数据库系统和信息管理知识复习——第一章数据库概述(Introduction)
目录:
0.前言
1.数据(Data)与信息(Information)
1.1数据库系统的组成
2.数据库系统与信息管理
2.1Manual Handling(人工处理)
2.2 File Systems(文件系统)
2.3 DatabaseSystem(数据库系统)
3.数据库的历史
3.1 1950s and early 1960s
3.2 Late 1960s and 1970s
3.3 1980s
3.4 1990s
3.5 2000s
3.6 2010s
4.数据库模型(Database Model)
4.1概念模型Conceptual Model
4.2 机器模型Machine Model
5.数据模式(Data Schemas)
6.数据库设计(DB Design)
7.数据库架构(Database Architecture)
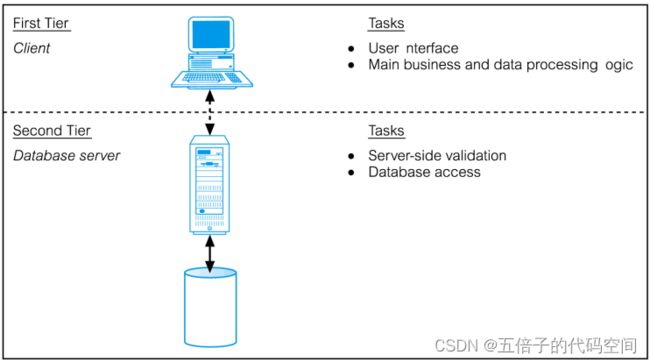
7.1Traditional Two-Tier Client-Server
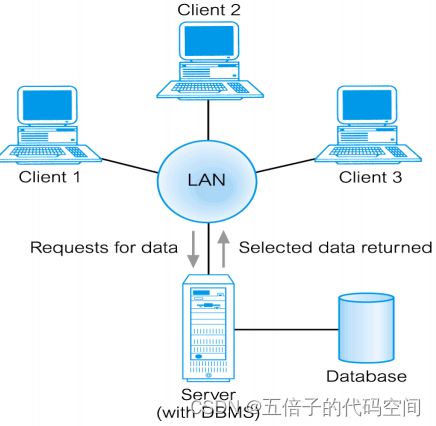
7.2 Three-Tier Client-Server
0.前言
本系列文章旨在记录数据库系统的知识点,可用于期末复习,笔者理解尚浅,文中不正之处静待批正。加粗高亮部分为重点。
1.数据(Data)与信息(Information)
数据(Data):是符号(symbol),是事实(facts)、统计数字(statistics)、信息的载体(item of information),总是数字的(numeric)。
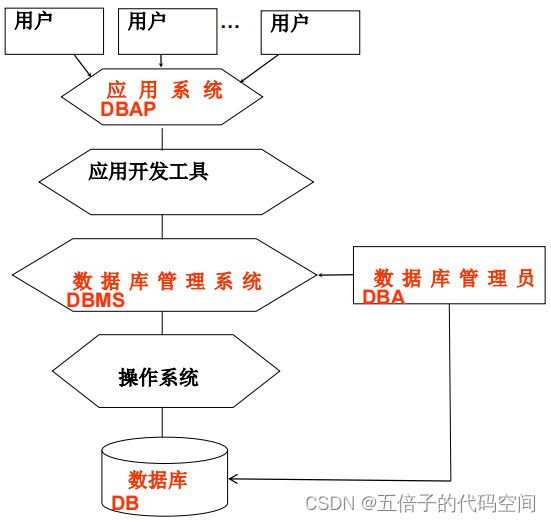
数据库系统(Database system):是一个相互关联(interrelated)的数据及一些程序的集合(collection),允许用户访问(access)和修改(modify)这些数据,用于管理一个特定企业或组织大量的信息。
1.1数据库系统的组成
1.DB(数据库)
有组织的数据集合,电子化的地存储、访问。
数据库中的数据是高价值的(highly valuable),拥有大量数据(relatively large),允许多用户访问,并且同时访问(accessed by multiple users and applications, often at the same time)。
2.DBMS(数据库管理系统)
是数据库系统的核心(engine of DBS)。
是允许用户定义(define)、创造(create)、维护(maintain)及控制访问(control)DB的软件系统。
DBMS的初始目的是方便(convenient)、高效地(efficinet)存储检索DB的信息。
是系统软件。
- A User-Accessible Catalog
- Data Storage, Retrieval, and Update
- Transaction Support
- Concurrency Control Services
- Recovery Services
- Integrity Services
- Services to Promote Data Independence
- Authorization Services
- Support for Data Communication
- Utility Services
- 存储管理器(Storage manager)——提供接口
- 查询处理器(Query processing)
- 事务管理器(Transaction manager)——保证DB的一致性(consistency)
3.DBAP(数据库应用)
比如bank,university
4.DBA(数据库管理员)
数据库与程序的核心控制者。
Summary:不同的描述可能对应不同的意思。
- 一系列相互关联的数据(collection of interrelated data )——DB
- 用于访问数据的一组程序(set of programs)——DBMS
- 一个对使用数据既方便又高效的环境(an environment)——DBAP
2.数据库系统与信息管理
- Paper tape(纸带)
- Tape(磁带)
- rotating disk(磁盘)
- Flash memory(闪存)
数据库管理系统:
- Manual Handling(人工处理)
- File Systems(文件系统)
- DatabaseSystem(数据库系统)
2.1Manual Handling(人工处理)
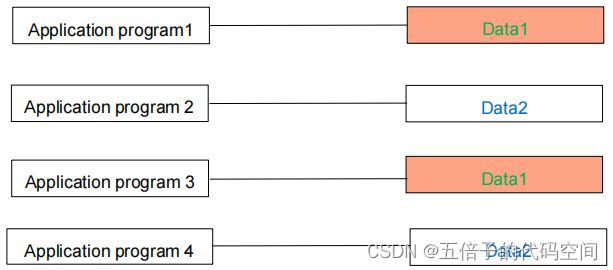
数据非持久性保留(not a persistent save),非共享(not shared),有大量冗余(large redundancy),不独立(not independent),完全依赖于程序(completely dependent
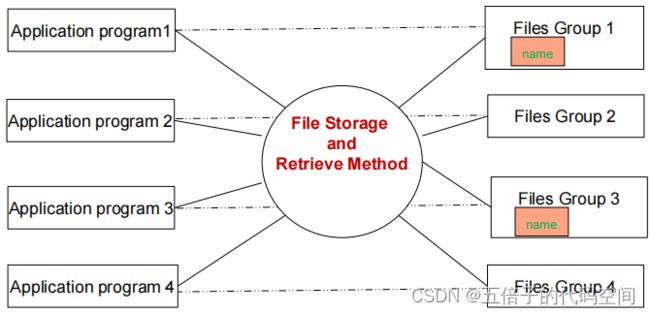
2.2 File Systems(文件系统)
数据持久性保留(persistent save),可共享(shared),仍有大量冗余(large redundancy),不独立(not independent),完全依赖于程序(completely dependent on the program)。
使用文件系统存数据的缺点:
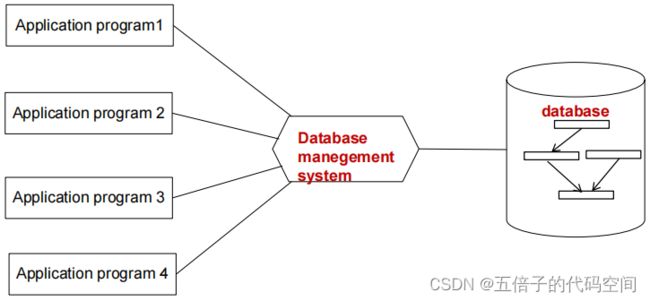
2.3 DatabaseSystem(数据库系统)
数据持久性保留(persistent save),可共享(shared),只有少量冗余(little redundancy),独立(independent),完全不依赖于程序(completely not dependent on the program)。
3.数据库的历史
3.1 1950s and early 1960s
- 使用磁带(Tapes provided only sequential access)
3.2 Late 1960s and 1970s
- 使用硬盘直接访问数据(Hard disks allowed direct access to data)
- 使用网络和分层数据模型(Network and hierarchical data models)
- Ted Codd定义了关系数据模型(Ted Codd defines the relational data model)
- 高性能事务处理(High-performance transaction processing)
3.3 1980s
- SQL成为行业标准
- 并行和分布式数据库系统(Parallel and distributed database systems)
- 面向对象的数据库系统(Object-oriented database systems)
3.4 1990s
- 决策支持和数据挖掘应用(Large decision support and data-mining applications)
- 数据仓库(data warehouses)
3.5 2000s
- 大数据存储系统(Big data storage systems),“NoSQL”系统
- 大数据分析:超越SQL(Big data analysis: beyond SQL)
3.6 2010s
- 分布式高可用(SQL front end to Map Reduce systems)
- 大规模并行数据库系统高性能(Massively parallel database systems)
- 多核内存数据库高性能(Multi-core main-memory databases)
4.数据库模型(Database Model)
一个用于描述数据、数据关系、数据语义(semantic)及一致性限制(consistency constraints)的概念(conceptual)工具的集合。
目的:用易于理解的方式表示数据
组成:数据结构(structural part)
数据操纵(manipulative part)
完整性规则(possibly a set of integrity rules)
4.1概念模型Conceptual Model
实体关系数据模型
4.2 机器模型Machine Model
- Hierarchical model
- Network model
- Relational model
- Object-based data models (Object-oriented and Object-relational)
- Semistructured data model (XML,JSON)
- Unstructured model(graph, document) ……
有且只有一个根结点(结点没有双亲结点),根以外的其它结点只有一个双亲结点。
b.Network Data Model(网络数据模块)
一个结点有多个双亲
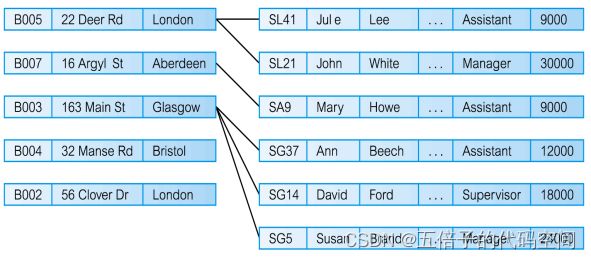
c.Relational Model(关系模型)
5.数据模式(Data Schemas)
隐藏数据结构的复杂性,以向用户表示数据库中数据的多个数据抽象级别。
schema:数据库的逻辑结构,类似于type
instance:数据库在特定时间点的实际内容,类似于value
三层模式:
①view level/external schema(视图模式/外模式)
数据库的局部视角(local view),能够看见和使用的局部数据的逻辑结构和特征的描述。
②logical level/conceptual schema(逻辑模式/模式/概念模式)
数据库的整体逻辑结构(overall logical structure),全体数据的逻辑结构和特征的描述,是所有用户的公共数据视图。
③physical level/internal schema(物理模式/存储模式/内模式)
数据库的整体物理结构(overall physical structure),数据再数据库系统内部的表示,对数据的物理结构和存储方式的描述。
Logical Data Independence(逻辑数据独立性)
外部模式不受概念模式变化的影响
例:概念模式改变不需要改变外部模式或重写应用程序