Python:字符串格式化
文章目录
- %用法
- 使用format方法进行格式化
%用法
| 格式字符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| %s | 字符串 |
| %c | 单个字符 |
| %d | 十进制整数 |
| %o | 八进制整数 |
| %x | 十六进制整数 |
| %e | 指数(基底写为e) |
| %E | 指数(基底写为E) |
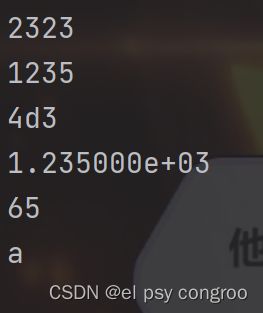
x = 1235
print('%o' % x)
print('%d' % x)
print('%x' % x)
print('%e' % x)
print('%s' % 65)
print('%c' % 'a')
使用format方法进行格式化
字符串类型格式化采用format()方法,基本使用格式是:
<模板字符串>.format(<逗号分隔的参数>)
(1)不带编号,即“{}”
(2)带数字编号,可调换顺序,即“{0}”、“{1}”(0是第一个参数,1是第二个参数)
(3)带关键字,即“{a}”、“{tom}”
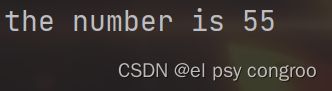
print("the number is {}".format(55))
format()方法中<模板字符串>的槽除了包括参数序号,还可以包括格式控制信息。此时,槽的内部样式如下:(借鉴https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27825451/article/details/105652244)
{<参数序号>: <格式控制标记>}
格式控制标记包括:<填充><对齐><宽度><,><.精度><类型>
| 填充 | 用于填充的单个字符 |
|---|---|
| 对齐 | < 左对齐 > 右对齐 ^ 居中 |
| 宽度 | 输出宽度 |
| , | 数字的千位分隔符,适用于整型 |
| 精度 | 浮点数小数部分的精度或字符串的最大输出长度 |
类别
| b | 输出整数的二进制方式 |
|---|---|
| d | 输出整数的十进制方式 |
| o | 输出整数的八进制方式 |
| x | 输出整数的字符小写十六进制方式 |
| X | 输出整数的字符大写十六进制方式 |
| c | 输出整数对应的 Unicode 字符 |
| e | 输出浮点数对应的小写字母 e 的指数形式 |
| E | 输出浮点数对应的大写字母 E 的指数形式 |
| f | 输出浮点数的标准浮点形式 |
| % | 输出浮点数的百分形式 |
| g | 指数(e)或浮点数 (根据显示长度) |
print("the number {0:*<8} in hex is: {0:#x} , the number {1:.2} ".format(1111111, 3.14159))
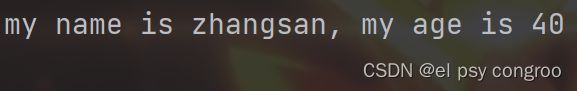
print("my name is {name}, my age is {age}".format(name="zhangsan",age=40))
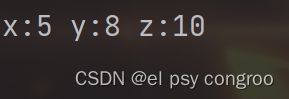
pos = (5, 8, 10)
print("x:{0[0]} y:{0[1]} z:{0[2]}".format(pos))
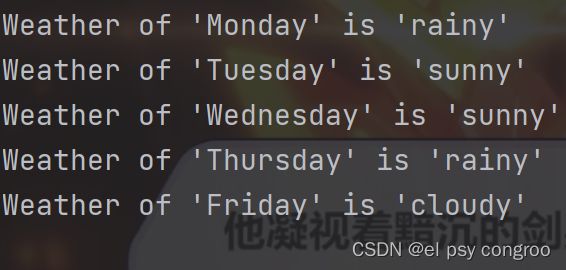
weather = [("Monday", "rainy"), ("Tuesday", "sunny"), ("Wednesday", "sunny"), ("Thursday", "rainy"), ("Friday", "cloudy")]
formatter = "Weather of '{0[0]}' is '{0[1]}'".format
for item in map(formatter, weather):
print(item)
for item in weather:
print(formatter(item))
print("{0:.4f}".format(1/3))
print("{0:.2%}".format(1/3))
print("{0:+>10.2%}".format(1/3))

从Python 3.6x 开始支持一种新的字符串格式化方式,在字符串前加字母 f ,含义与字符串对象format()方法类似