React Native | 启动流程
小手动一动,点赞转发加关注。微信搜索【大前端杂货铺】公众号关注大前端老司机带您遨游大前端知识的海洋。关注 Github https://github.com/big-frontend 还有大前端代码实践哦。
宿主应用的启动
在宿主应用的 Application 中必须实现 ReactApplication 接口的 getReactNativeHost 方法,该方法对整个宿主应用提供 ReactNativeHost 对象,ReactNativeHost 对象暴露了这么一些数据。
- React 应用的入口(getJSMainModuleName):e.g. “index.android”
- 要加载的 js bundle 的文件位置(getBundleAssetName/getJSBundleFile):e.g. “index.android.bundle”
- 自定义 js 执行器(getJavaScriptExecutorFactory):有苹果的 JavaScriptCore 还有 facebook 自研 Hermes
- Application 对象
- 用来管理 React 应用的 ReactInstanceManager 对象
- ReactPackage 集合(getPackages):暴露给 js 使用的 native api(NativeModule) 或者 native view
宿主应用的启动这里讲的主要是从点击应用启动图标到 Application#onCreate 这样一个流程,不包括 splash 启动页,因为对于有些 react native 应用 ReactActivit 就是启动页,这一块应该是属于 React 应用的启动。对于宿主应用的启动我们都比较熟悉就不展开,主要来讲讲 React 应用的启动。
React 应用的启动
React 应用的入口类为 ReactActivity 类,由于 ReactActivity 的生命周期都委托给 ReactActivityDelegate 对象,所以主要分析 ReactActivityDelegate
public class ReactActivityDelegate {
...
private final @Nullable Activity mActivity;
private final @Nullable String mMainComponentName;
private ReactDelegate mReactDelegate;
...
public ReactActivityDelegate(ReactActivity activity, @Nullable String mainComponentName) {
mActivity = activity;
mMainComponentName = mainComponentName;
}
protected ReactRootView createRootView() {
return new ReactRootView(getContext());
}
/**
* 入口组件,在index.android中注册的组件
* e.g. AppRegistry.registerComponent('RNTesterApp', () => RNTesterApp);
*/
public String getMainComponentName() {
return mMainComponentName;
}
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
String mainComponentName = getMainComponentName();
mReactDelegate =
new ReactDelegate(
getPlainActivity(), getReactNativeHost(), mainComponentName, getLaunchOptions()) {
@Override
protected ReactRootView createRootView() {
return ReactActivityDelegate.this.createRootView();
}
};
if (mainComponentName != null) {
loadApp(mainComponentName);
}
}
protected void loadApp(String appKey) {
mReactDelegate.loadApp(appKey);
getPlainActivity().setContentView(mReactDelegate.getReactRootView());
}
protected void onPause() {
mReactDelegate.onHostPause();
}
protected void onResume() {
mReactDelegate.onHostResume();
if (mPermissionsCallback != null) {
mPermissionsCallback.invoke();
mPermissionsCallback = null;
}
}
protected void onDestroy() {
mReactDelegate.onHostDestroy();
}
...
public void onWindowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus) {
if (getReactNativeHost().hasInstance()) {
getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager().onWindowFocusChange(hasFocus);
}
}
}
- 在 onCreate 中会 yload React App,异步创建全局 ReactApplicationContext 与 加载 js bundle
- 将 ReactRootView 对象 setContentView,等待 js 引擎加载完 js bundle 并且通过 bridge 将 js 组件对应的 native 组件 add 到 ReactRootView,然后等待页面的渲染
java 侧的 load js bundle
接下来我们来看看 load React App 的关键过程
public class ReactRootView extends SizeMonitoringFrameLayout
implements RootView, MeasureSpecProvider {
...
public void startReactApplication(
ReactInstanceManager reactInstanceManager,
String moduleName,
@Nullable Bundle initialProperties,
@Nullable String initialUITemplate) {
...
try {
...
mReactInstanceManager = reactInstanceManager;
mJSModuleName = moduleName;
mAppProperties = initialProperties;
mInitialUITemplate = initialUITemplate;
mReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground();
....
} finally {
...
}
}
...
}
createReactContextInBackground 的调用链路:
createReactContextInBackground—>recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner—>recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader—>recreateReactContextInBackground—>runCreateReactContextOnNewThread–[loop]–>runCreateReactContextOnNewThread
public class ReactInstanceManager {
....
private void runCreateReactContextOnNewThread(final ReactContextInitParams initParams) {
...
mCreateReactContextThread =
new Thread(
null,
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
...
try {
...
final ReactApplicationContext reactApplicationContext =
createReactContext(
initParams.getJsExecutorFactory().create(),
initParams.getJsBundleLoader());
mCreateReactContextThread = null;
ReactMarker.logMarker(PRE_SETUP_REACT_CONTEXT_START);
final Runnable maybeRecreateReactContextRunnable =
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (mPendingReactContextInitParams != null) {
runCreateReactContextOnNewThread(mPendingReactContextInitParams);
mPendingReactContextInitParams = null;
}
}
};
Runnable setupReactContextRunnable =
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
setupReactContext(reactApplicationContext);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO T62192299: remove this after investigation
FLog.e(
ReactConstants.TAG,
"ReactInstanceManager caught exception in setupReactContext",
e);
mDevSupportManager.handleException(e);
}
}
};
reactApplicationContext.runOnNativeModulesQueueThread(setupReactContextRunnable);
UiThreadUtil.runOnUiThread(maybeRecreateReactContextRunnable);
} catch (Exception e) {
mDevSupportManager.handleException(e);
}
}
},
"create_react_context");
ReactMarker.logMarker(REACT_CONTEXT_THREAD_START);
mCreateReactContextThread.start();
}
...
}
在创建 ReactContext 链路中 runCreateReactContextOnNewThread 是主要方法,该方法主要会有下面的核心步骤
- createReactContext:会启动一个线程创建 ReactApplicationContext 与 加载 js bundle。
- setupReactContext:监听来自 native 模块队列的消息,并且告知各个 native 模块 js 初始化完毕
ReactApplicationContext 的创建比较简单就 set 一些对象比如全局的 NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler 处理器,CatalystInstance 对象.其中解析 ReactPackage 的逻辑我们来分析一下。
解析 ReactPackage
ReactPackage
|--- TurboReactPackage
|--- CoreModulesPackage
|--- DebugCorePackage
|--- CompositeReactPackage
在 processPackage 过程中,TurboReactPackage 中的模块使用时才会加载,CompositeReactPackage 会立马被加载。 在早期 React Native 会加载所有模块,经过 turbo 改造之后,很多模块都是使用时才会被加载,NativeModuleRegistry 的模块都被移步到 TurboModuleRegistry
CoreModulesPackage 包含的模块如下
@ReactModuleList(
// WARNING: If you modify this list, ensure that the list below in method
// getReactModuleInfoByInitialization is also updated
nativeModules = {
AndroidInfoModule.class,
DeviceEventManagerModule.class,
DeviceInfoModule.class,
DevSettingsModule.class,
ExceptionsManagerModule.class,
LogBoxModule.class,
HeadlessJsTaskSupportModule.class,
SourceCodeModule.class,
TimingModule.class,
UIManagerModule.class,
NativeDevSplitBundleLoaderModule.class,
})
DebugCorePackage 包含模块如下
@ReactModuleList(
nativeModules = {
JSCHeapCapture.class,
})
我们主要关注的是有 CatalystInstace 负责的 js bundle 加载过程,这里我们需要说明一下,单单从 CatalystInstace 名字我们就能知道其职责,催生一个 React 应用实例,其是一个混合对象,一部分是由 JVM 堆分配的 java 对象,一部分是由操作系统分配的 cpp 对象。
CatalystInstanceImpl.java CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp
loadScriptFromAssets jniLoadScriptFromAssets
loadScriptFromFile/loadSplitBundleFromFile jniLoadScriptFromFile
CatalystInstanceImpl 的 cpp 对象持有 Instace 的 cpp 对象,Instance 对象是整个 java 与 js 通信的关键点,其内部通过 NativeToJsBridge 对象(封装了 js 引擎)加载 bundle,也能调用 js 的方法。
创建完 ReactContext 与 加载完 js bundle 之后,就会执行 setupReactContext 方法,通知各个模块 js 实例初始化完毕。
cpp 层的 load js bundle
当 CatalystInstanceImpl 类被加载到 classloader,就会调用其静态代码块的逻辑,ReactBridge.staticInit();开始 load so。load 的过程主要是将 java 侧的 native 方法与 cpp 层的方法进行映射.
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved) {
return initialize(vm, [] {
gloginit::initialize();
FLAGS_minloglevel = 0;
ProxyJavaScriptExecutorHolder::registerNatives();
CatalystInstanceImpl::registerNatives();
CxxModuleWrapperBase::registerNatives();
CxxModuleWrapper::registerNatives();
JCxxCallbackImpl::registerNatives();
NativeArray::registerNatives();
ReadableNativeArray::registerNatives();
WritableNativeArray::registerNatives();
NativeMap::registerNatives();
ReadableNativeMap::registerNatives();
WritableNativeMap::registerNatives();
#ifdef WITH_INSPECTOR
JInspector::registerNatives();
#endif
});
}
当实例化一个 CatalystInstanceImpl 对象之后,会在构造器中,初始化 native 到 js 的桥,在这条桥上游两条消息通道,一条通往 js,一条通往模块调用
void Instance::initializeBridge(
std::unique_ptr<InstanceCallback> callback,
std::shared_ptr<JSExecutorFactory> jsef,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue,
std::shared_ptr<ModuleRegistry> moduleRegistry) {
callback_ = std::move(callback);
moduleRegistry_ = std::move(moduleRegistry);
jsQueue->runOnQueueSync([this, &jsef, jsQueue]() mutable {
nativeToJsBridge_ = std::make_shared<NativeToJsBridge>(
jsef.get(), moduleRegistry_, jsQueue, callback_);
nativeToJsBridge_->initializeRuntime();
/**
* After NativeToJsBridge is created, the jsi::Runtime should exist.
* Also, the JS message queue thread exists. So, it's safe to
* schedule all queued up js Calls.
*/
jsCallInvoker_->setNativeToJsBridgeAndFlushCalls(nativeToJsBridge_);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(m_syncMutex);
m_syncReady = true;
m_syncCV.notify_all();
});
CHECK(nativeToJsBridge_);
}
当做完这些初始化工作之后,cpp 层接到 java 侧调用加载接口就会将控制权接手过来,其加载过程都是用 cpp 实现的。加载 js bundle 按照加载的源分为从 assets 加载、从远程调试器加载、从网络加载等,其抽象接口为 JSBundleLoader,我们从 assets 加载来分析,主要入口是 jniLoadScriptFromAssets
CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp
void CatalystInstanceImpl::jniLoadScriptFromAssets(
jni::alias_ref<JAssetManager::javaobject> assetManager,
const std::string &assetURL,
bool loadSynchronously) {
const int kAssetsLength = 9; // strlen("assets://");
auto sourceURL = assetURL.substr(kAssetsLength);
auto manager = extractAssetManager(assetManager);
auto script = loadScriptFromAssets(manager, sourceURL);
if (JniJSModulesUnbundle::isUnbundle(manager, sourceURL)) {
auto bundle = JniJSModulesUnbundle::fromEntryFile(manager, sourceURL);
auto registry = RAMBundleRegistry::singleBundleRegistry(std::move(bundle));
instance_->loadRAMBundle(
std::move(registry), std::move(script), sourceURL, loadSynchronously);
return;
} else if (Instance::isIndexedRAMBundle(&script)) {
instance_->loadRAMBundleFromString(std::move(script), sourceURL);
} else {
instance_->loadScriptFromString(
std::move(script), sourceURL, loadSynchronously);
}
}
react native 将 bundle 分为三种 plain bundle、ram bundle、hbc bundle(hemers 引擎支持),在 android 中 ram bundle 的实现为 file ram bundle(JniJSModulesUnbundle 类),也支持 indexed ram bundle(JSIndexedRAMBundle 类),ios 的实现则为 indexed ram bundle,具体看这文章,所以在选择哪种加载时,我们能看到对于 ram bundle 的判断有两种JniJSModulesUnbundle::isUnbundle与Instance::isIndexedRAMBundle
1. file ram bundle加载流程
auto bundle = JniJSModulesUnbundle::fromEntryFile(manager, sourceURL);
auto registry = RAMBundleRegistry::singleBundleRegistry(std::move(bundle));
instance_->loadRAMBundle(
std::move(registry), std::move(script), sourceURL, loadSynchronously);
2. indexed ram bundle加载流程
void Instance::loadRAMBundleFromString(
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> script,
const std::string &sourceURL) {
auto bundle = std::make_unique<JSIndexedRAMBundle>(std::move(script));
auto startupScript = bundle->getStartupCode();
auto registry = RAMBundleRegistry::singleBundleRegistry(std::move(bundle));
loadRAMBundle(std::move(registry), std::move(startupScript), sourceURL, true);
}
比较两种加载方式,我们就会发现他们都会调用 loadRAMBundle 函数,该函数有三个形参
1.bundleRegistry:ram bundle 的注册中心
2.startupScript:入口脚本的内容
3.startupScriptSourceURL:入口脚本的地址
4.loadSynchronously:加载方式,同步或者异步
loadRAMBundle 函数会调用 NativeToJsBridge 同步或者异步的 load ram bundle,采用哪种方式主要看传入的参数 loadSynchronously。
//同步
void NativeToJsBridge::loadBundleSync(
std::unique_ptr<RAMBundleRegistry> bundleRegistry,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> startupScript,
std::string startupScriptSourceURL) {
if (bundleRegistry) {
m_executor->setBundleRegistry(std::move(bundleRegistry));
}
try {
m_executor->loadBundle(
std::move(startupScript), std::move(startupScriptSourceURL));
} catch (...) {
m_applicationScriptHasFailure = true;
throw;
}
}
//异步
void NativeToJsBridge::loadBundle(
std::unique_ptr<RAMBundleRegistry> bundleRegistry,
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> startupScript,
std::string startupScriptSourceURL) {
runOnExecutorQueue(
[this,
bundleRegistryWrap = folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(bundleRegistry)),
startupScript = folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(startupScript)),
startupScriptSourceURL =
std::move(startupScriptSourceURL)](JSExecutor *executor) mutable {
auto bundleRegistry = bundleRegistryWrap.move();
if (bundleRegistry) {
executor->setBundleRegistry(std::move(bundleRegistry));
}
try {
executor->loadBundle(
std::move(*startupScript), std::move(startupScriptSourceURL));
} catch (...) {
m_applicationScriptHasFailure = true;
throw;
}
});
}
对比两个函数的调用链都一样,唯一不同的是异步加载通过消息队列异步完成调用链。接下来就到了很关键的地方,通过 JSExecutor#loadBundle 方法可以完成加载。对于 react native 的 JSExecutor 衍生类有三种,HermesExecutor、JSCExecutor、ProxyExecutor。他们分别封装了 hermes runtime 、 jsc runtime,而 ProxyExecutor 主要用于远程调试使用,他代理其余两个真正的执行器。那么我们就挑选 JSCExecutor 接下去往下读。
class JSCExecutorFactory : public JSExecutorFactory {
public:
std::unique_ptr<JSExecutor> createJSExecutor(
std::shared_ptr<ExecutorDelegate> delegate,
std::shared_ptr<MessageQueueThread> jsQueue) override {
auto installBindings = [](jsi::Runtime &runtime) {
react::Logger androidLogger =
static_cast<void (*)(const std::string &, unsigned int)>(
&reactAndroidLoggingHook);
react::bindNativeLogger(runtime, androidLogger);
react::PerformanceNow androidNativePerformanceNow =
static_cast<double (*)()>(&reactAndroidNativePerformanceNowHook);
react::bindNativePerformanceNow(runtime, androidNativePerformanceNow);
};
return std::make_unique<JSIExecutor>(
jsc::makeJSCRuntime(),
delegate,
JSIExecutor::defaultTimeoutInvoker,
installBindings);
}
};
void JSIExecutor::loadBundle(
std::unique_ptr<const JSBigString> script,
std::string sourceURL) {
SystraceSection s("JSIExecutor::loadBundle");
bool hasLogger(ReactMarker::logTaggedMarker);
std::string scriptName = simpleBasename(sourceURL);
if (hasLogger) {
ReactMarker::logTaggedMarker(
ReactMarker::RUN_JS_BUNDLE_START, scriptName.c_str());
}
runtime_->evaluateJavaScript(
std::make_unique<BigStringBuffer>(std::move(script)), sourceURL);
flush();
if (hasLogger) {
ReactMarker::logTaggedMarker(
ReactMarker::RUN_JS_BUNDLE_STOP, scriptName.c_str());
}
}
JSCExecutor 是 java 对象,JSExecutor 真正的衍生类为 JSIExecutor,注入的 runtime 是 jsc,所以当就会将 js bundle 内容注入到 jsc 的 evaluateJavaScript 方法,jsc 引擎开始渲染页面
javascript 层的 load js bundle
一个简单的 react native 项目结构
android/
ios/
...
App.js
index.js
package.json
...
当 js bundle 被加载到内存中,index.js 入口文件中的AppRegistry.registerComponent(appName, () => App);会被执行,通过 appName 与 ComponentProvider 函数类型的对象注册到 AppRegistry 中。
AppRegistry.js
registerComponent(
appKey: string,
componentProvider: ComponentProvider,
section?: boolean,
): string {
let scopedPerformanceLogger = createPerformanceLogger();
runnables[appKey] = {
componentProvider,
run: (appParameters, displayMode) => {
const concurrentRootEnabled =
appParameters.initialProps?.concurrentRoot ||
appParameters.concurrentRoot;
renderApplication(
componentProviderInstrumentationHook(
componentProvider,
scopedPerformanceLogger,
),
appParameters.initialProps,
appParameters.rootTag,
wrapperComponentProvider && wrapperComponentProvider(appParameters),
appParameters.fabric,
showArchitectureIndicator,
scopedPerformanceLogger,
appKey === 'LogBox',
appKey,
coerceDisplayMode(displayMode),
concurrentRootEnabled,
);
},
};
if (section) {
sections[appKey] = runnables[appKey];
}
return appKey;
},
AppRegistery 通过注册表 runnables 存储以 appName 为 key,类对象为 value。当 java 侧想要运行 App,就可以通过 appName 到 AppRegistery 查询并且运行。
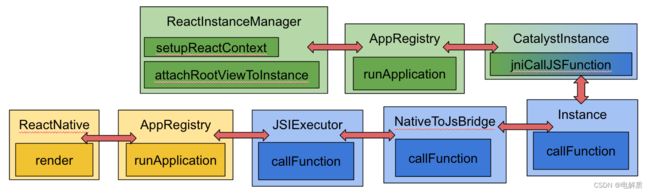
java 侧的 run application
执行 ReactRootView 的绘制流程,在 ReactRootView 的 onMeasure 时会执行 attachToReactInstanceManager,将 ReactRootView 注册到 UIManagerModule,紧接着调用 AppRegistry 的 runApplication 启动整个 js 框架,接着就是 js 组件的渲染,这个我们留给 React Native 渲染机制再讲.
public interface AppRegistry extends JavaScriptModule {
void runApplication(String appKey, WritableMap appParameters);
void unmountApplicationComponentAtRootTag(int rootNodeTag);
void startHeadlessTask(int taskId, String taskKey, WritableMap data);
}
javascript 层的 run application
调用 js 接口主要采用了 java 的动态代理,JavaScriptModuleRegistry#getJavaScriptModule 方法,返回一个 AppRegistry 的代理类。当调用 runApplication 方法,就会执行 CatalystInstance#jniCallJSFunction,最后会执行 JSIExecutor$callFunction 方法,执行 js 的 runApplication 接口
AppRegistry.js
//启动app
runApplication(
appKey: string,
appParameters: any,
displayMode?: number,
): void {
if (appKey !== 'LogBox') {
const logParams = __DEV__
? '" with ' + JSON.stringify(appParameters)
: '';
const msg = 'Running "' + appKey + logParams;
infoLog(msg);
BugReporting.addSource(
'AppRegistry.runApplication' + runCount++,
() => msg,
);
}
invariant(
runnables[appKey] && runnables[appKey].run,
`"${appKey}" has not been registered. This can happen if:\n` +
'* Metro (the local dev server) is run from the wrong folder. ' +
'Check if Metro is running, stop it and restart it in the current project.\n' +
"* A module failed to load due to an error and `AppRegistry.registerComponent` wasn't called.",
);
SceneTracker.setActiveScene({name: appKey});
runnables[appKey].run(appParameters, displayMode);
},
通过 caller 传递的 appName,运行对应的 App,而 run 函数体中会调用renderApplication接口进行组件的渲染。
function renderApplication<Props: Object>(
RootComponent: React.ComponentType<Props>,
initialProps: Props,
rootTag: any,
WrapperComponent?: ?React.ComponentType<any>,
fabric?: boolean,
showArchitectureIndicator?: boolean,
scopedPerformanceLogger?: IPerformanceLogger,
isLogBox?: boolean,
debugName?: string,
displayMode?: ?DisplayModeType,
useConcurrentRoot?: boolean,
) {
...
let renderable = (
<PerformanceLoggerContext.Provider value={performanceLogger}>
<AppContainer
rootTag={rootTag}
fabric={fabric}
showArchitectureIndicator={showArchitectureIndicator}
WrapperComponent={WrapperComponent}
initialProps={initialProps ?? Object.freeze({})}
internal_excludeLogBox={isLogBox}>
<RootComponent {...initialProps} rootTag={rootTag} />
</AppContainer>
</PerformanceLoggerContext.Provider>
);
if (__DEV__ && debugName) {
const RootComponentWithMeaningfulName = getCachedComponentWithDebugName(
`${debugName}(RootComponent)`,
);
renderable = (
<RootComponentWithMeaningfulName>
{renderable}
</RootComponentWithMeaningfulName>
);
}
...
if (fabric) {
require('../Renderer/shims/ReactFabric').render(
renderable,
rootTag,
null,
useConcurrentRoot,
);
} else {
require('../Renderer/shims/ReactNative').render(renderable, rootTag);
}
...
}
上面我们可以看到 PerformanceLoggerContext.Provider 、AppContainer 、 RootComponent,这是三个重要的类,其中的、AppContainer 主要封装了 Inspector, RootComponen 为 react 应用的树根。react native 为了优化渲染系统引入了 fabric,这里我们先不对其进行分析,先来看看在正式环境下面非 fabric 的逻辑代码,也就是require('../Renderer/shims/ReactNative').render(renderable, rootTag);。在正式环境下 require 导入的是 ReactNativeRenderer-prod.js 文件,其中 export 的接口类如下。
export type ReactNativeType = {
findHostInstance_DEPRECATED<TElementType: ElementType>(
componentOrHandle: ?(ElementRef<TElementType> | number)
): ?ElementRef<HostComponent<mixed>>,
findNodeHandle<TElementType: ElementType>(
componentOrHandle: ?(ElementRef<TElementType> | number)
): ?number,
dispatchCommand(
handle: ElementRef<HostComponent<mixed>>,
command: string,
args: Array<mixed>
): void,
sendAccessibilityEvent(
handle: ElementRef<HostComponent<mixed>>,
eventType: string
): void,
render(
element: Element<ElementType>,
containerTag: number,
callback: ?() => void
): ?ElementRef<ElementType>,
unmountComponentAtNode(containerTag: number): void,
unmountComponentAtNodeAndRemoveContainer(containerTag: number): void,
unstable_batchedUpdates: <T>(fn: (T) => void, bookkeeping: T) => void,
__SECRET_INTERNALS_DO_NOT_USE_OR_YOU_WILL_BE_FIRED: SecretInternalsType,
...
};
导出的 ReactNativeType#render 函数接下来就开始了渲染逻辑。其中传入的实参 rootTag 为 java 侧的 ReactRootView,React 会根据 rootTag 构造出一个 js 侧的根节点 FiberRootNode,来与 Java 侧的 ReactRootView 一一对应。当组件从PerformanceLoggerContext.Provider ---> AppContainer ---> RootComponent,一层一层往下渲染到 App,真正的页面渲染才开始。React Native 如何渲染,让我们来一一剖析一下React Native | 渲染机制
小手动一动,点赞转发加关注。微信搜索【大前端杂货铺】公众号关注大前端老司机带您遨游大前端知识的海洋。关注 Github https://github.com/big-frontend 还有大前端代码实践哦。
