SELinux 学习总结
-
- SELinux 学习
- 1 什么是SELinux
- 2 SELinux的运行模式
- 3 SELinux的启动关闭与查看
- 4 SELinux的策略与规则管理
- 小结
- SEAndroid 学习
- 1 SEAndroid各种资源定义
- 2 SEAndroid类型规则
- 3 SEAndroidwen文件全上下文
- 4 SEAndroidwen进程全上下文
- 5 SEAndroid常用命令
- 小结
- 总结
- SELinux 学习
1 SELinux 学习
1.1 什么是SELinux
SElinux,它的全称是”Securiry Enhanced Linux”,其字面的意思是安全强化的Linux之意。SELinux 是典型的MAC实现, 对系统中每个对象都生成一个安全上下文(Security Context), 每一个对象访问系统的资源都要进行安全上下文审查。审查的规则包括类型强制检测(type enforcement), 多层安全审查(Multi-Level Security), 以及基于角色的访问控制(RBAC: Role Based Access Control)。
1.2 SELinux的运行模式
SELinux是通过MAC(Mandatory Access Control)方式来控管进程,它控制的主体是进程,而目标则是该进程能否读取的”文件资源”。
- 主体
- SELinux 主要是想管理控制进程。
- 目标
- 主体进程能否访问的”目标资源”一般是文件系统。
- 策略
- 因为进程和文件的数量庞大,因此 SELiunx会根据某些服务来制定基本的访问安全性策略。这些策略内部还有详细的规则来指定不同的服务开放某些资源的访问与否。
- targeted :针对网络服务限制较多,针对本机限制较少,是默认的策略;
- strict: 完整的SELinux限制,限制方面较为严格。
安全上下文
安全上下文由4部分组成,其格式为user:role:type [level],其中
user:为指定用户,有3中类型。- user_u:代表普通用户,权限限制。
- system_u:代表系统及别的进程。
- root :代表root用户。
role:指定的角色,有2种类型。
- object_r:代表文件。
- r :代表进程。
type:定义主题和客体所属的类型,有2各种类型。
- 如果role是文件,则它称为type。
- 如果role是进程,则它称为domain。
level:可选项,定义的安全级别,可能的值是s0-s15。
通过命令ls-Z可以查看文件的安全上下文,具体如下图所示。

如图片中的u:object_r:rootfs:s0 boot.ver,u表示表示手机的唯一用户,object_r表示boot.ver是文件,rootfs是文件boot.ver的type,s0为安全级别。
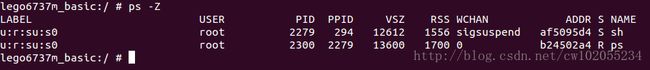
通过命令ps-Z可以查看进程的安全上下文,具体如下图所示。
1.3 SELinux的启动关闭与查看
SELinux的状态可以通过命令getenforce查看,具体效果如图所示:
![]()
如果是开启状态,则会显示Enforcing/Permissing,在中途需要改变SELinux的状态,可通过命令setenforce
Selinux支持3种状态,分别是:
- Enforcing:强制模式,表示Selinux正在运行中,且已按照正确规则进行限制;
- Permissing: 宽容模式,表示Selinux正在运行中,会有警告信息但并不限制domain/type的访问。
- Disable: 关闭,表示Selinux没有运行。
1.4 SELinux的策略与规则管理
selinux规定一个主体是否可以对一个客体资源的访问,其格式如下:
allow [source_type] [target_type] :[class] {permission}
- source_type(源类型):代表主体,常指某种属性为domain的类型
- target_type(目标类型):代表客体所属的某种类型
- class(客体类别):可以访问客体的类型,例如 File、Dir、socket等
- permission(访问许可):主体对客体可以进行何种操作
除了allow这访问规则外,还有 auditallow、ontaudit和neverallow
- allow 允许主体对客体执行某种操作。
- auditallow 含义就是记录某项操作。默认SELinux 只记录那些权限检查失败的操作。auditallow则使得权限检查成功的操作也被记录。注意,allowaudit 只是允许记录,它和赋予权限没关系。必须且只能使用allow语句。
- dontaudit :对那些权限检查失败的操作不做记录。
- neverallow:没有被allow到的动作默认就不允许执行的。neverallow只是显式地写出某个动作不被允许,如果添加了该的allow,则会编译错误。neverallow语句的作用只是在生成安全策略文件时进行检查,判断否有违反neverallow语句的语句。
小结
主要认识下linux的selinux方面的知识,全当入门,相关的细节可在网上搜索,能看到比较全面的概括。
2 SEAndroid 学习
SEAndroid从某种意义上来讲就是将SElinux移植到android项目中。它主要由2部分组成:
- 内核中的Selinux安全模块,位于
kernel-3.18/security/selinux/目录中 - selinux的策略文件,用来帮助用户设置进程的访问规则,用户可在
device/mediatek/common/sepolicy目录下添加对应的访问策略来改变平台的Selinux规则。在该目录中有如下几个相关文件:
- file_contexts: 保存的是系统中文件相关的安全上下文
- property_contexts:保存的是系统中属性相关的安全上下文
- seapp_contexts:保存的是系统中属性相关的安全上下文
- sepolicy:保存的是系统策略
2.1 SEAndroid各种资源定义
在/external/sepolicy目录中存放了很多SElinux的策略定义文件,在它当中定义了许多基本的类型。
1. 角色定义
在文件external/sepolicy/roles中定义了Selinux的角色,具体如下:
role r;
role r types domain;在android系统中只存在这一种角色。
2. 用户定义
在文件external/sepolicy/users中定义了Selinux的角色,具体如下:
user u roles { r } level s0 range s0 - mls_systemhigh;同样Selinux中只定义了一种u
3. 定义属性
在文件external/sepolicy/attributes中定义了Selinux的属性,具体如下:
######################################
# Attribute declarations
#
# All types used for devices.
attribute dev_type;
# All types used for processes.
attribute domain;
# All types used for filesystems.
attribute fs_type;
# All types used for context= mounts.
attribute contextmount_type;
# All types used for files that can exist on a labeled fs.
# Do not use for pseudo file types.
attribute file_type;
# All types used for domain entry points.
attribute exec_type;
# All types used for /data files.
attribute data_file_type;
# All types use for sysfs files.
attribute sysfs_type;
# Attribute used for all sdcards
attribute sdcard_type;
# All types used for nodes/hosts.
attribute node_type;
# All types used for network interfaces.
attribute netif_type;
# All types used for network ports.
attribute port_type;
# All types used for property service
attribute property_type;
# All service_manager types created by system_server
attribute system_server_service;
# services which should be available to all but isolated apps
attribute app_api_service;
# services which export only system_api
attribute system_api_service;
# All types used for services managed by service_manager.
attribute service_manager_type;
# All domains that can override MLS restrictions.
# i.e. processes that can read up and write down.
attribute mlstrustedsubject;
# All types that can override MLS restrictions.
# i.e. files that can be read by lower and written by higher
attribute mlstrustedobject;
# All domains used for apps.
attribute appdomain;
# All domains used for apps with network access.
attribute netdomain;
# All domains used for apps with bluetooth access.
attribute bluetoothdomain;
# All domains used for binder service domains.
attribute binderservicedomain;通过注释,很容易就能理解各个类型的定义具体表示什么意思。
4. Class定义
在文件external/sepolicy/security_classes中定义了Selinux中客体会用的到所有限制类别,通过它可以将客体限制到一个更小的范围,具体如下:
# FLASK
#
# Define the security object classes
#
# Classes marked as userspace are classes
# for userspace object managers
class security
class process
class system
class capability
# file-related classes
class filesystem
class file
class dir
class fd
class lnk_file
class chr_file
class blk_file
class sock_file
class fifo_file
# network-related classes
class socket
class tcp_socket
class udp_socket
class rawip_socket
class node
class netif
class netlink_socket
class packet_socket
class key_socket
class unix_stream_socket
class unix_dgram_socket
# sysv-ipc-related classes
class sem
class msg
class msgq
class shm
class ipc
#
# userspace object manager classes
#
# passwd/chfn/chsh
class passwd # userspace
# SE-X Windows stuff (more classes below)
class x_drawable # userspace
class x_screen # userspace
class x_gc # userspace
class x_font # userspace
class x_colormap # userspace
class x_property # userspace
class x_selection # userspace
class x_cursor # userspace
class x_client # userspace
class x_device # userspace
class x_server # userspace
class x_extension # userspace
# extended netlink sockets
class netlink_route_socket
class netlink_firewall_socket
class netlink_tcpdiag_socket
class netlink_nflog_socket
class netlink_xfrm_socket
class netlink_selinux_socket
class netlink_audit_socket
class netlink_ip6fw_socket
class netlink_dnrt_socket
class dbus # userspace
class nscd # userspace
# IPSec association
class association
# Updated Netlink class for KOBJECT_UEVENT family.
class netlink_kobject_uevent_socket
class appletalk_socket
class packet
# Kernel access key retention
class key
class context # userspace
class dccp_socket
class memprotect
class db_database # userspace
class db_table # userspace
class db_procedure # userspace
class db_column # userspace
class db_tuple # userspace
class db_blob # userspace
# network peer labels
class peer
# Capabilities >= 32
class capability2
# More SE-X Windows stuff
class x_resource # userspace
class x_event # userspace
class x_synthetic_event # userspace
class x_application_data # userspace
# kernel services that need to override task security, e.g. cachefiles
class kernel_service
class tun_socket
# Still More SE-X Windows stuff
class x_pointer # userspace
class x_keyboard # userspace
# More Database stuff
class db_schema # userspace
class db_view # userspace
class db_sequence # userspace
class db_language # userspace
class binder
# Property service
class property_service # userspace
# Service manager
class service_manager # userspace
# Keystore Key
class keystore_key # userspace
# debuggerd service
class debuggerd # userspace
class drmservice # userspace
# FLASKaccess_vectors定义
在文件external/sepolicy/access_vectors中定义了Selinux中所有对Class可以允许操作,主要分为2种定义方式,- common: 这种方式定义的是一种公共操作,对所有的客体都可以使用,且可以被继承
- class:这种方式定义操作只适用于特定限制类别,可以继承common语句中的定义操作
部分定义具体如下所示:
#
# Define common prefixes for access vectors
#
# common common_name { permission_name ... }
#
# Define a common prefix for file access vectors.
#
common file
{
ioctl
read
write
create
getattr
setattr
lock
relabelfrom
relabelto
append
unlink
link
rename
execute
swapon
quotaon
mounton
}
#
# Define the access vectors.
#
# class class_name [ inherits common_name ] { permission_name ... }
#
# Define the access vector interpretation for file-related objects.
#
class filesystem
{
mount
remount
unmount
getattr
relabelfrom
relabelto
transition
associate
quotamod
quotaget
}- 类型强制规则定义
类型强制规则定义文件都以.te结尾,通过它来设定具体的访问策略,如external/sepolicy/bootanim.te,它规定了bootanim进程对资源的访问策略
# bootanimation oneshot service
type bootanim, domain;
type bootanim_exec, exec_type, file_type;
init_daemon_domain(bootanim)
binder_use(bootanim)
binder_call(bootanim, surfaceflinger)
allow bootanim gpu_device:chr_file rw_file_perms;
# /oem access
allow bootanim oemfs:dir search;
allow bootanim oemfs:file r_file_perms;
allow bootanim audio_device:dir r_dir_perms;
allow bootanim audio_device:chr_file rw_file_perms;
allow bootanim surfaceflinger_service:service_manager find;2.2 SEAndroid类型规则
类型规则是在创建客体或在运行过程中重新标记并指定其默认类型,它仅提供一个新的默认类型标记。在策略语言中定义了两个类型规则:
- type_transition:在域转换过程中标记行为发生时以及创建客体时,指定其默认
的类型。 type_change:使用 SELinux 的应用程序执行标记时指定其默认类型。
我们叫这些规则为”类型规则”,因为它们与 AV 规则类似,除了规则的末尾是一个类型名而不是许可集外。类型规则的基本语法是:
[规则名称] [源类型集] [目标类型集]:[类别集] [单个默认类型];- 规则名称:有效的规则名称有 type_transition,type_change 和 type_membe。
- 源类型:创建或拥有进程的类型。
目标类型:包含新的或重新标记的客体的客体类型,在规则中源和目标类型有其独立的类型集,多个类型和属性使用空格进行分隔,并用大括号将它们括起来,如{bin_t sbin_t},可以在类型名前放一个(-)符合将其排除,如{exec_type –sbin_t}
类别集:新创建的或重新标记的客体的类别。类别集是一个或多个客体类别,多个客体类别必须使用大括号括起来,并用空格分开,如{file lnk_file}。
- 默认类型:为新创建的或重新标记的客体类别指定的单个默认类型,这里不能使用属性和多个类型。
如:
type_transition shell su_exec:process su;
当属于shell domain的进程执行文件type为su_exec的时候,会尝试的将新进程转化为su类型的domain。
2.3 SEAndroidwen文件全上下文
SEAndroid 是一种基于安全策略的 MAC 安全机制。这种安全策略实施在主体和客体的安全上下文之上。这意味着安全策略在实施之前,SEAndroid 安全机制中的主休和客体是已经有安全上下文的。在 SEAndroid 安全机制中,主体一般就是进程,而客体一般就是文件。
文件的全上下文产生方式主要分为两种,一种是预置在 ROM 里面的,另外一种是动态创建的,即在系统在运行的过程中创建的。
- 对于预置在ROM里面的文件,它们的安全上下文在是制作ROM的过程中设置的,以system.img文件为例,在打包的时候会使用到一个叫 file_contexts.bin的文件,该文件在编译最开始的时候会收集所有的 file_contexts 文件,经过编译后,就会保存在$OUT/root 目录中。在打包system.img文件的时候根据file_contexts.bin设置的规则给文件关联安全上下文,这样就获得了一个关联有安全上下文的 system.img 镜像文件了。
2.4 SEAndroidwen进程全上下文
在 SEAndroid 中,除了要给文件关联安全上下文外,还需要给进程关联安全上下文,因为只有当进程和文件都关联安全上下文之后,SEAndroid 安全策略才能发挥作用。当一个进程试图访问一个文件时,SEAndroid 会将进程和文件的安全上下文提取出来,根据安全策略规则,决定是否允许访问。
2.5 SEAndroid常用命令
getenforce和setenforce
如前面总结的,getenforce 命令用来返回系统当前处于enforcing状态还是permissing状态。setenforce用来切换系统的enforcing状态和permissing状态chcon命令
chcon命令用来改变文件或目录的安全上下文,如:
chcon example_t a.txtrestorecon命令
restorecon用来恢复文件或者目录的安全上下文为系统原始的设置。
小结
SEAndroid继承了Linux中的安全策略,并加入了自身的一些特性,Android 4.3 之前,应用程序安装时为每一个应用程序创建一个独立的 uid,基于 uid 来控制进程权限,即 DAC 机制。Android 5.0(L)之后,普遍性开启 SELinux Enforce mode。除了 init 进程,其他进程都不应该在 init 域中。
总结
本文主要是对SEAndroid进行一个简单的总结,参考老罗的《Android 系统源代码情景分析》和《深入android5.0系统》,以便在工作中对如何设置系统的SEAndroid有一个初步的认识,对于SEAndroid在系统源码中的实现并没涉猎。