SpringBoot 配置文件
目录
配置文件的作用
配置文件的格式
.properties文件说明
基本语法
读取配置文件
缺点分析
.yml 配置文件说明
优点分析
基本语法
使用yml连接数据库
yml配置不同数据类型及null
yml配置读取
value值加单双引号
yml对象
yml配置集合类
properties VS yml
SpringBoot 有几种读取配置文件的方法?
配置文件的作用
整个项目中所有重要的数据都是在配置文件中配置的, 例如:
- 数据库的连接信息, 包括用户名和密码的设置
- 项目的启动端口
- 第三方系统的调用密钥等信息
- 用于发现和定位问题的普通日志和异常日志等
想象一下如果没有配置信息, 那么springBoot项目就不能连接和操作数据库, 甚至是不能保存可以用于排查问题的日志, 所以配置文件是非常重要的.
配置文件的格式
配置文件spring boot分为以下两种:
- .properties
- .yml
如下图所示:
可以类比一下服装店的服装一样, 有两种不同的款式, properties相当于老款式, yml相当于新款式.
理论上将properties可以和yml一起存在于一个项目当中, 当properties和yml在一起的时候, 如果配置文件中出现了同样的配置, 比如properties和yml中都配置了server.port, 那么这个时候会以properties为主, 也就是properties的配置文件的优先级最高, 但是加载完.properties文件之后也会加载yml文件的配置信息
虽然理论上将properties可以和yml共存, 但实际业务当中, 我们通常会采用一种统一的配置文件格式, 这样可以更好的维护.
.properties文件说明
基本语法
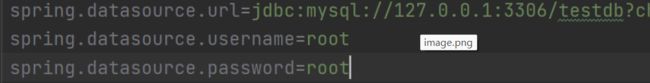
properties是以键值对的形式配置的, key 和 value之间是以 "=" 连接的, 例如:
server.port=8088
spring.datasource,url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=2222配置文件中使用#来添加注释
读取配置文件
如果在项目中, 想要主动的读取配置文件中的内容, 可以使用@Value注解来实现, @Value注解使用${} 的格式来读取, 如下代码:
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TestValue {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("Read server port : " + port);
}
}
启动项目, 如下:
@Component 在springboot启动的时候会注入到框架当中, 注入到框架中会执行@PostConstruct初始化方法, 这个时候就会在控制台输出这个配置信息了.
缺点分析
properties配置文件中的配置是以键值对的形式出现的, 也就是key-value形式出现的, 可以对比java集合体系中的map, 如下图所示:
.yml 配置文件说明
yml是YAML的缩写, 全称为yet another markup language, 中文示意为另外一种标记语言
优点分析
- yml是一个可读性高, 写法简单, 易于理解, 它的语法和JSON类似
- yml支持多种数据类型, 他可以简单表达清单, 也就是数组, 散列表, 标量等数据形态,它使用空白符号缩进和大量依赖外观的特色, 特别适合用来表达或编辑数据结构, 各种配置文件
- yml 支持更多的编程语言, 它不只是java , 还可以使用在golang, php, python, ruby js, perl中
基本语法
yml是树形结构的配置文件, 它的基础语法是key: value, 注意这里的冒号和value之间有一个空格, 这个空格是不能省略的.
基础语法如下:
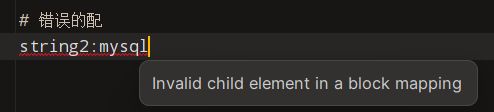
# 正确的配置方式
String: java
# 错误的配
string2:mysql显示无效子元素
使用yml连接数据库
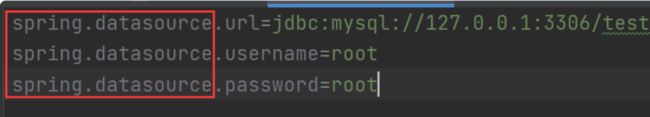
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: 2222和properties配置连接数据库进行对比:
server.port=8088
spring.datasource,url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=2222可以看见properties配置文件中有很多冗余项
yml配置不同数据类型及null
# 字符串
string.value: hello
# boolean: true or false
boolean.value: true
boolean.value2: false
# 整数
int.value: 12
int.value2: 0b1010_0111_1100_1111 # 二进制
# 浮点数
float.value: 3.1415926
float.value2: 31415926e-7 # 科学计数法
表示null:
null.value: ~yml配置读取
同样使用@Value("${value}") 来读取:
定义字符串:
进行读取:
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TestValue {
@Value("${string.value}")
private String value;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("read yml string.value : " + value);
}
}
启动项目, 输出:
尝试读取null.value: ~, 读取为null的配置和根本不存在的配置结果是否一致?
设置null:
null.value: ~读取null.value
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TestValue {
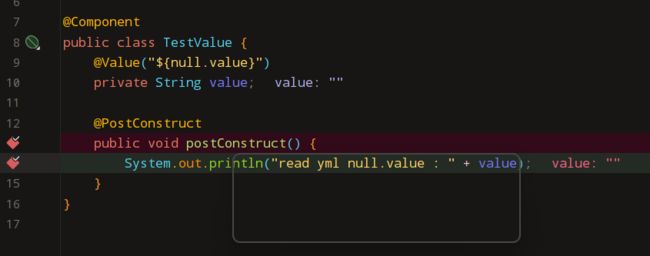
@Value("${null.value}")
private String value;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("read yml null.value : " + value);
}
}
输出:
通过调试发现, 获取的null.value为空字符串:
value值加单双引号
在配置文件中, 字符串时默认不用加上单双引号的, 如果加英文的单引号可以表示特殊含义.
例如尝试在application.yml中配置如下数组:
string:
str1: hello \n world
str2: 'hello \n world'
str3: "hello \n world"进行读取, 代码如下:
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TestValue {
@Value("${string.str1}")
private String str1;
@Value("${string.str2}")
private String str2;
@Value("${string.str3}")
private String str3;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("read str1:" + str1);
System.out.println("read str2:" + str2);
System.out.println("read str3:" + str3);
}
}
输出如下:
从上述结果可以看出:
- 字符串不需要加上单双引号
- 单引号会转义特殊字符, 特殊字符最终变成一个普通的字符串
- 双引号不会引起转义字符转义, 会表现出来特殊字符本来的意思
yml对象
对应java中的类, yml也可以配置对象, 例如下面配置一个Student对象:
stduent:
id: 2323
name: zhangSan
age: 18或者是写在一行, 使用{} 来表示:
student2: {id: 2323,name: zhangSan,age: 18}这个时候就不能使用@Value来读取对象了, 需要使用@ConfigurationProperties 来读取, 具体实现如下:
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student")
@Component
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
(注意这里的get和set方法不可以省略)
读取到yml中的配置文件之后, 就会注入此类对象. 然后再属性注入给下面的类:
package com.example.demo1.Test;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class TestValue {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}
输出--
yml配置集合类
例如如下代码:
listTable:
name:
- zhangsan
- lisi
- wangwu或者使用同一行的写法:
listTable2: {name: [zhangsan,lisi,wangwu]}集合的读取和对象的读取是一样的, 同样是使用@ConfigurationProperties来读取, 具体实现如下:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "listtable")
public class ListTable {
private List name;
public List getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(List name) {
this.name = name;
}
} 通过属性注入给:
@Component
public class TestValue {
@Autowired
private ListTable listTable;
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println(listTable.getName());
}
}启动项目, 输出如下--
properties VS yml
- properties 是以key=value的形式配置的, 而yml使用的是类似json的格式树形结构进行配置的,yml之间层级使用换行缩进的形式配置, key和value之间使用:间隔, 同时:后面需要有一个空格
- properties 为早期并且为默认的配置文件格式, 但其配置存在一定的冗余数据, 使用yml可以很好的解决数据冗余的问题
- yml通用性更好, 支持更多的语言, java, go, Python等, 如果是云服务器开发, 可以使用一份配置文件作为java和go的共同配置文件
- yml支持更多的数据类型
SpringBoot 有几种读取配置文件的方法?
Spring Boot 中读取配置文件有以下 5 种方法:
- 使用 @Value 读取配置文件。
- 使用 @ConfigurationProperties 读取配置文件。
- 使用 Environment 读取配置文件。
- 使用 @PropertySource 读取配置文件。
- 使用原生方式读取配置文件。
面试突击75:SpringBoot 有几种读取配置文件的方法? - 掘金