Diffusion Model: DDPM
本文相关内容只记录看论文过程中一些难点问题,内容间逻辑性不强,甚至有点混乱,因此只作为本人“备忘”,不建议其他人阅读。
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11239
DDPM
一、基于  已知的情况下,
已知的情况下, 分布的推导过程:推导过程中,直接递归迭代即可。同时,过程中使用了 —— 两个高斯分布的和也满足高斯分布,其中均值为两个高斯分布均值的和,方差为两个高斯分布方差的和。
分布的推导过程:推导过程中,直接递归迭代即可。同时,过程中使用了 —— 两个高斯分布的和也满足高斯分布,其中均值为两个高斯分布均值的和,方差为两个高斯分布方差的和。
二、逆向过程中,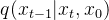 分布求解
分布求解
进一步根据 1 中的结果可得:
公式 9 中的 ![]() 就是 diffusion model 需要估计的噪声均值,而噪声的方式是由
就是 diffusion model 需要估计的噪声均值,而噪声的方式是由 ![]() 或者
或者 ![]() 直接得到的。
直接得到的。
三、具体训练过程:训练过程比较直接,利用 一 中的公式即可。
https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/models/diffusion/ddpm.py L274
def q_sample(self, x_start, t, noise=None):
noise = default(noise, lambda: torch.randn_like(x_start))
return (extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape) * x_start +
extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape) * noise)
def get_loss(self, pred, target, mean=True):
if self.loss_type == 'l1':
loss = (target - pred).abs()
if mean:
loss = loss.mean()
elif self.loss_type == 'l2':
if mean:
loss = torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(target, pred)
else:
loss = torch.nn.functional.mse_loss(target, pred, reduction='none')
else:
raise NotImplementedError("unknown loss type '{loss_type}'")
return loss
# 输入参数说明:
# x_start:原始图像 x0
# t:当前扩散步数
# noise:噪声,需要注意这里的 noise 与 x_start 维度相同;具体含义是每个位置上元素都服从 0-1 高斯分布
def p_losses(self, x_start, t, noise=None):
# 生成第 t 步的高斯噪声
noise = default(noise, lambda: torch.randn_like(x_start))
# 根据本文 一 中推导的公式得到第 t 步加噪后的图像
x_noisy = self.q_sample(x_start=x_start, t=t, noise=noise)
# 模型预测结果,根据具体的设置,好像可以回归加的噪声,也可以直接回归原始图像
model_out = self.model(x_noisy, t)
loss_dict = {}
if self.parameterization == "eps":
# 模型估计噪声
target = noise
elif self.parameterization == "x0":
# 模型直接估计原始图像
target = x_start
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Paramterization {self.parameterization} not yet supported")
# 使用 L1 或者 L2 Loss 计算误差
loss = self.get_loss(model_out, target, mean=False).mean(dim=[1, 2, 3])
log_prefix = 'train' if self.training else 'val'
loss_dict.update({f'{log_prefix}/loss_simple': loss.mean()})
loss_simple = loss.mean() * self.l_simple_weight
loss_vlb = (self.lvlb_weights[t] * loss).mean()
loss_dict.update({f'{log_prefix}/loss_vlb': loss_vlb})
loss = loss_simple + self.original_elbo_weight * loss_vlb
loss_dict.update({f'{log_prefix}/loss': loss})
return loss, loss_dict四、具体生成(采样)过程:根据 二 中推导的公式,依次计算前一步图像的分布。
需要注意:
-
具体回归的均值的维度与图像维度完全相同,即图像每个位置(包括不同通道)都建模为高斯分布,均值就是无随机时图像应该有的“样子”。PS:具体是对 8 倍下采样的特征图进行采样;因此在最后需要接一个 decoder 将采样出的特征值上采样得到最终的图像。
- 因此,在 T=0 步得到的均值就是最终生成的图像;不过在 T> 0 步依据均值和方差进行采样,可能的原因是增加生成图像的多样性。
https://github.com/CompVis/stable-diffusion/blob/main/ldm/models/diffusion/ddpm.py L222
# 根据本文 二 中的公式计算 x_t-1 的均值和方差
def q_posterior(self, x_start, x_t, t):
posterior_mean = (
extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_mean_coef1, t, x_t.shape) * x_start +
extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_mean_coef2, t, x_t.shape) * x_t
)
posterior_variance = extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_variance, t, x_t.shape)
posterior_log_variance_clipped = extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_log_variance_clipped, t, x_t.shape)
return posterior_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance_clipped
def p_mean_variance(self, x, t, clip_denoised: bool):
model_out = self.model(x, t)
if self.parameterization == "eps":
x_recon = self.predict_start_from_noise(x, t=t, noise=model_out)
elif self.parameterization == "x0":
x_recon = model_out
if clip_denoised:
x_recon.clamp_(-1., 1.)
model_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance = self.q_posterior(x_start=x_recon, x_t=x, t=t)
return model_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance
# 基于估计的图像每个位置的均值 model_mean 和方差 model_log_variance 生成对应随机图像
@torch.no_grad()
def p_sample(self, x, t, clip_denoised=True, repeat_noise=False):
b, *_, device = *x.shape, x.device
model_mean, _, model_log_variance = self.p_mean_variance(x=x, t=t, clip_denoised=clip_denoised)
noise = noise_like(x.shape, device, repeat_noise)
# no noise when t == 0
nonzero_mask = (1 - (t == 0).float()).reshape(b, *((1,) * (len(x.shape) - 1)))
return model_mean + nonzero_mask * (0.5 * model_log_variance).exp() * noise
# 从 T 步 ——> T-1 步 ——> ... ——> 0 步,依次进行反向估计
@torch.no_grad()
def p_sample_loop(self, shape, return_intermediates=False):
device = self.betas.device
b = shape[0]
img = torch.randn(shape, device=device)
intermediates = [img]
for i in tqdm(reversed(range(0, self.num_timesteps)), desc='Sampling t', total=self.num_timesteps):
img = self.p_sample(img, torch.full((b,), i, device=device, dtype=torch.long),
clip_denoised=self.clip_denoised)
if i % self.log_every_t == 0 or i == self.num_timesteps - 1:
intermediates.append(img)
if return_intermediates:
return img, intermediates
return img
# 采样入口函数,batch_size 一次生成的图像数量
@torch.no_grad()
def sample(self, batch_size=16, return_intermediates=False):
image_size = self.image_size
channels = self.channels
return self.p_sample_loop((batch_size, channels, image_size, image_size),
return_intermediates=return_intermediates)



