进行如下的编程:
开始为小狗登记
# Start a connection
es_db = Util.get_connection()
Util.delete_index(es_db, Util.get_index_name())
# Register one dog
dog_repo = DogRepository(es_db, Util.get_index_name())
dog_service = DogService(dog_repo)
# Visualize the inserted Dog
from IPython.display import display
from IPython.display import Image as ShowImage
filename = "/content/image-search-01/dataset/dogs/Luigi.png"
display(ShowImage(filename=filename, width=300, height=300))输出:
登记 Luigi
dog = Dog('Luigi', filename, 'Jack Russel/Rat Terrier', 'Ully')
dog_service.register_dog(dog)登记所有其他小狗
import json
# JSON data
data = '''
{
"dogs": [
{"dog_id": "Buddy", "image_path": "", "breed": "Labrador Retriever", "owner_name": "Berlin Red"},
{"dog_id": "Bella", "image_path": "", "breed": "German Shepherd", "owner_name": "Tokyo Blue"},
{"dog_id": "Charlie", "image_path": "", "breed": "Golden Retriever", "owner_name": "Paris Green"},
{"dog_id": "Bigu", "image_path": "", "breed": "Beagle", "owner_name": "Lisbon Yellow"},
{"dog_id": "Max", "image_path": "", "breed": "Bulldog", "owner_name": "Canberra Purple"},
{"dog_id": "Luna", "image_path": "", "breed": "Poodle", "owner_name": "Wellington Brown"},
{"dog_id": "Milo", "image_path": "", "breed": "Rottweiler", "owner_name": "Hanoi Orange"},
{"dog_id": "Ruby", "image_path": "", "breed": "Boxer", "owner_name": "Ottawa Pink"},
{"dog_id": "Oscar", "image_path": "", "breed": "Dachshund", "owner_name": "Kabul Black"},
{"dog_id": "Zoe", "image_path": "", "breed": "Siberian Husky", "owner_name": "Cairo White"}
]
}
'''
# Convert JSON string to Python dictionary
dogs_data = json.loads(data)
# Traverse the list and print dog_id of each dog
image_dogs = "/content/image-search-01/dataset/dogs/"
for dog_info in dogs_data["dogs"]:
dog = Dog(dog_info["dog_id"], image_dogs + dog_info["dog_id"] + ".png" , dog_info["breed"], dog_info["owner_name"])
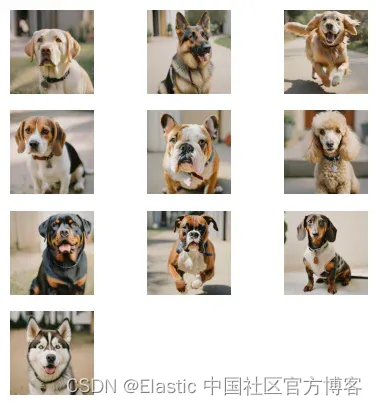
dog_service.register_dog(dog)可视化新狗
# visualize new dogs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import math
image_dogs = "/content/image-search-01/dataset/dogs/"
num_dogs = len(dogs_data["dogs"])
cols = int(math.sqrt(num_dogs))
rows = int(math.ceil(num_dogs / cols))
# Configurar o tamanho da figura
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
# Loop para exibir as imagens dos cães
for i, dog_info in enumerate(dogs_data["dogs"]):
filename = image_dogs + dog_info["dog_id"] + ".png"
img = mpimg.imread(filename)
plt.subplot(rows, cols, i+1) # (número de linhas, número de colunas, índice do subplot)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()输出:
第二阶段:寻找丢失的狗
现在我们已经登记了所有小狗,让我们进行搜索。 我们的开发人员拍了这张丢失小狗的照片。
filename = "/content/image-search-01/dataset/lost-dogs/lost_dog1.png"
display(ShowImage(filename=filename, width=300, height=300))输出:
看看我们能找到这只可爱的小狗的主人吗?
# find dog by image
result = dog_service.find_dog_by_image(filename)获取结果
让我们看看我们发现了什么......
filename = result['hits']['hits'][0]['_source']['image_path']
display(ShowImage(filename=filename, width=300, height=300))输出:
瞧! 我们找到了!!!
但谁将是所有者和他们的名字?
# Print credentials
print(result['hits']['hits'][0]['_source']['dog_id'])
print(result['hits']['hits'][0]['_source']['breed'])
print(result['hits']['hits'][0]['_source']['owner_name'])输出:
- Luigi
- Jack Russel/Rat Terrier
- Ully
好结局
我们找到了路易吉!!! 我们通知 Ully 吧。
filename = "/content/image-search-01/dataset/lost-dogs/Ully.png"
display(ShowImage(filename=filename, width=300, height=300))输出:
很快,Ully 和 Luigi 就团聚了。 小狗高兴地摇着尾巴,Ully 紧紧地抱住它,保证再也不会让它离开她的视线。 他们经历了一阵情感旋风,但现在他们在一起了,这才是最重要的。 就这样,Ully 和 Luigi 心中充满了爱和欢乐,从此幸福地生活在一起。
结论
在这篇博文中,我们探索了如何使用 Elasticsearch 通过向量搜索来寻找丢失的小狗。 我们演示了如何生成狗的图像嵌入,在 Elasticsearch 中对其进行索引,然后使用查询图像搜索相似的狗。 该技术可用于寻找丢失的宠物,以及识别图像中其他感兴趣的物体。
向量搜索是一个强大的工具,可用于多种应用。 它特别适合需要根据外观搜索相似对象的任务,例如图像检索和对象识别。
我们希望这篇博文能够提供丰富的信息,并且你会发现我们讨论的技术对你自己的项目很有用。
原文:Finding your puppy with Image Search — Elastic Search Labs