微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(三)
微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba:
- 微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(一)
- 微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(二)
- 微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(三)
在微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(一)中,学习了搭建三大微服务并完成交互开发与测试。
在微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(二)中,针对微服务会遇到的一些问题,使用了一些微服务组件来解决,实现了用户微服务、商品微服务和订单微服务之间的远程调用,并且实现了服务调用的负载均衡。也基于阿里开源的Sentinel实现了服务的限流与容错,并详细介绍了Sentinel的核心技术与配置规则 。如下:
- 使用
Nacos来实现服务的注册与发现 - 使用
Ribbon来实现服务调用的负载均衡 - 使用
Sentinel实现接口限流
在微服务实战系列之SpringCloud Alibaba学习(三)中,将继续学习使用微服务组件来解决微服务中的一些问题:
- 项目整合
SpringCloud Gateway网关,可以参考SpringCloud架构之整合Gateway网关
文章目录
-
-
- 1. 项目整合SpringCloud Gateway网关
-
- 1.1 网关概述
-
- 1.1.1 没有网关的弊端
- 1.1.2 引入API网关
- 1.2 主流的API网关
-
- 1.2.1 Nginx+Lua
- 1.2.2 Kong网关
- 1.2.3 Zuul网关
- 1.2.4 Apache Shenyu网关
- 1.2.5 SpringCloud Gateway网关
- 1.3 SpringCloud Gateway网关
-
- 1.3.1 SpringCloud Gateway概述
- 1.3.1 SpringCloud Gateway核心架构
- 1.4 项目整合网关
-
- 1.4.1 新建网关模块
- 1.4.2 初步整合SpringCloud Gateway
- 1.4.3 网关整合Nacos
- 1.4.4 网关整合Nacos最简配置
- 1.5 网关整合Sentinel限流
-
- 1.5.1 实现route维度限流
- 1.5.2 实现自定义API分组维度限流
-
1. 项目整合SpringCloud Gateway网关
1.1 网关概述
当采用分布式、微服务的架构模式开发系统中,服务网关是整个系统中必不可少的一部分。
1.1.1 没有网关的弊端
当一个系统使用分布式、微服务架构后,系统会被拆分为一个个小的微服务,每个微服务专注一个小的业务。那么,客户端如何调用这么多微服务的接口呢?如果不做任何处理,没有服务网关,就只能在客户端记录下每个微服务的每个接口地址,然后根据实际需要去调用相应的接口。
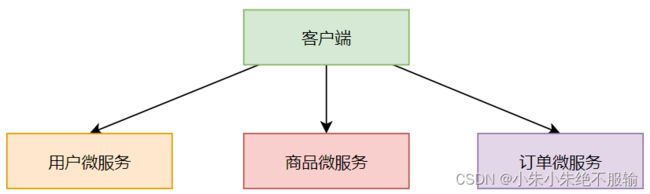
这种直接使用客户端记录并管理每个微服务的每个接口的方式,存在着太多的问题。比如,这里我列举几个常见的问题。
- 由客户端记录并管理所有的接口缺乏安全性。
- 由客户端直接请求不同的微服务,会增加客户端程序编写的复杂性。
- 涉及到服务认证与鉴权规则时,需要在每个微服务中实现这些逻辑,增加了代码的冗余性。
- 客户端调用多个微服务,由于每个微服务可能部署的服务器和域名不同,存在跨域的风险。
- 当客户端比较多时,每个客户端上都管理和配置所有的接口,维护起来相对比较复杂。
1.1.2 引入API网关
API网关,其实就是整个系统的统一入口。网关会封装微服务的内部结构,为客户端提供统一的入口服务,同时,一些与具体业务逻辑无关的通用逻辑可以在网关中实现,比如认证、授权、路由转发、限流、监控等。引入API网关后,如下所示。
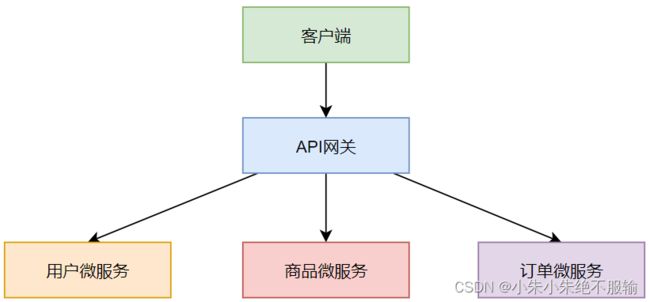
可以看到,引入API网关后,客户端只需要连接API网关,由API网关根据实际情况进行路由转发,将请求转发到具体的微服务,同时,API网关会提供认证、授权、限流和监控等功能。
1.2 主流的API网关
当系统采用分布式、微服务的架构模式后,API网关就成了整个系统不可分割的一部分。业界通过不断的探索与创新,实现了多种API网关的解决方案。目前,比较主流的API网关有:Nginx+Lua、Kong官网、Zuul网关、Apache Shenyu网关、SpringCloud Gateway网关。
1.2.1 Nginx+Lua
Nginx的一些插件本身就实现了限流、缓存、黑白名单和灰度发布,再加上Nginx的反向代理和负载均衡,能够实现对服务接口的负载均衡和高可用。而Lua语言可以实现一些简单的业务逻辑,Nginx又支持Lua语言。所以,可以基于Nginx+Lua脚本实现网关。
1.2.2 Kong网关
Kong网关基于Nginx与Lua脚本开发,性能高,比较稳定,提供多个限流、鉴权等插件,这些插件支持热插拔,开箱即用。Kong网关提供了管理页面,但是,目前基于Kong网关二次开发比较困难。
1.2.3 Zuul网关
Zuul网关是Netflix开源的网关,功能比较丰富,主要基于Java语言开发,便于在Zuul网关的基础上进行二次开发。但是Zuul网关无法实现动态配置规则,依赖的组件相对来说也比较多,在性能上不如Nginx。
1.2.4 Apache Shenyu网关
Dromara社区开发的网关框架,ShenYu 的前名是 soul,最近正式加入了 Apache 的孵化器,因此改名为 ShenYu。其是一个异步的,高性能的,跨语言的,响应式的API网关,并在此基础上提供了非常丰富的扩展功能:
- 支持各种语言(http协议),支持Dubbo, Spring-Cloud, Grpc, Motan, Sofa, Tars等协议。
- 插件化设计思想,插件热插拔,易扩展。
- 灵活的流量筛选,能满足各种流量控制。
- 内置丰富的插件支持,鉴权,限流,熔断,防火墙等等。
- 流量配置动态化,性能极高。
- 支持集群部署,支持 A/B Test,蓝绿发布。
1.2.5 SpringCloud Gateway网关
Spring为了替换Zuul而开发的网关,SpringCloud Alibaba技术栈中,并没有单独实现网关的组件。在后续的案例实现中,我们会使用SpringCloud Gateway实现网关功能。
1.3 SpringCloud Gateway网关
Spring Cloud Gateway是Spring公司基于Spring 5.0, Spring Boot 2.0 和 Project Reactor 等技术开发的网关,它旨在为微服务架构提供一种简单有效的统一的 API 路由管理方式。
它的目标是替代Netflix Zuul,其不仅提供统一的路由方式,并且基于 Filter 链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控和限流、重试等。
1.3.1 SpringCloud Gateway概述
Spring Cloud Gateway是Spring Cloud的一个全新项目,基于Spring 5.0 + Spring Boot 2.0和Project Reactor等技术开发的网关,它旨在为微服务架构提供一种简单有效的统一的API路由管理方式。
Spring Cloud Geteway作为Spring Cloud生态系统中的网关,目标是替代Zuul,在Spring Cloud2.0以上版本中,没有对新版本的Zuul 2.0以上最新高性能版本进行集成,仍然还是使用的Zuul 1.x非Reactor模式的老版本。
为了提升网关性能,Spring Cloud Gateway是基于WebFlux框架实现的,而WebFlux框架底层则使用了高性能的Reactor模式通信框架Netty。
Spring Cloud Gateway的目标提供统一的路由方式且基于Filter链的方式提供了网关基本的功能,例如:安全,监控/指标,和限流。
总结一句话:Spring Cloud Gateway使用的Webflux中的reactor-netty响应式编程组件,底层使用Netty通讯框架。
1.3.1 SpringCloud Gateway核心架构
客户端请求到 Gateway 网关,会先经过 Gateway Handler Mapping 进行请求和路由匹配。匹配成功后再发送到 Gateway Web Handler 处理,然后会经过特定的过滤器链,经过所有前置过滤后,会发送代理请求。请求结果返回后,最后会执行所有的后置过滤器。
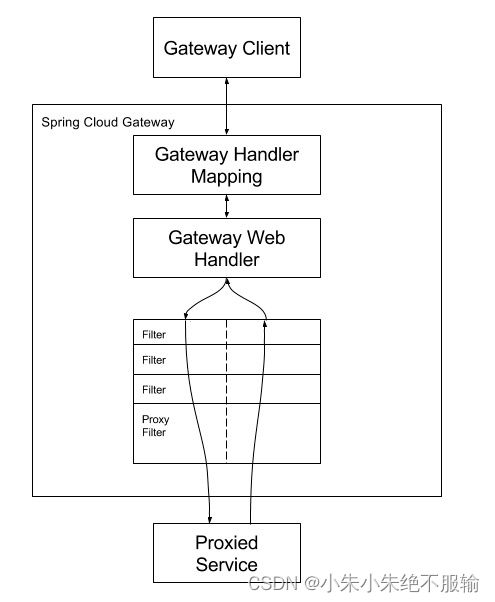
由上图可以看出,SpringCloud Gateway的主要流程为:客户端请求会先打到Gateway,具体的讲应该是DispacherHandler(因为Gateway引入了WebFlux,作用可以类比MVC的DispacherServlet)。
Gateway根据用户的请求找到相应的HandlerMapping,请求和具体的handler之间有一个映射关系,网关会对请求进行路由,handler会匹配到RoutePredicateHandlerMapping,匹配请求对应的Route,然后到达Web处理器。
WebHandler代理了一系列网关过滤器和全局过滤器的实例,这些过滤器可以对请求和响应进行修改,最后由代理服务完成用户请求,并将结果返回。
1.4 项目整合网关
我们需要在项目中增加一个服务网关模块shop-gateway,在服务网关模块中实现网关的能力。此时,我们的项目中就会有用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关。
1.4.1 新建网关模块
在项目中新建shop-gateway模块,新增网关模块后项目的结构如下图所示。

1.4.2 初步整合SpringCloud Gateway
(1)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的pom.xml文件中添加如下依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
(2)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的resources目录下新建application.yml文件,并在文件中添加如下配置信息。
server:
port: 10001
spring:
application:
name: server-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
globalcors:
cors-configurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: "*"
allowedMethods: "*"
allowCredentials: true
allowedHeaders: "*"
routes:
- id: user-gateway
uri: http://localhost:8060
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-user/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: product-gateway
uri: http://localhost:8070
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-product/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: order-gateway
uri: http://localhost:8080
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-order/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
我们重点来看下 spring.cloud.gateway 节点下的配置。
globalcors:此节点下的配置是为了解决SpringCloud Gateway跨域的问题。routes:表示一个路由数组,可以在此节点下配置多个路由信息。id:当前路由的唯一标识。order:路由的优先级,数字越小表示优先级越高。predicates:网关断言,也就是路由转发的条件,也是一个数组,可以配置多个路由转发条件。Path:当客户端请求的路径满足Path的规则时,进行路由转发操作。filters:网关过滤器,在过滤器中可以修改请求的参数和header信息,以及响应的结果和header信息,网关过滤器也是一个数组,可以配置多个过滤规则。StripPrefix:网关在进行路由转发之前,会去掉1层访问路径。
(3)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的io.binghe.shop包下新建GatewayStarter类,表示服务网关的启动类,源码如下所示。
/**
* @description 服务网关启动类
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class GatewayStarter {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(GatewayStarter.class, args);
}
}
(4)由于之前项目中整合了Nacos和Sentinel,所以,在启动项目前,要分别启动Nacos和Sentinel。
- 进入到Nacos的bin目录下,输入如下命令启动Nacos。
startup.cmd -m standalone
- 进入Sentinel Jar包所在的目录,输入如下命令启动Sentinel。
java -Dserver.port=8888 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8888 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.8.4.jar
(5)分别启动用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关。
(6)通过服务网关访问用户微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/get/1001,如下所示。
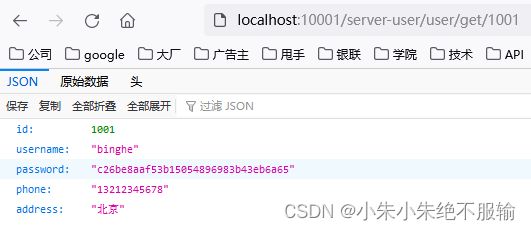
用户微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"username": "binghe",
"password": "c26be8aaf53b15054896983b43eb6a65",
"phone": "13212345678",
"address": "北京"
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到用户微服务。
(7)通过服务网关访问商品微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-product/product/get/1001,如下所示。
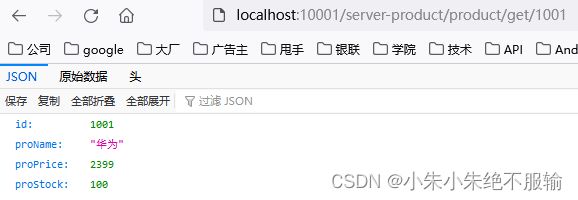
商品微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"proName": "华为",
"proPrice": 2399,
"proStock": 100
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到商品微服务。
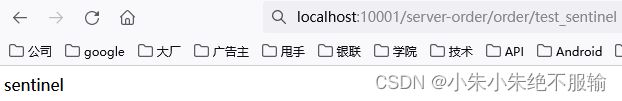
(8)通过服务网关访问订单微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-order/order/test_sentinel,如下所示。
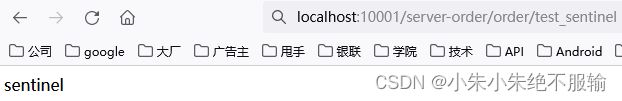
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到订单微服务。
1.4.3 网关整合Nacos
在初步整合SpringCloud Gateway中,我们在服务网关模块的application.yml文件中硬编码配置了服务转发的地址,如下所示。
- 硬编码用户微服务地址
uri: http://localhost:8060
- 硬编码商品微服务地址
uri: http://localhost:8070
- 硬编码订单微服务地址
uri: http://localhost:8080
这里,我们将网关整合Nacos实现从Nacos注册中心获取转发的服务地址。
(1)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的pom.xml文件中继续添加如下依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
(2)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的启动类io.binghe.shop.GatewayStarter上添加@EnableDiscoveryClient注解,如下所示。
/**
* @description 服务网关启动类
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class GatewayStarter {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(GatewayStarter.class, args);
}
}
(3)将application.yml备份一份,命名为application-simple.yml,并修改application.yml配置文件,修改后的文件如下所示。
server:
port: 10001
spring:
application:
name: server-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
globalcors:
cors-configurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: "*"
allowedMethods: "*"
allowCredentials: true
allowedHeaders: "*"
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
routes:
- id: user-gateway
uri: lb://server-user
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-user/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: product-gateway
uri: lb://server-product
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-product/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
- id: order-gateway
uri: lb://server-order
order: 1
predicates:
- Path=/server-order/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
上述配置中增加了Nacos相关的配置,如下所示。
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
新增了让SpringCloud Gateway可以发现Nacos中的服务配置,如下所示。
Spring:
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
另外,将硬编码的服务转发地址修改成从Nacos中按照名称获取微服务地址,并按照负载均衡策略分发。
- 从Nacos中获取用户微服务
uri: lb://server-user
- 从Nacos中获取商品微服务
uri: lb://server-product
- 从Nacos中获取订单微服务
uri: lb://server-order
其中,lb指的是从Nacos中按照微服务的名称获取微服务地址,并按照负载均衡的策略分发。使用lb从Nacos中获取微服务时,遵循如下的格式。
lb://微服务名称
微服务的名称就是各个微服务在application.yml文件中配置的服务名称。
spring:
application:
name: 服务名称
(4)分别启动用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关。
(5)通过服务网关访问用户微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/get/1001,如下所示。
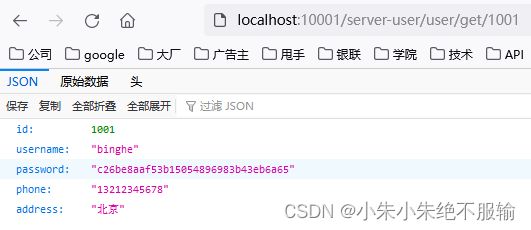
用户微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"username": "binghe",
"password": "c26be8aaf53b15054896983b43eb6a65",
"phone": "13212345678",
"address": "北京"
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到用户微服务。
(6)通过服务网关访问商品微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-product/product/get/1001,如下所示。
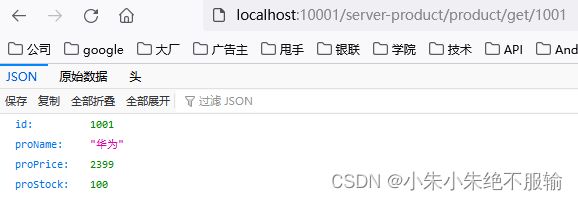
商品微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"proName": "华为",
"proPrice": 2399,
"proStock": 100
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到商品微服务。
(7)通过服务网关访问订单微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-order/order/test_sentinel,如下所示。
1.4.4 网关整合Nacos最简配置
SpringCloud Gateway整合Nacos后,可以不用手动指定其他微服务的名称来从Nacos中获取微服务的地址。接下来,我们就来实现SpringCloud Gateway网关整合Nacos的最简配置。
(1)将application.yml备份一份,命名为application-nacos.yml,并修改application.yml配置文件,修改后的文件如下所示。
server:
port: 10001
spring:
application:
name: server-gateway
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
gateway:
globalcors:
cors-configurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: "*"
allowedMethods: "*"
allowCredentials: true
allowedHeaders: "*"
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
可以看到,在application.yml文件中,去掉了spring.cloud.gateway.routes 节点及其下面的所有配置。
(2)分别启动用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关。
(3)通过服务网关访问用户微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/get/1001,如下所示。
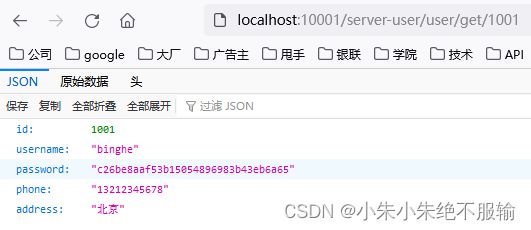
用户微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"username": "binghe",
"password": "c26be8aaf53b15054896983b43eb6a65",
"phone": "13212345678",
"address": "北京"
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到用户微服务。
(4)通过服务网关访问商品微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-product/product/get/1001,如下所示。
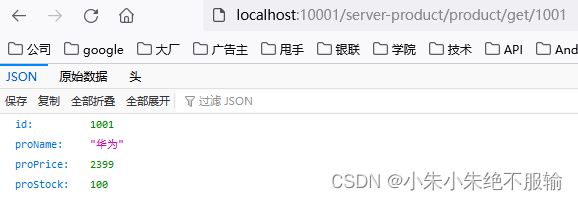
商品微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"id": 1001,
"proName": "华为",
"proPrice": 2399,
"proStock": 100
}
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到商品微服务。
(5)通过服务网关访问订单微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-order/order/test_sentinel,如下所示。
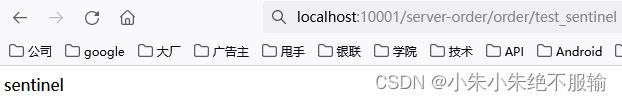
可以看到,通过服务网关能够正确访问到订单微服务。
注意:SpringCloud Gateway整合Nacos最简配置时,通过网关访问微服务的格式如下所示。
http(s)://网关IP:网关端口/访问的目标微服务名称/接口地址
1.5 网关整合Sentinel限流
Sentinel从1.6.0版本开始,提供了SpringCloud Gateway的适配模块,并且可以提供两种资源维度的限流,一种是route维度;另一种是自定义API分组维度。
route维度:对application.yml文件中配置的spring.cloud.gateway.routes.id限流,并且资源名为spring.cloud.gateway.routes.id对应的值。自定义API分组维度:利用Sentinel提供的API接口来自定义API分组,并且对这些API分组进行限流。
1.5.1 实现route维度限流
(1)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的pom.xml文件中添加如下依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-sentinel-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-spring-cloud-gateway-adapter</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
(2)在服务网关shop-gateway模块中新建io.binghe.shop.config包,并在包下新建GatewayConfig类。基于Sentinel 的Gateway限流是通过其提供的Filter来完成的,使用时只需注入对应的SentinelGatewayFilter实例以及 SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler 实例即可。
GatewayConfig类的源代码如下所示。
/**
* @description 网关配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class GatewayConfig {
private final List<ViewResolver> viewResolvers;
private final ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer;
@Value("${spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}")
private String routeIdPrefix;
public GatewayConfig(ObjectProvider<List<ViewResolver>> viewResolversProvider,
ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer) {
this.viewResolvers = viewResolversProvider.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
this.serverCodecConfigurer = serverCodecConfigurer;
}
/**
* 初始化一个限流的过滤器
*/
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public GlobalFilter sentinelGatewayFilter() {
return new SentinelGatewayFilter();
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
this.initGatewayRules();
this.initBlockHandlers();
}
/**
* 配置初始化的限流参数
*/
private void initGatewayRules() {
Set<GatewayFlowRule> rules = new HashSet<>();
/**
* Sentinel整合SpringCloud Gateway使用的API类型为Route ID类型,也就是基于route维度时,
* 由于Sentinel为SpringCloud Gateway网关生成的API名称规则如下:
* 生成的规则为:${spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}后面直接加上目标微服务的名称,如下所示。
* ${spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}目标微服务的名称
* 其中,${spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}是在yml文件中配置的访问前缀
*
* 为了让通过服务网关访问目标微服务链接后,请求链路中生成的API名称与流控规则中生成的API名称一致,以达到启动项目即可实现访问链接的限流效果,
* 而无需登录Setinel管理界面手动配置限流规则,可以将
* resource参数设置为${spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}目标微服务的名称
*
* 当然,如果不按照上述配置,也可以在项目启动后,通过服务网关访问目标微服务链接后,在Sentinel管理界面的请求链路中找到对应的API名称所代表的请求链路,
* 然后手动配置限流规则。
**/
// //用户微服务网关
// rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule("user-gateway"));
// //商品微服务网关
// rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule("product-gateway"));
// //订单微服务网关
// rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule("order-gateway"));
//用户微服务网关
rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule(getResource("server-user")));
//商品微服务网关
rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule(getResource("server-product")));
//订单微服务网关
rules.add(this.getGatewayFlowRule(getResource("server-order")));
//加载规则
GatewayRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
private String getResource(String targetServiceName){
if (routeIdPrefix == null){
routeIdPrefix = "";
}
return routeIdPrefix.concat(targetServiceName);
}
private GatewayFlowRule getGatewayFlowRule(String resource){
//传入资源名称生成GatewayFlowRule
GatewayFlowRule gatewayFlowRule = new GatewayFlowRule(resource);
//限流阈值
gatewayFlowRule.setCount(1);
//统计的时间窗口,单位为
gatewayFlowRule.setIntervalSec(1);
return gatewayFlowRule;
}
/**
* 配置限流的异常处理器
*/
@Bean
@Order(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
public SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler sentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler() {
return new SentinelGatewayBlockExceptionHandler(viewResolvers, serverCodecConfigurer);
}
/**
* 自定义限流异常页面
*/
private void initBlockHandlers() {
BlockRequestHandler blockRequestHandler = new BlockRequestHandler() {
@Override
public Mono<ServerResponse> handleRequest(ServerWebExchange serverWebExchange, Throwable throwable) {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", 1001);
map.put("codeMsg", "接口被限流了");
return ServerResponse.status(HttpStatus.OK).
contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8).
body(BodyInserters.fromObject(map));
}
};
GatewayCallbackManager.setBlockHandler(blockRequestHandler);
}
}
GatewayConfig类的源代码看上去比较多,但是都是一些非常简单的方法,冰河在这里就不再赘述了。
这里有个需要特别注意的地方:
Sentinel1.8.4整合SpringCloud Gateway使用的API类型为Route ID类型时,也就是基于route维度时,由于Sentinel为SpringCloud Gateway网关生成的API名称规则如下:
- 生成的规则为:
{spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}后面直接加上目标微服务的名称,如下所示。 {spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}目标微服务的名称。其中,{spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}是在yml文件中配置的访问前缀。- 为了让通过服务网关访问目标微服务链接后,请求链路中生成的API名称与流控规则中生成的API名称一致,以达到启动项目即可实现访问链接的限流效果,而无需登录Setinel管理界面手动配置限流规则,可以将生成GatewayFlowRule对象的resource参数设置为
{spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix}目标微服务的名称 - 当然,如果不按照上述配置,也可以在项目启动后,通过服务网关访问目标微服务链接后,在Sentinel管理界面的请求链路中找到对应的API名称所代表的请求链路,然后手动配置限流规则。
(3)将服务网关shop-gateway模块的application.yml文件备份一份名称为application-nacos-simple.yml的文件,并将application.yml文件的内容修改成如下所示。
server:
port: 10001
spring:
application:
name: server-gateway
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
sentinel:
transport:
port: 7777
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8888
web-context-unify: false
eager: true
gateway:
globalcors:
cors-configurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: "*"
allowedMethods: "*"
allowCredentials: true
allowedHeaders: "*"
discovery:
locator:
enabled: true
route-id-prefix: gateway-
其中:
spring.cloud.sentinel.eager表示程序启动时,流控规则是否立即注册到Sentinel,配置为true表示立即注册到Sentinel。spring.cloud.gateway.discovery.locator.route-id-prefix:生成流控规则API名称的前缀。
(4)在IDEA中配置启动服务网关shop-gateway模块的参数-Dcsp.sentinel.app.type=1,如下所示。
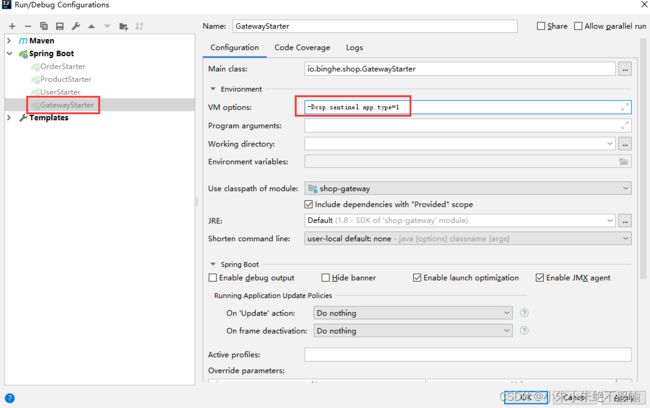
如果是在命令行启动网关服务的Jar包,则可以使用如下命令。
java -Dcsp.sentinel.app.type=1 shop-gateway.jar
或者在启动类io.binghe.shop.GatewayStarter的main()方法中添加一行System.setProperty("csp.sentinel.app.type", "1");代码,如下所示。
/**
* @description 服务网关启动类
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class GatewayStarter {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.setProperty("csp.sentinel.app.type", "1");
SpringApplication.run(GatewayStarter.class, args);
}
}
(5)分别启动用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关,启动后会在Sentinel管理界面左侧菜单栏中看到server-gateway菜单,如下所示。
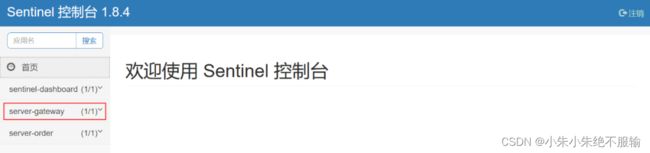
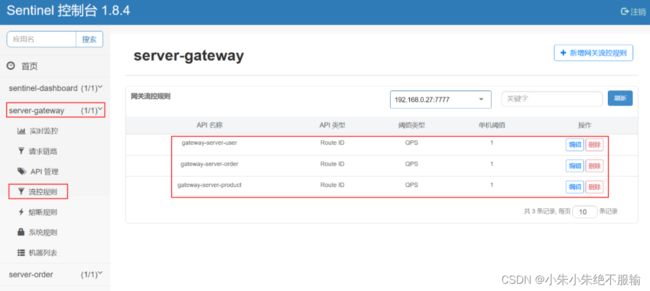
在server-gateway菜单下的流控规则子菜单中可以看到网关的流控规则已经注册到Sentinel,如下所示。
(6)通过服务网关访问用户微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/get/1001,不断刷新页面,如下所示。
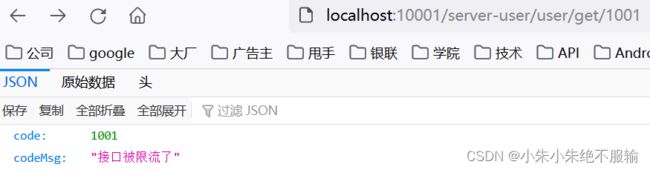
用户微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"code": 1001,
"codeMsg": "接口被限流了"
}
可以看到,通过服务网关不断刷新用户微服务时,触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
(7)通过服务网关访问商品微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-product/product/get/1001,不断刷新页面,如下所示。
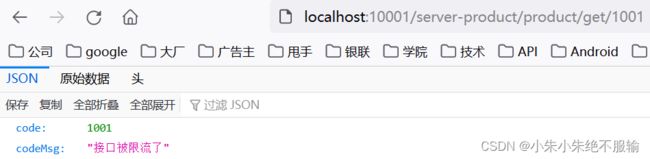
商品微服务返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"code": 1001,
"codeMsg": "接口被限流了"
}
可以看到,通过服务网关不断刷新商品微服务时,触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
(8)通过服务网关访问订单微服务,在浏览器中输入http://localhost:10001/server-order/order/test_sentinel,不断刷新页面,如下所示。
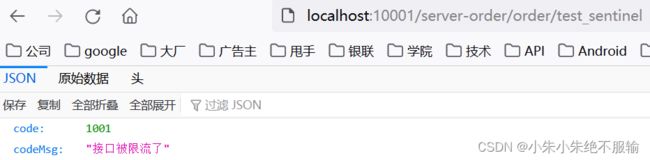
可以看到,通过服务网关不断刷新订单微服务时,触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
1.5.2 实现自定义API分组维度限流
前面,我们实现了route维度的限流,接下来,我们再基于Sentinel与SpringCloud gateway实现自定义API分组维度的限流。
(1)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的io.binghe.shop.config.GatewayConfig配置类中新增initCustomizedApis()方法,初始化API管理的信息,源码如下所示。
private void initCustomizedApis() {
Set<ApiDefinition> definitions = new HashSet<>();
ApiDefinition api1 = new ApiDefinition("user_api1")
.setPredicateItems(new HashSet<ApiPredicateItem>() {{
// 以/server-user/user/api1 开头的请求
add(new ApiPathPredicateItem().setPattern("/server-user/user/api1/**").
setMatchStrategy(SentinelGatewayConstants.URL_MATCH_STRATEGY_PREFIX));
}});
ApiDefinition api2 = new ApiDefinition("user_api2")
.setPredicateItems(new HashSet<ApiPredicateItem>() {{
// 以/server-user/user/api2/demo1 完成的url路径匹配
add(new ApiPathPredicateItem().setPattern("/server-user/user/api2/demo1"));
}});
definitions.add(api1);
definitions.add(api2);
GatewayApiDefinitionManager.loadApiDefinitions(definitions);
}
上述代码中,配置了两个API分组,每个API分组的规则如下。
user_api1分组:匹配以/product-serv/product/api1开头的所有请求。user_api2分组:精确匹配/server-user/user/api2/demo1。
(2)在服务网关shop-gateway模块的io.binghe.shop.config.GatewayConfig配置类中init()方法中调用initCustomizedApis()方法,为了避免route维度的限流对自定义API分组维度的限流产生影响,这里,同时在init()方法中注释掉调用initGatewayRules()方法,修改后的init()方法的代码如下所示。
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
//this.initGatewayRules();
this.initBlockHandlers();
this.initCustomizedApis();
}
(3)在用户微服务shop-user的io.binghe.shop.user.controller.UserController类中新增四个测试接口,源码如下所示。
@GetMapping(value = "/api1/demo1")
public String api1Demo1(){
log.info("访问了api1Demo1接口");
return "api1Demo1";
}
@GetMapping(value = "/api1/demo2")
public String api1Demo2(){
log.info("访问了api1Demo2接口");
return "api1Demo2";
}
@GetMapping(value = "/api2/demo1")
public String api2Demo1(){
log.info("访问了api2Demo1接口");
return "api2Demo1";
}
@GetMapping(value = "/api2/demo2")
public String api2Demo2(){
log.info("访问了api2Demo2接口");
return "api2Demo2";
}
(4)分别启动用户微服务、商品微服务、订单微服务和服务网关,启动后会在Sentinel管理界面左侧菜单栏中看到server-gateway菜单,如下所示。
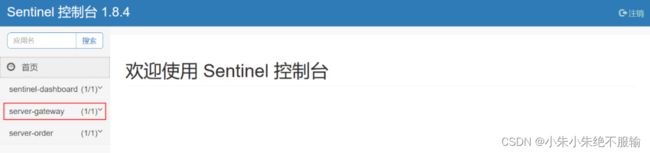 此时,由于我们注释了调用以route维度限流的方法,所以,在流控规则里的限流规则为空,如下所示。
此时,由于我们注释了调用以route维度限流的方法,所以,在流控规则里的限流规则为空,如下所示。
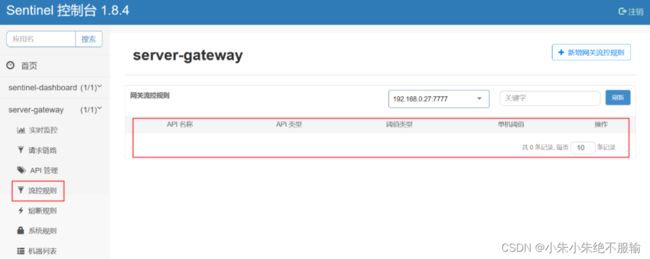
在API管理里面会发现我们定义的API分组已经自动注册到Sentinel中了,如下所示。
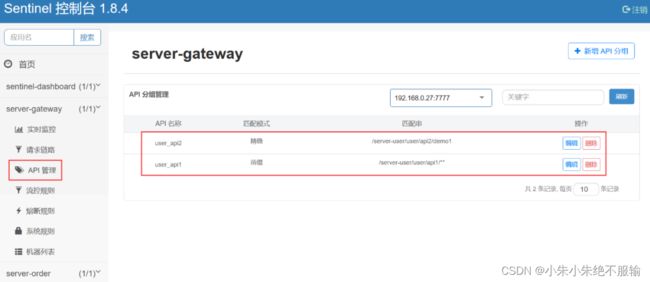
(5)在Sentinel管理界面的流控规则中,新增网关流控规则,如下所示。
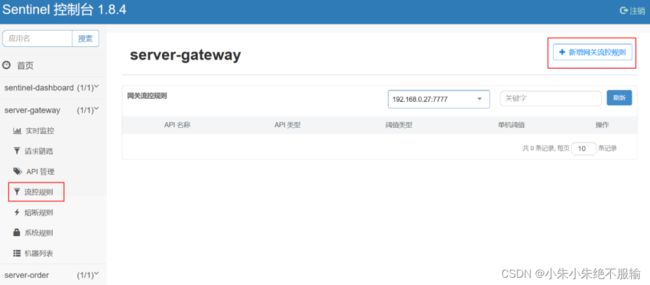
点击新增网关流控规则后,会弹出新增网关流控规则配置框,按照如下方式为user_api1分组配置限流规则。
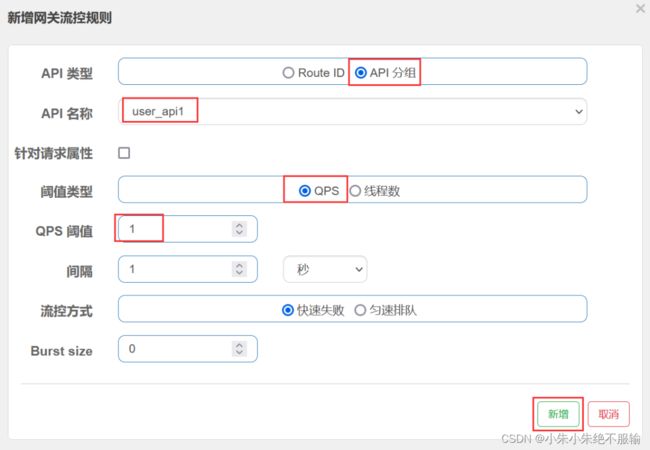
点击新增按钮后,按照同样的方式为user_api2分组配置限流规则。
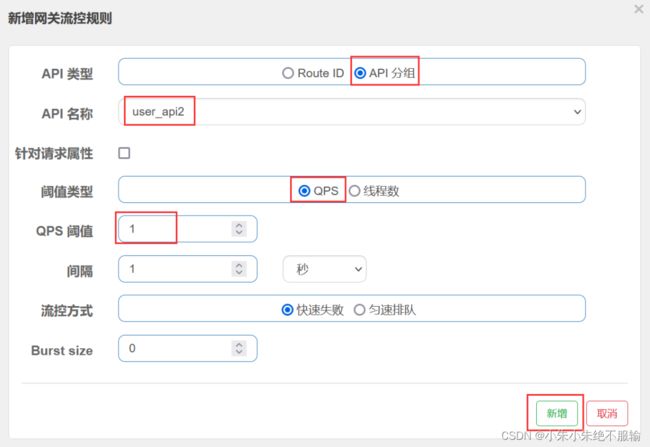
配置完毕后,在流控规则中的限流规则如下所示。
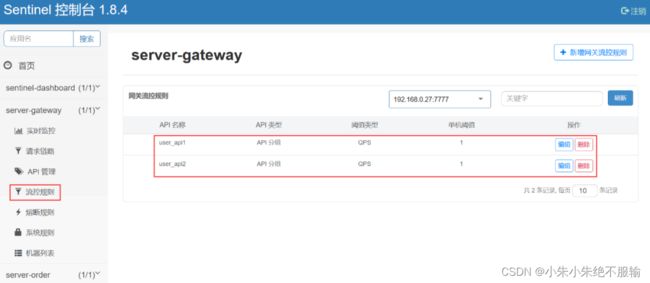
(6)预期的测试结果如下。
- 当频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api1/demo1时会被限流。
- 当频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api1/demo2时会被限流。
- 当频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api2/demo1时会被限流。
- 当频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api2/demo2时不会被限流。
注意:只有最后一个不会被限流。
(7)在浏览器上频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api1/demo1,如下所示。
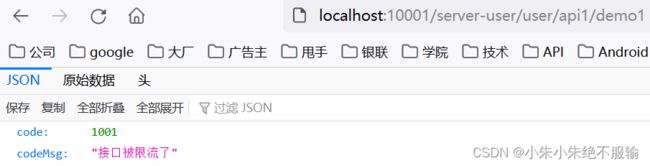 返回的原始数据如下所示。
返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"code": 1001,
"codeMsg": "接口被限流了"
}
说明触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
(8)在浏览器上频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api1/demo2,如下所示。
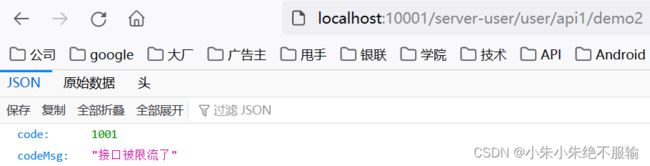 返回的原始数据如下所示。
返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"code": 1001,
"codeMsg": "接口被限流了"
}
说明触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
(9)在浏览器上频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api2/demo1,如下所示。
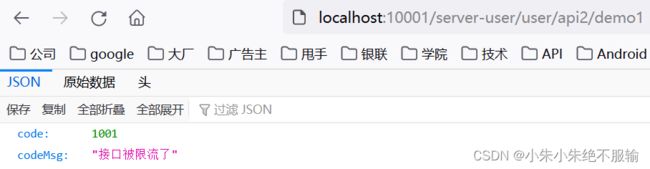
返回的原始数据如下所示。
{
"code": 1001,
"codeMsg": "接口被限流了"
}
说明触发了服务限流,并返回了自定义的限流结果数据。
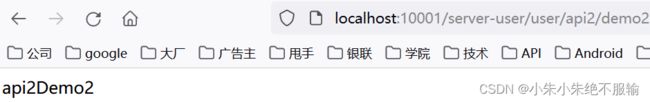
(10)在浏览器上频繁访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api2/demo2,如下所示。
可以看到,访问http://localhost:10001/server-user/user/api2/demo2时,无论访问的频率多频繁,都不会触发Sentinel限流。
至此,我们就成功在项目中整合了SpringCloud Gateway网关,并通过Sentinel整合SpringCloud Gateway实现了网关的限流操作。
参考:
本文是参考冰河技术得SpringCloud Alibaba实战专栏内容整理的,只是方便学习使用(侵权删),具体想要了解或想要获取源码的,请参考下面冰河技术的链接,关注公众号获取源码。
SpringCloud Alibaba
冰河技术:《SpringCloud Alibaba实战》