C++练习题库
1.矩阵类
Description
实现矩阵类matrix,行数和列数均不超过10
成员方法如下:
构造函数matrix(int m,int n):m为矩阵的行数,n为矩阵的列数,第i行第j列的元素赋值为按行优先顺序存放的元素的序号;
at(int, i)返回按行顺序优先的第i个元素
at(int i,int j):返回第i行第j列元素的值,注意和二维数组下标的差别。比如at(3,4)是矩阵的第3行第4列的元素,而非行标为3 列标为4的元素,在下面的示范数据中at(3,4)的结果为12。
sum():计算矩阵所有元素的和。
如3行4列矩阵构造为:
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
主函数如下:
int main()
{
int rowNum,colNum;
cin>>rowNum>>colNum;
matrix mat(rowNum,colNum);
cout<
Input
行数和列数
Output
输出第4个元素的值,第3行第4列元素的值,所有元素的和,中间用空格隔开。
Samples
Input 复制
3 4
Output
4 12 78
#include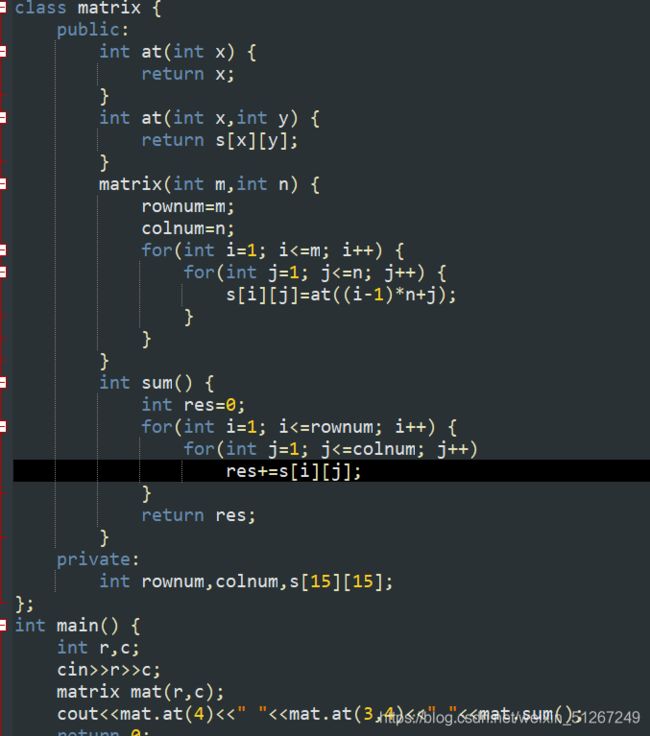
类其实相当于结构体,类可以拥有函数和变量。
this 是在类外面定义函数的时候一个自动的指针,指的就是调用这个函数的那个类的对象。
类和对象的总结
2.长方形类:
Description
定义长方形类rectangle,数据成员包括长length和宽width,均为double类型,成员函数包括:
(1)构造函数2个,一个无参的构造函数,长和宽的默认值为0,带两个参数的构造函数;
(2)设置长方形尺寸函数assign,即任意输入2个实数,大的数赋值给长,小的数赋值给宽
(3)计算长方形周长函数double circumference();
(4)计算长方形面积的函数double area();
(5)输出长方形的长和宽
要求在main函数中创建3个长方形的对象,第1,2个长方形分别由无参构造函数和有参构造函数初始化实现,第3个长方形对象通过输入数据,调用设置长方形尺寸函数,给长宽赋值,然后分别计算3个长方形的周长和面积,并输出结果
int main()
{
rectangle c1,c2(2.0,1.0),c3;
double x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
c3.assign(x,y);
… 其余代码自己填写…
return 0;
}
Input
输入仅一行数据,输入2个实数,数据之间用空格分开
Output
3个长方形输出3行数据,每行数据先输出长方形的长、宽,再输出它对应的周长和面积,小数点后保留2位数字,一行中4个数据之间用逗号分隔
Samples
Input 复制
2.5 3.8
Output
0.00,0.00,0.00,0.00
2.00,1.00,6.00,2.00
3.80,2.50,12.60,9.50
#include3.圆柱体类
Description
定义圆柱体类cylinder,要求具有以下成员:半径 高
成员函数如下:
默认构造函数:半径和高设置为1
构造函数:其参数包括半径和高两个参数。
volume函数:返回圆柱体的体积;
area函数:计算圆柱体的表面积数据均为double PI的值取3.14
int main()
{
double radius,height;
cin>>radius>>height;
cylinder cylinder1,cylinder2(radius,height);
cout<}
Input
录入圆柱体的半径和高。
Output
见main函数
Samples
Input 复制
2 3
Output
3.14 12.56 37.68 62.80
#include4.盒子类
Description
定义盒子Box类,要求具有以下成员:长、宽、高分别为x,y,z,可设置盒子形状;可计算盒子体积;可计算盒子的表面积。
定义盒子Box类,要求具有以下成员:盒子的长、宽、高(x,y,z),数据均为整型;初始化类成员的带参构造函数;计算盒子体积的成员函数volumn;计算盒子的表面积的成员函数area。
Input
按顺序分别录入盒子的长、宽、高
Output
输出盒子的体积和表面积。中间用空格隔开。
Samples
Input 复制
3 4 5
Output
60 94
在这里#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=1e5+9;
class Box{
private:
int a;
int b;
int c;
ll v,s;
public:
void InitBox(int x,int y,int z);
void volumn();
void area();
void show();
};
void Box::InitBox(int x,int y,int z)
{
a=x;b=y;c=z;
return;
}
void Box::volumn(){
v=a*b*c;
}
void Box::area(){
s=2*(a*b+a*c+b*c);
}
void Box::show(){
cout<<v<<" "<<s;
return;
}
int main()
{
int a,b,c;Box box;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
box.InitBox(a,b,c);
box.volumn();
box.area();
box.show();
return 0;
}
5.学生类
(输出输入的信息)
Description
编写程序,定义student类,并声明私有数据成员如下:num(学号 字符串),name(姓名)和三门课的成绩sumScore,总分
,建立成员函数如下:
构造函数:五个参数分别为学号,姓名和三门课的成绩
计算三门课的总成绩sum函数,总成绩放入sumScore数据成员。
显示学生的所有数据信息,各信息之间空格隔开。display()函数
Input
学生的学号,姓名和三门课的成绩
Output
学生的学号,姓名,三门课的成绩,总成绩,中间用空格隔开。
Samples
Input 复制
0100 zhangling 80 90 100
Output
0100 zhangling 80 90 100 270
#include6.student类
Description
定义student类,私有数据成员包括:stuNum(学号 字符串),stuName(姓名 字符串)和高数、英语和程序设计三门课的成绩,总成绩,成绩均为整型,成员函数包括:
(1)构造函数2个,一个含2个参数,分别为学号,姓名,成绩都默认为0;另一个含学号、姓名和三门课的成绩,总分默认为0
(2)计算三门课的总成绩函数,函数名统一用sumfun
(3)显示学生信息函数,各信息之间用空格隔开,函数名统一用display
(4)输入学生三门课成绩的函数,函数名统一用inputscore
要求在main函数中创建2个学生对象,第1个对象需要用inputscore函数输入三门课成绩,第2个学生对象由参数给出成绩,然后计算出2个学生的总分,最后输出这2个学生的信息。main函数部分代码如下:
int main()
{
student st1(“111”, “John”), st2(“222”,“Mike”,67,89,92) ;
…. // 请补充 其他代码
return0;
}
Input
三门课的成绩,成绩用空格分开
Output
输出学生的各信息,按学号、姓名、高数成绩、英语成绩、程序设计成绩以及总成绩,每一个数据之间用空格隔开,每个学生的信息占一行。
Samples
Input 复制
75 86 96
Output
111 John 75 86 96 257
222 Mike 67 89 92 248
#include7.teacher 类
程序在线评测平台(Programming Online Judge Platform)
主页
状态
题库
竞赛
排名
IWSXQY
注册帐号请注意
概览
状态
榜单 [ acm ]
告示
O . teacher类
Description
定义teacher类,私有数据成员包括:jobNO(工号 字符串),Name(姓名 字符串)和基本工资(base_pay),补贴(allowance), 保险金(insurance),工资总和,实发工资,均为double型,成员函数包括:
(1)构造函数2个,一个含2个参数,分别为工号,姓名,其他值都默认为0;另一个含工号、姓名和基本工资、补贴、保险金,工资总和与实发工资的值默认为0
(2)计算应发工资和实发工资的函数,函数名统一用salary。
工资总和=基本工资+补贴; 实发工资=工资总和—保险金
(3)显示教师信息函数,各信息之间用空格隔开,函数名统一用display
(4)输入教师基本工资、补贴、保险金的函数,函数名统一用input
要求在main函数中创建2个教师对象,第1个对象需要用input函数输入基本工资、补贴、保险金,第2个教师对象由参数给出基本工资、补贴、保险金,然后计算出2个教师的工资总和及实发工资,最后输出这2个教师的信息。main函数部分代码如下:
int main()
{
teacher t1(“111”, “Mary”),t2(“222”,“Alex”,4256.78,1234.56, 895.17) ;
…. // 请补充 其他代码
return0;
}
Input
输入基本工资、补贴、保险金的金额,用空格分开
Output
输出教师的信息,按工号、姓名、基本工资、补贴、保险金、工资总和、实发工资,每一个数据之间用空格隔开,每个教师的信息占一行。
Samples
Input 复制
6589.45 1549.21 985.47
Output
111 Mary 6589.45 1549.21 985.47 8138.66 7153.19
222 Alex 4256.78 1234.56 895.17 5491.34 4596.17
#include
8.专业类
Description
设计一个关于专业(my_major)的类,需要描述专业的名字(无空格),专业的学生人数,专业的老师的人数。
成员函数包括:
默认的构造函数:字符串类型的成员变量设置为空格,数值型的成员设置为0。
构造函数:分别为专业名,学生人数以及老师人数赋值。
显示专业信息函数:分别显示专业名,学生人数以及老师人数,不同的成员之间用空格隔开。
Input
专业名、学生人数、老师人数。
Output
用显示专业信息函数显示输入成员构造对象的信息和用默认构造函数构造的对象信息。
Samples
Input 复制
computer 3000 30000
Output
computer 3000 30000
0 0
#include9.复数类
Description
定义一个复数类complex,数据成员包括实部real和虚部imag,均为double类型。成员函数包括:
(1) 默认构造函数(即无参的构造函数),实部和虚部分别赋值为1.0,1.0 ;
(2) 带两个参数的构造函数(假设实参值是1.5,2.8);
(3) 输出复数的函数display, 输出格式为 实部+虚部i,例如: 1.00+1.00i ;
(4) 输入复数的函数input, 从键盘输入复数的实部和虚部;
(5) 计算复数的模的函数magnitude(函数返回值为double型),即对于复数 z=a+bi,它的模 |z|=sqrt(a2+b2)。
要求在main函数中创建3个复数对象,第1个复数的实部和虚部用input函数从键盘输入,第2、3个复数分别由用默认构造函数和带参数的构造函数实现初始化,最后分别输入这3个复数以及它们的模。
int main()
{
complex val1,val2,val3(1.5,2.8);
val1.input();
val1.display();
cout<<" "<}
Input
输入复数的实部和虚部,两个实数之间用空格分开
Output
3个复数应输出3行数据,每行输出数据分两部分,先输出复数,再输出该复数的模,复数和它的模之间用2个空格分隔,所有实数小数点后保留两位
Samples
Input 复制
1.0 2.0
Output
1.00+2.00i 2.24
1.00+1.00i 1.41
1.50+2.80i 3.18
#include10.字符串反转
Description
编写函数完成字符串反转。要求必须使用C++字符串,必须使用函数
Input
输入有多行,每一行代表一个字符串。 输入行数不确定,以ctrl+z结束。
Output
输出翻转后的字符串。每个字符串占一行。
Samples
Input 复制
who’s your daddy
my daddy is Li Gang
Output
yddad ruoy s’ohw
gnaG iL si yddad ym
Hint
对于多行判断,可采用while(getline(cin, str))来实现,如果getline获取到ctrl+z,则退出while循环。
#include11.六边形
Description
六边形类包括成员函数如下:
hexagons(double sideValue=10);边长设置为默认值10
double circumference();周长函数
double area();面积函数
void setSide(double sideValue);设置边长
double getSide();读边长
类成员自定
主函数如下:
int main() } Input Output Samples Description 构造函数:输入年,月,日初始化日期 int orderOfYear():计算所输入日期在本年中是第几天,注意闰年问题。 Input Output Samples Description Input Output Samples Description 类的成员函数如下: 构造函数:包括两个参数,其两个参数的默认值为0。 重载运算符 +、- +:两个点相应的坐标相加,比如(1,1)+(2,2)=(3,3) -:两个点相应的坐标相减,比如(2,2)-(1,1)=(1,1) 输出函数output,输出点的横坐标和纵坐标如下:(2,3)其中2为横坐标,3为纵坐标 输入函数input,:输入点的横坐标和纵坐标,中间以空格隔开比如输入2 3 ,给点的横坐标和纵坐标赋值. Input Output Samples Description 编写派生类cylinder,包含数据成员圆半径radius和高度length(double类型);带参构造函数,初始化其成员;编写成员函数display,输出cylinder的基本信息。 编写派生类sphere,包含圆半径radius(double类型);编写带参构造函数,初始化其成员;成员函数display,输出cylinder的基本信息。 完成以上三个类,使下列主函数能够正确运行。 int main() { } 在shape类中添加纯虚函数volume,cylinder和sphere也分别添加虚函数volume(),该函数用于计算体积。完成上述功能,使下列主函数能够正确运行。(注,pi取3.14,使用double类型进行计算) #include “iomanip” … int main() { } Input Output Samples Description Input Output Samples Description Input Output Samples 29 . 删除字符串中的子串 若str字符串为aaas1kaaas,substr字符串为aaa,则输出结果s1ks。 Input Output 对于每组测试数据,输出结果占一行,即去掉substr后的str。 Samples Description 主函数如下: int main() cin>>ID>>name; class vehicle vehicle1(ID,name); } Input 输入自行车的编号,名称,重量 Output 输出自行车的信息 Samples Description 编写函数模板max_arr,返回数组的最大元素。数组元素可以为任意数据类型。完成上述功能,是下列主函数能够正确执行。 int main() { } Input Output Samples Description Input 录入外设对象的组件号,组件名,进价,销售价,生产厂家 Output 输出外设对象的组件号,组件名,进价,销售价,生产厂家 Samples Description 对称图形类figure: 图形圆类circle: 矩形类rectangle: 主函数如下: int main() } Input Output Samples Description 类的定义如下: class settype void getdata(int *a, int& num) const; //读值函数 settype operator+(settype B); //重载运算符+,实现集合并运算 private: Input Output Samples Description Input Output Samples Description (2)编写student类的默认构造函数,默认姓名为空字符串,年龄为0 (3)编写student类的输入函数input,能够输入每个学生的姓名,年龄 (4)编写student类的输出函数display,能够输出每个学生的姓名,年龄 (5)编写排序函数sort,能够按照年龄从小到大对学生进行排序 主函数输入班级人数,创建数组,输入学生信息,对学生年龄进行排序,然后输入排序后的信息 Input Output Samples Description Input Output Samples Description (a) 电梯从第1层启动 (b) 按+时电梯上升一层,当电梯在10层时忽略此命令 © 按-时电梯下降一层,当电梯在1层时忽略此命令 (d) 按S时电梯将返回到第1层,并停止。 (e) 电梯从一层升/降到另一层,显示楼层数字 编写主函数生成一个电梯对象,从键盘输入字符运行电梯,输入字符S结束。 Input Output Samples Input 复制 + + + - S Output Description (1) 构造函数Date (int year, int month, int day ),可以设定默认的形参值为2008年1月1日 (2) 赋值函数,assign(int year, int month, int day) 用来给三个数据成员赋值,暂时不考虑非法赋值的情况. (3) 显示日期函数,display( ),按规定格式“年-月-日”输出,例如2000年5月1日,输出 2000-5-1 (4) 判断闰年函数,bool Leap_year ( ),返回值为布尔型,是闰年返回true,否则返回false (5) 计算当前日期后1天的日期的函数,void increment(),计算时必须注意闰年、跨月、跨年的情况 例如:若当前日期为2016-12-31,执行increment();则日期为2017-1-1 若当前日期为2017-2-28,执行increment();则日期为2017-3-1 若当前日期为2017-1-31,执行increment();则日期为2017-2-1 (6) 计算当前日期后n天的日期的函数,void increment(int n),计算时必须注意闰年、跨月、跨年的情况 例如:若当前日期为2016-8-10,执行increment(5);则日期为2016-8-15 若当前日期为2016-2-27,执行increment(3);则日期为2016-3-1 若当前日期为2016-12-30,执行increment(5)则日期为2017-1-4 (提示:可先完成增加1天的函数,然后循环执行该函数即可。) 主函数如下所示,先输出date1和date2的日期,然后按“日 月 年”的格式输入一个日期,用assign函数给date3赋值,并输出date3,再输入一个天数,即输入n(1<=n<=30),对象date3调用increment函数,最后输出计算后的新日期 int main() { Date date1, date2(2016,5,1),date3; int n,day,month,year; date1.display(); date2.display(); cin>>year>>month>>day; date3.assign(year,month,day); date3.display(); cin>>n; date3.increment(n); date3.display(); return 0; } Input Output Samples Description (1) 构造函数 Date (int day, int month, int year ),可以设定默认的形参值为2008年1月1日 (2) 赋值函数,void assign(int day, int month, int year) 用来给三个数据成员赋值,需要对日,月的数据进行判断,如果日期数据大于当月的天数,月份数据大于12,则可以用取余运算使数据在合法的取值区间内。 例如: 若输入32 3 2018,期中32是非法数据,32%31=1,所以最后得到的合法日期应该是1/3/2018 若输入15 20 2018,期中20是非法数据,20%12=8,所以最后得到的合法日期应该是15/8/2018 如果算出来余数为0,则月份赋值为12,日期则为对应月份的最大天数,注意区分大小月和2月(注意闰月情况) (3) 显示日期函数,void display( ),按规定格式“日/月/年”输出,例如:2000年5月1日,输出 1/5/2000 (4) 判断闰年函数,bool Leap_year ( ),返回值为布尔型,是闰年返回true,否则返回false (5) 计算当前日期后n天的日期的函数,void increment(int n),计算时必须注意闰年、跨月、跨年的情况,假设测试数据中的n的范围为1<=n<=30 例如: 若当前日期为10/8/2016,执行increment(5);则日期为15/8/2016 若当前日期为27/2/2016,执行increment(3);则日期为1/3/2016 若当前日期为30/12/2016,执行increment(5);则日期为4/1/2017 主函数如下所示,先输出date1和date2的日期,然后按“日 月 年”的格式输入一个日期,用assign函数给date3赋值,并输出date3,再输入一个天数,即输入n(1<=n<=30),对象date3调用increment函数,最后输出计算后的新日期 int main() { Date date1, date2(1,5,2016),date3; } Description 机器人类的构造函数及成员变量为: class robot 补充其中的成员方法,使之能运行以下的main函数 int main() Input Output Samples Description class robot { public: ...需要补充的其它成员函数 ... private: double x_coord, y_coord ; // 看main函数确定这两个数据成员代表的含义 补充其它的成员函数有6个:left(), right(), forward(), back(), goto_position(), void return_to_base(),使之能运行以下的main函数,函数的参数如何定义,请根据main函数中的函数调用来确定(请仔细阅读main函数),前5个函数 left(), right(), forward(), back(), goto_position()返回值类型为bool型,如果要移动的位置超出范围,则返回false,如果移动移动成功,则返回true, int main() { double px, py; robot puppy( 59.6, 28.1 ) ; // Constructor sets the initial position. if( puppy.left( 1.3 ) ) else cout<<“position error!\n”; else cout<<“position error!\n”; else cout<<“position error!\n”; } Input Output Samples
{
double side;
cin>>side;
class hexagons hex1;
cout<<"The side of the hxagons is "hex1.getSide()<
cout<<"The circumference of the hex1 is “<return 0;
边长
输出其边长,以及周长和面积
Input 复制
5
Output
The side of the hxagons is 10
The circumference of the hex1 is 30 and area is 64.9519#include12. 日期转换
声明一个类,有数据成员年,月,日,建立两个成员函数:
按年,月,日输入三个整数
一年中的第几天
Input 复制
2013 3 1
Output
60#include 13.数组类
建立模板数组类:array
成员方法如下:
array(int n);其中n用来设置数组元素的个数
~array();
int sizeOfArray();返回数组中元素的个数
重载 operator[](int index),返回下标为index的数组元素。
定义setElement()函数 ,该函数有2个参数,其中第一个参数为数组元素的下标,第二个参数为数组元素的值。
输入有3行,第1行输入模板数组类型,其中1代表建立整数数组类, 2代表建立double数组类,3代表char数组类;
第2行输入数组中元素的个数;
第3行输入数组中各个元素.
输出数组中各元素,元素之间用一个空格分开,注意最后一个元素后没有空格
Input 复制
1
3
1 2 3
Output
1 2 3#include14.简单point类
定义类point,其中包括两个数据成员,均为 int 类型,为点的横坐标和纵坐标。
分别输入两个点的横坐标和纵坐标, 中间空格隔开
第1行输出 x,y 两点之和,第2行输出x,y 两点之差
Input 复制
3 4
1 2
Output
(4,6)
(2,2)#include15.shape类
编写图形类shape,其中包含数据成员color(string类型),表示图形的颜色;编写带参构造函数,初始化成员color;编写成员函数display,输出shape的基本信息。 string color;
double x, y, z;
cin >> color;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
shape s(color);
cylinder c(color, x, y);
sphere s1(color, z);
s.display();
c.display();
s1.display();
shape *p;
int x;
cin >> x;
if (x == 1)
{
double r, l;
string color;
cin >> color >> r >> l;
p = new cylinder(color, r, l);
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << p->volume() << endl;
delete p;
}
else if (x == 2)
{
double r;
string color;
cin >> color >> r;
p = new sphere(color, r);
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << p->volume() << endl;
delete p;
}
一个整数,表示选择生成的图形;一个字符串表示颜色,一个小数表示半径,一个小数表示高(图形为球是不需要)。
图形的体积
Input 复制
1 red 1.2 2.2
Output
9.95#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include16.动态内存分配求整型数组元素之和
编程输入数组元素的个数n,0
输入有2行,第1行为一个整数,即数组元素个数,第2行依次输入数组元素的值,每个数据之间用空格分开
输出有2行,第1行输出数组元素的值,第2行输出元素之和,具体格式见Sample Output
Input 复制
3
1 2 3
Output
a[3]={1,2,3}
sum=6#include17.动态内存分配求整型数组元素之和
首先输入数组元素的个数n,0
输入有2行,第1行为一个整数,即数组元素个数,第2行依次输入数组元素的值,每个数据之间用空格分开
输出有2行,第1行输出原数组的元素,第2行输出替换后的数组元素,具体格式见Sample Output
Input 复制
5
2 -3 6 -8 9
Output
a[5]={2,-3,6,-8,9}
a[5]={2,0,6,0,9}#include18.删除字符串的子串
Description
编写函数,去掉str字符串中出现的substr字符串。要求实参和形参之间按引用传递
第一行有一个正整数T,表示测试数据的组数。后跟T组测试数据,每组测试数据占两行,第一行是字符串str,第二行是字符串substr。
Input 复制
2
aaas1kaaas
aaa
zhangwangli
an
Output
s1ks
zhgwgli#include19.交通工具类
定义交通工具类(vehicle),成员包括编号,颜色. 成员函数包括构造函数,包括两个参数分别对成员进行赋值,display()用于显示成员的值.
定义交通工具类的子类自行车类(bike),成员包括编号,颜色,重量(weight整型),重写display()函数显示其所有成员值.
{
int ID;
string name;
int weight;
vehicle1.display();
cout<
class bike bike1(ID,name,weight);
bike1.display();
cout<return 0;
输入交通工具对象的编号,名称
输出交通工具的信息
Input 复制
1 vehicle1
2 bike1 30
Output
vehicleID=1 vehicleName=vehicle1
vehicleID=2 vehicleName=bike1 weight=30#include20.max_arr
int i_arr[10];
char c_arr[10];
string s_arr[10];
int n;
cin >> n;
input(i_arr, n);
cout << max_arr(i_arr, n) << endl;
cin >> n;
input(c_arr, n);
cout << max_arr(c_arr, n) << endl;
cin >> n;
input(s_arr, n);
cout << max_arr(s_arr, n) << endl;
输入数据为一行,第一个为正整数n(n<=10),表示数组元素的数目,其余为数组元素
数组的最大元素
Input 复制
5 1 2 3 4 5
3 b c a
4 red blue yellow green
Output
5
c
yellow#include21.组件类
定义件组件类(component),成员包括组件号(整型),组件名。 成员函数包括构造函数,包括三个参数分别对成员进行赋值,output()用于显示成员的值.
定义component类的子类外设类(device),成员包括除了父类的成员外,还包括生产厂家,进价,销售价(整数型),重写output()函数显示其所有成员值.
录入组件对象的组件号,组件名
输出组件对象的组件号,组件名
Input 复制
1 lingjian1
2 lingjian2 100 150 lianxiang
Output
1 lingjian1
2 lingjian2 100 150 lianxiang#include22.图像的继承
点类point
成员变量包括其横坐标x和纵坐标y。均为double类型。
构造函数,参数列表为x值和y值
display函数,显示形式如(1,2)其中1和2为点的横坐标和纵坐标。
成员变量包括其图形的中心点。
构造函数,参数列表为point类型的对象。
display函数,在屏幕上显示其成员,显示形式如"I am a figure. The center is: (1,2)"。
说明:circle是figure的子类。
成员变量包括:中心点,半径。
成员方法如下:
circle(point p,double r):构造函数
move(point p):函数的功能为把中心点移至p。
display();在屏幕上显示其成员,显示形式如"I am a circle, the center is: (1,2), the radius is: 2."
说明:rectangle是figure的子类。
成员变量包括:中心点,长度,宽度。
成员方法如下:
rectangle (point p,double lengthVal,double widthVal):构造函数
display();在屏幕上显示其成员,显示形式如"I am a rectangle, the center is: (1,2), the length is: 1, the width is: 2."
{
double x,y,radius,width,length;
cin>>x>>y;
point p(x,y);
p.display();
cout<
circle cir1(p,radius);
cir1.display();
cout<
rectangle rectangle1(p,length,width);
rectangle1.display();
cout<
录入一个点的横坐标和纵坐标.
输出点。
输出圆。
输出矩形。
Input 复制
1 2
5
10 20
Output
(1,2)
I am a circle, the center is: (1,2), the radius is:5.
I am a rectangle, the center is: (1,2), the length is: 10, the width is: 20.#include23.集合类的实现
定义一个集合类,集合的大小是不确定的,需要使用指针数据成员, 重载运算符“+”,“*”,“-”实现集合的并、交、差运算,对赋值运算符进行重载,定义拷贝构造函数,重载流运算符实现集合的输入、输出。注意,假设A={1,3,5},B={1,5,9},两个集合的差运算A-B,是指从集合A中减去集合B的元素,上面集合A-B的结果是{3}
{
public:
settype(); //构造函数,默认空集,n=0, set=NULL;
settype( const settype& B); //拷贝构造函数
~settype(); //析构函数
void setdata(int *a, int num); //设值函数
int get_n() const; // 获取集合当前元素数目
settype operator*(settype B); //重载运算符*,实现集合交运算
settype operator-(settype B); //重载运算符-,实现集合差运算
settype operator=(settype B); //重载运算符=
int *set; //数组指针
int n; //元素的个数
};
输入有4行, 第1行输入集合A 的元素个数,第2行输入A 的元素值(数据之间用空格分开),第3行输入集合 B的元素个数,第4行输入B 的元素值,注意集合A,B的元素个数不能超过10
输出有5行,分别输出集合A,集合B,A+B的结果, A*B的结果, A-B的结果,具体输出格式见Sample Output
Input 复制
5
1 3 5 7 9
3
1 4 6
Output
A={1,3,5,7,9}
B={1,4,6}
A+B={1,3,5,7,9,4,6}
A*B={1}
A-B={3,5,7,9}#include 24复数类(重载加减运算符)
定义类表示复数,成员包括实部real和虚部imaginary,均为double类型
成员函数包括:无参的构造函数(实部和虚部分别赋值为1.0), 带两个参数的构造函数,重载“+”和“-”运算符 , display函数(输出格式形如"2.00+3.00i"),输出时要求 实部和虚部分别精确到两位小数
分别输入两个复数的实部和虚部,一行输入一个复数,实部和虚部用空格分开,具体格式见Sample Input
输出有2行,分别输出两个复数"+“和”-"的结果,具体格式见Sample Output
Input 复制
2 3
4 5
Output
6.00+8.00i
-2.00-2.00i#include25.学生类数组
(1)输入班级人数,使用new动态创建学生信息数组存储学生信息。学生信息使用student类存放,包括姓名(不包含空格),年龄。
输入信息有多个,第一行N表示班级人数,其余每一行为学生的信息(姓名,年龄,中间空格隔开)
排序后的学生信息
Input 复制
3
Mary 22
Lucy 12
Mike 19
Output
Lucy 12
Mike 19
Mary 22#include26. reverse_arr
编写函数模板reverse_arr,将数组元素逆置。数组元素可以为任意数据类型。
输入数据为一行,第一个为正整数n(n<=10),表示数组元素的数目,其余为数组元素
逆置后的数组
Input 复制
4 5 10 15 7
3 2.3 4.7 3.5
2 english chinese
Output
7 15 10 5
3.5 4.7 2.3
chinese english#include27. 电梯类
设有一栋十层的建筑物,创建一个电梯类,实现以下功能
输入字符’+’,’-’,‘S’,每个字符占一行。注意:输入字符个数为任意多个,遇到S,输入结束。
输出电梯运行层数。
current floor:2
current floor:3
current floor:4
current floor:3
current floor:2
current floor:1#include28 日期类
定义日期类Date,数据成员包含:year,month,day,成员函数包括:
输入年,月,日,增加天数n,输入用空格隔开。
输出main函数执行结果
Input 复制
2017 12 31 70
Output
2008-1-1
2016-5-1
2017-12-31
2018-3-11#include29 日期类加强版
定义日期类Date,数据成员包含:day,month,year,成员函数包括:int n,day,month,year;
cin>>day>>month>>year;
date3.assign(day,month,year);
cin>>n;
date1.display();
date2.display();
date3.display();
date3.increment(n);
date3.display();
return 0;
#include30 机器人类
{
public:
robot(float x = 0, float y = 0) : x_coord( x ), y_coord(y)
{}
void display_position()
{
cout << “(” << x_coord << “,” << y_coord << “)” << endl ;
}
private:
float x_coord, y_coord ;
} ;
{
float x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
robot r2d2(x, y); // Constructor sets the initial position.
r2d2.left(1.3); // Move robot left 1.3 cms.
r2d2.display_position();
r2d2.back(4.21); // Move robot back 4.21 cms.
r2d2.display_position();
r2d2.right(3.1); // Move robot right 3.1 cms.
r2d2.display_position();
r2d2.return_to_base(); // Sets the position to (0,0).
r2d2.forward(0.3); // Move robot forward 3.1 cms.
r2d2.display_position();
r2d2.goto1(x, y);
r2d2.display_position();
return 0;
}
输入机器人的初始坐标
输出结果
Input 复制
12 22
Output
(10.7,22)
(10.7,17.79)
(13.8,17.79)
(0,0.3)
(12,22)#include31 机器人类
假设有一个机器人,它可以在一个有限的区域内前,后,左,右的移动,该区域为正方形,4个顶点的坐标为:(0,0),(0,100),(100,100),(100,0),机器人可以通过调用不同的函数来实现移动,但是在机器人移动的过程中,如果要移动到的位置坐标超出这个范围,则不能进行移动,此时需要输出错误提示信息“position error! ”,如果机器人可以移动,则移动成功后应输出机器人新的位置坐标。机器人类的部分定义如下:robot(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x_coord( x ), y_coord(y) { }
void display_position() // Inspector function to display the robot's position
{ cout << "(" << x_coord << "," << y_coord << ")" << endl ; }
} ; puppy.display_position() ; // Move robot left 1.3 cms, New position is ( 58.3,28.1)
if(puppy.back(12.0))
puppy.display_position() ; // Move robot back 12.0 cms, New position is ( 58.3,16.1)
if(puppy.right( 60.0 ) )
puppy.display_position() ; // Move robot right 60.0 cms, 58.3+60=118.3>100, output "position error!"
puppy.return_to_base() ; // Sets the position to (0,0)
puppy.display_position() ;
puppy.forward( 3.5 ); // Move robot forward 3.5 cms, New position is ( 0, 3.5 )
puppy.display_position();
cin>>px>>py;
if(puppy.goto_position( px, py ))
puppy.display_position();
else cout<<"position error!\n";
return 0;
只有一行输入数据,依次输入px, py 的值,两个实数用空格分开
输出有6行,每行输出一个位置,若位置错误则输出信息“position error!”具体格式见Sample Output
Input 复制
18.5 65.3
Output
(58.3,28.1)
(58.3,16.1)
position error!
(0,0)
(0,3.5)
(18.5,65.3)#include