C++分数类(有理数类)重载四则运算、比较逻辑运算
任何有理数都可以表示为“分子/分母”的方式,其中分子、分母都是整数。
现实现一个有理数类,为这个有理数类重载四则运算(+、-、*、/)和所有的比较逻辑运算符(==、!=、>=、>、<=、<)
class Rational
{
private:
int numerator; // 分子
int denominator; // 分母
public:
//构造函数及运算符重载的函数声明
};
//重载函数的实现及用于测试的main()函数
重载四则运算(+、-、*、/)和所有的比较逻辑运算符(==、!=、>=、>、<=、<)
方法一:所有重载均以类的成员函数的方式实现。
#include 测试1
输入:
1
3
2
3
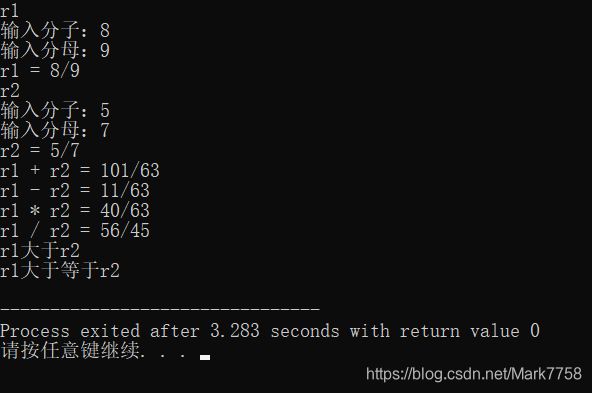
输入:
8
9
5
7
**方法2:使用友元函数实现 **
#include