JS实现数据结构与算法
队列
1、普通队列
利用数组push和shif 就可以简单实现
2、利用链表的方式实现队列
class MyQueue {
constructor(){
this.head = null
this.tail = null
this.length = 0
}
add(value){
let node = {value}
if(this.length === 0){
this.head = node
this.tail = node
}else{
this.tail.next = node
this.tail = node
}
this.length++
}
delete(){
if(this.length <= 0) {return null}
let value = null
if(this.length === 1){
value = this.head.value
this.head = null
}else{
value = this.head.value
this.head = this.head.next
}
return value
this.length--
}
}
// 功能测试
const queue = new MyQueue()
queue.add(100)
console.log('length1', queue.length) // 1
queue.add(200)
console.log('length2', queue.length) // 2
console.log('delete1', queue.delete()) // 100
queue.add(300)
console.log('length3', queue.length) // 2
console.log('delete2', queue.delete()) // 200
console.log('length4', queue.length) // 1
console.log('delete3', queue.delete()) // 300
console.log('length5', queue.length) // 0
栈
1、普通栈
2、用Js链表实现入栈和出栈
class MyNode{
//这个类似于一个替换值t
constructor(val){
this.value = val
this.next = null
}
}
class MyStack{
constructor(){
this.stack = null
}
add(val){
const node = new MyNode(val)
//首先将入栈的值给t.value里:{value:100,next:null}
node.next = this.stack
//其次将上一个入栈的值赋值给t.next
//形成新入的值在最外层,{value:200,next:{value:100,next:null}}
this.stack = node
//最后将t的整体包裹了新入栈的数据的对象赋值给当前的内容
console.log('this.next',this.stack);
}
delete(){
const t = this.stack
//当前栈已空,直接返回,t是 MyStack.stack
if(t === null){
return '当前栈已空'
}else{
//将内层的next的赋值给原本的值,实现出栈
this.stack = t.next
return t.value
}
}
}
const stack = new MyStack()
stack.add(100)
stack.add(200)
console.log('delete',stack.delete());
console.log('delete',stack.delete());
console.log('delete',stack.delete());3、用栈来翻转字符串,只能用push和pop两个API
function onStack(val){
let arr1 = []
//入栈
for(let i of val){
arr1.push(i)
}
let arr2 = ''
let popValue = null
//出栈
while(arr1.length){
popValue = arr1.pop()
arr2 += popValue
}
return arr2
}
console.log(onStack('12345'));排序
1、冒泡排序
2、选择排序
3、快速排序
注意:快速排序的规则就是先找中间的数,比中间大的放在左边,小的放在右边,再去对两边的数进行同样的操作。
注意:循环一次是O(n),双层循环是O(n^2),二分查找O(logn),快速排序是O(n*logn)
function quickSort(arr) {
if(arr.length <= 0){
return arr
}
let midIndex = Math.floor(arr.length/2)
let midValue = arr[midIndex]
let left = []
let right = []
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(i !== midIndex){
if(midValue > arr[i]){
left.push(arr[i])
}else{
right.push(arr[i])
}
}
}
return [...quickSort(left),midValue,...quickSort(right)]
}
let arr = [12, 45, 78, 25, 12, 3, 45, 74, 1, 14, 85]
console.log(quickSort(arr));
查找
1、二分查找
注意:二分查找首先是查找的内容是已排序
时间复杂度是O(logn)
需要找的数先去找数组中中间的值,去作对比,大于就往右边找,小于就往左边找。下一次继续这个操作。
方法:递归或循环
求中间元素的值mid,即:mid = left + (right - left) / 2 得到中间下标
function find(arr, x) {
let left = 0
let right = arr.length - 1
let mid = 0
while (left <= right) {
mid = Math.floor(left + (right - left) / 2)
if (arr[mid] === x) {
return {
type: true,
position: mid
}
} else if (arr[mid] < x) {
left = mid + 1
} else {
right = mid - 1
}
}
return {
type: false,
position: null
}
}
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
let x = 3
console.log(find(arr, x));
树
1、树的优先遍历
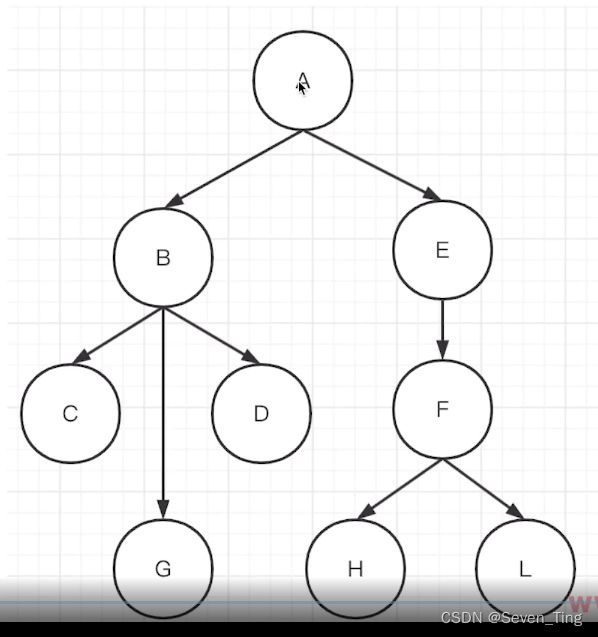
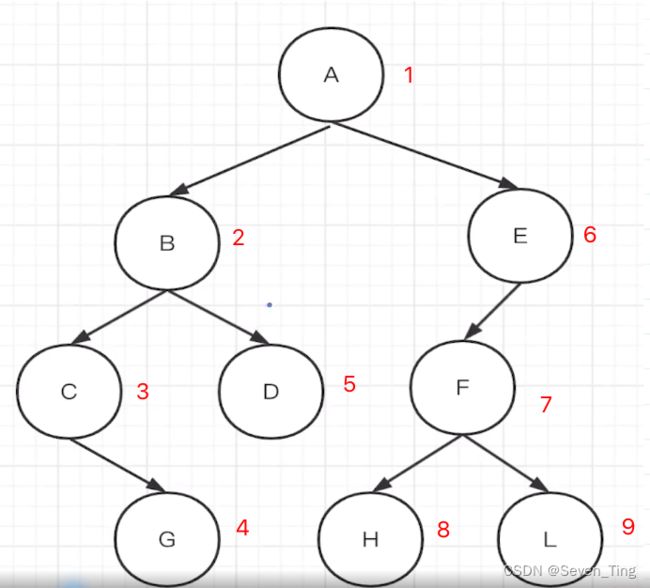
一、树的深度优先结果:ABCGDEFHL
注意:
- 访问根节点;
- 对根节点的
children持续进行深度优先遍历(递归);
function dfs(root) {
console.log(root.value)
if(root.children){
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
}
dfs(tree) // 这个tree就是前面定义的那个树
二、广度优先遍历结果:ABECGDFHL
注意:广度优先遍历是,先遍历根节点,再同层从左到右遍历
注意:
- 创建要给队列,把根节点入队;
- 把队头出队并访问;
- 把队头的
children依次入队; - 重复执行2、3步,直到队列为空。
function deep(tree){
let queue = []
queue.push(tree)
while(queue.length > 0){
const node = queue.shift()
console.log(node.value);
if(node.children){
node.children.forEach(val => {
queue.push(val)
})
}
}
}
2、二叉树
一、用JS对象表达树
let tree = {
value:'A',
left:{
value:'B',
left:{
value:'C',
left:null,
right:{
value:'G',
left:null,
right:null
}
},
right:{
value:'D',
left:null,
right:null
}
},
right:{
value:'E',
left:{
value:'F',
left:{
value:'H',
left:null,
right:null
},
right:{
value:'L',
left:null,
right:null
}
},
right:null
}
}3、二叉树的前、中、后序遍历
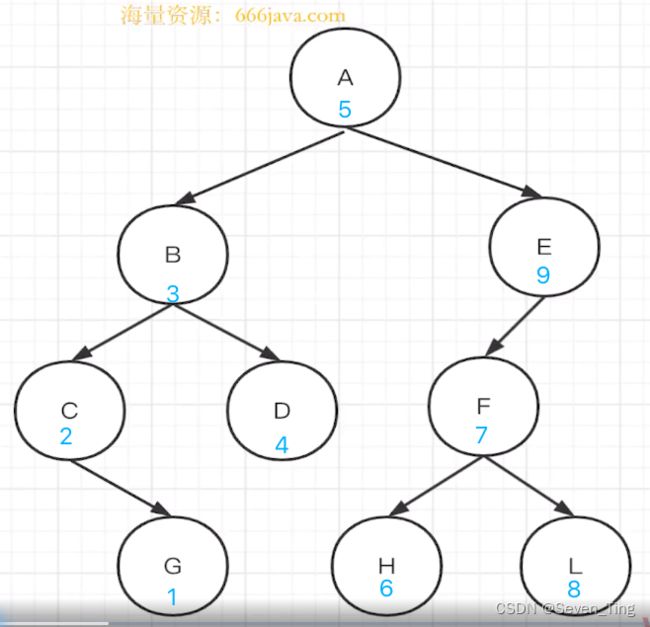
1、前序遍历:中、左、右
2、中序遍历:左、中、右
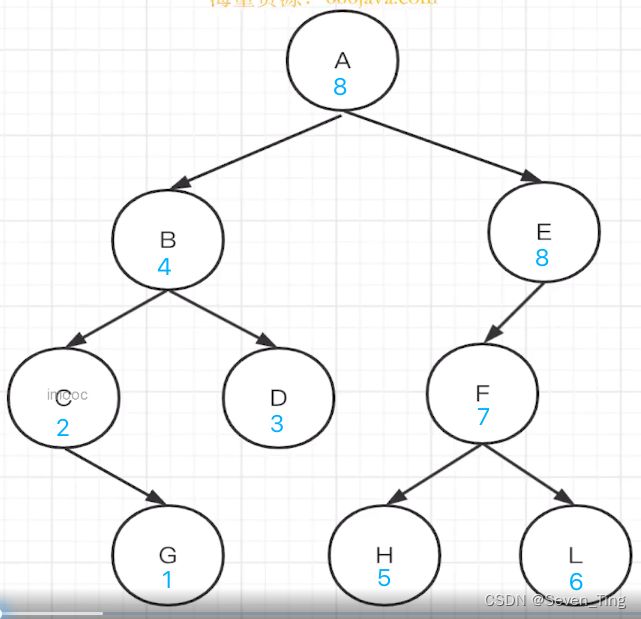
3、后序遍历:左、中、右