JDK1.8新特性之Stream流讲解
JDK1.8新特性之Stream流讲解
Lambda表达式:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/426075566
上个小节,整理Lambda表达式的内容。那么,这个小节,准备整理些Stream流的内容!
Stream 流:该流同IO流,没有半毛钱关系
一种专门用于针对集合元素进行处理的技术!
实际上,Stream流,可以看成是非常高级的Iterator(迭代器),在迭代时,顺便可以针对元素进行过滤,筛选,汇总,转换……
理论不想太多的讲解,使用案例来理解……
数字集合
案例一:统计集合中非null元素的个数
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
count() 统计流中元素的个数
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 使用stream流过滤统计集合中非null元素的个数
long c = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).count();
System.out.println(c);
}
流程分析:
案例二:将集合中的非null元素进行排序
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
sorted() 针对流对象中的元素进行排序,得到新的流
collect() 将流重新转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 使用stream流将过滤后的数据排序后,然后再转换为List
datas = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).sorted((a, b) -> a - b).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
流程分析:
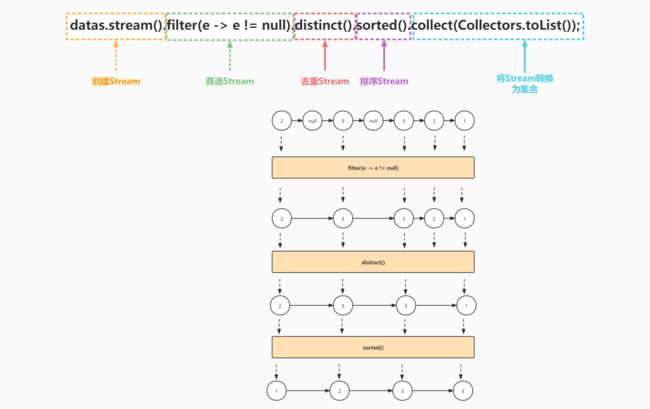
案例三:将集合中的非null元素进行去重排序
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
distinct() 针对流对象中的元素进行去重,得到新的流
sorted() 针对流对象中的元素进行排序,得到新的流
collect() 将流重新转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 去重
datas = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).distinct().sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
流程分析:
案例四:判断集合中所有非null元素是否都小于5
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
allMatch(e -> e < 5) 判断是否所有元素,都小于5
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 取判断集合中非null元素,是否都 小于 5
boolean flag = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).allMatch(e -> e < 5);
System.out.println(flag);
}
流程分析:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-riBimPrq-1635939782772)(https://woniumd.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/java/puxubo/20211103142617.jpg)]
案例五:判断集合中所有非null元素是否有小于5的数据
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
anyMatch(e -> e < 5) 判断集合中是否有小于5元素,有1个都返回true
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 取判断集合中非null元素,是否都 小于 5
boolean flag = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).anyMatch(e -> e < 5);
System.out.println(flag);
}
流程分析:
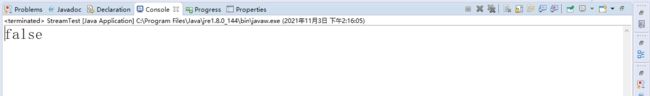
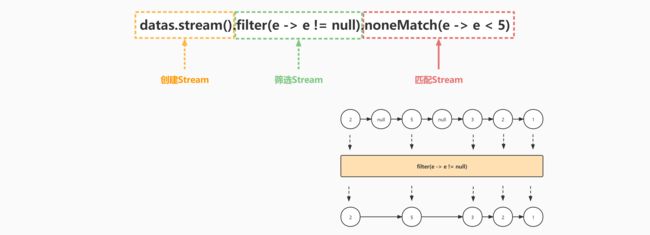
案例六:判断集合中所有非null元素是否都不小于5
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
noneMatch(e -> e < 5) 判断集合中,是否所有元素都 >=5
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
// 取判断集合中非null元素 是否都不小于5
boolean flag = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).noneMatch(e -> e < 5);
System.out.println(flag);
}
流程分析:
案例七:得到集合中最大值,以及最小值
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
max((a,b) -> a - b) 排序后,取得最大的那个值
min((a,b) -> a - b) 排序后,取得最小的那个值
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
//得到集合中最大值
Optional<Integer> o = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).max((a,b) -> a - b);
System.out.println("最大值:" + o.get());
//得到集合中最小值
o = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).min((a,b) -> a - b);
System.out.println("最小值:" + o.get());
}
流程分析:
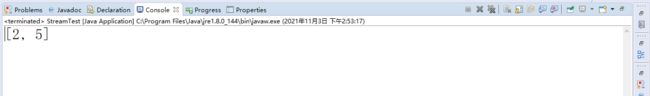
案例八:在集合中完成分页查询
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
skip(0) 跳过多少条数据 值 = (page -1) * rows; 0是指从0号位开始
limit(2) 获得多少条数据 值 = rows
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
//获得集合中非null元素的前2个元素
datas = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).skip(0).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
流程分析:
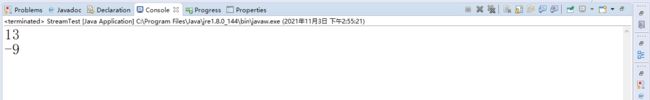
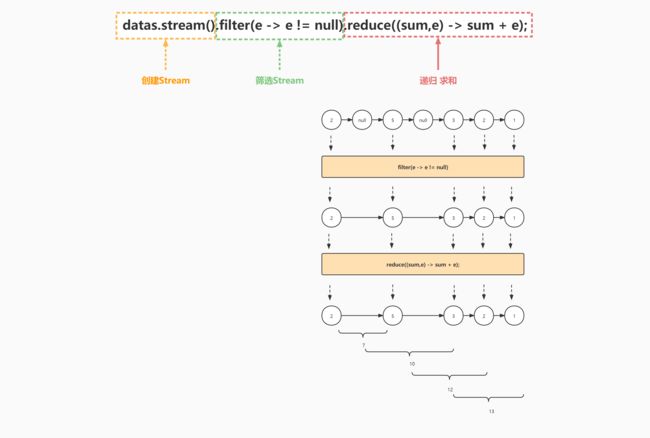
案例九:得到集合中元素的和,差
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
reduce() 归纳,简化 该函数2个参数,sum指:sum + e 的结果
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
//计算集合中所有元素的总和
//reduce((sum,e)-> sum + e); 将sum + e的结果,代入到函数的sum中,再次计算
Optional<Integer> o = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).reduce((sum,e) -> sum + e);
System.out.println(o.get());
//计算集合中所有元素的总差
o = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).reduce((sum,e)-> sum - e);
System.out.println(o.get());
}
流程分析:
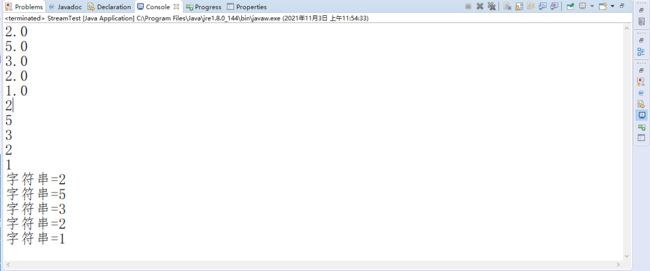
案例十:元素类型转换
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
mapToDouble() 将流对象中的元素,转换为double
mapToLong() 将流对象中的元素,转换为long
更为灵活的方式:map(),往下面看
collect() 将流对象转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Integer> datas = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, 2, null, 5, null, 3, 2, 1);
//将元素转换类型为Double
datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).mapToDouble(e -> e).forEach(System.out::println);
datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).mapToLong(e -> e).forEach(System.out::println);
datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null).map(e -> "字符串=" + String.valueOf(e)).forEach(System.out::println);
}
字符串集合
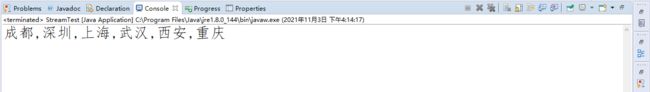
案例一:拼接字符串
stream() 得到流对象
collect() 将流对象转换为字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, "成都","深圳","上海","武汉","西安","重庆");
//将集合中数据拼接成字符串,并使用“,”进行分割
String str = datas.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(str);
}
案例二:集合排除null 以及""字符串
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
collect() 将流对象转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, "成都","深圳","","武汉",null,"重庆");
//针对集合中的所有空元素进行排除
datas = datas.stream().filter(e -> e !=null && !e.isEmpty()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
案例三:得到集合中长度 大于等于 2的不重复元素
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
distinct() 剔除流对象中的重复元素
collect() 将流对象转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, "成都","深圳","成都","武汉",null,"重庆","上");
//得到集合中长度 大于等于 2的不重复元素
datas = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null && !e.isEmpty()).filter(e -> e.length() >= 2).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
案例四:将字符串集合转换为数值集合
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
map() 将流对象中的元素,进行类型转换
collect() 将流对象转换为集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, "2", "3", "5", "2", null, "1", "3");
// 将字符串集合转换为数值集合
List<Integer> nums = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null && !e.isEmpty())
.map(e -> Integer.valueOf(e)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(nums);
}
案例五:将字符串转换为日期的集合
stream() 得到流对象
filter() 针对流对象进行元素筛选,得到新的流
map() 将流对象中的元素,进行类型转换
collect() 将流对象转换为集合
/**
* Stream流的讲解
*
* @author 蜗牛老蒲
*
*/
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
// 向集合中添加7个元素
Collections.addAll(datas, "2021-11-03", "2021-11-04", "2021-11-05", "2021-11-06", null, "2021-11-07",
"2021-11-08");
// 将字符串集合转换为日期集合
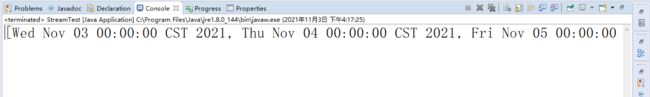
List<Date> dates = datas.stream().filter(e -> e != null && !e.isEmpty()).map(e -> {
try {
return DateUtil.str2Date(e, "yyyy-MM-dd");
} catch (ParseException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(dates);
}
}
/**
* 日期格式类
* @author 蜗牛老蒲
*
*/
class DateUtil {
public static Date str2Date(String str, String pattern) throws ParseException {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
return sdf.parse(str);
}
}
同理,其他类型的转换,一样的处理模式!O(∩_∩)O哈哈~
综合案例
/**
* Stream流的讲解
*
* @author 蜗牛老蒲
*
*/
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个集合
List<Student> datas = new ArrayList<Student>();
Collections.addAll(datas,
new Student(1L, "张三", 20, '男'),
new Student(2L, "李四", 12, '女'),
new Student(3L, "王五", 24, '男'),
new Student(4L, "赵六", 35, '女'),
new Student(5L, "田七", 65, '男'));
// 统计集合中,男性学生有多少个
long c = datas.stream().filter(e -> e.getGender().equals('男')).count();
System.out.println(c);
//得到20岁以下,所有女学生的数据
List<?> girls = datas.stream()
.filter(e -> e.getGender().equals('女'))
.filter(e -> e.getAge() < 20).collect(Collectors.toList());
//遍历输出所有的女生集合数据
girls.forEach(System.out::println);
// 针对集合中的男性学生进行升序排序
datas = datas.stream()
.filter(e -> e.getGender().equals('男'))
.sorted((a, b) -> a.getAge() - b.getAge())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
// 针对集合中的男性学生进行降序排序
datas = datas.stream()
.filter(e -> e.getGender().equals('男'))
.sorted((a, b) -> b.getAge() - a.getAge())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(datas);
}
}
class Student {
private Long id;
private String stuName;
private Integer age;
private Character gender;
public Student(Long id, String stuName, Integer age, Character gender) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.stuName = stuName;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStuName() {
return stuName;
}
public void setStuName(String stuName) {
this.stuName = stuName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Character getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(Character gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", stuName=" + stuName + ", age=" + age + ", gender=" + gender + "]";
}
}