C++学习之路(五)C++ 实现简单的文件管理系统命令行应用 - 示例代码拆分讲解
简单的文件管理系统示例介绍:
这个文件管理系统示例是一个简单的命令行程序,允许用户进行文件的创建、读取、追加内容和删除操作。这个示例涉及了一些基本的文件操作和用户交互。
功能概述:
-
创建文件 (
createFile()):- 用户可以输入文件名和内容,创建新的文件。
-
读取文件 (
readFile()):- 用户可以输入文件名,读取并显示文件的内容。
-
追加文件内容 (
appendToFile()):- 用户可以输入文件名和内容,将新内容追加到已存在的文件末尾。
-
删除文件 (
deleteFile()):- 用户可以输入文件名,删除指定的文件。
涉及的知识点:
-
文件输入输出 (
- 使用
std::ifstream和std::ofstream实现文件读取和写入功能。
- 使用
-
文件流的打开和关闭:
is_open()和close()函数用于检查文件流是否打开以及关闭文件。
-
命令行交互:
- 使用
std::cin和std::cout实现与用户的交互。
- 使用
-
文件操作函数:
std::remove()函数用于删除文件。
-
循环和条件语句:
- 使用
do-while循环处理菜单选项,根据用户输入的选择执行相应的功能。
- 使用
通过这个示例,初学者可以了解如何使用 C++ 实现基本的文件操作、用户交互和函数封装,以及如何处理文件的创建、读取、追加和删除等操作。同时也涉及了条件语句、循环等基本的程序控制结构。
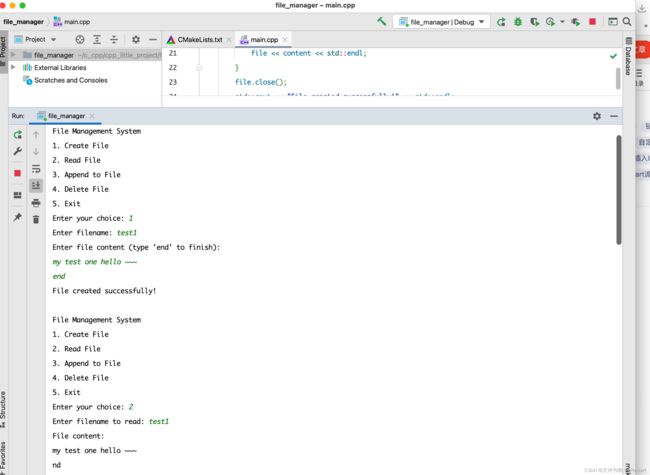
示例在Clion中运行步骤:
1. 新建项目
2. 粘贴代码
#include 3. 编译运行
代码拆解,知识点总结
当我们拆分讲解这个文件管理系统示例时,可以按照功能模块来逐步解释每个部分的作用和实现。
1. 创建文件功能 (createFile()):
void createFile() {
std::string filename, content;
std::cout << "Enter filename: ";
std::cin >> filename;
std::ofstream file(filename);
// 检查文件是否成功打开
if (file.is_open()) {
std::cout << "Enter file content (type 'end' to finish):\n";
while (true) {
std::cin.ignore(); // 忽略上一个输入中的换行符
std::getline(std::cin, content);
if (content == "end") {
break;
}
file << content << std::endl;
}
file.close();
std::cout << "File created successfully!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Error! Unable to create file." << std::endl;
}
}
- 这个函数允许用户输入文件名和内容,在给定的文件名下创建文件并将用户输入的内容写入文件。
- 使用
std::ofstream打开文件,使用file.is_open()检查文件是否成功打开,然后读取用户输入的内容,并将内容写入文件。
2. 读取文件功能 (readFile()):
void readFile() {
std::string filename, line;
std::cout << "Enter filename to read: ";
std::cin >> filename;
std::ifstream file(filename);
// 检查文件是否成功打开
if (file.is_open()) {
std::cout << "File content:" << std::endl;
while (std::getline(file, line)) {
std::cout << line << std::endl;
}
file.close();
} else {
std::cout << "Error! Unable to open file." << std::endl;
}
}
- 这个函数允许用户输入文件名,然后打开文件并将文件内容逐行读取并显示在屏幕上。
3. 追加文件内容功能 (appendToFile()):
void appendToFile() {
std::string filename, content;
std::cout << "Enter filename to append: ";
std::cin >> filename;
std::ofstream file(filename, std::ios::app);
// 检查文件是否成功打开
if (file.is_open()) {
std::cout << "Enter content to append (type 'end' to finish):\n";
while (true) {
std::cin.ignore(); // 忽略上一个输入中的换行符
std::getline(std::cin, content);
if (content == "end") {
break;
}
file << content << std::endl;
}
file.close();
std::cout << "Content appended to file successfully!" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "Error! Unable to open file." << std::endl;
}
}
- 这个函数允许用户输入文件名和内容,在给定的文件名下打开文件,并在文件末尾追加用户输入的内容。
Tips: std::getline() 是什么意思?
std::getline() 是 C++ 标准库
std::getline()接受两个参数:输入流和字符串。- 它从输入流(在这个例子中是
std::cin,标准输入)中读取一行文本,并将读取的内容存储到字符串line中,直到遇到换行符\n或文件结束符。 - 这个函数能够读取整行文本,包括空格和制表符等,直到换行符为止。
std::getline() 的特点:
-
读取整行文本: 不像
std::cin >> variable会在遇到空格或换行符时停止读取,std::getline()会读取整行文本。 -
可以指定定界符(可选): 可以传递第三个参数作为定界符,以指定特定的字符作为终止符号,例如
std::getline(std::cin, line, '\t')将在遇到制表符时停止读取。 -
常用于读取用户输入: 在命令行交互中,特别适用于读取用户输入的完整一行文本,例如文件名、描述等信息。
std::getline() 是处理输入流中文本数据时常用的函数,能够方便地读取整行文本并存储到字符串中,适用于许多交互式的输入场景。
4. 删除文件功能 (deleteFile()):
void deleteFile() {
std::string filename;
std::cout << "Enter filename to delete: ";
std::cin >> filename;
// 删除文件
if (std::remove(filename.c_str()) != 0) {
std::cout << "Error! Unable to delete file." << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "File deleted successfully!" << std::endl;
}
}
- 这个函数允许用户输入文件名,然后尝试删除该文件。
5. 主函数 (main()):
主函数提供了用户和程序的交互菜单,根据用户的选择调用相应的功能函数。
整个程序通过以上几个模块,实现了文件的创建、读取、追加和删除等功能,并通过命令行菜单和用户输入来控制程序的执行。
Tips: 别忘了跑起来,检查检查有没有BUG ~
本文就到这里了,感谢您的阅读,明天还有更多的实例学习文章等着你 。别忘了点赞、收藏~ Thanks♪(・ω・)ノ 。