哈夫曼树与哈夫曼编码(c++实现)
哈夫曼树与哈夫曼编码
- 一、字符的机内表示
- 二、 哈夫曼树的概念
- 三、 哈夫曼树的理论实现
- 四、 哈夫曼树的代码实现
-
- 理论设计
- 代码实现
- 代码总结和测试
- 更正日志
一、字符的机内表示
在计算机中每个西文字符是用一个编码表示,大多数编码系统都采用等长编码,如ASCII编码
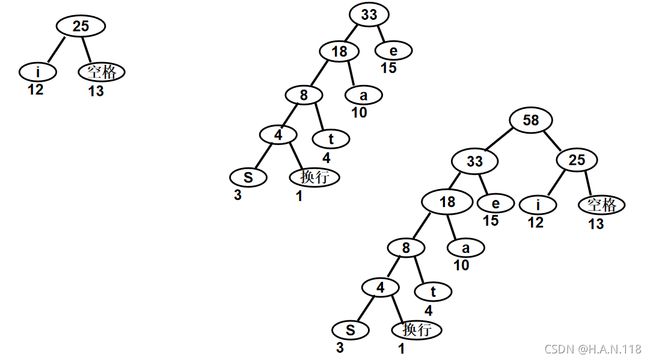
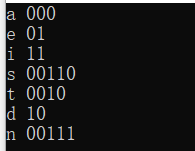
例如在某段文本中用到了下列字符,括号中是它们出现的频率:a(10), e(15), i(12), s(3), t(4), 空格(13), 换行(1)。如采用定长编码,7个不同的字符至少要用3位编码。
下图给出了一种编码对应方法:

上述编码形式可以对应下面的二叉树,左支为0,右枝为1

- 总存储量:3*(10+15+12+3+4+13+1)= 3*58 = 174 bit
很显然,将换行上移一层可以减少存储量

不等长编码可以减少存储量
两种编码方式对比:

右侧所对应的编码方式:

如何构造这个使所用存储空间最小的编码,便引出了哈夫曼树的概念
二、 哈夫曼树的概念
哈夫曼树是一棵最小代价的二叉树,在这棵树上,所有的字符都包含在叶结点上,要使得整棵树的代价最小,显然权值大的叶子应当尽量靠近树根,权值小的叶子可以适当离树根远一些。
一些相关概念定义:
- 两个结点间的路径长度为其路径上的分支总数
- 二叉树的路径长度为根到树中各个结点的路径长度之和
- 加权路径长度特指从根结点到各个叶子结点路径上的分支数乘以该叶子的权值之和
- 使WPL达到最小的二叉树,称为最优二叉树
W P L = ∑ k = 1 n w k L k WPL=\sum_{k=1}^nw_kL_k WPL=k=1∑nwkLk
三、 哈夫曼树的理论实现
构建方法:
- 给定一个具有 n n n个权值 { w 1 , w 2 , … … … w n } \{ w1,w2,………wn \} {w1,w2,………wn}的结点的集合 F = { T 1 , T 2 , ⋯ T n } F=\{T1,T2,\cdots Tn\} F={T1,T2,⋯Tn}
- 初始时,设集合 A = F。
- 执行 i = 1 至 n -1 的循环,在每次循环时执行以下操作:
- 从当前集合中选取权值最小、次最小的两个结点,以这两个结点作为内部结点 bi 的左右儿子,bi 的权值为其左右儿子权值之和。
- 在集合中去除这两个权值最小、次最小的结点,并将内部结点bI 加入其中。这样,在集合A中,结点个数便减少了一个。
- 这样,在经过了n-1 次循环之后,集合A中只剩下了一个结点,这个结点就是根结点。
存储方法:
- 在哈夫曼树中,每个要编码的元素是一个叶结点,其它结点都是度数为2的节点
- 一旦给定了要编码的元素个数,由 n 0 = n 2 + 1 n0=n2+1 n0=n2+1可知哈夫曼树的大小为 2 n − 1 2n-1 2n−1(在二叉树中,度为0的节点个数=度为1的节点个数+1,具体证明见https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51352359/article/details/121089511?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501)
- 哈夫曼树可以用一个大小为2n的数组来存储。0节点不用,根存放在节点1。叶结点依次放在n到2n-1下标位置
- 每个数组元素保存的信息:结点的数据、权值和父结点和左右孩子的位置

生成过程: - 初始化数组为0
- 找权值最小且父节点为0的两个节点,权值相加并填入前面空的序列
- 写左子和右子下标
- 给左子和右子添上父亲下标
编码的产生:
对每个结点,从叶子往根推进,是左枝加0,是右枝加1

四、 哈夫曼树的代码实现
理论设计
- 存储设计
一个节点需存储:节点的数据、权值、父节点和左右孩子的位置
利用一个节点数组以及一个整形数据成员,保存数组的大小 - 操作
构建一个哈夫曼树
获取树上节点的哈夫曼编码
代码实现
- 哈夫曼树类的定义
template<class Type>
class hfTree {
private:
struct Node {
Type data;//节点值
int weight;//节点的权值
int parent, left, right;//父节点下标,左右孩子下标
};
Node* elem;
int length;//数组长度
public:
struct hfCode {
Type data;
string code;//哈夫曼编码
};
hfTree(const Type* x, const int* w, int size);
void getCode(hfCode result[]);
~hfTree() {
delete[]elem;
}
};
- 构造函数
//构造函数
template<class Type>
hfTree<Type>::hfTree(const Type* v, const int* w, int size) {
const int MAX_INT = 32767;
int min1, min2;//最小树、次小数的权值
int x, y;//最小树、次最小树的下标
//置初值
length = 2 * size;//数组长度
elem = new Node[length];
for (int i = size; i < length; ++i) {
elem[i].weight = w[i - size];
elem[i].data = v[i - size];
elem[i].parent = elem[i].left = elem[i].right = 0;
}
//构造新的二叉树
for (int i = size - 1; i > 0; --i) {
min1 = min2 = MAX_INT;
x = y = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; ++j) {
if (elem[j].parent == 0)
if (elem[j].weight < min1) {//如果有元素的权值比当前最小值小,则更新次小值和最小值
min2 = min1;
min1 = elem[j].weight;
y = x;
x = j;
}
else if (elem[j].weight < min2) {//元素的权值大于当前最小值但小于次小值,更新次小值
min2 = elem[j].weight;
y = j;
}
}
elem[i].weight = min1 + min2;
elem[i].left = y;//次小值(作为左子)的下标
elem[i].right = x;//最小值的下标
elem[i].parent = 0;
elem[x].parent = i;
elem[y].parent = i;
}
}
- 求哈夫曼编码
伪代码如下:
getCode(hfCode<Type> result[]) //求哈夫曼编码的伪代码
{
for (int i = size; i < length; ++i)
{ result[i - size].data = elem[i].data;
result[i - size].code = "";
p = elem[i].parent; s = i;
while (p不等于0) {
if (p的左孩子是 == s) result[i - size].code 前添加‘0’;
else result[i - size].code 前添‘1’;
移到上一层;
}
}
}
代码如下:
//求哈夫曼编码
template<class Type>
void hfTree<Type>::getCode(hfCode result[]) {
int size = length / 2;
int p, s;//s是正在处理的节点,p是s的父节点下标
for (int i = size; i < length; ++i) {
result[i - size].data = elem[i].data;
result[i - size].code = "";
p = elem[i].parent;
s = i;
while (p) {//即当p!=0时
if (elem[p].left == s) {//如果s所对应的数为p的左子,则加0
result[i - size].code = '0' + result[i - size].code;
}
else result[i - size].code = '1' + result[i - size].code;
s = p;
p = elem[p].parent;
}
}
代码总结和测试
- 全代码总结hfTree.h
#include- 代码测试main.cpp
#include更正日志
- 在构造新的二叉树的代码部分,被循环整蒙了,一定要注意每个括号的作用位置!!!