skynet源码解析--启动篇之三大模块
主要模块
- 基本信息初始化
- 优先启动的服务
- 监视器
- 定时器模块
- 网络模块
- 工作模块
- 总结
基本信息初始化
初始化配置之后,就要开始启动skynet的主要模块。不过,启动模块之前要先初始化一些基本信息。
- 生成harbor ID。这个ID用一个整型的高八位表示,也就是说master/harbor模式中,同一个集群最多只有256个harbor服务器。
- 句柄池初始化。这个句柄池主要用来管理服保存务对象的句柄,其中还包括句柄和服务的映射关系,这个句柄具有唯一新(harbor模式下在集群都是唯一的),因此只要知道地址(句柄)你就可以快速找到对应的服务对象。还有skynet采用的是Actor模型,所以这个服务对象其实对应的就是Actor对象。
- 一级队列初始化。skynet的消息处理采用的是两级消息队列方式,二级消息队列保存在服务对象上,就是说每个服务对象有独立的消息队列。
- module接口初始化。这个modules类型的全局变量主要保存了加载到skynet中c库的基本信息以及对外提供调用c库的方法。这个可以看作面向对象范畴里面的接口对象,每个加载的c库可以认为是继承了这个接口的类的实例化,所有加载的c库对象都是通过这个接口调用。
- 定时器模块初始化。
- 网络模块初始化。这里主要是创建一个管道,作为服务对象和网络IO的桥梁从避免IO阻塞对服务器对象的影响。后续讲到服务调度就会知道服务阻塞的危害
下面是skynet_start文件中的代码,加上了简略的注释:
//初始化基本信息
skynet_harbor_init(config->harbor); //生成harbor ID 高八位表示 所以master/harbor模式下同个集群里最多只有256台harbor
skynet_handle_init(config->harbor); //句柄池初始化,管理服务对象句柄(地址),以及地址和服务的映射关系。
skynet_mq_init(); //一级消息队列初始化(skynet采用的是两级消息队列模式)
skynet_module_init(config->module_path); // module接口,这里主要存储加载到skynet中的c库,并对外提供c库方法的接口。这个可以看做是一个接口类,每加载一个c库相当于实例化一个继承该接口的对象。
skynet_timer_init(); // 定时器模块初始化。
skynet_socket_init(); // 网络模块初始化,这个并非skynet的网络库,这里主要是创建一个管道,作为服务对象和网络IO的桥梁从避免IO阻塞对服务器对象的影响。
skynet_profile_enable(config->profile); // debug
优先启动的服务
日志服务:主要负责输出与记录,程序运行中的日志。通用引导服务:用于拉起其他的服务。
struct skynet_context *ctx = skynet_context_new(config->logservice, config->logger); // 生成日志服务Actor
bootstrap(ctx, config->bootstrap); //生成通用lua引导服务Actor
监视器
create_thread(&pid[0], thread_monitor, m); //启动监视模块
监视器的作用监控工作模块(其中的工作线程)对可能出现的死循环通过打印信息发出警告。下面是monitor的数据结构。
struct skynet_monitor {
int version; // 版本号 -- 其实就是消息的流水号
int check_version; // 检查版本号
uint32_t source; // 源地址
uint32_t destination; // 目标地址
};
监视器的工作方式,工作线程每次处理消息之前,version自增,记录源地址(source)和目标地址(destination),然后5秒钟检测一次目标地址是否为空(处理完消息之后置空源地址)且version与check_version相等则提示该工作线程可能死循环(因为该消息已经占用工作线程5秒)。
thread_monitor中每次检查间隔5秒。
for (i=0;i<5;i++) { // 休息5秒
CHECK_ABORT
sleep(1);
}
监视器的消息版本号更新与检测。
void
skynet_monitor_trigger(struct skynet_monitor *sm, uint32_t source, uint32_t destination) {
sm->source = source;
sm->destination = destination;
ATOM_INC(&sm->version);
}
void
skynet_monitor_check(struct skynet_monitor *sm) {
if (sm->version == sm->check_version) { // 版本一致
if (sm->destination) {
skynet_context_endless(sm->destination); //检查目标服务的引用,引用为0则回收,释放工作线程
skynet_error(NULL, "A message from [ :%08x ] to [ :%08x ] maybe in an endless loop (version = %d)", sm->source , sm->destination, sm->version);
}
} else {
sm->check_version = sm->version; // 不一致的时候更新
}
}
定时器模块
create_thread(&pid[1], thread_timer, m); //启动定时器模块
skynet的主要模块之一,为服务器提供基础的定时器功能。skynet的定时器是通过计数器的方式实现的,把时间段分成5级,一级为时间近点,即将发生超时的时间段,等待通知处理。后面4级是时间远点,随着时间增长一级一级向前移动直至近点,等待处理。下面是主要的数据结构:
//定时事件
struct timer_event {
uint32_t handle; // 服务地址
int session; // 回话ID
};
//定时节点
struct timer_node {
struct timer_node *next;
uint32_t expire;
};
//链表
struct link_list {
struct timer_node head;
struct timer_node *tail;
};
struct timer {
struct link_list near[TIME_NEAR]; // 时间近点哈希链表
struct link_list t[4][TIME_LEVEL];// 时间4级远点哈希链表
struct spinlock lock;
uint32_t time;
uint32_t starttime;
// 两个时间都是10ms一滴答
uint64_t current; // 系统时间
uint64_t current_point; // 服务器时间:相对于服务器重启的时间
};
- TIME_NEAR值为8,TIME_LEVEL为6,所以5级分为6/6/6/6/8,时间槽需要256+64+64+64+64=512个槽。这样的划分在空间和时间上做到很好的均衡。级分多了,槽虽然变少了但是会增加哈希链表的操作,级分少了,槽就增加需要的空间就增多。
- 计数器的一个滴答等于10ms。所以skynet提供的定时器接口,超时时间单位是10ms。
static void
add_node(struct timer *T,struct timer_node *node) {
uint32_t time=node->expire;
uint32_t current_time=T->time;
if ((time|TIME_NEAR_MASK)==(current_time|TIME_NEAR_MASK)) { // 近点时间槽
link(&T->near[time&TIME_NEAR_MASK],node);
} else {
int i;
uint32_t mask=TIME_NEAR << TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
for (i=0;i<3;i++) {
// 根据分段找出远点4级时间槽的落点
if ((time|(mask-1))==(current_time|(mask-1))) {
break;
}
mask <<= TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
}
// 加入对应的时间槽
link(&T->t[i][((time>>(TIME_NEAR_SHIFT + i*TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)) & TIME_LEVEL_MASK)],node);
}
}
static void
timer_add(struct timer *T,void *arg,size_t sz,int time) {
struct timer_node *node = (struct timer_node *)skynet_malloc(sizeof(*node)+sz);
memcpy(node+1,arg,sz);
SPIN_LOCK(T); // 加锁
node->expire=time+T->time; // 计算出超时时间点
add_node(T,node);
SPIN_UNLOCK(T); // 解锁
}
int
skynet_timeout(uint32_t handle, int time, int session) {
if (time <= 0) { // 超时时间到 直接发送消息
struct skynet_message message;
message.source = 0;
message.session = session;
message.data = NULL;
message.sz = (size_t)PTYPE_RESPONSE << MESSAGE_TYPE_SHIFT;
if (skynet_context_push(handle, &message)) {
return -1;
}
} else {
struct timer_event event;
event.handle = handle;
event.session = session;
timer_add(TI, &event, sizeof(event), time); // 加入5级时间槽
}
return session;
}
- skynet中的嵌入式语言(lua)调用定时器,最终到skynet_timeout这里,如果设置的超时时间小于等于0,立即处理,否则进入5级时间槽处理流程。
- 计算出超时时间点,通过时间掩码比较当前时间和超时时间可以知道槽的落点,最终根据落点的时间段确定哈希值把超时任务加入到链表中。
- tips:基于当前服务器时间,加上超时的时间,发生变化的最高分段的时间段就是该超时事的落点时间段。
#define TIME_NEAR_SHIFT 8
#define TIME_NEAR (1 << TIME_NEAR_SHIFT)
#define TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT 6
#define TIME_LEVEL (1 << TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT)
#define TIME_NEAR_MASK (TIME_NEAR-1) // 近点时间掩码
#define TIME_LEVEL_MASK (TIME_LEVEL-1) // 远点4级时间分段掩码
// 移动时间槽
static void
timer_shift(struct timer *T) {
int mask = TIME_NEAR;
uint32_t ct = ++T->time; // 滴答自增
// 溢出,移动最后一个时间分段
if (ct == 0) {
move_list(T, 3, 0);
} else {
uint32_t time = ct >> TIME_NEAR_SHIFT;
int i=0;
// 6/6/6/6 远点4级,滴答增加引起变化的时间分段,前向移动
while ((ct & (mask-1))==0) {
int idx=time & TIME_LEVEL_MASK;
if (idx!=0) {
move_list(T, i, idx);
break;
}
mask <<= TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
time >>= TIME_LEVEL_SHIFT;
++i;
}
}
}
// 执行
static inline void
timer_execute(struct timer *T) {
int idx = T->time & TIME_NEAR_MASK;
// 执行时间近点超时事件通知
while (T->near[idx].head.next) {
struct timer_node *current = link_clear(&T->near[idx]); // 清除超时时间事件
SPIN_UNLOCK(T);
// dispatch_list don't need lock T
dispatch_list(current);
SPIN_LOCK(T);
}
}
static void
timer_update(struct timer *T) {
SPIN_LOCK(T);
// try to dispatch timeout 0 (rare condition)
timer_execute(T); // 执行
// shift time first, and then dispatch timer message
timer_shift(T); // 移动
timer_execute(T); // 执行
SPIN_UNLOCK(T);
}
void
skynet_updatetime(void) {
uint64_t cp = gettime();
if(cp < TI->current_point) { // 时钟混乱
skynet_error(NULL, "time diff error: change from %lld to %lld", cp, TI->current_point);
TI->current_point = cp;
} else if (cp != TI->current_point) {
uint32_t diff = (uint32_t)(cp - TI->current_point); // 每次唤醒与上次的时间差(10ms一个滴答)
TI->current_point = cp;
TI->current += diff;
int i;
for (i=0;i<diff;i++) {
timer_update(TI);
}
}
}
- 周期性检查执行近点的超时事件timer_execute,然后根据滴答数的变化移动远点超时事件节点,最后再检查一次近点的超时事件,防止遗漏刚移进来的事件节点。
- 滴答数溢出后,移动末级时间段的事件节点,因为溢出表明已经最高为字节都发生了变化,最高为节点对应第三级的远点时间段。
- 通过时间段划分6/6/6/6/8,每个周期只需要通过近点时间掩码将当前时间映射到近点时间哈希链表中就可以找出是否有事件需要执行,每次只有当远点的4级分段的字节位发生变化时才需要检查移动事件节点,最终当事件节点移动到近点时,说明其高24位的和当前时间的高24位一致,逻辑又回到之前的近点时间判断,只需要判断低8位只可以知道是否超时,并且通过低8位很快映射到时间节点上。所以整个定时器模块的执行效率非常的高。
网络模块
create_thread(&pid[2], thread_socket, m); //启动网络模块
网络模块比较复杂,提供了tcp,udp的网络的接口,内容比较多且与lua层交互密切,后面单独章节讲述。
工作模块
create_thread(&pid[i+3], thread_worker, &wp[i]); // 启动工作线程
工作模块根据配置的thread,启动相应的数量的工作线程。skynet的业务逻辑的基本单位是服务,每个服务对象都是嵌入式语言(这里指lua)的宿主主机,但是服务的本质计算能力是由工作线程提供的。服务的调度方式采用先到先得,没有优先级,不让出,所以服务阻塞,会影响的整个skynet的计算能力,毕竟工作线程的数量是有限的。工作线程通过处理两级队列的方式驱动服务的运行。
struct message_queue *
skynet_context_message_dispatch(struct skynet_monitor *sm, struct message_queue *q, int weight) {
if (q == NULL) {
q = skynet_globalmq_pop(); // 一级队列pop出一个节点,实质就是服务对象的独立消息队列。
if (q==NULL)
return NULL;
}
uint32_t handle = skynet_mq_handle(q);
// 检查服务对象的正确性
struct skynet_context * ctx = skynet_handle_grab(handle);
if (ctx == NULL) {
struct drop_t d = { handle };
skynet_mq_release(q, drop_message, &d);
return skynet_globalmq_pop();
}
int i,n=1;
struct skynet_message msg;
for (i=0;i<n;i++) {
// 服务消息队列消息出列
if (skynet_mq_pop(q,&msg)) {
skynet_context_release(ctx);
return skynet_globalmq_pop();
} else if (i==0 && weight >= 0) {
n = skynet_mq_length(q);
n >>= weight;
}
// 消息队列过载警示
int overload = skynet_mq_overload(q);
if (overload) {
skynet_error(ctx, "May overload, message queue length = %d", overload);
}
// 监视器处理
skynet_monitor_trigger(sm, msg.source , handle);
if (ctx->cb == NULL) {
skynet_free(msg.data);
} else {
// 通知宿主上的lua处理事件
dispatch_message(ctx, &msg);
}
skynet_monitor_trigger(sm, 0,0);
}
assert(q == ctx->queue);
struct message_queue *nq = skynet_globalmq_pop();
if (nq) {
// If global mq is not empty , push q back, and return next queue (nq)
// Else (global mq is empty or block, don't push q back, and return q again (for next dispatch)
skynet_globalmq_push(q);
q = nq;
}
skynet_context_release(ctx);
return q;
}
static void *
thread_worker(void *p) {
struct worker_parm *wp = p;
int id = wp->id;
int weight = wp->weight;
struct monitor *m = wp->m;
struct skynet_monitor *sm = m->m[id];
skynet_initthread(THREAD_WORKER);
struct message_queue * q = NULL;
while (!m->quit) {
q = skynet_context_message_dispatch(sm, q, weight);
// 一级队列为空时,线程休眠,通过调节变量控制等待外部唤醒
if (q == NULL) {
if (pthread_mutex_lock(&m->mutex) == 0) {
++ m->sleep;
// "spurious wakeup" is harmless,
// because skynet_context_message_dispatch() can be call at any time.
if (!m->quit)
pthread_cond_wait(&m->cond, &m->mutex);
-- m->sleep;
if (pthread_mutex_unlock(&m->mutex)) {
fprintf(stderr, "unlock mutex error");
exit(1);
}
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
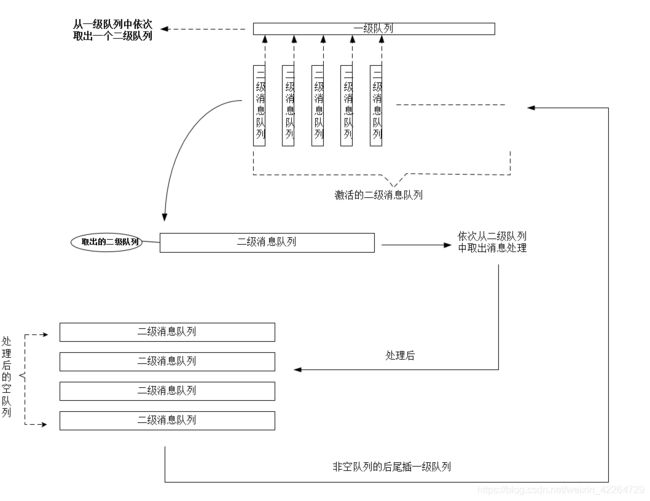
- 工作方式:一级队列依次pop出服务消息队列,然后依次把消息队列的消息pop出来,最终把消息投递到宿主的lua中处理,处理后把消息队列不为空的push回一级队列。当一级队列为空时线程进入睡眠,等待外部唤醒。
1) 两级队列的处理方式:每个线程取不到同一个服务消息队列,即保证了服务消息处理不会出现并发的情况,这个最大的意义在于,即使再多线程中服务消息队列的操作也不会出现竞争,所以可以不加锁,减少了线程锁的碰撞而损耗的时间,大大提高了工作效率。
2)一级队列为空,即所有消息都处理完毕,通过条件变量处理cpu空转,让出cpu使线程休眠。
3)当线程休眠时,通过外部唤醒:一个是socket消息触发唤醒,一个是timer周期性唤醒。
下图是两级队列的处理流程:
总结
skynet从配置初始化,再到基本资源初始化,最终一步一步启动主要的模块。当然,这里只是简单的描述整个启动过程且尽量不涉及c层到lua层的控制权交接,这里是为了单纯的讲述c部分的内容,发散到lua的话涉及c与lua交互内容且还离不开这些基础模块的作用,所以先单纯描述c部分的工作,后续对lua层的逻辑描述才更清晰。