模拟实现string类——【C++】
W...Y的主页
代码仓库分享
前言:
我们已经将STL中的string类重要接口全部认识并熟练掌握,为了让我们对string与C++类与对象更深层次的了解,我们这篇博客将string类进行模拟实现。
目录
string类的模拟实现
构造函数与析构函数
拷贝构造函数
其余string类对象接口模拟实现
string类的模拟实现
我们第一步就是区分自己模拟实现的string与STL中的string的区别,所以我们得实用命名域进行区分。然后就是私有成员的设定,string的底层就是一个数组,所以我们得创建一个字符指针,还有两个变量分别是_size检测数组中内容的大小,与_capacity检测数组的空间大小的,与顺序表的数据是相同的。
构造函数与析构函数
这两个函数是非常关键的,承载了整个string类,string的初始化与销毁都是依靠与这两个函数。
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size == 0 ? 4 : _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}因为我们知道在STL提供的构造函数中既可以传参也可以不传参进行初始化,所以我们也使用这种初始化类型,当我们没有进行传参数时,默认创建一个空字符串。当我们传参后,我们创建的构造函数默认开辟传入字符串大小的参数,反之开辟大小为4bit的空间。如果我们选择在不传参数时不开辟空间大小,在后面的函数中会起冲突。
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}析构函数就非常简单,将开辟的空间进行释放,最后将_size与_capacity进行制空即可。
拷贝构造函数
针对拷贝构造函数,我们已经不能使用C++默认生成的拷贝构造函数了,因为数据类型已经不是简单的内置类型,里面有我们开辟的空间,如果使用浅拷贝就会在析构函数中释放两次相同的空间导致程序崩溃。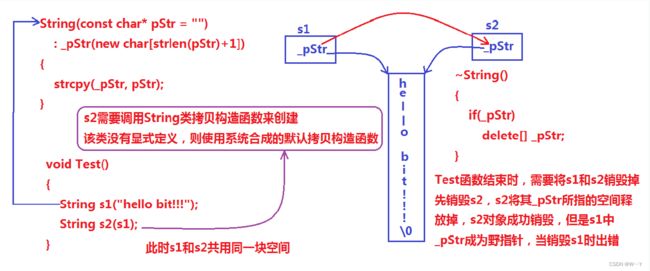
如果一个类中涉及到资源的管理,其拷贝构造函数、赋值运算符重载以及析构函数必须要显式给出。一般情况都是按照深拷贝方式提供。
使用深拷贝使每个对象都有一份独立的资源,不要和其他对象共享 。
string(const string& s)
:_size(s._size)
, _capacity(s._capacity)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}其余string类对象接口模拟实现
在string的模拟实现中,我们有许多类似接口可以实现,在这里我想说针对模拟实现时,我们可以使用复用已经C库中的各种函数来简单实现,并不需要进行大规模的写代码,这样可以巩固我们对函数的使用。
以下是string类函数的模拟实现完整代码:
string.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace why
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return _str + _size;
}
typedef const char* const_iterator;
iterator begin()const
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()const
{
return _str + _size;
}
/*string()
:_str(new char[1])
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{
_str[0] = '\0';
}*/
string(const char* str = "")
:_size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size == 0 ? 4 : _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
const char* c_str()
{
return _str;
}
char& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& operator[](size_t pos)const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity()const
{
return _capacity;
}
~string()
{
delete[] _str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
//拷贝构造
string(const string& s)
:_size(s._size)
, _capacity(s._capacity)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
/*delete[] _str;
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, s._str);*/
//防止new开辟空间失败导致原数据被释放
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
_str = tmp;
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const string& s)const
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0;
}
bool operator>(const string& s)const
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) > 0;
}
bool operator<(const string& s)const
{
return !(*this > s || *this == s);
}
bool operator<=(const string& s)const
{
return *this == s || *this < s;
}
bool operator>=(const string& s)const
{
return *this == s || *this > s;
}
bool operator!=(const string& s)const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (_capacity < n)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[] _str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity * 2);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
_size++;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void append(const char* s)
{
size_t len = sizeof(s);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, s);
_size += len;
}
string& operator+=(char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* s)
{
append(s);
return *this;
}
void resize(size_t n, char ch = '\0')
{
if (n < _size)
{
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
size_t i = _size;
while (i < n)
{
_str[i] = ch;
}
_size = n;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
void insert(size_t pos, char x)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)
{
reserve(2 * _capacity);
}
size_t _end = _size + 1;
while (_end > pos)
{
_str[_end] = _str[_end - 1];
_end--;
}
_str[pos] = x;
_size++;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* s)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(s);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len );
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos + len - 1)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
--end;
}
/*size_t i = 0;
while (i < len)
{
_str[pos] = s[i];
pos++;
i++;
}*/
strncpy(_str+pos, s, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || pos + len >= _size)
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
void swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
}
size_t find(char ch, size_t pos = 0)
{
assert(pos < _size);
for (size_t i = pos; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == ch)
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0)
{
assert(pos < _size);
// kmp
char* p = strstr(_str + pos, str);
if (p == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return p - _str;
}
}
void clear()
{
_str[0] = '\0';
_size = 0;
}
private:
char* _str;
size_t _size;
size_t _capacity;
static const size_t npos;
//static const size_t npos = -1;
};
const size_t string::npos = -1;
void print(const string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i] << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void test1()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
std::cout << s1.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << s2.c_str() << std::endl;
s2[0]++;
std::cout << s2.c_str() << std::endl;
}
void test2()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello world");
string s3(s2);
std::cout << s2.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << s3.c_str() << std::endl;
s2[0]++;
std::cout << s2.c_str() << std::endl;
std::cout << s3.c_str() << std::endl;
s1 = s3;
std::cout << s1.c_str() << std::endl;
}
void test3()
{
string s1("hello world");
print(s1);
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << ' ';
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s1)
{
cout << ch << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void test4()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello world");
string s3("wwwwwww");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 != s2) << endl;
cout << (s1 > s2) << endl;
}
void test5()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
string s2 = "xxxxxxxxxx";
s1.append("xxxxxxxx");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1 += 'c';
s2 += "yyyyyyy";
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
cout << s2.c_str() << endl;
string s3;
s3 += "ssssssss";
cout << s3.c_str() << endl;
string s4;
s4 += '1';
cout << s4.c_str() << endl;
}
void test6()
{
string s1("hello worlddddddddddddddd");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.reserve(10);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test7()
{
string s1;
s1.resize(20, 'x');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.resize(30, 'y');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.resize(10);
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
void test8()
{
string s1("xxxxx");
s1.insert(0, 'y');
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
s1.insert(0, "wwwwww");
cout << s1.c_str() << endl;
}
} test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"string.h"
int main()
{
//why::test1();
//why::test2();
//why::test3();
//why::test4();
//why::test5();
//why::test7();
why::test8();
return 0;
}我们在模拟实现时一定要边写边测试,从而将问题进行模块纠正,这样可以以最快的速度完成大量代码。
以上就是本次博客全部内容,感谢大家观看。
