数据结构之队列【超详解】
队列FIFO
- 顺序队列的定义
-
- 队列初始化
- 队列是否为空
- 队尾插入
- 返回队头
- 队头删除
- 双端队列
- 链队列
-
- 单链队列初始化
- 队列初始化
- 销毁队列
- 队尾插入
- 队头删除
- 队列的遍历
- 测试
- 循环队列
-
- 初始化循环队列
- 清空对列
- 判断队列是否为空
- 循环队列的长度
- 获取队头元素
- 队尾插入
- 队头删除
- 队列打印
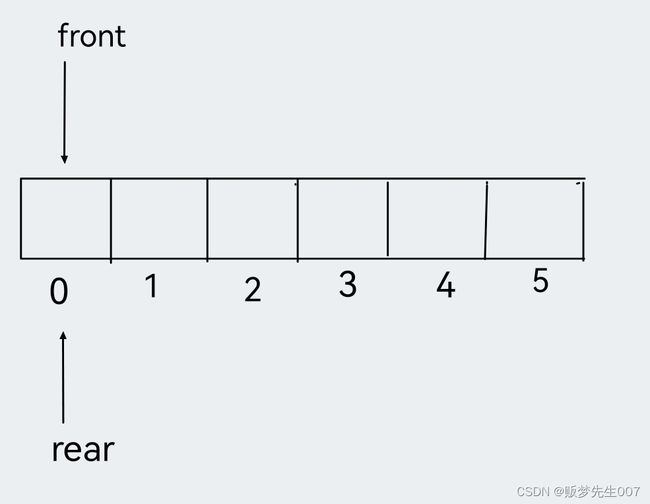
顺序队列的定义
和栈相反,队列是一种先进先出的线性表,它只允许在表的一端进行插入,二在另一端删除元素,允许插入的一端叫队尾,删除元素的一端叫对头
typedef int status;
typedef int qeelemtype;
typedef struct {
qeelemtype data[MAXSIZE];
int front;//队头指针
int rear;//队尾指针
}squeue;
队列初始化
//队列初始化
status initsqueue(squeue *sq){
sq->front = sq->rear = 0;
return OK;
}
队列是否为空
//队列是否为空
status emptysq(squeue *q){
if(q->front == q->rear)
return OK;
else return FALSE;
}
队尾插入
//队尾插入
status insqueue(squeue *q,qeelemtype e){
if((q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE ==q->front)
return ERROR;
q->data[q->rear] = e;
q->rear = (q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
返回队头
//返回对头
status gethead(squeue *q,qeelemtype *e){
if(q->front == q->rear)
return ERROR;
*e = q->data[q->front];
return OK;
}
队头删除
//出队
status dqueue(squeue *q,qeelemtype *e) {
if(q->front == q->rear)
return ERROR;
*e = q->data[q->front];
q->front = (q->front+1)%MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
双端队列
双端队列是限定插入和删除操作在表的两端进行的线性表,但实际的应用却很少
链队列
单链队列初始化
typedef int Status;
typedef int qeelemtype;
typedef struct QNode
{
qeelemtype data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode,*Queueptr;
typedef struct
{
Queueptr front;//队头指针
Queueptr rear;//队尾指针
}LinkQueue;
队列初始化
//队列初始化
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue& Q)
{
Q.front = Q.rear = (Queueptr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!Q.front)exit(-1);
Q.front->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
销毁队列
//销毁队列
Status DestroyQueue(LinkQueue& Q)
{
while (Q.front)
{
Q.rear = Q.front->next;
free(Q.front);
Q.front = Q.rear;
}
return OK;
}
队尾插入
//队尾插入
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue& Q, qeelemtype e)
{
Queueptr p = (Queueptr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!p)exit(-1);
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
Q.rear->next = p;
Q.rear = p;
return OK;
}
队头删除
//队头删除
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue& Q, qeelemtype& e)
{
if (Q.front == Q.rear)return ERROR;
Queueptr p = Q.front->next;
e = p->data;
Q.front->next = p->next;
if (Q.rear == p) Q.rear = Q.front;
free(p);
return OK;
}
队列的遍历
//输入元素↓
int PrintQueue(LinkQueue& Q)
{
QueuePtr p;
printf("链式队列中的元素");
if (Q.front->next != NULL)
{
p = Q.front->next;
do
{
printf("%5d", p->data);
p = p->next;
} while (p != NULL);
}
else
printf("队列为空\n");
printf("\n");
return 0;
}//遍历链式队列
测试
void main()
{
int n, e, i;
LinkQueue Q;
InitQueue(Q);
printf("\n"); printf("\n");
printf("初始化队列成功!");
printf("\n"); printf("\n");
printf("请输入要进队的元素个数:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
printf("请输入要进队的元素:\n");
scanf("%d", &e);
if (EnQueue(Q, e))
printf("元素 %d 进队成功\n", e);
else
printf("进队失败\n");
}
printf("\n");
PrintQueue(Q);
printf("\n"); printf("\n");
printf("删除元素后的队列:\n");
printf("\n");
DeQueue(Q, e);
PrintQueue(Q);
printf("\n"); printf("\n");
}
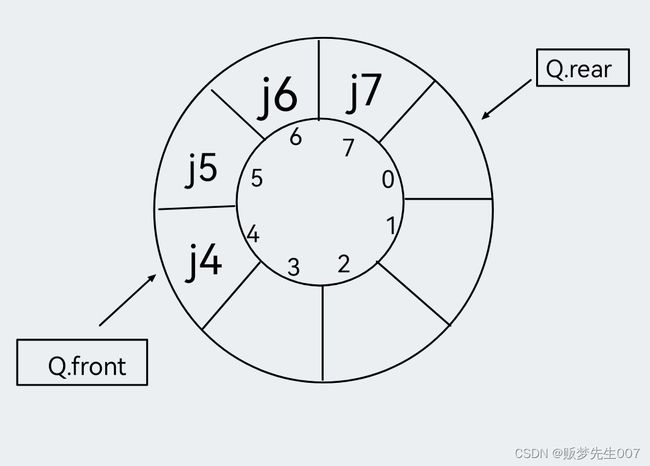
循环队列

当队列处于图d时,不可再继续插入新的队尾元素,否则会因为数组越界导致代码被破坏,如果继续扩大空间的话,就造成了空间的浪费,所以我们将顺序队列假想成如下图一样的环状空间,称之为循环队列
循环队列有头指针和尾指针:
头指针指向对列头部元素,随着对列出队而变化,元素入队时不变化
尾指针指向对列尾部元素,随着对列入队而变化,元素出队时不变化
- 所以我们只需移动指针来控制插入和删除元素
- 遍历的时间复杂度为O(1)
- 插入、删除的时间复杂度为O(1)
初始化循环队列
/*
初始化循环队列
*/
Status InitSeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue)
{
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
return OK;
}
清空对列
/*
清空队列
*/
Status ClearSeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue)
{
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
return OK;
}
判断队列是否为空
/*
判断循环队列是否为空
*/
Status EmptySeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue)
{
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return TRUE;
}
return FALSE;
}
循环队列的长度
/*
循环队列的元素个数
*/
int LengthSeqQueue(SeqQueue* queue)
{
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return 0;
}
//留的那个空单元不算做元素个数
return (queue->rear - queue->front + QUEUESIZE) % QUEUESIZE;
}
获取队头元素
/*
获取循环队列头元素
*/
Status GetHead(SeqQueue* queue)
{
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return ERROR;
}
return queue->data[queue->front];
}
队尾插入
*
往队尾添加元素
*/
Status AddQueue(SeqQueue* queue, EleType e)
{
//队满或空指针
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
//刚好队尾再走一个单元就到队头,说明栈满了。
if ((queue->rear + 1) % QUEUESIZE == queue->front)
{
return ERROR;
}
queue->data[queue->rear] = e;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % QUEUESIZE;//若到队尾转到数组头部
return OK;
}
队头删除
/*
队头删除元素
*/
Status DelQueue(SeqQueue* queue, EleType* e)
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return ERROR;
}
//队空
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return ERROR;
}
*e = queue->data[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % QUEUESIZE;//若到队尾转到数组头部
return OK;
}
队列打印
void PrintfQueue(SeqQueue* queue)
{
//空指针
if (!queue)
{
return;
}
//队空
if (queue->front == queue->rear)
{
return;
}
int begin = queue->front;
while (begin != queue->rear)
{
printf("%d,", queue->data[begin]);
if (begin < QUEUESIZE - 1)
{
begin++;
}
else
{
begin = begin + 1 - QUEUESIZE;
}
}
printf("\n");
return;
}