二叉树的链式存储结构(线索二叉树)
一、链式存储结构
由于顺序存储二叉树的空间利用率较低,因此二叉树一般都采用链式存储结构,用链表结点来存储二叉树中的每个结点。在二叉树中,结点结构通过包括若干数据域和若干指针域,二叉链表至少包含3个域:数据域 data、左指针域 lchild和右指针域 rchild,如下图所示:

其中,n 个结点的二叉链表中含有 n+1 [ 2n-(n-1)=n+1 ] 个空指针域。
二、线索二叉树
传统的二叉链表仅能体现出一种父子关系,不能直接得到结点在遍历中的前驱或后继。引入线索二叉树正是为了加快查找结点前驱和后继的速度。
规定:若无左子树,令 lchild指向其前驱结点;若无右子树,令rchild执行指向其后继结点。增加两个标志域标识是指向左/右孩子还是指向前驱/后继。

其标志位含义如下:

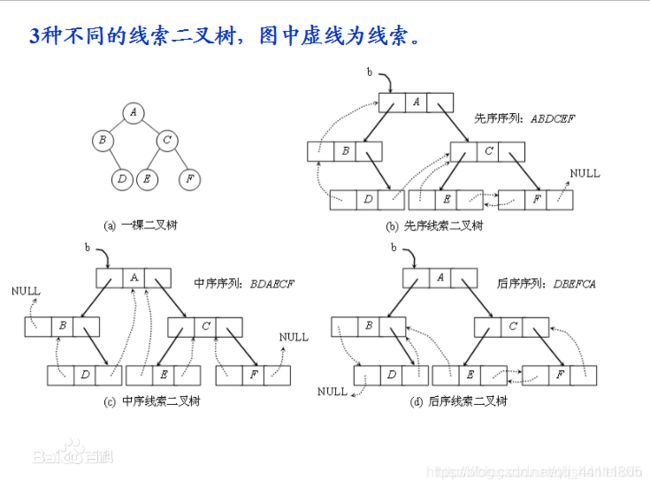
这种加上线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树。根据线索性质的不同, 线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树、 中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种。
1.1、中序线索二叉树
1.1.1 中序线索二叉树的构造
设置结点pre指向刚刚访问过的结点,结点node指向正在访问的结点,即pre指向node的前驱。在遍历过程中,检查node的左指针是否为空,若为空就将它指向pre;检查pre的右指针是否为空,若为空就将它指向node。
public static void inthreadNode(Node node) {
if(node==null) {//结点为空无法线索化
return;
}
//线索化左子树
inthreadNode(node.getLeft());
//线索化当前结点
if(node.getLeft()==null) {
node.setLeft(pre);//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLtag(1);//修改当前结点的左指针的类型,指向前驱结点
}
if(pre!=null&&pre.getRight()==null) {
pre.setRight(node);//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRtag(1);//修改当前结点的右指针的类型,指向后继结点
}
pre=node;//每处理一个结点后,让当前结点成为刚刚访问过的结点
//线索化右子树
inthreadNode(node.getRight());
}
1.1.2 中序线索二叉树的遍历
因为线索化后, 各个结点指向有变化, 因此原来的遍历方式不能使用, 需要使用新的方式遍历线索化二叉树。中序线索二叉树的结点中隐含了线索二叉树的前驱和后继信息。在对其遍历时,需要找到第一个具有前驱结点的左结点,然后依次找结点的后继。在中序线索二叉树中找结点后继的规律是:若其右标志为1,则右链为线索,指示其后继,否则遍历右子树中第一个访问的结点(右子树中最左下的结点)为其后继。
public static void inthreadlist(Node node) {
node=root;//存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
while(node!=null) {
while(node.getLtag()==0) {
node=node.getLeft();
}
System.out.println(node);//打印当前结点
while(node.getRtag()==1) {//获取到当前结点的后继结点
node=node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
node=node.getRight();//依次替换遍历的结点
}
}
1.1.3 中序线索二叉树完整代码
package Tree;
public class InThreadedBinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root=new Node(7,"A");//创建二叉树
Node a=new Node(4,"B");
Node b=new Node(9,"C");
Node c=new Node(2,"D");
Node d=new Node(5,"E");
Node e=new Node(8,"F");
Node f=new Node(11,"G");
Node g=new Node(1,"H");
Node h=new Node(3,"I");
Node i=new Node(10,"J");
Node j=new Node(12,"K");
root.setLeft(a);
root.setRight(b);
a.setLeft(c);
a.setRight(d);
b.setLeft(e);
b.setRight(f);
c.setLeft(g);
c.setRight(h);
f.setLeft(i);
f.setRight(j);
inThreadBinaryTree thread=new inThreadBinaryTree(root);
inThreadBinaryTree.inthreadNode(root);//创建中序线索二叉树
inThreadBinaryTree.inthreadlist(root);//遍历中序线索二叉树
}
}
class Node{
private int data;
private String name;
private Node left;//默认null
private Node right;//默认null
//若ltag == 0,说明指向的是左子树;ltag == 1,指向的是前驱结点
//若rtag == 0,说明指向的是右子树;rtag == 1,指向的是后继结点
private int ltag;
private int rtag;
public Node(int data,String name) {
this.data=data;
this.name=name;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Node getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(Node left) {
this.left = left;
}
public Node getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(Node right) {
this.right = right;
}
public int getLtag() {
return ltag;
}
public void setLtag(int ltag) {
this.ltag = ltag;
}
public int getRtag() {
return rtag;
}
public void setRtag(int rtag) {
this.rtag = rtag;
}
@Override
public String toString() {//重写toString方法
return "Node [data=" + data + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}
//中序线索化二叉树(左->根->右)
class inThreadBinaryTree{
private static Node root;
private static Node pre=null;//pre表示刚刚访问过的结点,即前一个结点
public inThreadBinaryTree(Node root) {//inThreadBinaryTree构造函数
this.root=root;
}
public static void inthreadNode(Node node) {
if(node==null) {//结点为空无法线索化
return;
}
//线索化左子树
inthreadNode(node.getLeft());
//线索化当前结点
if(node.getLeft()==null) {
node.setLeft(pre);//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLtag(1);//修改当前结点的左指针的类型,指向前驱结点
}
if(pre!=null&&pre.getRight()==null) {
pre.setRight(node);//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRtag(1);//修改当前结点的右指针的类型,指向后继结点
}
pre=node;//每处理一个结点后,让当前结点成为刚刚访问过的结点
//线索化右子树
inthreadNode(node.getRight());
}
//中序线索化二叉树的遍历(遍历次序和中序遍历保持一致)
public static void inthreadlist(Node node) {
node=root;//存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
while(node!=null) {
while(node.getLtag()==0) {
node=node.getLeft();
}
System.out.println(node);//打印当前结点
while(node.getRtag()==1) {//获取到当前结点的后继结点
node=node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
node=node.getRight();//依次替换遍历的结点
}
}
}
运行结果:
Node [data=1, name=H]
Node [data=2, name=D]
Node [data=3, name=I]
Node [data=4, name=B]
Node [data=5, name=E]
Node [data=7, name=A]
Node [data=8, name=F]
Node [data=9, name=C]
Node [data=10, name=J]
Node [data=11, name=G]
Node [data=12, name=K]