python 树 数据结构_Python 数据结构 树
什么是树
数是一种抽象的数据类型(ADT)或是作这种抽象数据类型的数据结构,用来模拟具有树状结构性质的数据集合,它是由n(n>1)的有限个节点和节点之间的边组成的一个有层次关系的集合。
树的组成元素:
根节点:树的最上层的节点,任何非空的树都有一个节点
路径:从起始节点到终止节点经历过的路径
父节点:除了根节点,每个节点的上一层边连接的节点就是它的父节点
子节点:每一节点由边指向的下一层节点
兄弟节点:同一父节点且处在同一层的节点
子树:每个节点包含它所有的后代组成的子树
叶子节点:没有子节点的节点,称为叶子节点
树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次
树具有以下的特点:
每个节点有零个或多个子节点;
没有父节点的节点称为根节点;
每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点;
除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树。
树的种类
无序树:树中的任意节点的子节点之间没有顺序关系,也称为自由树。
有序树:树中的任意节点的子节点之间有顺序关系。
二叉树:每个节点最多含有两个子树
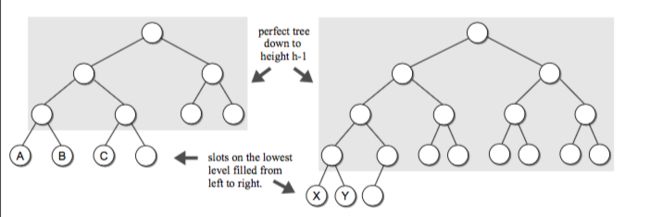
完全二叉树:当一个高度为h的完美二叉树减少到h-1,并且最底层的槽被毫无间隙地从左到右填充,我们就叫它完全二叉树
满二叉树:如果每个内部节点(非叶子节点)都有两个子节点,就成为满二叉树
完美二叉树:当所有的叶子节点都在同一层就是完美二叉树,毫无间隙填充了h层
如下图所示:
满二叉树:
完美二叉树:
完全二叉树:
数的存储和表示
顺序存储:将数据结构存储在固定的数组中,所以在遍历速度上有一定的优势,同时所占用的空间比较大,是非主流二叉树。二叉树通常以链式方式存储:
如下图所示是简单的顺序存储:
链式存储: 结构采用链表存储二叉树中的数据元素,用链表建立二叉树中节点之间关系,二叉树最常用的链式存储结构是二叉链,每个节点包含三个域,分别是数据元素域data,
左还在链域Child和右孩子链域Child,与单链表头结点和不带头节点的两种情况相似,二叉链存储结构的二叉树也有带头节点和不带头结点两种。
树的常用场景
xml,html等,那么编写这些东西的解析器的时候,不可避免用到树
路由协议就是使用了树的算法
mysql数据库索引
文件系统的目录结构
所以很多经典的AI算法其实都是树搜索,此外机器学习中的decision tree也是树结构
二叉树
二叉树的基本概念
二叉树是由n(n>=0)个节点组成的集合,每个节点最多有两个子树的有序树,它或者是空集,或者是一个根和左右子树的两个不相交的二叉树组成。
二叉树的特点:
二叉树是有序树,即使是只有一个子树,也必须区分左右树。
二叉树的每个节点的的度,不能大于2.
二叉树的遍历
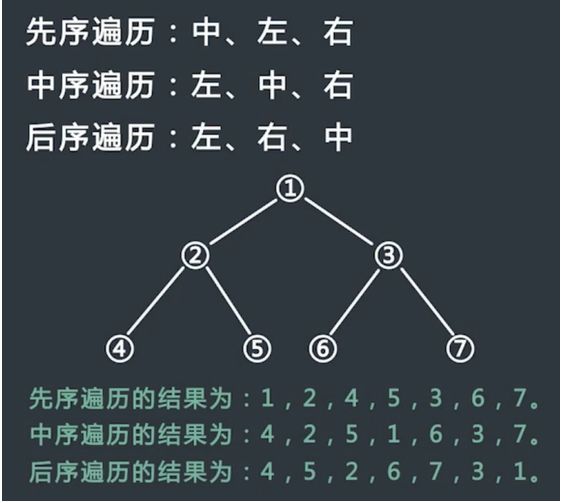
前序遍历:先访问根节点, 然后前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树
中序遍历:中序遍历根节点的左子树,然后再访问根节点,最后遍历右子树
后序遍历:从左到右叶子节点的方式遍历访问左子树,最后访问根节点
层序遍历:从根节点从上往下逐层遍历,在同一层,按从左到右的顺序对节点逐个访问
二叉树实现方式:
#节点定义
classNode(object):def __init__(self, value, left_child, right_child):
self._value=value
self._left_child=left_child
self._right_child=right_child
@propertydefvalue(self):returnself._value
@value.setterdefvalue(self, value):
self._value=self.value
@propertydefleft_child(self):returnself._left_child
@left_child.setterdefleft_child(self, value):
self._left_child=value
@propertydefright_child(self):returnself._right_child
@right_child.setterdefright_child(self, value):
self._right_child=value#树的定义
classTree(object):def __init__(self, value):
self._root=Node(value, None, None)
@propertydefroot(self):return self._root
遍历树的代码实现:以下遍历方式亲测有效
#递归后续遍历
defpre_order(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):return[]
pre_order_tmp=[]if root is notNone:
pre_order_tmp.append(root.value)
pre_order_tmp+=pre_order(root.left_child)
pre_order_tmp+=pre_order(root.right_child)returnpre_order_tmp#非递归后续遍历
defpre_order_not_recursion(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNone
stack=[root]
result=[]whilestack:
node= stack.pop(-1)ifnode:ifisinstance(node, Node):
result.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)
stack.append(node.left_child)else:
result.append(node)returnresult#递归中序遍历
defmiddle_order(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):return[]
middle_order_tmp=[]if root is notNone:
middle_order_tmp+=middle_order(root.left_child)
middle_order_tmp.append(root.value)
middle_order_tmp+=middle_order(root.right_child)returnmiddle_order_tmp#非递归中序遍历
defmiddle_order_not_recursion(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNone
stack=[root.right_child, root.value, root.left_child]
result=[]whilestack:
node= stack.pop(-1)ifnode:ifisinstance(node, Node):
stack.append(node.left_child)
stack.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)else:
result.append(node)returnresult#递归后续遍历
defpost_order(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):return[]
post_order_tmp=[]if root is notNone:
post_order_tmp+=pre_order(root.left_child)
post_order_tmp+=pre_order(root.right_child)
post_order_tmp.append(root.value)returnpost_order_tmp#非递归后续遍历
defpost_order_recursion(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNone
stack=[root.value, root.right_child, root.left_child]
result=[]whilestack:
node= stack.pop(-1)ifnode:ifisinstance(node, Node):
result.append(node.value)
stack.append(node.right_child)
stack.append(node.left_child)else:
result.append(node)returnresult#分层遍历
deflayer_order(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):return[]
queue=[root.value, root.left_child, root.right_child]
result=[]whilequeue:
tmp=queue.pop(0)iftmp:ifisinstance(tmp, Node):
queue.append(tmp.value)
queue.append(tmp.left_child)
queue.append(tmp.right_child)else:
result.append(tmp)return result
二叉树的其他方法:
#递归方式计算节点个数
defnode_count(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNoneelse:ifroot:return node_count(root.left_child)+node_count(root.right_child)+1
else:returnNone#借用分层遍历实现
defnode_count_not_recursion(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNonereturnlen(layer_order(root))#计算二叉树深度
deftree_deep(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNoneifroot:return 1+max(tree_deep(root.left_child), max(root.right_child))else:return0#非递归方式实现
deftree_deep_not_recursion(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNone
stack= [(root, 1)]
result=0whilestack:
tmp_node, tmp_layer=stack.pop(0)iftmp_node:
stack.append((tmp_node.left_child, tmp_layer+1))
stack.append((tmp_node.ritht_child, tmp_layer+1))
result= tmp_layer+1
returnresult#计算第K层节点的个数
defkth_node_count(root, k):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNoneif not root or k <=0:return0if k == 1:return 1
return kth_node_count(root.left_child, k-1)+kth_node_count(root.right_child, k-1)#计算二叉树叶子节点的个数
defleaf_account(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):returnNoneif notroot:return0if not root.left_child and notroot.right_child:return 1
return leaf_account(root.left_child)+leaf_account(root.right_child)#判断是否为二分查找树BST#判断是否为二分查找树BST,递归方式#二分查找树的定义搞清楚,二分查找树的中序遍历结果为递增序列
defis_bst_tree(root):if notisinstance(root, Node):return[]defis_asc(order):for i in range(len(order)-1):if order[i] > order[i+1]:returnFalsereturnTruereturnis_asc(middle_order_not_recursion(root))if __name__ == '__main__':
tree= Tree(1)
tree1= Tree(1)
node7= Node(5, None,None)
node6= Node(4, None,None)
node5= Node(3, None,None)
node4= Node(2, None,None)
node3= Node(1, None,None)
node2= Node(3, node5, node6)
node1= Node(4, node3, node4)
tree.root.left_child=node1
tree.root.right_child=node2
tree1.root.left_child=node2
tree1.root.right_child=node2print(post_order_recursion(tree.root))print(is_bst_tree(tree.root))print(is_bst_tree(tree1.root))