leetcode刷题错误笔记(树之前)
1.简单数据结构
1.1 数组一
二分查找:
看题目,数组升序,复杂度log n,想到二分查找。
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 避免当 target 小于nums[0] nums[nums.length - 1]时多次循环运算
if (target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]) {
return -1;
}
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
}1.1.1 35搜索插入位置:(复杂度要求log n)
1.while(left<=right)
2.要把mid的判断写在前面,先判断nums[mid]==target插入就是后移 ,不能前移。所以如果最后没找到target,应该插在left最后的位置。
最后的left比right大。
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = (left +right)>>1;
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
else if (nums[mid] > target)
right = mid - 1;
}
return left;
}
}1.1.2 34 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个的位置(复杂度要求log n)
犯的错误,我的代码,复杂度应该是n,而不是log n。
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int maxindex=0,minindex=0,left=0,right=nums.length-1;
int[] a=new int[2];
a[0]=-1;
a[1]=-1;
if(targetnums[nums.length-1]){
return a;
}
while(left<=right){
int mid=left+((right-right)>>1);
if(nums[mid]==target){
if(midmaxindex){
maxindex=mid;
}
}else if(nums[mid]target){
right=mid-1;
}
}
a[0]=minindex;
a[1]=maxindex;
return a;
}
} 正确思路:先用二分法找到位置。然后while,从这点出发找到左边界。然后再找右边界。
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int index=getindex(nums,target);
int [] a=new int[2];
if(index==-1){
a[0]=-1;
a[1]=-1;
return a;
}
int left=index;
int right =index;
while(left-1>=0&&nums[left-1]==nums[index])
{left--;
}
while((right+1<=nums.length-1)&&nums[right+1]==nums[index])
{
right++;
}
a[0]=left;
a[1]=right;
return a;
}
public int getindex( int[] nums ,int target){
int left=0,right=nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid=left+((right-right)>>1);
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}else if(nums[mid]target){
right=mid-1;
}
}
return -1;
}
} 1.1.3 求x得平方根
思路:反正要的整数,直接for循环遍历一遍,满足 i *i < x and (i+1)*(i+1)>x,即可。
public int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x==0||x==1){
return x;
}
int result=x;
for(int i=1;ix)
{
result=i;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
1.1.4 删除升序数组中重复元素(快慢 指针)
思路:双指针:j指针找到不重复的元素。然后让i加1,放在i这个位置。
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0|| nums.length==1)
{
return nums.length;
}
int i=0;
int j=1;
while(j1.1.5 把数组里的0放在数组最后(快慢指针,跟上一题类似)
思路:用双指针,把四种情况,想明白怎么做,即可。
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0||nums.length==1)
{
return ;
}
int i=0;
int j=1;
while(j1.1.6 比较含退格的字符串
给定 s 和 t 两个字符串,当它们分别被输入到空白的文本编辑器后,如果两者相等,返回 true 。# 代表退格字符。
这种一对一的消除关系,还是用栈。
思路:用栈。碰到#号,出栈即可。不是#就入栈。
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String s, String t) {
StringBuilder s1=new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder s2=new StringBuilder();
for(char c :s.toCharArray()){
if(c!='#'){
s1.append(c);
}else if(s1.length()>0){
s1.deleteCharAt(s1.length() -1);
}
}
for(char c :t.toCharArray()){
if(c!='#'){
s2.append(c);
}else if(s2.length()>0){
s2.deleteCharAt(s2.length() -1);
}
}
return s1.toString().equals(s2.toString());
}
}1.1.7 有序数组的平方
给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。
思路:用Array工具类里的sort,对这个数组进行排序。
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int [] array=new int[nums.length];
for (int i=0;i< nums.length;i++){
array[i]=nums[i]*nums[i];
}
Arrays.sort(array);
return array;
}
}
思路2:用双指针指向两端,数组其实是有序的, 只不过负数平方之后可能成为最大数了。
那么数组平方的最大值就在数组的两端,不是最左边就是最右边,不可能是中间。然后挨个排序。
拿一个中间数组,把最大的挨个往里面放。
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int pre=0;
int p=nums.length-1;
int[] result = new int[nums.length];
int index = result.length - 1;
while(pre<=p){
int t=0;
if(nums[pre]*nums[pre]>nums[p]*nums[p])
{
result[index--]=nums[pre]*nums[pre];
pre++;
}else{
result[index--]=nums[p]*nums[p];
p--;
}
}
return result;
}
}
1.2 数组二(两次没做出来)
1.2.1 长度最小的子数组
输入:target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
输出:2
解释:子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的子数组。
里面的数和为7的。
核心代码:sum>=target,在的时候减去,正好减一位那种,
在for的下一层又会满,又能用result比较一次最小长度。
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int i=0;
int sum=0;
int result=Integer.MAX_VALUE;;
for(int j =0;j=target){
result=Math.min(result,j - i + 1);
sum-=nums[i++];
}
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
} 1.2.2 水果成篮(第二次做错)
筛选数组里的最长子数组,这个子数组里面只能有两种元素。比如,题中只有1.2。
思路:整一个count数组,里面放每种水果有多少个(一定成立:让count数组的长度等于树的长度n,一个树上只有一个水果,最坏种类也是n)。
让right每个回合都往右移动。移动一下,判定一下篮子里的种类是否超过2,
用size标记种类个数。
超过种类2的时候,从左面开始删,让left右移,右移动一个扔掉一个,直到size=2。
那size什么时候减呢?用left的下标移动时,去除里面的 fruits[left],之后判断
count[fruits[left]] == 0。
这个时候记录一下,right右移一位产生的新的小数组长度,也就是right -left +1。
class Solution {
public int totalFruit(int[] fruits) {
int left = 0;
int maxLen = 0;
int[] count = new int[fruits.length];
int size = 0;
for (int right = 0; right < fruits.length; right ++) {
if (count[fruits[right]] == 0) size++;
count[fruits[right]]++;
// 滑动窗口内水果种类大于 2 个时
while (size > 2) {
count[fruits[left]]--;
if (count[fruits[left]] == 0) {
size--;
}
left++;
}
// 扩大窗口的时候更新 最大长度
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, right - left + 1);
}
return maxLen;
}
}
1.2.3最小覆盖子串(困难题)
利用滑动窗口,让count刚开始等于小字符串的长度。
1.然后用上标J遍历大字符串,如果时,小字符串里所有的元素都出现了,那就开始在while里,给下标i移动到子串的边界(边界的左边最左边那中元素只有一个,就是边界那个)。
2.然后不断获得在J到I,区间里最小子串,比较它们的长度。
具体做法,去掉最左面那个元素,count一定加1,然后再让J往右边走,直到count再次为0,再次判断。
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
// 存储需要的字符个数
int[] needs = new int[128];
// 循环t把每个字符存到相应的数组下标中
for (int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++) {
needs[t.charAt(i)]++;
}
// i左边界,j右边界,start为s中包含t的开始下标,count为所需t字符的总数,len为最小子序列长度
int i=0,j=0,start=0,count=t.length(),size=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while(j0) {
count--;
}
// 把遍历到的所有字符,都记录,小于0说明,不需要或者多包含
needs[c]--;
// 当count为0,缩小窗口,找出start和size
if(count==0){
// 当s中i下标字符不需要时,一直缩小窗口,直到需要这个字符
while (i 1.2.4 螺旋矩阵
确定好每次填放的方向,cnt的增量必须设为n-1。每四圈,确定好下一次起始的地方即可。
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] a=new int[n][n];
int T=0;//指示变量,看一圈走了几次,来确定方向
int H=0;//纵坐标
int Z=0;//横坐标
int mi=n*n;
int sum=1;//从1到n的平方
int cnt=n-1;//增量
int p=0;//用来遍历的
//cnt 分三种,>=2,=1,0;
while(sum<=mi&&cnt>=2){
if(T%4==0){
while(p1.2.5 螺旋矩阵进阶版(万能,不仅可以用作方阵)
思路:走一圈,需要两个增量来指示。如果有剩下的,那cnt一定是0,因为正常cnt=1,在while里也全走完了。
窄的那边为偶数,也可以顺带着在while里走完。
while里最重要的是,每过4次,就要 重新找个起始点,H++或Z++。
最终可能存在一个cnt 为0,一个cnt 不为0,那就 剩下一列,或者一行。
窄的那边如果为基数,的情况,最后剩下黑色的。此时cnt1已经变成0了。竖着排,大小是cnt2+1,因为cnt之前减了2。
同类,存在一种横着的剩余,此时cnt2=0
class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int T=0;//指示变量,看一圈走了几次,来确定方向
int H=0;//纵坐标
int Z=0;//横坐标
int Slength=0;
if(matrix.length==0){
int [] a={};
return a;
}
int cnt1=matrix.length-1;//增量
int cnt2=matrix[0].length-1;//增量
int maxSize=Math.max(matrix.length,matrix[0].length);
int[] sum= new int[matrix.length*matrix[0].length];
int p=0;//用来遍历的
//cnt 分三种,>=2,=1,0;
while(cnt1 >=1 &&cnt2 >=1){
if(T%4==0){
while(p2.链表
2.1 移除链表中指定元素
设置一个虚拟结点让pre指着,然后让cur从头开始指(头结点有元素)
如果cur指的指是val,则pre.next=p.next,如果不是val,就让pre移过来。
不管怎么样,cur作为遍历指针,每轮都要往后移动一位。
最后返回虚拟节点的next,肯定与链表相连,因为返回head,head结点可能已经被删除。
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
// 因为删除可能涉及到头节点,所以设置dummy节点,统一操作
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1, head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == val) {
pre.next = cur.next;
} else {
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
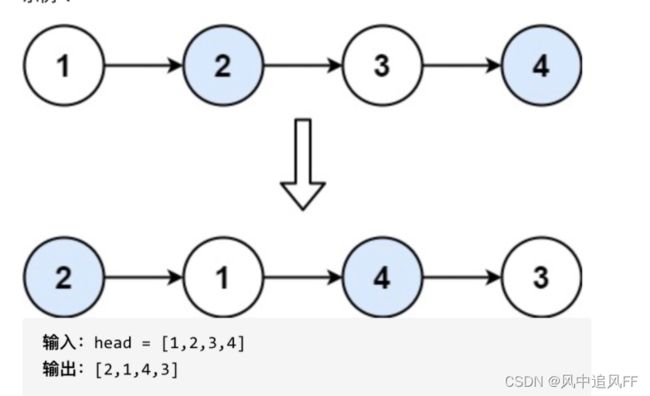
}2.2 两两交换链表中的结点
整个虚拟节点。用了三个位置进行交换。三个步骤。
pre和head指向的结点没变,只是结点的指针发生了变化,比如第一轮交换完了,head指向1,pre还指向cur(虚拟节点)。
这个时候就更新一下,让head指向3,pre指向1。然后在下一层里继续,这三个步骤,重点在于prev和head的更新。
prev = head; // 步进1位
head = head.next; // 步进1位while的判断条件也很重要,prev始终作为辅助结点,在交换的两个结点之前。
我们要判断,交换的两个结点是否存在。
while (prev.next != null && prev.next.next != null) 因为head.next的next会变化指向第三个,所以先找一个存一下。
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummyNode = new ListNode(0);
dummyNode.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummyNode;
while (prev.next != null && prev.next.next != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next.next; // 缓存 next
prev.next = head.next; // 将 prev 的 next 改为 head 的 next
head.next.next = head; // 将 head.next(prev.next) 的next,指向 head
head.next = temp; // 将head 的 next 接上缓存的temp
prev = head; // 步进1位
head = head.next; // 步进1位
}
return dummyNode.next;
}
}最后返回 虚拟结点的下一个,才是链表的开始,head结点已经不是开始。
2.3 删除链表的倒数第N个结点(一趟解决)
建议自己弄一个虚拟头结点。
思路:用双指针,都从虚拟结点出发,让P先走n下。维持一个大小为N+1的窗口。因为要删倒数第N个,得有它前面的。
最后得返回t.next,不能返回head,因为可能存在链表只有一个结点,head指向这个结点。
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode t=new ListNode(-1);
t.next =head;
ListNode pre=t;
ListNode p=t;
int cnt=0;
while(cnt2.4 找出两个链表之间的交点
注意:是指针相等,而不是两个链表的元素值相等。
思路:既然相交,那肯定末尾一样。因为是单链表,不能维护两个指针从末尾开始挨个前进。
所以得计算出两个链表长度的差距。然后移动两个比较指针,让它们剩下的结点个数一样。
然后从差距的那个结点挨个遍历比较即可,直到出现相等。
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode p1=headA;
ListNode p2=headB;
int lengthA=0;
int lengthB=0;
while(p1!=null){
lengthA++;
p1=p1.next;
}
while(p2!=null){
lengthB++;
p2=p2.next;
}
p1=headA;
p2=headB;
if(lengthA>=lengthB){
int t1=lengthA-lengthB;
while(t1>0){
t1--;
p1=p1.next;
}
}else{
int t2=lengthB-lengthA;
while(t2>0){
t2--;
p2=p2.next;
}
}
while(p1!=p2&&p1!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return p1;
}
}2.5 判断链表是否有环,如果有环,从哪个顶点开始入环。
思路:判断哪个指针入环,不能判断结点值。设置一个快指针fast速度为走两步,一个慢指针slow走一步,当slow与fast在环内相遇的时候,slow一定不会走完一圈。
判断为环:如果fast能与slow相遇,则一定有环。
那怎么判断环从哪开始呢?
相遇时:
slow指针走过的节点数为: x + y,
fast指针走过的节点数:x + y + n (y + z),n为fast指针在环内走了n圈才遇到slow指针, (y+z)为 一圈内节点的个数A。
因为fast指针是一步走两个节点,slow指针一步走一个节点, 所以 fast指针走过的节点数 = slow指针走过的节点数 * 2:
(x + y) * 2 = x + y + n (y + z)
两边消掉一个(x+y): x + y = n (y + z)
因为要找环形的入口,那么要求的是x,因为x表示 头结点到 环形入口节点的的距离。
所以要求x ,将x单独放在左面:x = n (y + z) - y ,
再从n(y+z)中提出一个 (y+z)来,整理公式之后为如下公式:x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z 注意这里n一定是大于等于1的,因为 fast指针至少要多走一圈才能相遇slow指针。
当 n为1的时候,公式就化解为 x = z,当n为2的时候,就是走了两圈才碰到。
因为x = (n - 1) (y + z) + z,所以我们只要在第一次的相遇点那里设置一个Index1,让它每次走一步,在起始点设置一个Index2,每次也只走一步,后面它们相遇的地方一定是环的起点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {// 有环
ListNode index1 = fast;
ListNode index2 = head;
// 两个指针,从头结点和相遇结点,各走一步,直到相遇,相遇点即为环入口
while (index1 != index2) {
index1 = index1.next;
index2 = index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}那么while该怎么写呢?
因为fast要一次移动两下。它不能是空。又因为我们里面直接让
fast = fast.next.next;需要用到fast.next这个值,所以它也不能是个空指针。
while (fast != null && fast.next != null)用map一下就做出来
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
Map map =new HashMap<>();
ListNode work=head;
while(work!=null)
{
if(map.containsKey(work))
{
return work;
}
map.put(work,0);
work=work.next;
}
return null;
}
} 3.哈希表与双指针
3.1 有效的字母异位词
思路:整个数组(大小为26),字母也只有a到z,遍历这两个字符串,记录两个字符串中相同字母出现的频率是否相同。
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
char [] word=new char[26];
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
word[c - 'a'] += 1;
}
for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
word[c - 'a'] -= 1;
}
for (int i : word) {
if (i != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}3.2 赎金信
思路:(暴力)遍历ransomNote里的字符,看看在magazine里是否出现。
用哈希表的思想:整一个数组里面全都是1,先遍历ransomNote字符串,再遍历magazine数组。
具体操作如下:第二个for那里检查一下,如果是新出现的字符,那就不用再减了。
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
char [] word=new char[26];
for (char c : ransomNote.toCharArray()) {
word[c - 'a'] += 1;
}
for (char c : magazine.toCharArray()) {
if(word[c - 'a']>0)
word[c - 'a'] -= 1;
}
for (int i : word) {
if (i != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}3.3 字母异位词分组。
用hashMap存集合即可。用sort排序字符数组即可,这样所有的都一样。
key的值,是字符串的。用valueOf把字符数组转化为字符串。
get(key),得到key的value。
class Solution {
public List> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i());
map.get(temp).add(strs[i]);
}else
{
map.get(temp).add(strs[i]);
}
}
return new ArrayList(map.values());
}
} 3.4 两个数组的交集(不带重复的)
题意:给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
用两个set来存,然后用contains来判断另一个集合中是否有这个元素。
集合的元素都能用for循环遍历。
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
if (nums1 == null || nums1.length == 0 || nums2 == null || nums2.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
Set set1 = new HashSet<>();
Set resSet = new HashSet<>();
//遍历数组1
for (int i : nums1) {
set1.add(i);
}
//遍历数组2的过程中判断哈希表中是否存在该元素
for (int i : nums2) {
if (set1.contains(i)) {
resSet.add(i);
}
}
int[] resArr = new int[resSet.size()];
int index = 0;
//将结果几何转为数组
for (int i : resSet) {
resArr[index++] = i;
}
return resArr;
}
} 3.5 两个数组的交集(带重复的)
这回不用set,用list对象。List的remove方法是删除一条数据。removeAll才是批量操作。
弄两个list,list1用来放随便一个集合的,然后遍历另一个数组,看看有没有包含的。
这样可以一一对应,list2里放结果。
for(int num:nums2){
if(list1.contains(num)){
list2.add(num);
list1.remove(Integer.valueOf(num));
}
}list里放重复元素,用contains看看
class Solution {
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
List list1=new ArrayList<>();
for(int num : nums1){
list1.add(num);
}
List list2=new ArrayList<>();
for(int num:nums2){
if(list1.contains(num)){
list2.add(num);
list1.remove(Integer.valueOf(num));
}
}
int[] p=new int[list2.size()];
int index=0;
for(int num :list2){
p[index++]=num;
}
return p;
}
} 3.6 快乐数
定义为:对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和,然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。如果 可以变为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
思路:得用set,可能在途中会被无限循环,如果再碰到相同的,说明就存在循环,不可能是快乐数。用set来做。
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
int sum2=0;
Set set=new HashSet<>();
while(n!=1){
int[] p=mode(n);
sum2=0;
for(int num:p){
sum2+=num*num;
}
if(!set.contains(sum2)){
set.add(sum2);
n=sum2;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
//这个方法用来将每位记录在数组。
public int []mode(int n){
int sum=n;
int cnt=0;
while(sum>0){
sum=sum/10;
cnt++;
}
int [] p=new int[cnt];
sum=n;
int index=0;
while(sum>0){
p[index++]=sum%10;
sum/=10;
}
return p;
}
} 3.7 两数之和
思路:用map,key存元素值,value存下标。先用map存一遍数组。然后挨个遍历数组,检查target-当前元素的值 的key是否存在,如果存在,返回这俩下标即可。
这题存在的问题,没说数组里有没有重复元素,也没说,满足target的是不是只有一组。建议弄个二维数组。
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int a[]=new int[2];
if(nums==null||nums.length==0){
return a;
}
Map map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i 3.8 四数相加
我自己写的用了三层for循环,感觉很麻烦。
思路:用map,记录元素和,与它们出现的次数。
两两分开,统计两个数组内元素之和,并且记录这个元素和的次数。
然后统计剩下两个数组的元素之和,然后用contain。
map集合根据key来更新value值。所以我们把更新后的put进去。
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
Map map=new HashMap<>();
int sum;
int target;
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i 3.9 三数相加(卡了很久,建议背诵)
思路:弄三个指针。i 标记小于0的。如果遍历到nums[i+1]=nums[i],跳过去。
剩下的让head=i+1;tail=length-1;这俩也得去重,在ret判断等于0后对下一个位置进行判断,去重。
class Solution {
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
//一个map,双指针即可。然后把这三个下标存进List里即可。
List> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(nums==null&&nums.length<3){
return list;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int len=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i0) break;//i只标记小于0的。
if(i>0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue;//去重,如果跟前面的一样,那就后移
int left=i+1;
int right=len-1;
int ret=0;
while(left0)
{
right--;
}else
{
left++;
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
3.10 去除list里的重复集合。
用冒泡排序,挨个比较。复杂度是n的平方。
for (List list : lists) {
System.out.print(list.toString());
}
System.out.println();
// 采用冒泡排序的比较规则,当然可以换成一个更高效的比较方法
for (int i = 0; i < lists.size() - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < lists.size(); j++) {
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++) {
// 判断当前list是否和后面的list三个元素相同
if (lists.get(i).contains(lists.get(j).get(k))) {
count++;
}
}
if (count == 3) {
lists.remove(j);
// 因为删除一个元素,长度会减一,所以j要退回一位
j--;
} 3.11 四数之和
四数之和,和三数之和是一个思路,都是使用双指针法, 基本解法就是在三数之和的基础上再套一层for循环。
外层不能这样再break了,因为我们可能要的target是负数。所以去掉这句话。
就是在三数相加外面再套一层for循环。可以让i遍历到length-1,因为下面对j也有for循环检查。
class Solution {
public List> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(nums==null||nums.length<4) return list;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int len=nums.length;
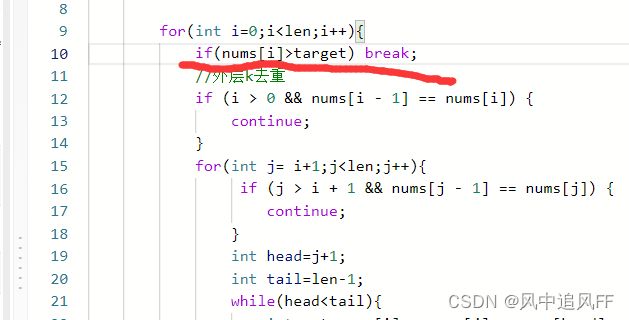
for(int i=0;itarget && nums[i]>0) return list;
//外层k去重
if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i]) {
continue;
}
for(int j= i+1;j i + 1 && nums[j - 1] == nums[j]) {
continue;
}
int head=j+1;
int tail=len-1;
while(head 4.字符串操作
4.1 反转字符串
思路:每隔k个反转k个,末尾不够k个时全部反转,
卡在不知道什么时候反转K个,找不到时机。
新的交换方式,用异或。a=a^b,b=a^b,a=a^b
class Solution {
//每次start增加2k个,然后对剩下的k个进行反转。
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < ch.length; i += 2 * k){
int start=i;
int end = Math.min(ch.length - 1, start + k - 1);//这一步全文最关键。
//我只用剩下的前k个,如果不够k个,那么就剩下的全部反转。
while(start < end){
ch[start] ^= ch[end];
ch[end] ^= ch[start];
ch[start] ^= ch[end];
start++;
end--;
}
}
return new String(ch);
}
}4.2 删除字符串里的空格。
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
if (s== null) {
return null;
}
StringBuilder sb =new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i4.3 反转字符串里的单词
思路:从右开始遍历,找到单词的右界,然后找到单词的左界。把这个单词装进新的字符数组。
只要while里有减减,那就得保证不越界。
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
List list1 =new ArrayList<>();
//从右到左挨个把里面的字符串摘出来,最后再输出的时候处理一下。
int i=s.length()-1;
//从右到左遍历
while(i>=0)
{
while(i>=0&& s.charAt(i)==' ')i--; //先找到不是空格的的第一位。
int right=i;
while(i>=0 && s.charAt(i)!=' ') i--; //然后找到空格,那么left+1和right之间就是我们要的字符串
int left=i+1;//这里必须得是i+1,while停下来,可能是i<0或者i位置是空格了。
String work=s.substring(left,right+1);
list1.add(work);
}
String result="";
if(list1.size()==0)
{
return null;
} else
{
//这里直接无脑放字符串和空格
for(String t:list1)
{
result+=t;
result+=" ";
}
}
//最后再去除尾部的空格即可。
int j=result.length()-1;
while(j>=0&&result.charAt(j)==' ') j--;
return result.substring(0,j+1);
}
}
1.注意,这里的i>=0,要写在前面。这样对后面数组检查时,不会越界异常。
4.4 左旋字符串
StringBuilder sb =new StringBuilder(s);
StringBuilder里有reverse方法,但是是颠覆整个字符串里的长度,不能定长颠覆。。
几个常用的方法。
1.sb.length(),求sb的长度。
2.长度表示的是字符的个数,容量表示的是可用于最新插入字符的存储量。
sb.capacity()。
String s=sb.toString();可以把这个再转回String类型。
3.可以用StringBuilder的setChar方法修改,里面的字符。
setCharAt(下标,值)。
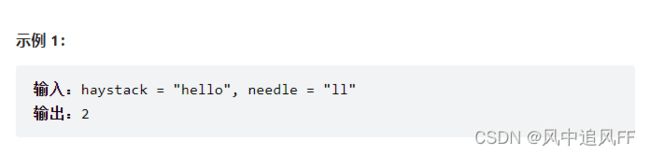
4.5 实现strStr()。
class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if(needle==""){
return 0;
}
char[] a=haystack.toCharArray();
char[] b=needle.toCharArray();
int Aindex=0;
int Bindex=0;
while(Aindex4.6 检查一个字符串是否可以由它的子字符串多次构成。(KMP算法讲解)
其实还可以,遍历一遍字符串s, 整个char [] a=new int char[26] ,记录每个字符出现的次数。
1.次数必须都相等。
2.用索引 Index遍历 字符串s,用[0 ,index] 区间的字符串来 重复处理,看看字符数组里的结果,是否最终都为0。
class Solution {
//只需要判断 该字符串是不是循环的即可。
//整一个辅助字符串,作为循环子串。
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
char c=s.charAt(0);
String work=s.substring(0,1);
boolean flag=false;
for(int i=1;i4.6.1 kmp算法理论
KMP算法,解决字符串匹配的问题。
前缀:不包括最后一个。
后缀,不包括首字母。
最长相等前缀。拿aabaa来说事,这个最长相等前后缀,不能是aba。应该是前缀aa,和后缀aa,一个从左面出发不能跳过首字母,一个从右边出发不跳过最后一个字母。
这就是aabaaf的的前缀表。在f点不匹配的时候,我们看这里最长相等前缀是2,然后我们跳转到下标为2的位置,也就是b那里。
思路:f点不匹配,看除去f点,串的最长相等前后缀,实际就是一个对称。我们找到那个点就行。
那个点下标就是最长相等前后缀的长度。
很多KMP算法里用next数组或者prefix作为数组名。
有的算法里,有人把长度整体往左移动以为,-1,后面找到了,还会加回来。
4.6.2 kmp求next数组(代码篇)
求前缀表的具体代码。f那个位置就是冲突位置,遇见冲突位置,我们要回到前面去。
3种寻找方式:
类型2: f那里的0不要了,直接所有的数右移动,左面补-1。这样不用在往左走一步读取。
类型3:还是找前一位,但是会把这个1加上来。
代码硬背即可。最后一个判断是否有重复字符串的操作。
看图即可。
背即可:如果len % (len - (next[len - 1] )) == 0 ,则说明 (数组长度-最长相等前后缀的长度) 正好可以被 数组的长度整除,说明有该字符串有重复的子字符串
class Solution {
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
if (s.equals("")) return false;
int len = s.length();
// 原串加个空格(哨兵),使下标从1开始,这样j从0开始,也不用初始化了
s = " " + s;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int[] next = new int[len + 1];
// 构造 next 数组过程,j从0开始(空格),i从2开始
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= len; i++) {
// 匹配不成功,j回到前一位置 next 数组所对应的值
while (j > 0 && chars[i] != chars[j + 1]) j = next[j];
// 匹配成功,j往后移
if (chars[i] == chars[j + 1]) j++;
// 更新 next 数组的值
next[i] = j;
}
// 最后判断是否是重复的子字符串,这里 next[len] 即代表next数组末尾的值
if (next[len] > 0 && len % (len - next[len]) == 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}5.栈与队列
5.1 用栈实现队列功能
思路:用两个栈,来模拟一个队列。连续删除俩一样的元素。栈顶的,和没进来的就不让它进来了。
用栈实现队列的下列功能。
class MyQueue {
//指定俩,作为出入。
Stack stackIn;
Stack stackOut;
public MyQueue() {
stackIn = new Stack<>(); // 负责进栈
stackOut = new Stack<>(); // 负责出栈
}
public void push(int x) {
stackIn.push(x);//队列的push放入栈里。
}
//把一个栈的元素在塞到另一个栈。
public int pop() {
dumpstackIn();//
return stackOut.pop();//然后从用来出的这个栈出即可。
}
//返回队列首部的元素。也就是返回第二个用来出的栈的首部元素。
public int peek() {
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty();
//如果这俩都空,则说明这个也空了。
}
// 如果stackOut为空,那么将stackIn中的元素全部放到stackOut中
private void dumpstackIn(){
if (!stackOut.isEmpty()) return;
while (!stackIn.isEmpty()){
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
}
5.2 用队列实现栈
思路:一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时在去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
实现以下的功能。
队列的6个功能
我们用java的deque这个数据结构。
Deque是double ended queue,将其理解成双端结束的队列,双端队列,可以在首尾插入或删除元素。
Deque
class MyStack {
// Deque 接口继承了 Queue 接口
// 所以 Queue 中的 add、poll、peek等效于 Deque 中的 addLast、pollFirst、peekFirst,两个方向,一个是first,队列首部方向,一个last队列尾部方向。
Deque que1;
public MyStack() {
que1= new ArrayDeque<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
que1.addLast(x);//添加的时候,添加到队列尾部。
}
//移除栈顶元素的时候,就把前面所有的值,除了最后一个,再重新加到队列尾部。
public int pop() {
int size = que1.size();
size-=1;
// 将 que1 导入 que2 ,但留下最后一个值,比如有5个,我们现在还操作4次。
while (size> 0) {
que1.addLast(que1.peekFirst());//addlast从尾部加进去。
que1.pollFirst();
size--;
}
int res = que1.pollFirst();
return res;
}
//peaklast是获取队尾部元素,栈顶就是它的尾部。
public int top() {
return que1.peekLast();
}
public boolean empty() {
return que1.isEmpty();
}
}
5.3 有效的括号
就是看字符串里的括号是否闭合。
第一种情况:已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false
第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有要匹配的字符。所以return false
第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号return false
那么什么时候说明左括号和右括号全都匹配了呢,就是字符串遍历完之后,栈是空的,就说明全都匹配了。
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque deque = new LinkedList<>();//泛型里放字符是这样的。
char ch;
//然后挨个遍历字符串。
for(int i=0;i 5.4 删除字符串里相邻重复项(得用栈,我第二次用了数组,很难受)
思路:用一个栈,相邻对对碰。
如果输入的正好等于栈顶,那么我们就不让这个进去,并且让栈顶的出来。
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
//ArrayDeque会比LinkedList在除了删除元素这一点外会快一点
ArrayDeque deque=new ArrayDeque<>();
char ch;
for(int i=0;i 5.5 逆波兰表达式
逆波兰表达式就是运算符写在后面的后缀表达式。
老思路:一个栈放运算符,另一个栈放运算数和结果。
新思路:一个栈解决。两个字符挨后面跟着一个运算符就要被转化成和,重新放进栈。
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Deque stack = new LinkedList();
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.length; ++i) {
if ("+".equals(tokens[i])) { // leetcode 内置jdk的问题,不能使用==判断字符串是否相等
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop()); // 注意 - 和/ 需要特殊处理
} else if ("-".equals(tokens[i])) {
stack.push(-stack.pop() + stack.pop());
} else if ("*".equals(tokens[i])) {
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
} else if ("/".equals(tokens[i])) {
int temp1 = stack.pop();
int temp2 = stack.pop();
stack.push(temp2 / temp1);
} else {
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(tokens[i]));
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
} 5.6 滑动窗口最大值
这题本来打算暴力破解。
用O(m*k)的复杂度解决。
结果最后几个测试用例,数据集太大。
无奈只能改思路:弄一个单调的队列。左面pop,右边push。
pop的规则是,如果要pop的元素等于队头的最大的元素,则pop队头,否则不管。
push的规则是,如果入口里呆着的元素,比要push的元素小,就从入口里滚蛋。从入口给你弹出!
如果入口里呆着的元素比要push进来的元素大,则让这个数push进来。
这样可以形成,出口最大的,单调递减队列。
所以,对于这个队列的定义,我们得重写pop和push的方法。
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length==1){
return nums;
}
int[] result=new int[nums.length-k+1];
int index=0;
MyQueue que=new MyQueue();
int pre=0;
int last=k-1;//先为前k个维护初始队列。
for(int i=0;i<=last;i++){
que.add(nums[i]);
}
result[index++]=que.front();
//然后滑动。
//双指针维护滑动窗口删除与新入。
while(last deque= new LinkedList<>();
void poll(int val){
if(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekFirst()==val){
deque.poll();
}
}
void add(int val){
while(!deque.isEmpty()&& val>deque.peekLast()){
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(val);
}
int front(){
return deque.peekFirst();
}
} 5.7 前k个高频元素。
map记录频率。然后用堆对权值进行排序。发·
那么问题来了,定义一个大小为k的大顶堆,在每次移动更新大顶堆的时候,每次弹出都把最大的元素弹出去了,那么怎么保留下来前K个高频元素呢。
而且使用大顶堆就要把所有元素都进行排序,那能不能只排序k个元素呢?
所以我们要用小顶堆,因 为要统计最大前k个元素,只有小顶堆每次将最小的元素弹出,最后小顶堆里积累的才是前k个最大元素。
5.7.1 堆结构的优秀实现类。
用到一个类,Priorityqueue ,里面用lamda表达式,书写了,排序规则。
构造器里传入了比较器,来形成最小堆。传入了一个comparetor里的compare方法的重写。
compare(int o1, int o2)方法
return o1 - o2 是升序
return o2 - o1 是降序。
(o1, o2) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue()class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] result=new int[k];
Map map= new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i> entries = map.entrySet();
//定义一个最小堆,和传入比较器,最小堆里默认升序。
PriorityQueue> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1.getValue() - o2.getValue());
//然后遍历从map里拿出来的键值对。挨个放进我们的最小堆。
for (Map.Entry entry : entries) {
queue.offer(entry);
if (queue.size() > k) {
queue.poll();//小的先出,最后出的就剩K个了。
}
}
//然后遍历我们的最小堆。装进数组里,从后往前装。
for(int i=k-1;i>=0;i--){
result[i]=queue.poll().getKey();
}
return result;
}
} 6.二叉树
完全二叉树可以用数组存储。如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i * 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i * 2 + 2。
java树节点的数据结构:
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}6.1 二叉树的递归遍历
// 前序遍历·递归·LC144_二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List result = new ArrayList();
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, result);
preorder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 中序遍历·递归·LC94_二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {
public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void inorder(TreeNode root, List list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
inorder(root.right, list);
}
}
// 后序遍历·递归·LC145_二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void postorder(TreeNode root, List list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
}
} 6.2 二叉树的迭代遍历
递归的实现就是:每一次递归调用都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中,然后递归返回的时候,从栈顶弹出上一次递归的各项参数,所以这就是递归为什么可以返回上一层位置的原因。
放进栈里,拿出来,再压进去,的反复过程。
6.2.1前序遍历(迭代法)
前序遍历是中左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将根节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
C+,st是声明的栈。中右左放进栈。先对中处理,读到中,然后让它出来。
中已经出栈了,根据读到的,放进右左子。
while (!st.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = st.top(); // 中
st.pop();
result.push_back(node->val);
if (node->right) st.push(node->right); // 右(空节点不入栈)
if (node->left) st.push(node->left); // 左(空节点不入栈)
}6.2.2 后续遍历(迭代法)
中左右,然后把数组里
翻转一下即可。
6.2.3 中序遍历(迭代法)。
方法:一直走左面,把左面所有的结点都入栈。然后挨个访问,再访问它的右子即可。
class Solution {
public:
vector inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector result;
stack st;
TreeNode* cur = root;
while (cur != NULL || !st.empty()) {
if (cur != NULL) { // 指针来访问节点,访问到最底层
st.push(cur); // 将访问的节点放进栈
cur = cur->left; // 左
} else {
cur = st.top(); // 从栈里弹出的数据,就是要处理的数据(放进result数组里的数据)
st.pop();
result.push_back(cur->val); // 中
cur = cur->right; // 右
}
}
return result;
}
}; 6.3 二叉树的层次遍历(从上往下遍历)
老思路:拿个队列做辅助。
class Solution {
//双层嵌套,后面的也得加上泛型。
List> result=new ArrayList>();
public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
check(root);
return result;
}
void check(TreeNode node){
//BFS,一个队列即可。
if(node==null){
return;
}
//队列里装的是结点,因为还要访问它的儿子们。
Queue que=new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(node);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
List floor=new ArrayList<>();
int len=que.size();//len记录这一层的个数。
while(len>0){
TreeNode temp=que.poll();
floor.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left!=null) que.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right!=null) que.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
result.add(floor);//把这层的加进去。
}
}
} 6.4 二叉树的层次遍历(从下往上遍历)
思路很容易,
//我们已经换成LinkedList,它实现了List接口。双向队列。
//每次都往头塞,每次往头塞。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
LinkedList> result=new LinkedList<>();
//我们已经换成LinkedList,它实现了List接口。双向队列。
public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
check01(root);
return result;
}
void check01(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return ;
}
Queue que=new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(node);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
List list=new ArrayList<>();
int len=que.size();
while(len>0){
TreeNode temp =que.poll();
list.add(temp.val);
if(temp.left!=null) que.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right!=null) que.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
//每次都往头塞
result.addFirst(list);
}
}
} 6.5 二叉树的右视图
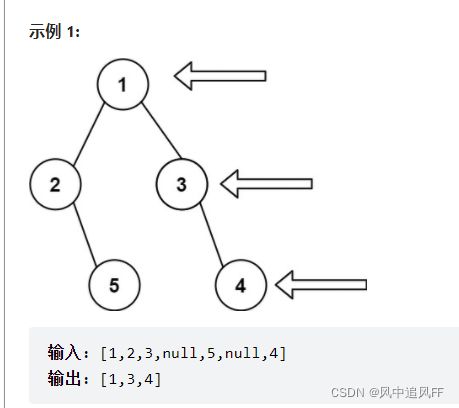
只看二叉树的右边。
思路:使用层次遍历,每次保存这一层的最后一个结点即可。
最后一个,就是len等于1的时候。
class Solution {
List result=new ArrayList<>();
public List rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
check(root);
return result;
}
void check(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return;
}
Queue que=new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(node);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int len=que.size();
while(len>0){
TreeNode temp=que.poll();
if(len==1){
result.add(temp.val);
}
if(temp.left!=null) que.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right!=null) que.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
}
}
} 6.6 二叉树的层平均值
每层while结束后,求一下,放进result即可。
6.7遍历N叉树
不同之处,node的数据结构里,有孩子的数组。
6.8 在每个树行中找最大值。
这里让max等于peek的值。提前读入下一行,第一个的值,以免下一行只有一个。
6.9 填充每个结点的下一个指针,让它指向它的右边。
数据结构多了个next指针。层次遍历即可。
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
check(root);
return root;
}
void check(Node node){
if(node==null){
return;
}
Queue que=new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(node);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int len=que.size();
while(len>0){
Node temp=que.poll();
if(len==1){
temp.next=null;
}else{
temp.next=que.peek();
}
if(temp.left!=null) que.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right!=null) que.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
}
}
} 6.10 二叉树的最小深度
思路:发现这个结点没有子的时候,立马记下这个层数与最小的比较。
1.层次遍历做法:
class Solution {
int min=0;
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
return check(root);
}
int check(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
Queue que=new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(node);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
min+=1;
int len=que.size();
while(len>0){
TreeNode temp=que.poll();
if(temp.left==null&&temp.right==null) return min;
if(temp.left!=null) que.offer(temp.left);
if(temp.right!=null) que.offer(temp.right);
len--;
}
}
return min;//如果是一趟斜着下来的,就只能最后返回min。
}
} 2. 递归尽量别用,处理大数据,对空间要求大。
6.11 交换左右子树
思路:返回值为root。
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}
TreeNode temp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=temp;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}6.12 对称二叉树
看看是不是对称的,我们可以比较一下
左子树的右子树是否等于右子树的左子树 以及右子树是否等于左子树。
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
} else if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
} else if (p.val != q.val) {
return false;
} else {
return isSameTree(p.left, q.right) && isSameTree(p.right, q.left);
}
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isSameTree(root.left,root.right);
}6.13 完全二叉树的结点个数
层次遍历的同时,统计一下个数。
6.14 平衡二叉树的判定
class Solution {
//先判断根结点平衡不,再去判断俩子结点是否平衡。
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
int left=getHigh(root.left);
int right=getHigh(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left-right)>1) return false;
return isBalanced(root.left)&&isBalanced(root.right);
}
public int getHigh(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int a=getHigh(root.left);
int b=getHigh(root.right);
return a>b?a+1:b+1;
}
}6.15 访问到所有叶子结点的路径
list集合的remove方法可以删除指定地方的数据。这题可以用栈来回溯。
用到栈里的局部变量:如果局部变量S这一层是1,进入下一层了,我让S+=1;在下一层它是2,
回到这一层它还是1。
本函数里没对这个S进行操作,把String的值作为参数传了过去。String有个特点就是你对他修改他就创建新对象了。
class Solution {
public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List ret = new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return ret;
solve(root, "", ret);
return ret;
}
public void solve(TreeNode root, String cur, List ret){
if(root==null) return;
cur += root.val;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
ret.add(cur);
}else{
solve(root.left, cur+"->", ret);
solve(root.right, cur+"->", ret);
}
}
} 回溯的算法:
class Solution {
List list=new ArrayList<>();
List resulet=new ArrayList<>();
public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
pre(root);
return resulet;
}
void pre(TreeNode node){
if(node!=null){
list.add(node.val);
}else{
return;
}
if(node.left==null&&node.right==null){
int len=list.size();
String a=""+list.get(0);
for(int i=1;i<=len-1;i++){
a+="->";
a+=list.get(i);
}
resulet.add(a);
}
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
//回溯,这里返回上一层之前,去掉栈里的元素。
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return;
}
} 6.16 判断两只二叉树是否相等。
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(q==null&&p!=null){
return false;
}else if(q!=null&&p==null){
return false;
}else if(q==null&&p==null){
return true;
}else{
if(q.val==p.val){
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left)&&isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
}6.17 二叉树的左叶子之和
思路:不能用层次遍历。出现这种情况不好处理。
随便用一个遍历,加上一句判断即可。
class Solution {
int sum=0;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
pre(root);
return sum;
}
void pre(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return ;
}
if(node.left!=null&&node.left.left==null&node.left.right==null){
sum+=node.left.val;
}
pre(node.left);
pre(node.right);
}
}6.18 找到树,最左下角的值
层次遍历找到最后一层第一个。
6.19 是否存在路径之和等于目标值
需要一个辅助栈。
题目:给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,所有到叶子结点的这条路径上的结点和,如果等于target,那么返回true,否则为false。
思路:回溯,找到所有到叶子结点的路径,然后与target比较。
class Solution {
List list =new ArrayList<>();//用栈放自己到过的路径。
Boolean flag=false;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
pre(root,targetSum);
return flag;
}
void pre(TreeNode root,int targetSum){
if(root!=null){
list.add(root.val);
}else{
return ;
}
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
int sum=0;
for(int num:list){
sum+=num;
}
if(sum==targetSum){
flag=true;
}
}
pre(root.left,targetSum);
pre(root.right,targetSum);
//这里回溯。
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return ;
}
} 6.20 路径之和等于目标值的全部路径
用6.19里的栈回溯,如果碰到目标值,就把这个路径添加。
class Solution {
List list =new ArrayList<>();
List> result=new ArrayList>();
public List> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
pre(root,targetSum);
return result;
}
void pre(TreeNode root,int targetSum){
if(root!=null){
list.add(root.val);
}else{
return ;
}
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
int sum=0;
List list1 =new ArrayList<>();
for(int num:list){
sum+=num;
list1.add(num);
}
if(sum==targetSum){
result.add(list1);
}
}
pre(root.left,targetSum);
pre(root.right,targetSum);
//这里回溯。
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return ;
}
} 6.21 用中序遍历结果和后序遍历结果构造二叉树。
找到分割区间,然后将整个序列分成左右子树,分别创建全新数组传进去。
然后递归建立。
步骤:找到根,建立结点,然后递归左右子树,然后返回根节点。
用Arrays.copyOfRange,可以拷贝【),数组,建立一个新数组。
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
int len_in=inorder.length;
int len_out=postorder.length;
if(len_in==0||len_out==0){//如果有一个空了,返回null。
return null;
}
int index=0;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[len_out-1]);
for(int i=0;i6.22 从前序与中序遍历构造二叉树
判断条件,有一个长度为0,返回null。注意代码里参数传递的顺序。
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int len_pre=preorder.length;
int len_in=inorder.length;
if(len_pre==0||len_in==0){//如果有一个空了,返回null。
return null;
}
int index=0;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[0]);
for(int i=0;i6.23 最大二叉树
思路:找到最大的index和最大值,建立根节点。然后左边剩下的数组递归建左子树,右边剩下的数组递归建立右子树。
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0){
return null;
}
if(nums.length==1){
return new TreeNode(nums[0]);
}
int max=0;
int maxIndex=0;
for(int i=0;i6.24 合并二叉树
递归这两个树,用它们的值。建一个新二叉树。
注意:有空时,还得继续往下走。
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
//挨个遍历即可。
//新建一个子树。
TreeNode t=null;
if(root1==null&&root2!=null){
t=new TreeNode(root2.val);
//这里要记住,还得继续往下走,谁空。谁的子树传空。
t.left=mergeTrees(null,root2.left);
t.right=mergeTrees(null,root2.right);
}else if(root1!=null&&root2==null){
t=new TreeNode(root1.val);
t.left=mergeTrees(root1.left,null);
t.right=mergeTrees(root1.right,null);
}else if(root1==null&&root2==null){
return null;
}else{
t=new TreeNode(root2.val+root1.val);
t.left=mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
t.right=mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
}
return t;
}
}6.25 验证是不是二叉搜索树(二叉排序树)
二叉搜索树,左子小于它右子大于他。
题目1:查找target结点,无脑先序遍历即可。
题目2:验证是不是二叉搜索树。思路:中序遍历即可。中序遍历二叉排序树的序列,生成一个数组。如果是二叉排序树,则数组里装的遍历结果是有序的。
中序遍历之前得判断是不是空。
题目2:代码
class Solution {
List list=new ArrayList<>();
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
in(root);
for(int i=0;i=list.get(i+1)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public void in(TreeNode root){
if(root.left!=null)
in(root.left);
if(root==null){
return ;
}else{
list.add(root.val);
}
if(root.right!=null)
in (root.right);
}
} 6.26 二叉搜索树的最小差值。
思路:中序遍历即可。中序遍历二叉排序树的序列,生成一个数组。如果是二叉排序树,则数组里装的遍历结果是有序的。然后我们挨个比较相邻两个结点,找出最小差值。
class Solution {
List list=new ArrayList<>();
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
in(root);
int min=list.get(list.size()-1)-list.get(0);
//初始值设为最大相差值。
for(int i=0;i 6.27 二叉搜索树中的众数
中序遍历,然后找众数即可。相同的数,肯定是相邻的。
用map记录出现的次数,在map里找到最大,然后把它们都装进数组。
class Solution {
Map map=new HashMap<>();
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
in(root);
//遍历map
int max=1;
Set> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry thisSet : entrySet) {
if(thisSet.getValue()>max){
max=thisSet.getValue();
}
}
int index=0;
List list=new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry thisSet : entrySet) {
if(thisSet.getValue()==max){
list.add(thisSet.getKey());
}
}
int[] result=new int[list.size()];
for(int num:list){
result[index++]=num;
}
return result;
}
public void in(TreeNode root){
if(root.left!=null)
in(root.left);
if(root==null){
return ;
}else{
if(!map.containsKey(root.val)){
map.put(root.val,1);
}else{
int a=map.get(root.val);
map.put(root.val,a+1);
}
}
if(root.right!=null)
in (root.right);
}
} 6.28 二叉树中最近的公共祖先。
用栈,当找到该点时,把结果添加到list里。然后在两个list里,从后往前寻找,第一个公共祖先是最近的。
class Solution {
//整两个栈,栈里都是的祖先。
List list1=new ArrayList<>();
List list2=new ArrayList<>();
Deque que=new LinkedList<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
preFind1(root,p);
preFind2(root,q);
int i1=list1.size();
int i2=list2.size();
TreeNode a=null;
//从后往前找,第一个就是最近的
for(int i=i1-1;i>=0;i--){
a=list1.get(i);
if(list2.contains(a)){
return a;
}
}
return a;
}
void preFind1(TreeNode root, TreeNode p){
if(root==null){
return;
}else{
que.offer(root);
if(root==p){
while(!que.isEmpty()){
list1.add(que.poll());
}
}
}
preFind1(root.left,p);
preFind1(root.right,p);
que.pollLast();//必须得从尾部出去,模拟栈。
}
void preFind2(TreeNode root, TreeNode p){
if(root==null){
return;
}else{
que.offer(root);
if(root==p){
while(!que.isEmpty()){
list2.add(que.poll());
}
}
}
preFind2(root.left,p);
preFind2(root.right,p);
que.pollLast();//必须得从尾部出去,模拟栈。
}
} 6.29 二叉排序树中最近的公共祖先。
思路:上到下遍历的时候,cur节点是数值在[p, q]区间中则说明该节点cur就是最近公共祖先了。
class Solution {
TreeNode t=null;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p.val=val1&&root.val<=val2){
if(t==null){//这里t只需要记录第一个出现在区间里的即可,因为我们从上到下遍历。
t=root;
}
}
}
pre(root.left,val1,val2);
pre(root.right,val1,val2);
}
} 6.30. 二叉排序树中插入。
步骤:只要遍历二叉搜索树,找到空节点 插入元素就可以了,那么这道题其实就简单了。
遍历规则:如果比当前结点大,走右边,如果比当前结点小,走左边。
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null){
return new TreeNode(val);
}
if(root.val6.31 删除二叉排序树中的结点(有结点变动的,返回值都得是TreeNode)。
情况1:没找到删除的结点,遍历到空直接返回了。
情况2:删除的结点,为叶子结点,直接删除该结点,返回null给根节点即可。
情况3:删除的结点,一个孩子空,一个孩子不空,则返回它的孩子作为替补的根结点。
情况4:删除7的过程。
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root==null){
return root;
}
if(root.val==key){
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return null;
}else if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null){
return root.left;
}else if(root.left==null&&root.right!=null){
return root.right;
}else{
//如果两个子树都在,就找到右边的最左,让这个最左的左为root.left。这个时候root.right当根,返回root.right。
TreeNode t=root.right;
while(t.left!=null){
t=t.left;
}
t.left=root.left;
return root.right;
}
}else{
root.left=deleteNode(root.left,key);//因为左子或右子会发生变动,所以这么遍历,类似于建树。
root.right=deleteNode(root.right,key);
return root;
}
}
}7 树
7.1 修建二叉排序树
给了一个区间[a,b],确保树上所有的结点都在这个区间,如果不在,就移除这个结点,同时保持二叉排序树的有序性。
思路:遍历二叉树上的结点呗,如果不在这个区间就用 。6.31章的删除算法,需要改动的地方,
找到不在这个区间的点了还不算完,继续往子树里找。
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root==null){
return root;
}
if(root.valhigh){
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return null;
}else if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null){
// //删除了还不算完,还得往下再找,子树里可能出现。
root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
return root.left;
}else if(root.left==null&&root.right!=null){
//删除了还不算完,还得往下再找,子树里可能出现。
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root.right;
}else{
//如果两个子树都在,就找到右边的最左,让这个最左的左为root.left。这个时候root.right当根,返回root.right。
TreeNode t=root.right;
while(t.left!=null){
t=t.left;
}
t.left=root.left;
//删除了还不算完,还得往下再找,子树里可能出现。
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root.right;
}
}else{
root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);//因为左子或右子会发生变动,所以这么遍历,类似于建树。
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root;
}
}
} 7.2 往二叉排序树树里插入结点
TreeNode insert(TreeNode root,int val){
//如果是叶子结点。
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
if(root.val7.3 将有序数组转换为二叉排序树「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」
思路:自己规定根结点,分割数组为左右子树。然后用这些数组建立二叉排序树。
给他们分好区,每到一层,选中间的为根结点,建立。
class Solution {
//有序数组已经给咱们排好序了。取数组中间的作为根结点,就普通建个树就完事。
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return nums==null?null : build(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
//这个建树方法牛逼了。
TreeNode build(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right){
return null;
}
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;//找到中间点的坐标,用它来建。
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=build(nums,left,mid-1);
root.right=build(nums,mid+1,right);
return root;
}
}7.4 把二叉排序树转换为累加树。
题目:从最右边开始加,7的15,是上一个结点的8。
就是一个中序遍历的对称版,改一下遍历的顺序即可。
class Solution {
int sum=0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return root;
}
travel(root);
return root;
}
void travel(TreeNode root){
if(root.right!=null)//改变一下遍历顺序,这里先right
travel(root.right);
sum+=root.val;
root.val=sum;
if(root.left!=null)
travel(root.left);
}
}