DGL在异构图上的GraphConv模块
回顾同构图GraphConv模块
首先回顾一下同构图中实现GraphConv的主要思路(以GraphSAGE为例):
在初始化模块首先是获取源节点和目标节点的输入维度,同时获取输出的特征维度。根据SAGE论文提出的三种聚合操作,需要获取所使用的聚合类型,方便后面使用Pytorch中的nn模块实现。最后是特征归一化操作。
其具体的代码段为:
获取相关输入特征
# 获取源节点和目标节点的输入特征维度
self._in_src_feats, self._in_dest_feats = expand_as_pair(in_feats)
# 输出特征维度
self._out_feats = out_feats
self._aggre_type = aggregator_type
self.norm = norm
self.activation = activation
根据聚合类型选择Pytorch对应的nn模块中的函数
# 聚合类型:mean、pool、lstm、gcn
if aggregator_type not in ['mean', 'pool', 'lstm', 'gcn']:
raise KeyError('Aggregator type {} not supported.'.format(aggregator_type))
if aggregator_type == 'pool':
self.fc_pool = nn.Linear(self._in_src_feats, self._in_src_feats)
if aggregator_type == 'lstm':
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(self._in_src_feats, self._in_src_feats, batch_first=True)
if aggregator_type in ['mean', 'pool', 'lstm']:
self.fc_self = nn.Linear(self._in_dst_feats, out_feats, bias=bias)
self.fc_neigh = nn.Linear(self._in_src_feats, out_feats, bias=bias)
权重初始化
构造函数的最后调用了 reset_parameters() 进行权重初始化。
def reset_parameters(self):
"""重新初始化可学习的参数"""
gain = nn.init.calculate_gain('relu')
if self._aggre_type == 'pool':
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc_pool.weight, gain=gain)
if self._aggre_type == 'lstm':
self.lstm.reset_parameters()
if self._aggre_type != 'gcn':
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc_self.weight, gain=gain)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc_neigh.weight, gain=gain)# 上面代码里的 norm 是用于特征归一化的可调用函数。在SAGEConv论文里,归一化可以是L2归一化: hv=hv/∥hv∥2
forward函数
在NN模块中, forward() 函数执行了实际的消息传递和计算。与通常以张量为参数的PyTorch NN模块相比,DGL NN模块额外增加了1个参数 :class:dgl.DGLGraph。forward() 函数的内容一般可以分为3项操作:
- 检测输入图对象是否符合规范。
- 消息传递和聚合
- 聚合后,更新特征作为输出。
检测输入图对象的规范性
# 输入图对象的规范检测
with graph.local_scope():
# 指定图类型,然后根据图类型扩展输入特征
feat_src, feat_dst = expand_as_pair(feat, graph)
对于expand_as_pair()函数,其实现的操作是如果输入的特征不是一对的话(源节点和目标节点),就根据图Graph将特征变成一对,但要求图必须是一个block,其对应的源码为:
def expand_as_pair(input_, g=None):
"""Return a pair of same element if the input is not a pair.
如果输入不是一对,则返回相同元素的一对。
If the graph is a block, obtain the feature of destination nodes from the source nodes.
如果图是块,则从源节点中获取目的节点的特征。
Parameters
----------
input_ : Tensor, dict[str, Tensor], or their pairs
The input features
g : DGLGraph or None
The graph.
If None, skip checking if the graph is a block.
Returns
-------
tuple[Tensor, Tensor] or tuple[dict[str, Tensor], dict[str, Tensor]]
The features for input and output nodes
输入和输出节点的特性
"""
if isinstance(input_, tuple):
return input_
elif g is not None and g.is_block:
if isinstance(input_, Mapping):
input_dst = {
k: F.narrow_row(v, 0, g.number_of_dst_nodes(k))
for k, v in input_.items()
}
else:
input_dst = F.narrow_row(input_, 0, g.number_of_dst_nodes())
return input_, input_dst
else:
return input_, input_
消息传递和聚合
聚合部分的代码执行了消息传递和聚合的计算。这部分代码会因模块而异。请注意,代码中的所有消息传递均使用 update_all() API和 DGL内置的消息/聚合函数来实现,以充分利用 2.2 编写高效的消息传递代码 里所介绍的性能优化。
# 消息传递和聚合
if self._aggre_type == 'mean':
graph.srcdata['h'] = feat_src
graph.update_all(fn.copy_u('h', 'm'), fn.mean('m', 'neigh'))
h_neigh = graph.dstdata['neigh']
elif self._aggre_type == 'gcn':
check_eq_shape(feat)
graph.srcdata['h'] = feat_src
graph.dstdata['h'] = feat_dst
graph.update_all(fn.copy_u('h', 'm'), fn.sum('m', 'neigh'))
# 除以入度
degs = graph.in_degrees().to(feat_dst)
h_neigh = (graph.dstdata['neigh'] + graph.dstdata['h']) / (degs.unsqueeze(-1) + 1)
elif self._aggre_type == 'pool':
graph.srcdata['h'] = F.relu(self.fc_pool(feat_src))
graph.update_all(fn.copy_u('h', 'm'), fn.max('m', 'neigh'))
h_neigh = graph.dstdata['neigh']
else:
raise KeyError('Aggregator type {} not recognized.'.format(self._aggre_type))
如果是gcn聚合方式的话还需要用到它自身的特征,但是SAGE不需要,它只需要聚合邻居的特征,这里通过一条判断语句加以区分:
# GraphSAGE中gcn聚合不需要fc_self
if self._aggre_type == 'gcn':
rst = self.fc_neigh(h_neigh)
else:
rst = self.fc_self(h_self) + self.fc_neigh(h_neigh)
更新特征
聚合后,更新特征作为输出——forward() 函数的最后一部分是在完成消息聚合后更新节点的特征。 常见的更新操作是根据构造函数中设置的选项来应用激活函数和进行归一化。
# 更新特征作为输出
# 激活函数
if self.activation is not None:
rst = self.activation(rst)
# 归一化
if self.norm is not None:
rst = self.norm(rst)
return rst
异构图GraphConv模块
DGL提供了 HeteroGraphConv,用于定义异构图上GNN模块。 实现逻辑与消息传递级别的API multi_update_all() 相同,它包括:
- 每个关系上的DGL NN模块。
- 聚合来自不同关系上的结果。
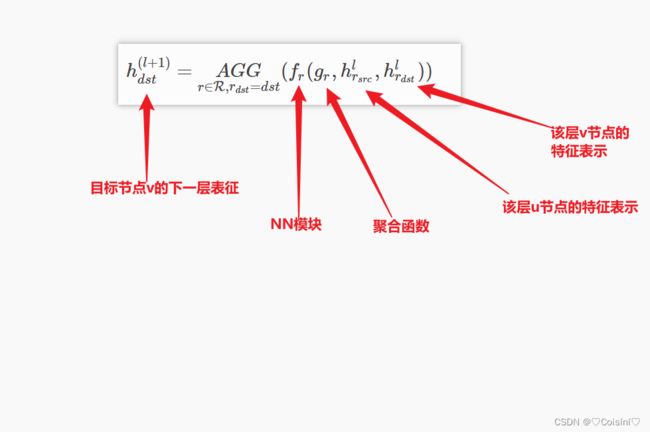
其对应的数学公式为:(r表示关系)
__ init __函数
异构图的卷积操作接受一个字典类型参数 mods。这个字典的键为关系名,值为作用在该关系上NN模块对象。参数 aggregate 则指定了如何聚合来自不同关系的结果。
class HeteroGraphConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mods, aggregate='sum'):
super(HeteroGraphConv, self).__init__()
self.mods = nn.ModuleDict(mods)
if isinstance(aggregate, str):
# 获取聚合函数的内部函数
self.agg_fn = get_aggregate_fn(aggregate)
else:
self.agg_fn = aggregate
nn.ModuleDict() 用于保存字典中的子模块。Pytorch官方也给出了对应的示例:
class MyModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.choices = nn.ModuleDict({
'conv': nn.Conv2d(10, 10, 3),
'pool': nn.MaxPool2d(3)
})
self.activations = nn.ModuleDict([
['lrelu', nn.LeakyReLU()],
['prelu', nn.PReLU()]
])
def forward(self, x, choice, act):
x = self.choices[choice](x)
x = self.activations[act](x)
return x
forward函数
对于前向传播函数,除了需要输入图和输入张量以外,它还需要2个额外的字典参数mod_args 和 mod_kwargs。这2个字典与 self.mods 具有相同的键,值则为对应NN模块的自定义参数。
forward() 函数的输出结果也是一个字典类型的对象。其键为 nty,其值为每个目标节点类型 nty 的输出张量的列表, 表示来自不同关系的计算结果。HeteroGraphConv 会对这个列表进一步聚合,并将结果返回给用户。聚合操作主要是:
if g.is_block:
src_inputs = inputs
dst_inputs = {k: v[:g.number_of_dst_nodes(k)] for k, v in inputs.items()}
else:
src_inputs = dst_inputs = inputs
for stype, etype, dtype in g.canonical_etypes:
rel_graph = g[stype, etype, dtype]
if rel_graph.num_edges() == 0:
continue
if stype not in src_inputs or dtype not in dst_inputs:
continue
dstdata = self.mods[etype](
rel_graph,
(src_inputs[stype], dst_inputs[dtype]),
*mod_args.get(etype, ()),
**mod_kwargs.get(etype, {}))
outputs[dtype].append(dstdata)
输入 g 可以是异构图或来自异构图的子图区块。和普通的NN模块一样,forward() 函数需要分别处理不同的输入图类型。
上述代码中的for循环为处理异构图计算的主要逻辑。
- 首先我们遍历图中所有的关系(通过调用
canonical_etypes)。 - 通过关系名,我们可以使用
g[ stype, etype, dtype ]的语法将只包含该关系的子图(rel_graph)抽取出来。 - 对于二分图,输入特征将被组织为元组
(src_inputs[stype], dst_inputs[dtype])。 - 接着调用用户预先注册在该关系上的
NN模块,并将结果保存在outputs字典中。
最后,HeteroGraphConv 会调用用户注册的 self.agg_fn 函数聚合来自多个关系的结果。
rsts = {}
for nty, alist in outputs.items():
if len(alist) != 0:
rsts[nty] = self.agg_fn(alist, nty)